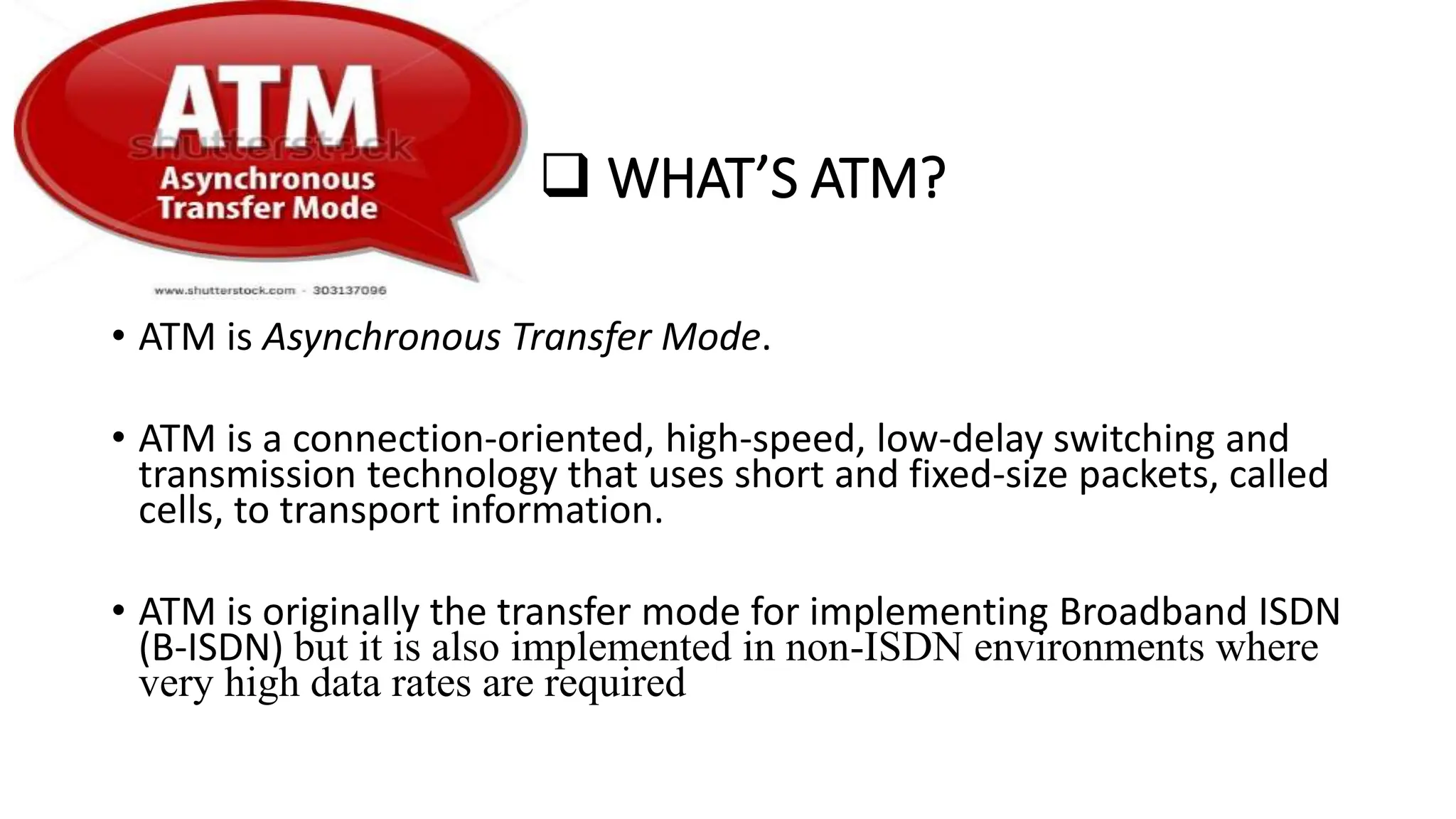
