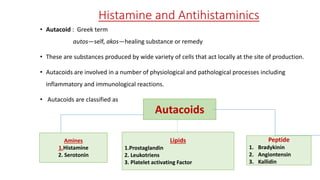
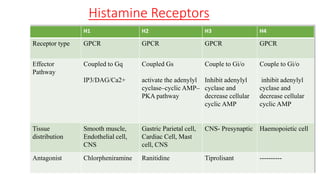
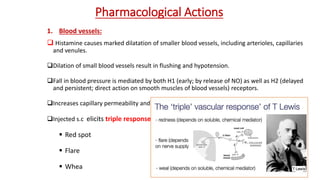
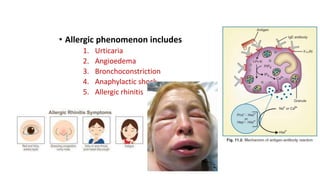
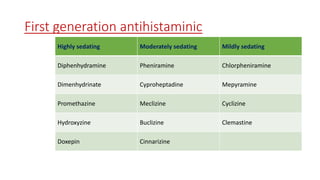
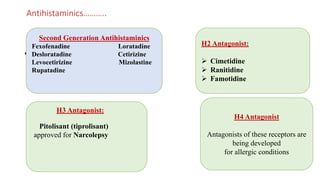
This document discusses histamine and antihistamines. It provides details on histamine including its synthesis, storage, receptors, and role in allergic reactions and inflammation. It then describes first and second generation antihistamines that act as H1 receptor antagonists to relieve symptoms of allergic rhinitis, urticaria, and other conditions by blocking the effects of histamine. The patient described has seasonal allergic rhinitis, so a second generation antihistamine with fewer side effects would be most suitable. First generation antihistamines that cause drowsiness should be avoided.