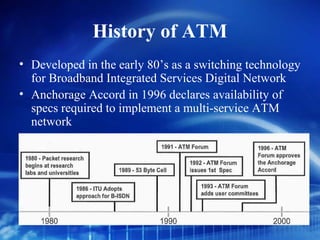
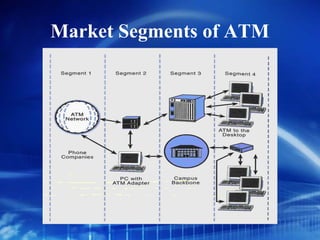
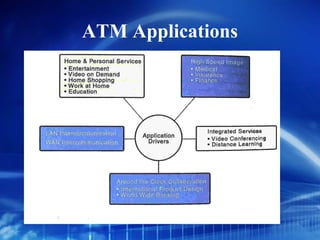
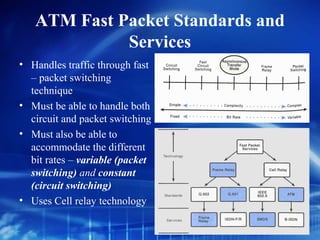
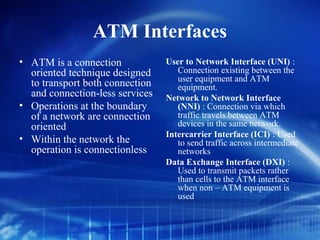
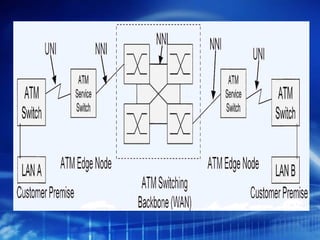
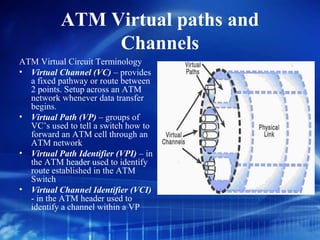
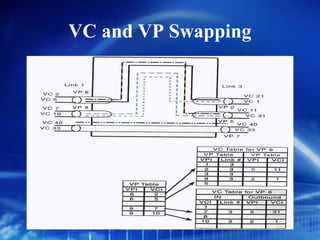
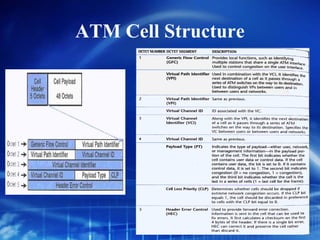
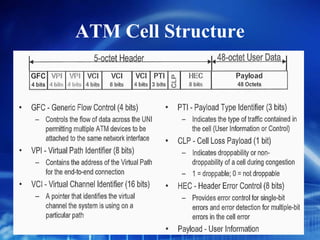
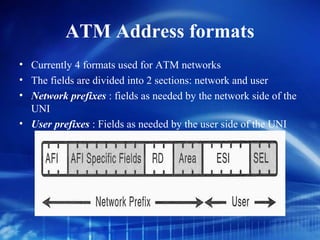
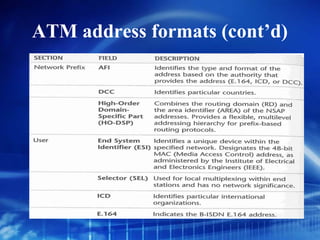
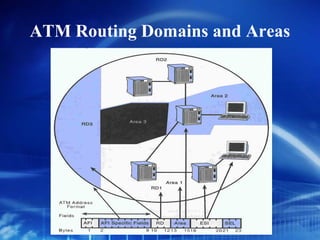
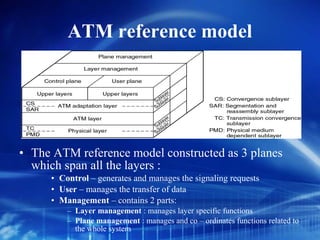
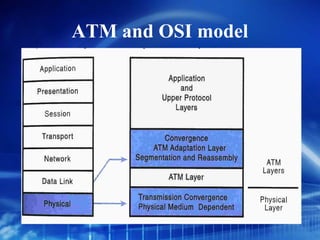
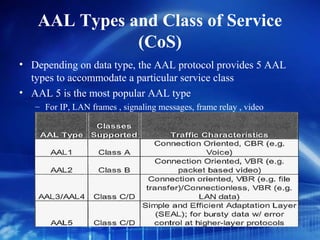
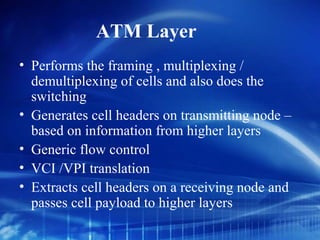
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a network technology that allows different types of digital data such as voice, video, and data to be transmitted over the same physical medium. It uses fixed-length cells known as ATM cells that are 53 bytes long, consisting of a 5-byte header and 48-byte payload. ATM provides guaranteed bandwidth and quality of service for real-time, interactive applications through connection-oriented virtual circuits identified by a virtual path/channel identifier in each cell header. ATM supports both connection-oriented and connectionless services and can accommodate both constant and variable bit rate traffic.