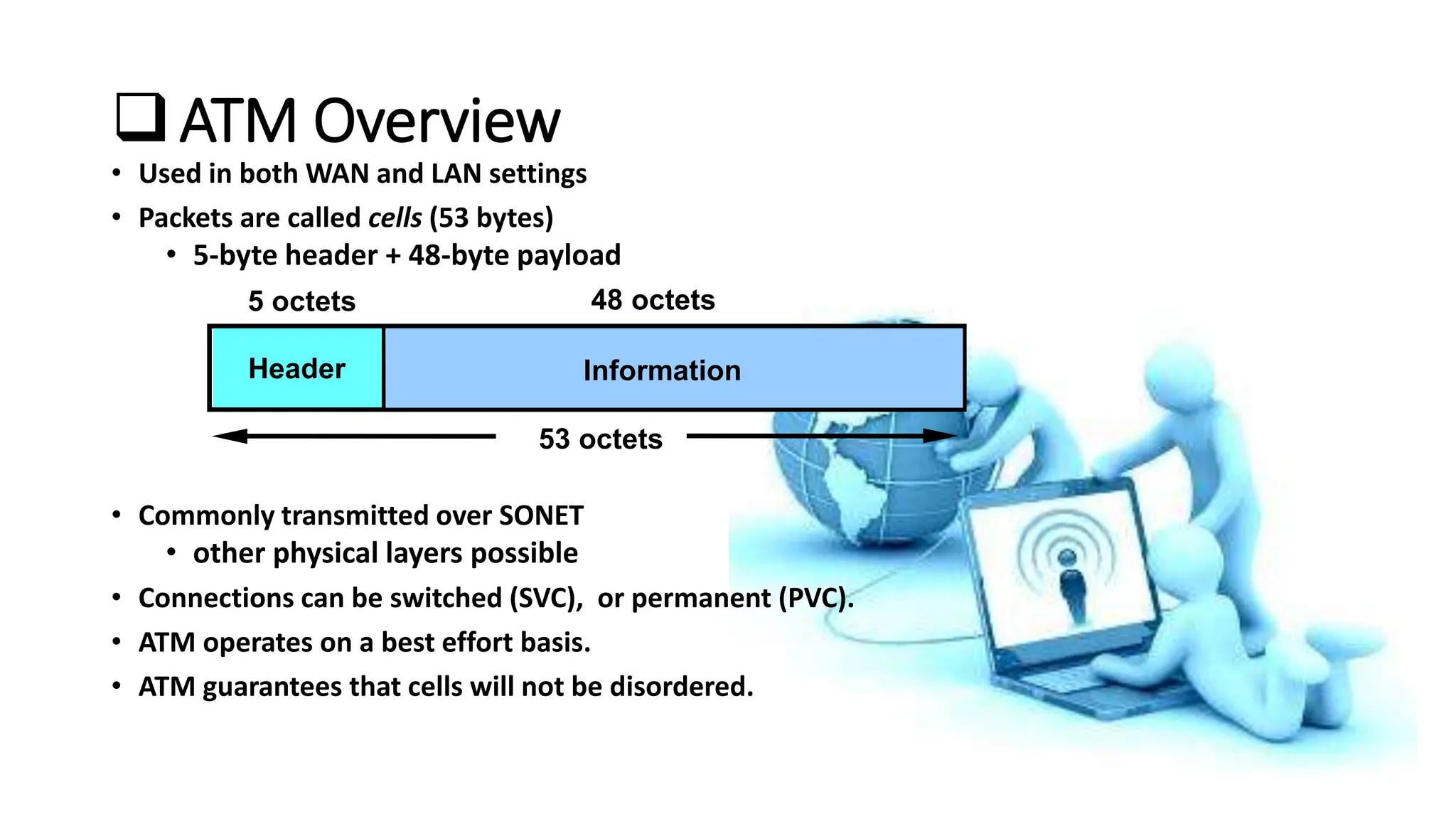
