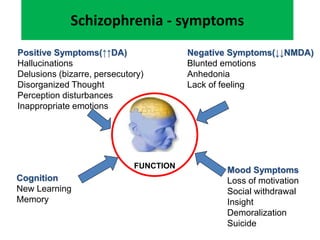
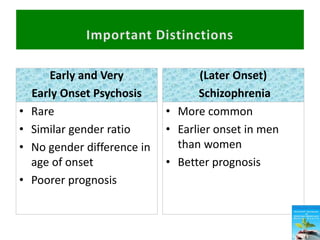
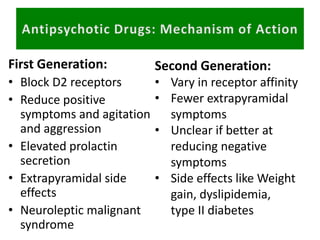
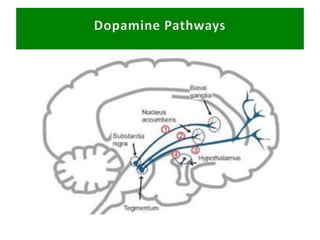
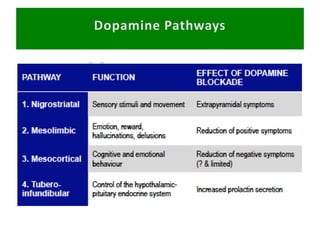
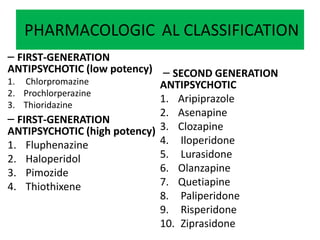
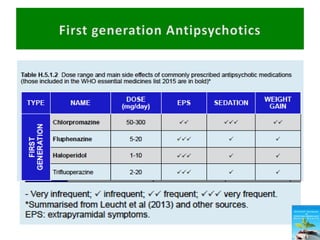
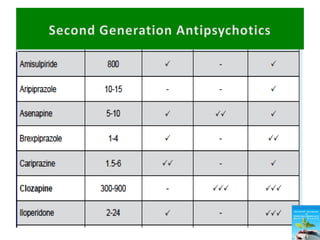
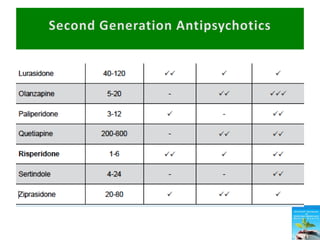
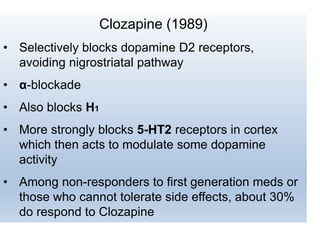
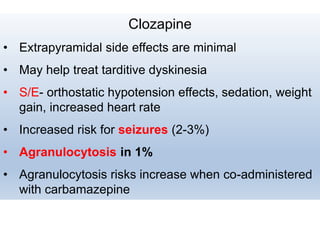
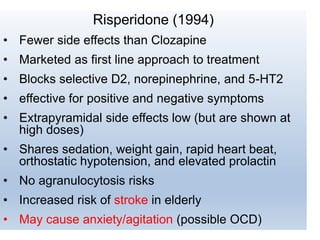
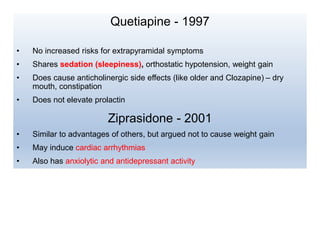
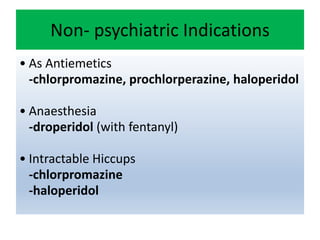
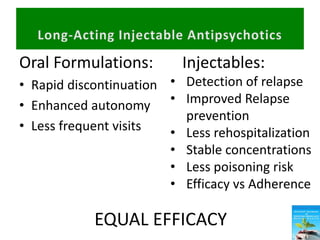
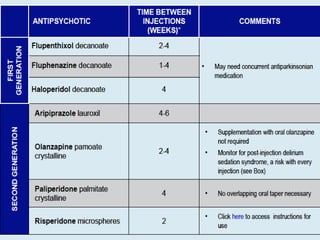
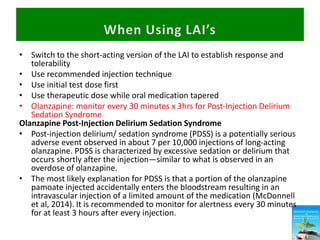
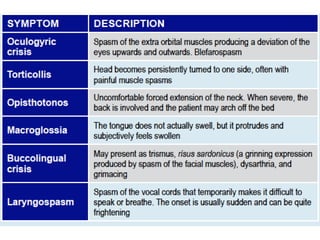
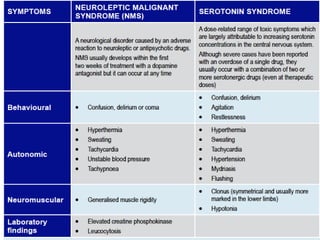
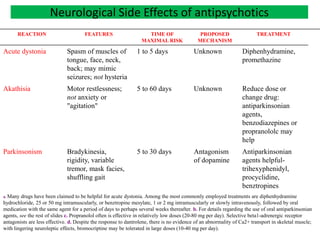
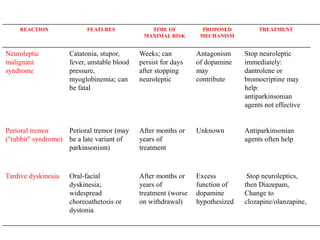
