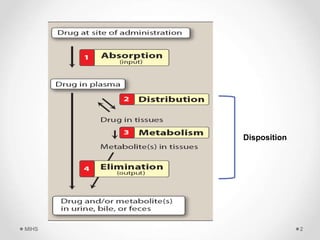
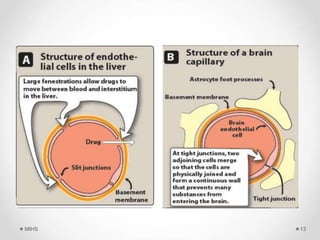
The document discusses the concept of drug disposition, which includes processes such as distribution and elimination that affect plasma concentration. Factors influencing drug distribution include regional blood flow, capillary permeability, and binding to plasma and tissue proteins. It also details the concept of drug reservoirs in the body, including various storage sites and compartments that impact the distribution of drugs.