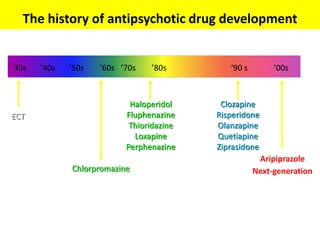
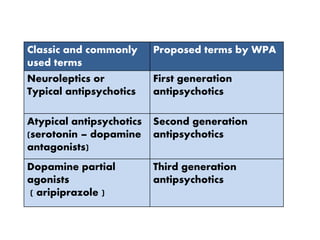
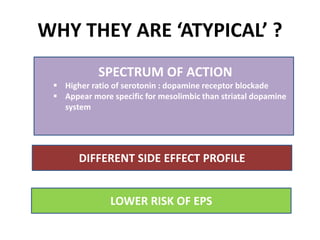
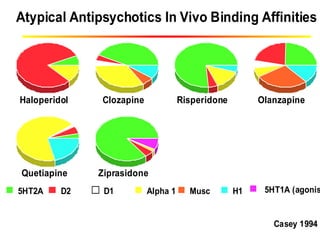
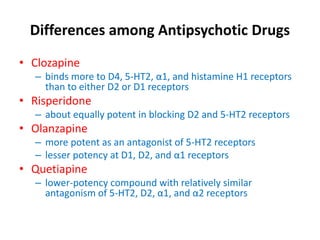
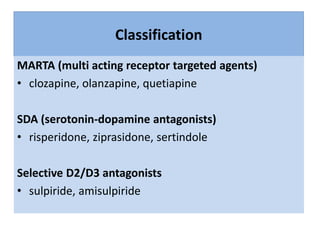
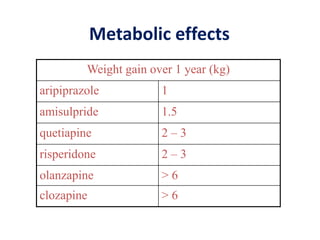
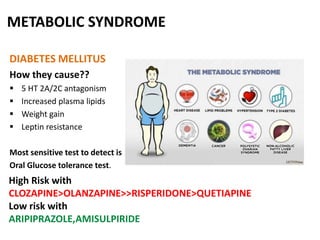
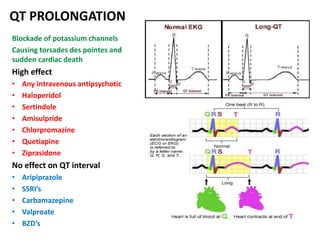
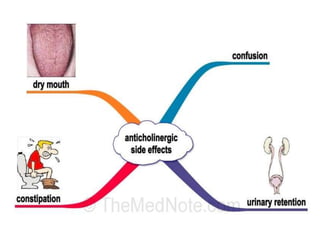
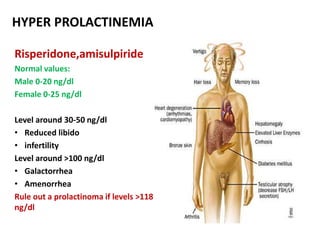
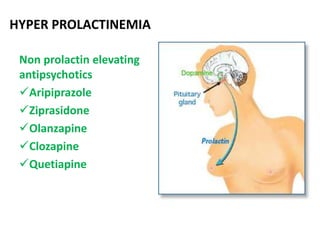
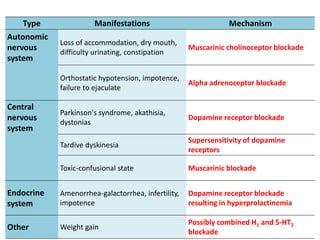
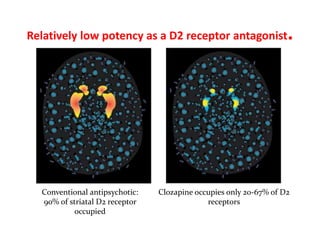
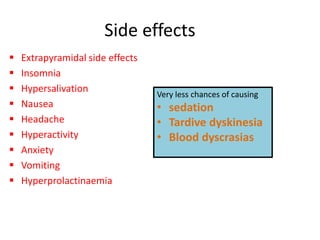
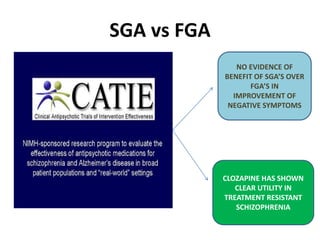
This document discusses the history and development of atypical antipsychotic medications. It begins with an overview of the serendipitous discoveries that led to the development of early antipsychotics like chlorpromazine in the 1950s. It then covers the development of second-generation atypical antipsychotics from the 1990s onward, including clozapine, risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, and others. The rest of the document details the mechanisms of action, therapeutic indications, side effect profiles, and dosing of various atypical antipsychotics.