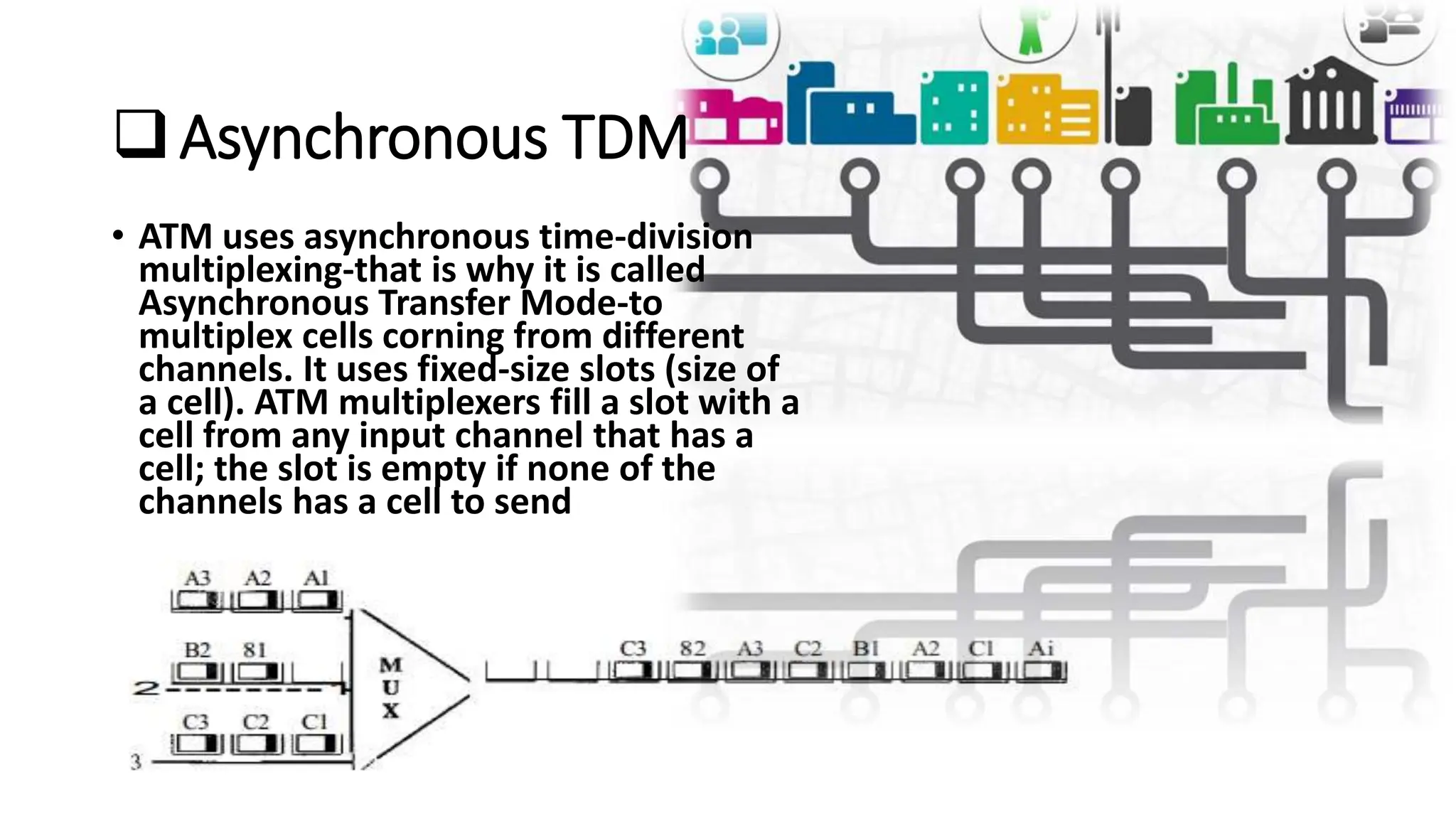
