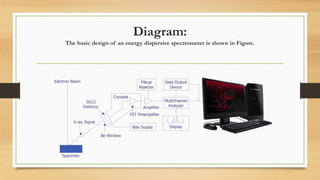
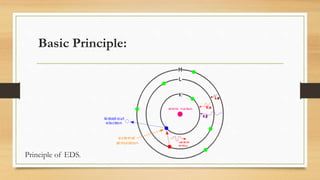
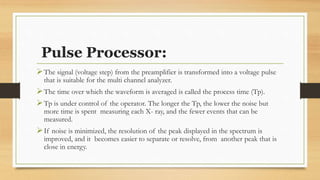
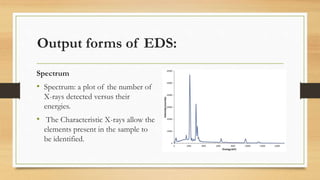
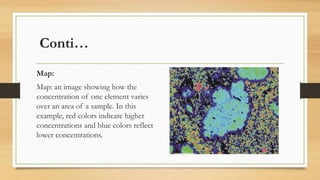
Energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) is a technique used to determine the elemental composition of materials. EDS relies on detecting X-rays emitted from a sample when it is exposed to an electron beam. The X-ray energies are characteristic of elements present in the sample. EDS systems consist of a detector that converts X-ray energies to voltage pulses, a pulse processor that amplifies the signals, and a multi-channel analyzer that sorts the pulses by energy and displays the results as an X-ray spectrum or elemental maps. EDS allows elemental analysis of micrometer-scale sample volumes and provides both qualitative and quantitative chemical information.