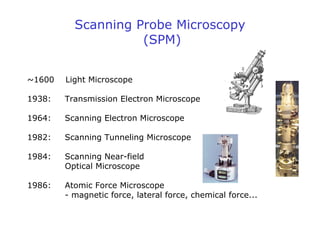
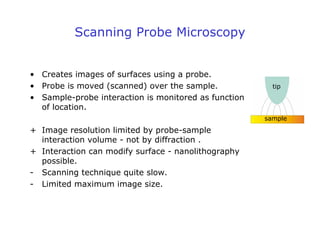
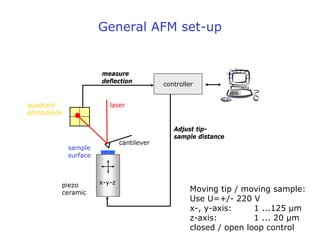
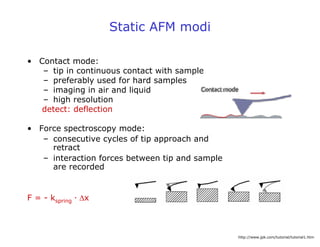
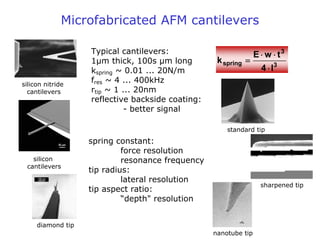
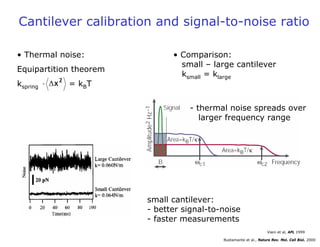
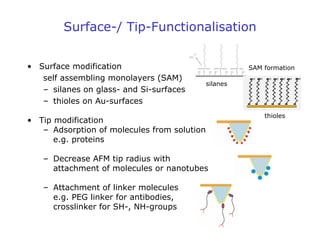
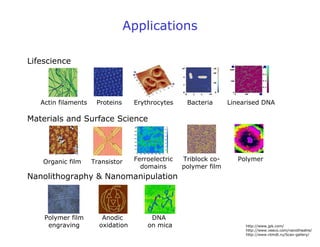
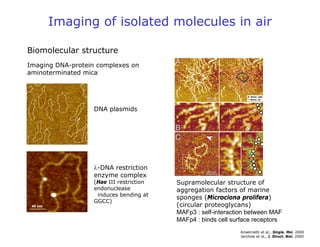
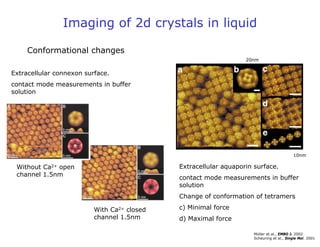
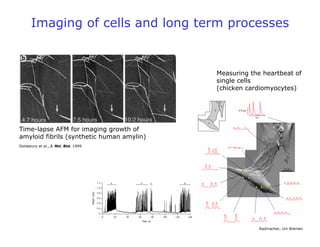
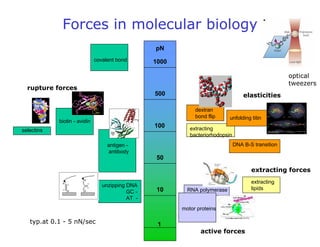
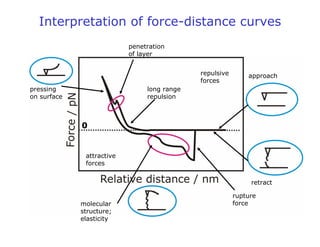
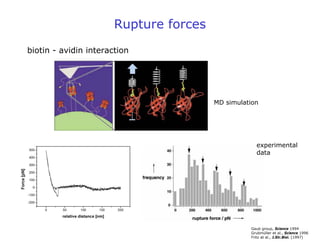
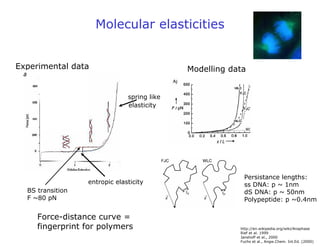
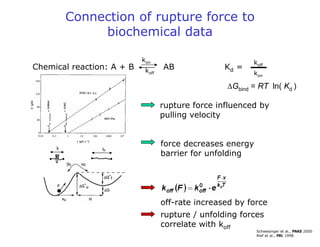
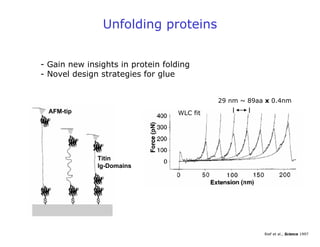
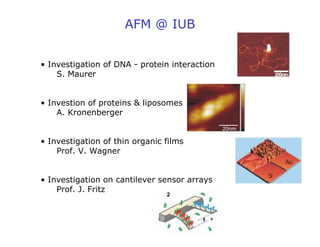
- Atomic force microscopy (AFM) uses a cantilever with a sharp tip to scan over a sample surface and produce images of its topography. The tip is moved in the x, y, and z directions using a piezoelectric scanner. Interactions between the tip and sample are measured to create images with sub-nanometer resolution.
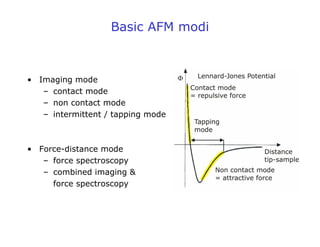
- AFM can operate in different modes depending on whether the tip is in contact with the surface or oscillating above it. Force-distance curves can also be collected to measure interaction forces. AFM has various applications in biology, materials science, and nanotechnology.