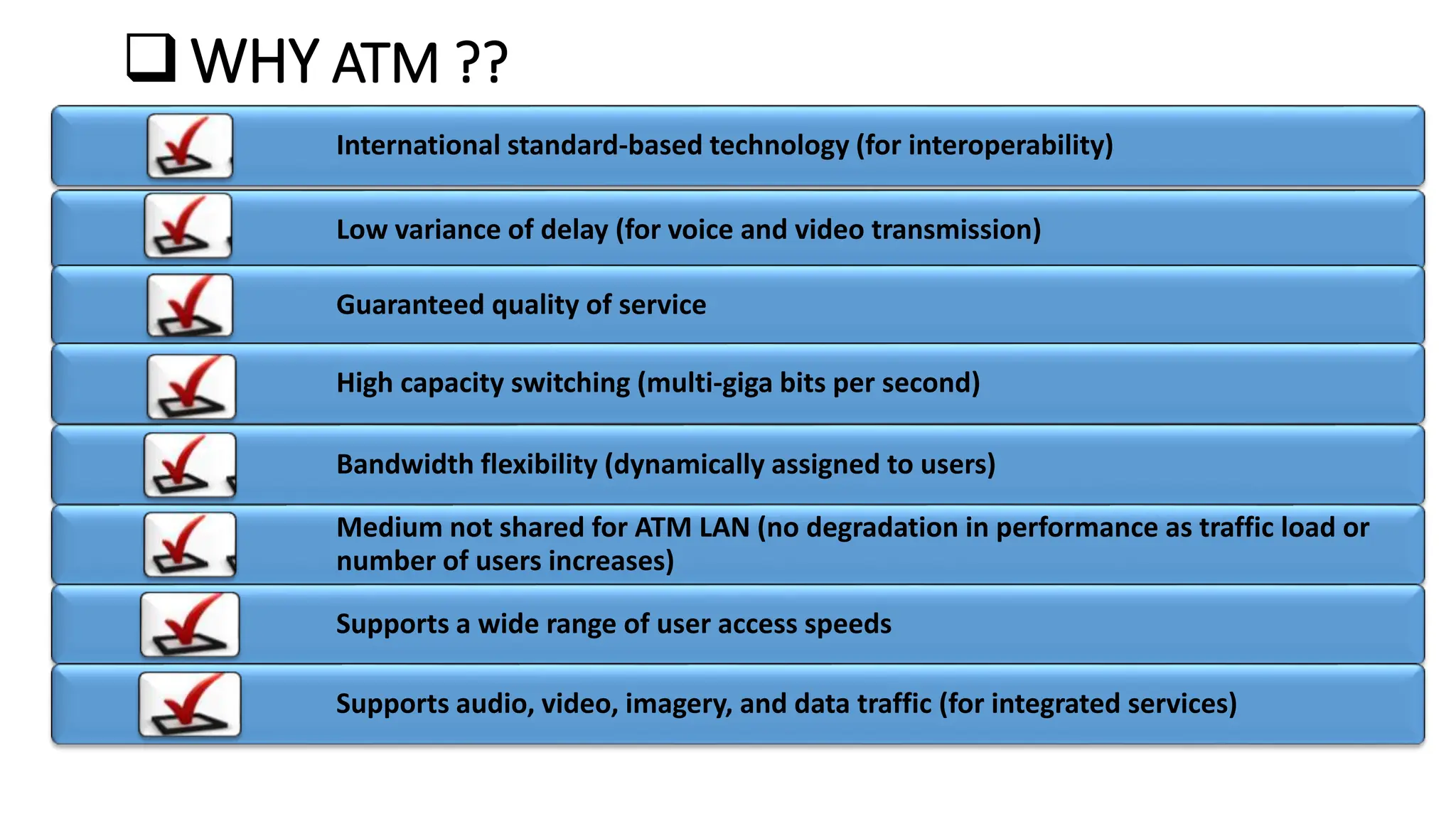
