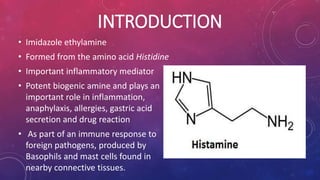
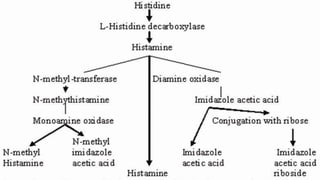
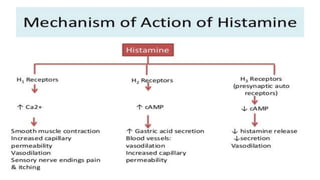
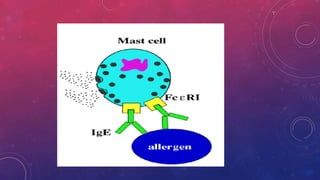
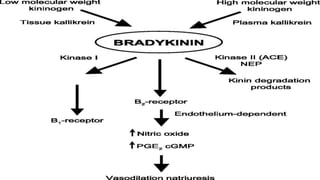
Histamine and bradykinin are important autacoids or local hormones that act near their site of synthesis to exert physiological effects. Histamine is released from mast cells and basophils during allergic reactions and binds to H1, H2, H3 and H4 receptors, causing effects like vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, and bronchioconstriction. It is involved in allergic diseases. Bradykinin is produced from kininogen and acts on B1 and B2 receptors to cause vasodilation, smooth muscle contraction, increased vascular permeability and pain. Both histamine and bradykinin are inactivated by enzymatic degradation and their effects can be blocked by receptor antagonists.