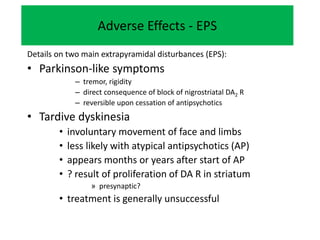
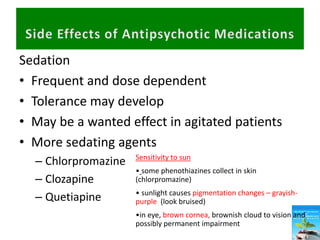
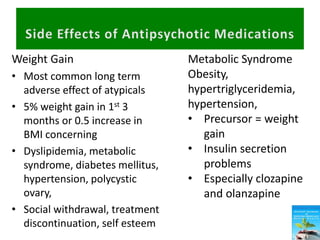
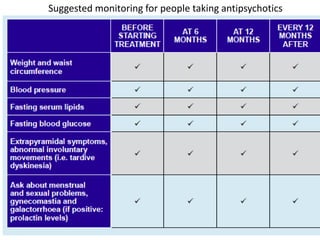
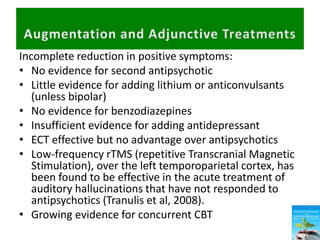
First generation antipsychotics block dopamine receptors and were introduced in the 1950s-1970s. Second generation antipsychotics emerged in the 1980s and target multiple receptors with fewer side effects. Clozapine was the first second generation antipsychotic and has fewer extrapyramidal side effects but requires blood monitoring. Other second generation antipsychotics include risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, aripiprazole, and ziprasidone, which vary in their receptor profiles and side effect risks. Long-acting injectable antipsychotics provide consistent drug levels and can improve adherence compared to oral medications.