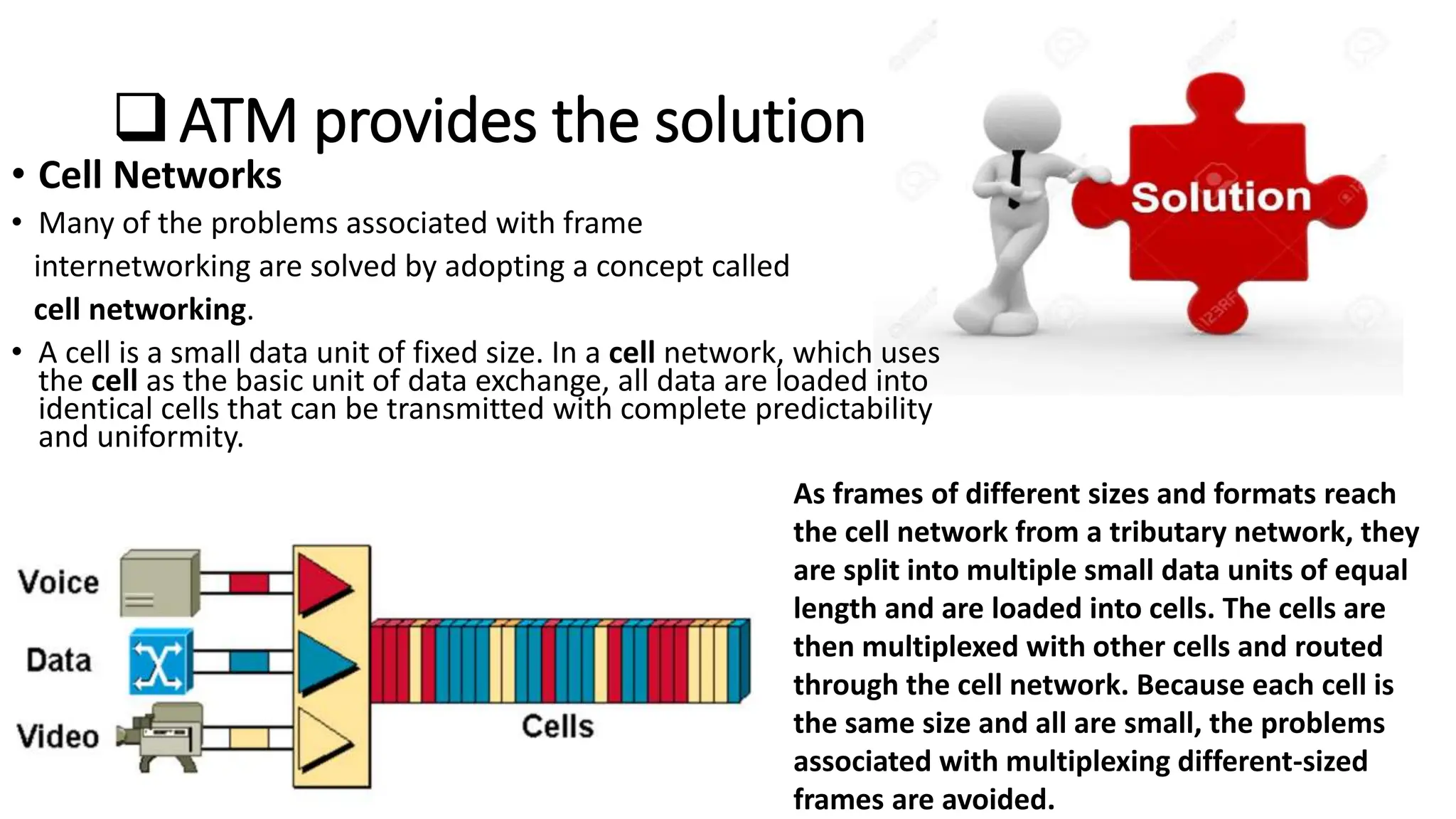
