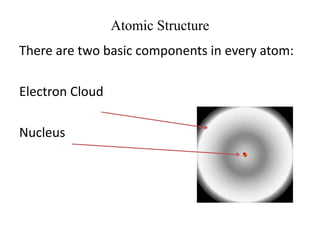
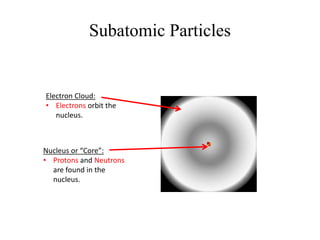
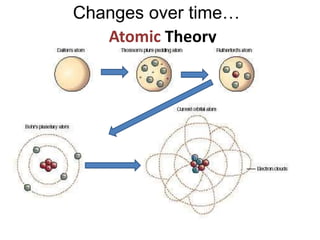
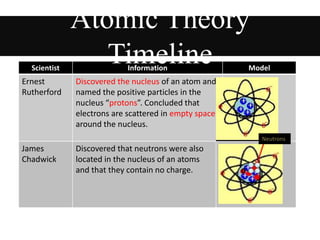
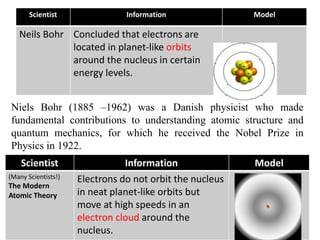
This document provides an overview of atomic theory and the laws of chemical combination. It discusses the early Greek philosophers' debates on the nature of matter and whether it is continuous or made of discrete particles. John Dalton developed the modern atomic theory in the early 19th century, which included five main points. The document outlines the contributions of scientists like Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr to models of atomic structure. It describes the three states of matter and defines the fundamental laws of conservation of mass, definite proportions, and multiple proportions discovered by scientists like Lavoisier, Proust, and Dalton. Examples are provided to illustrate applications of these laws.