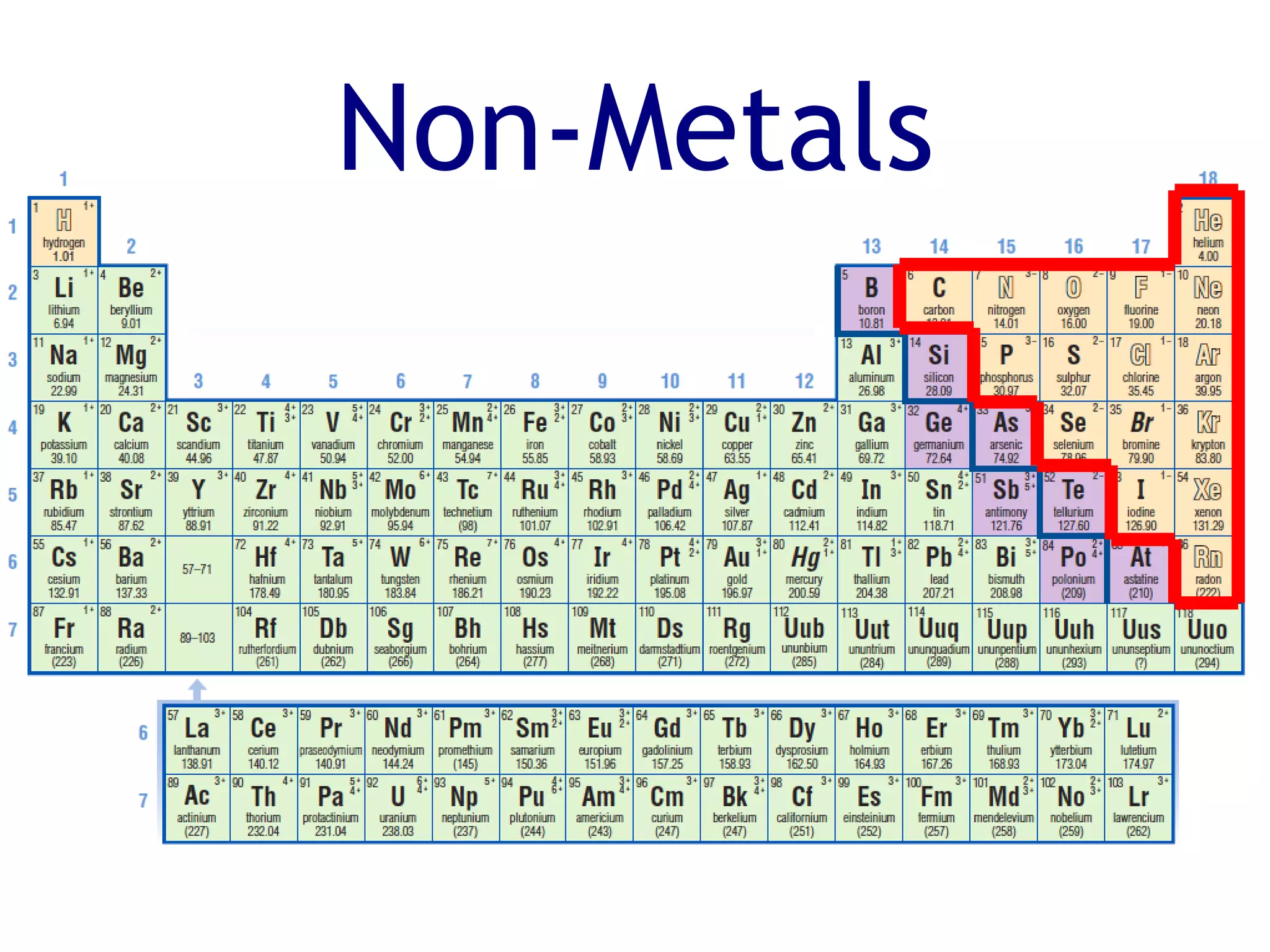
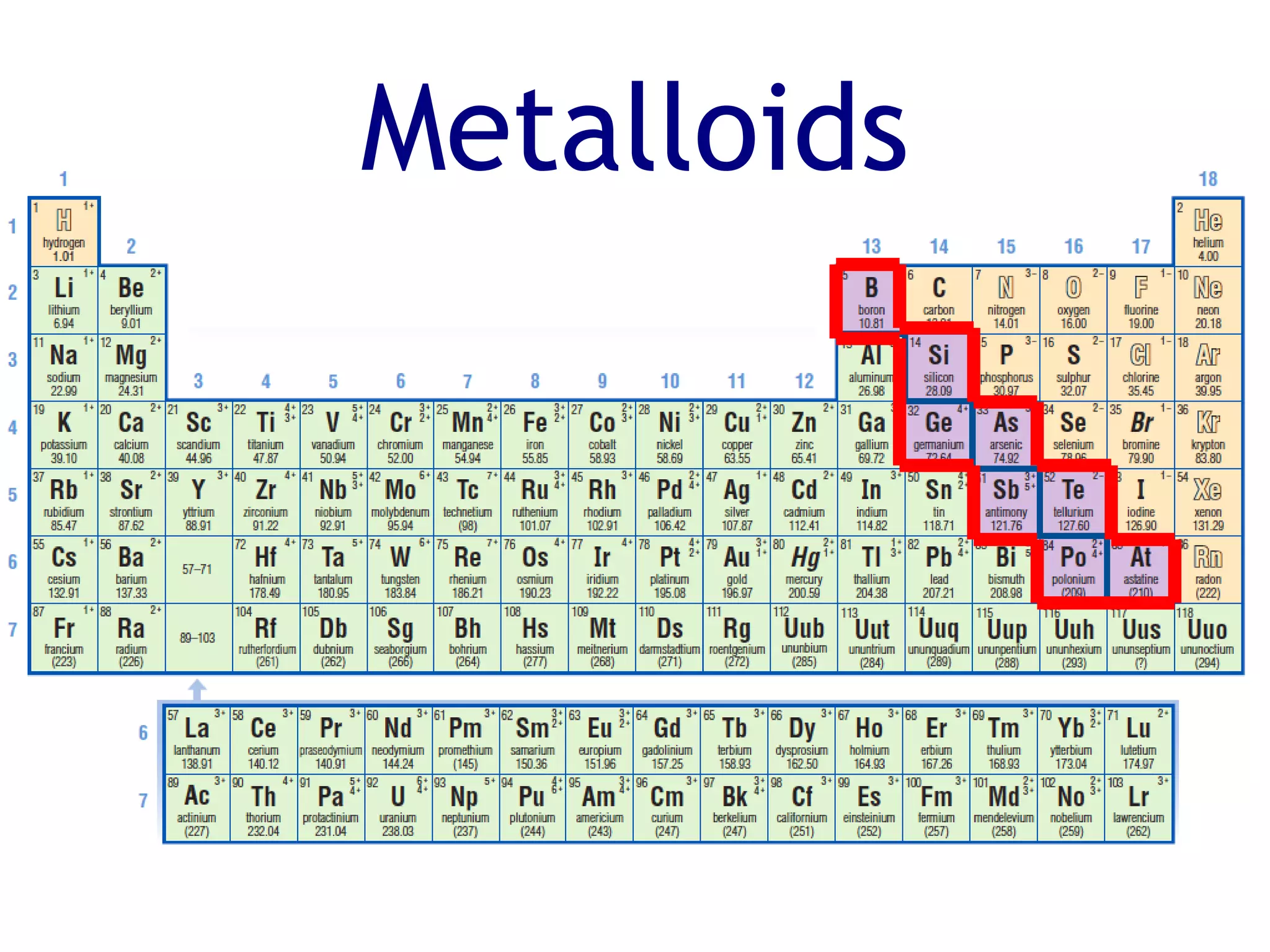
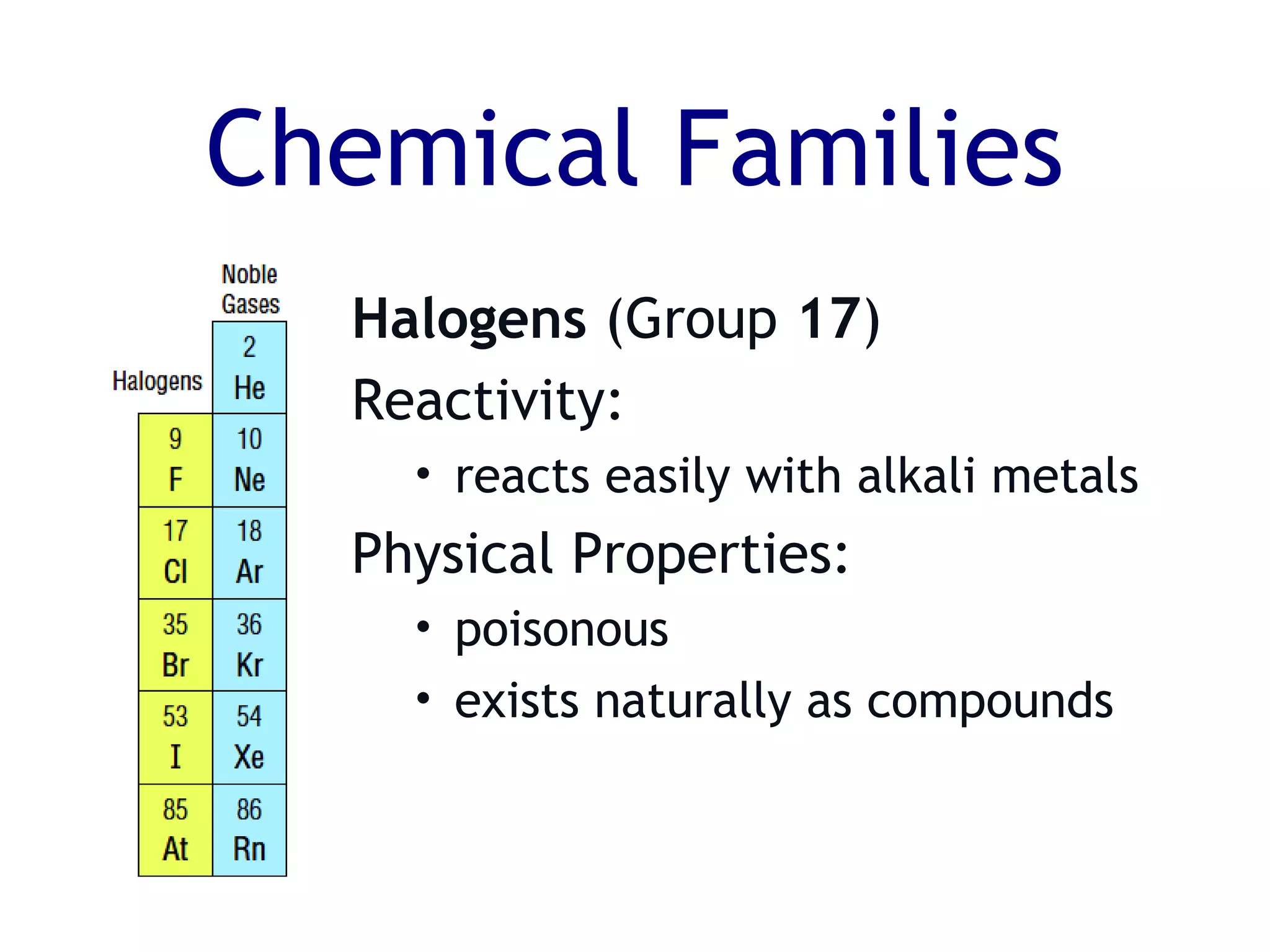
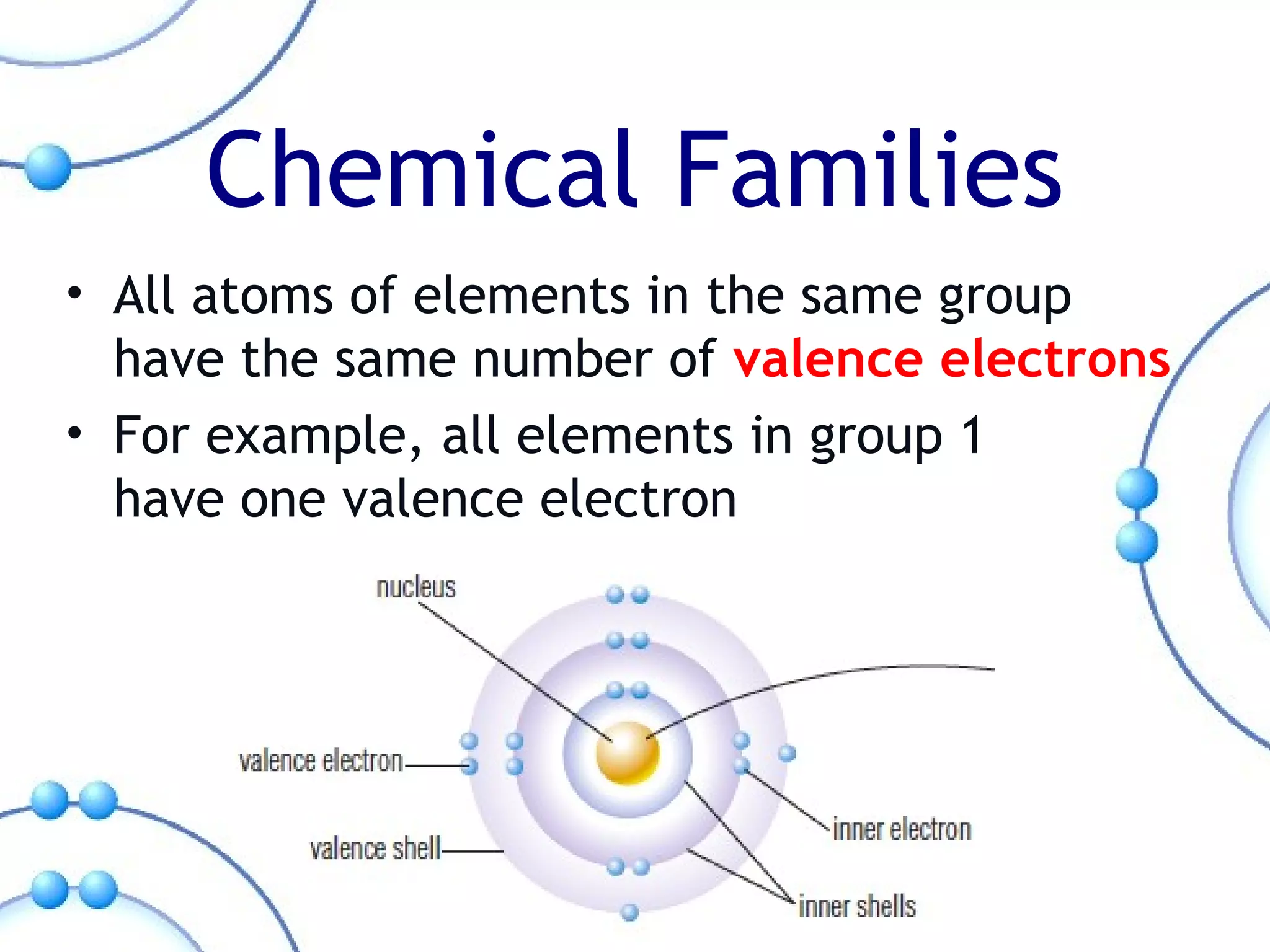
The document summarizes key aspects of the periodic table. It describes how the periodic table is organized into horizontal rows called periods and vertical columns called families or groups. Elements within the same group have similar physical and chemical properties. Metals are found on the left and center of the periodic table and have properties like conductivity and malleability. Non-metals are on the right and have varying properties, often gaining electrons in reactions. Metalloids between metals and non-metals have intermediate properties. Different families like alkali metals, halogens, and noble gases are also described in terms of their physical properties and reactivity.