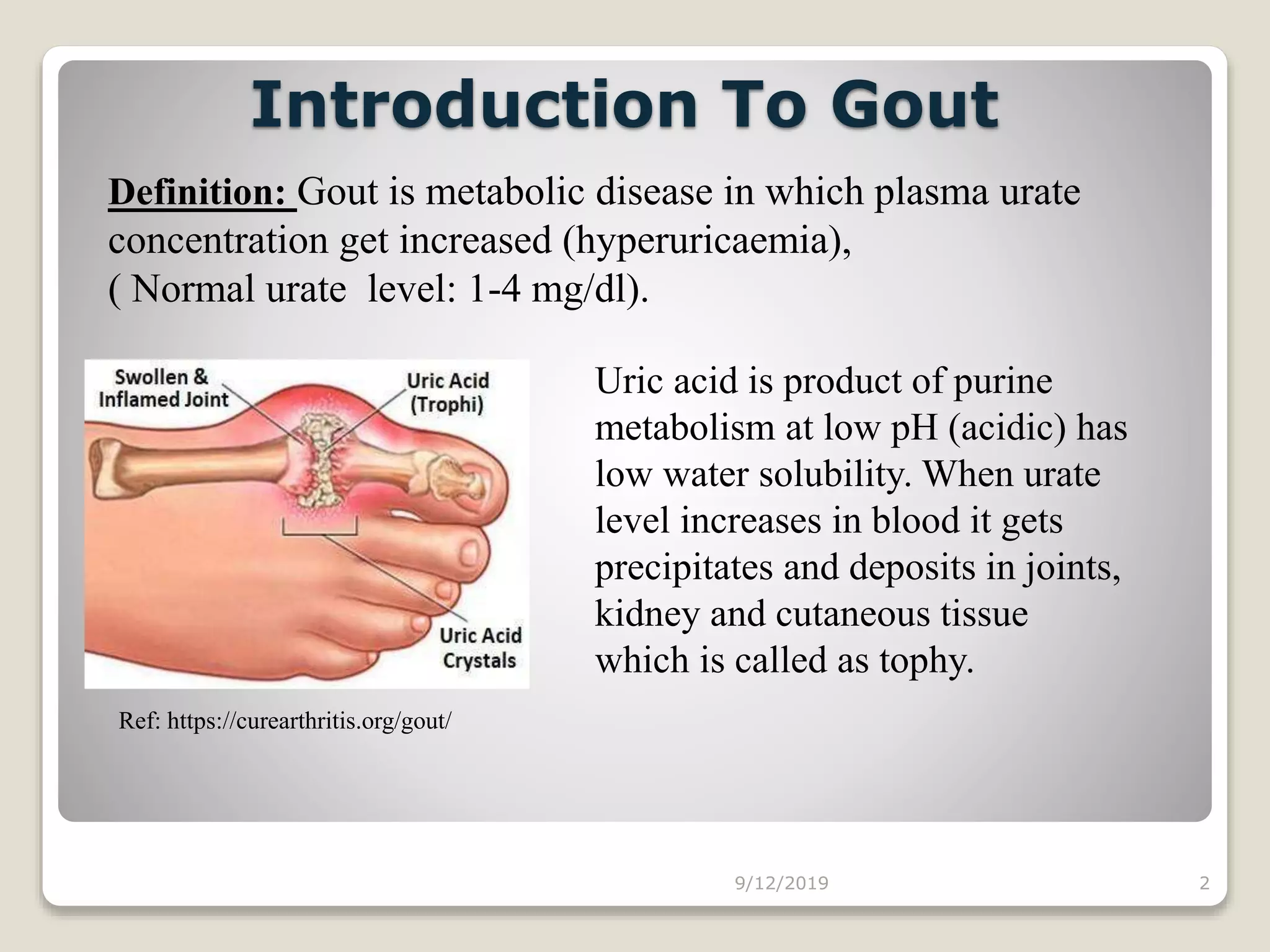
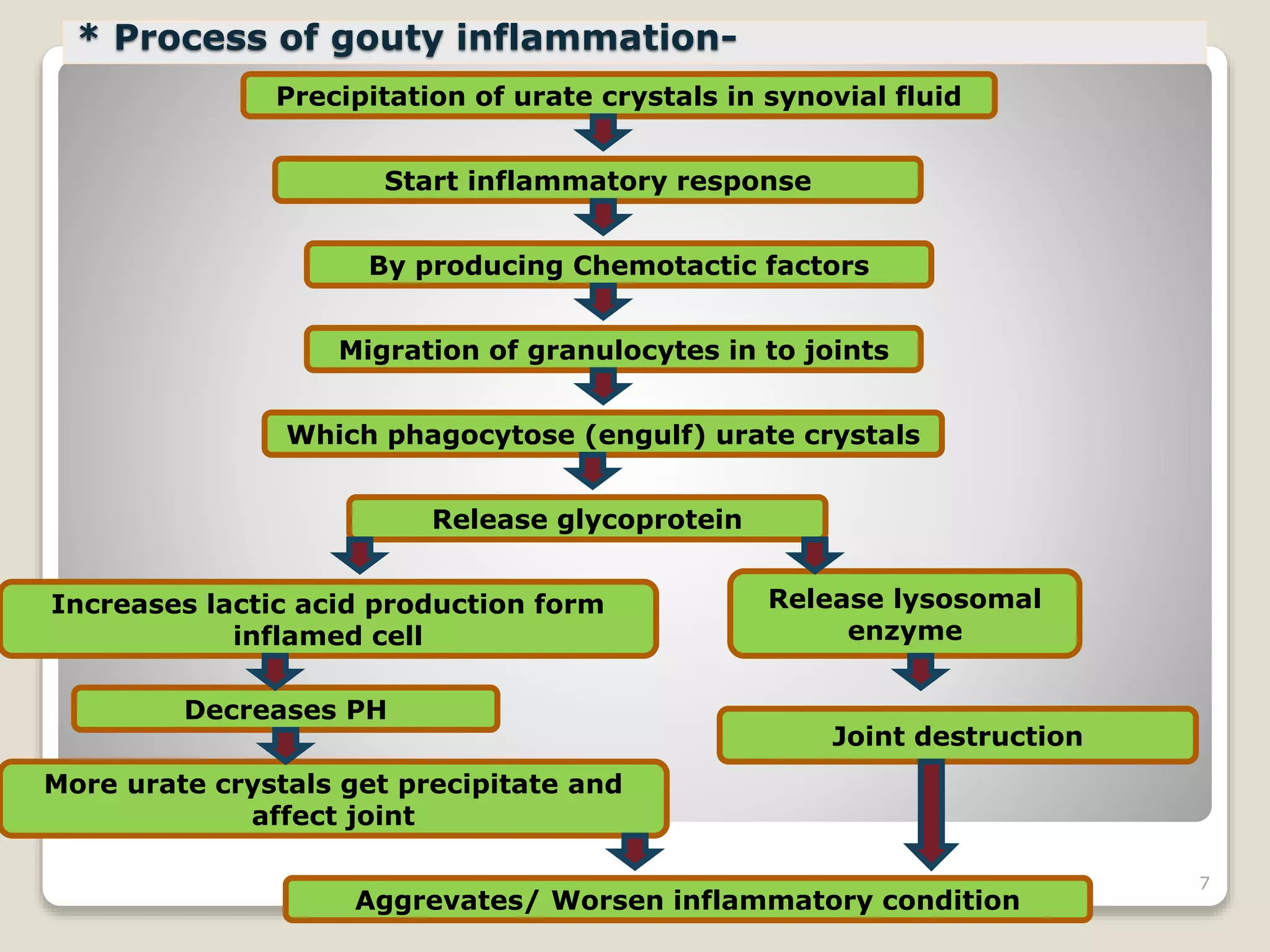
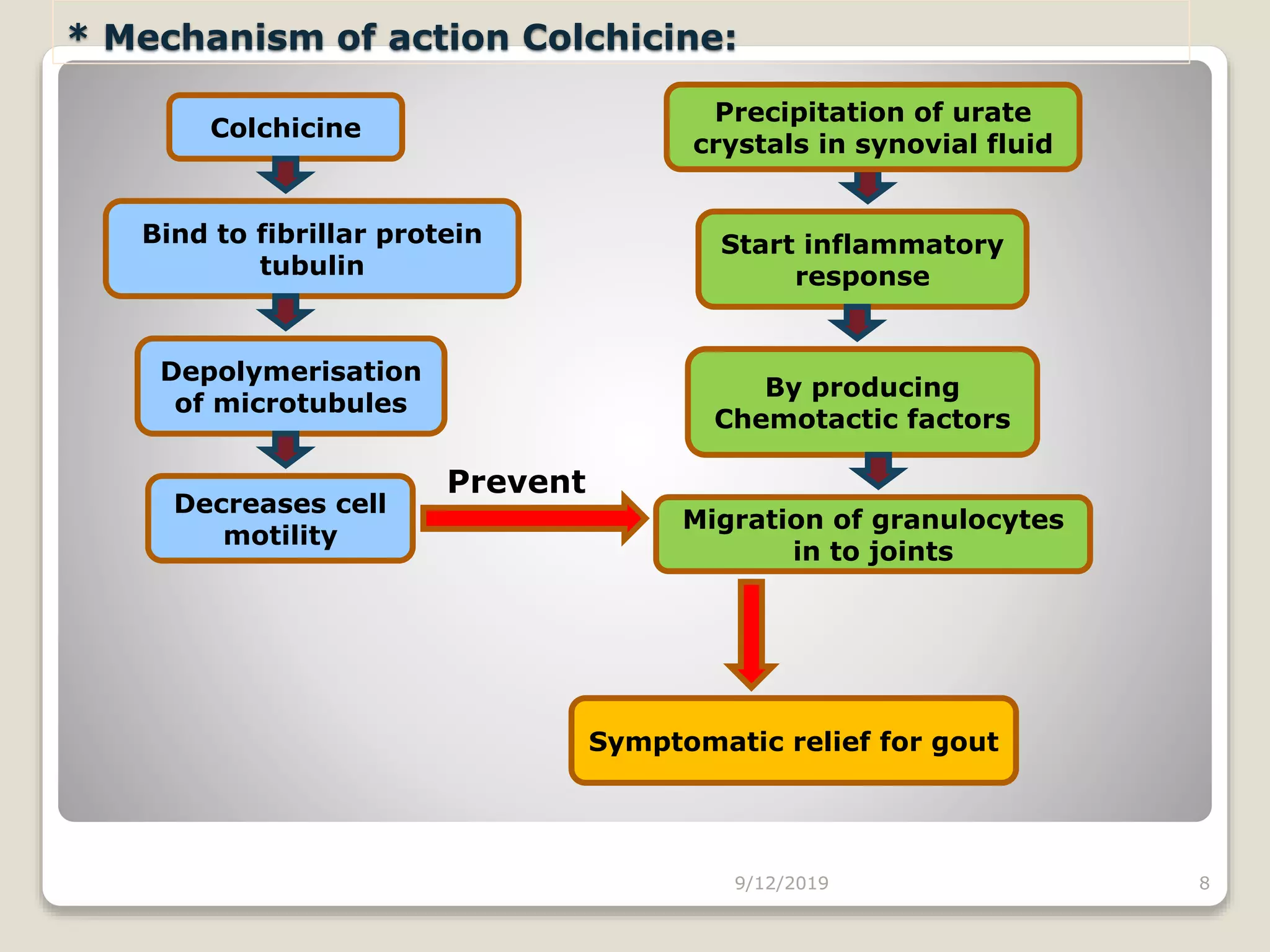
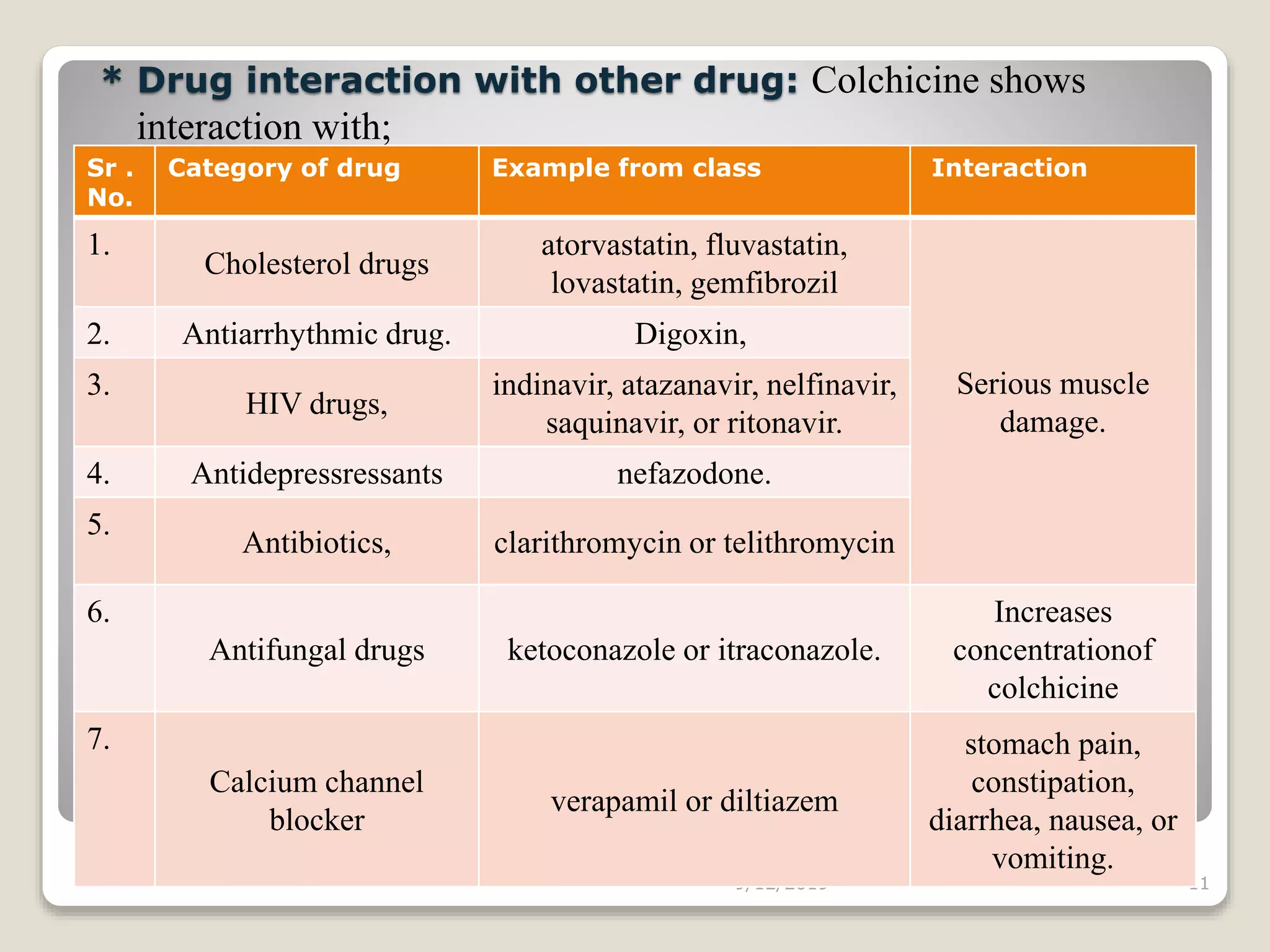
This document discusses antigout drugs used to treat gout. It begins by defining gout as a metabolic disease caused by increased uric acid levels in the blood. It then describes the mechanisms and classifications of various antigout drugs including allopurinol, probenecid, sulfinpyrazone, corticosteroids, NSAIDs, and colchicine. For each drug, it discusses their mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, uses, interactions, toxicity, and administration guidelines for treating both acute and chronic gout. The document provides an in-depth overview of different drug classes used to manage hyperuricemia and gouty arthritis.