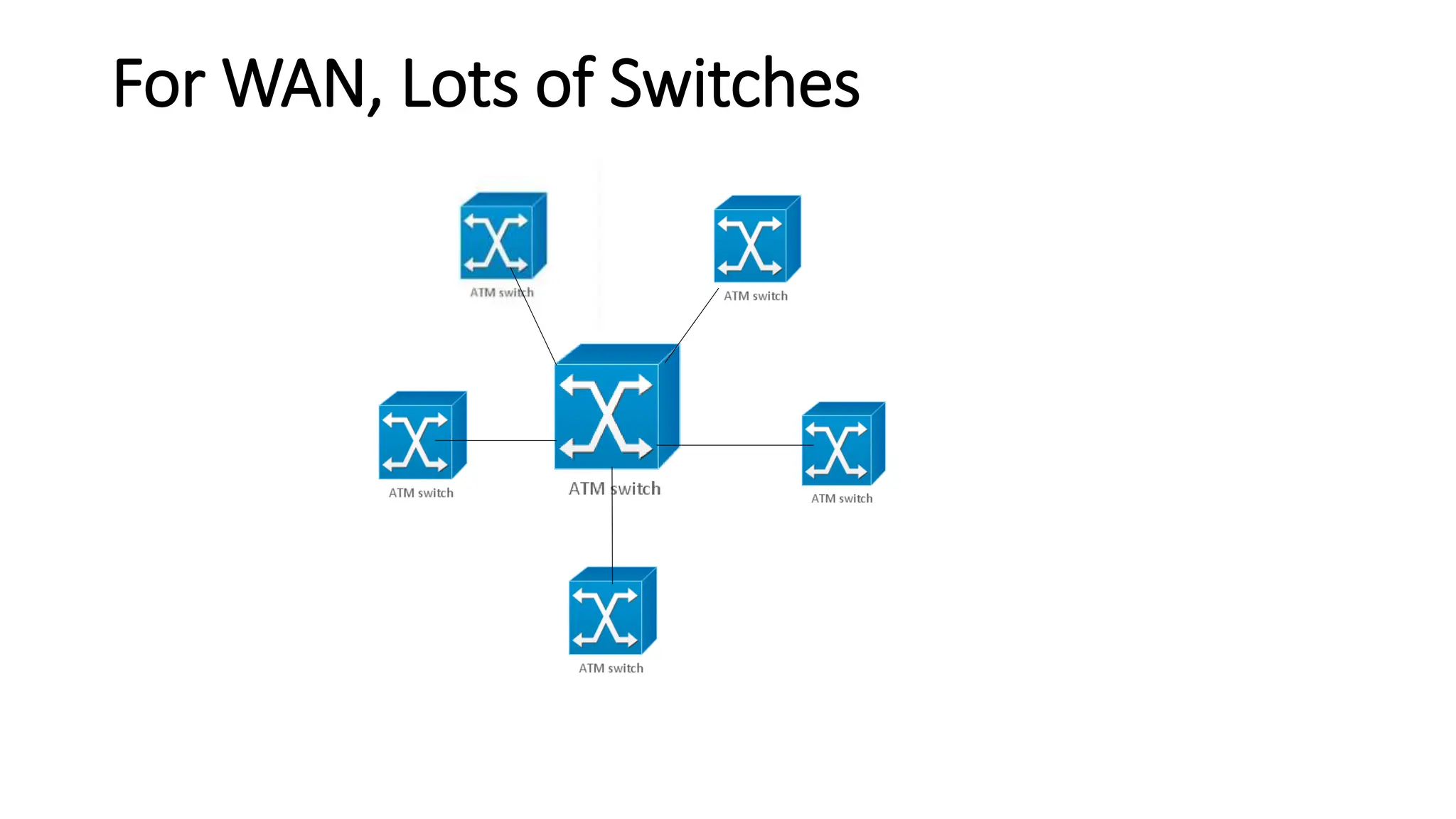
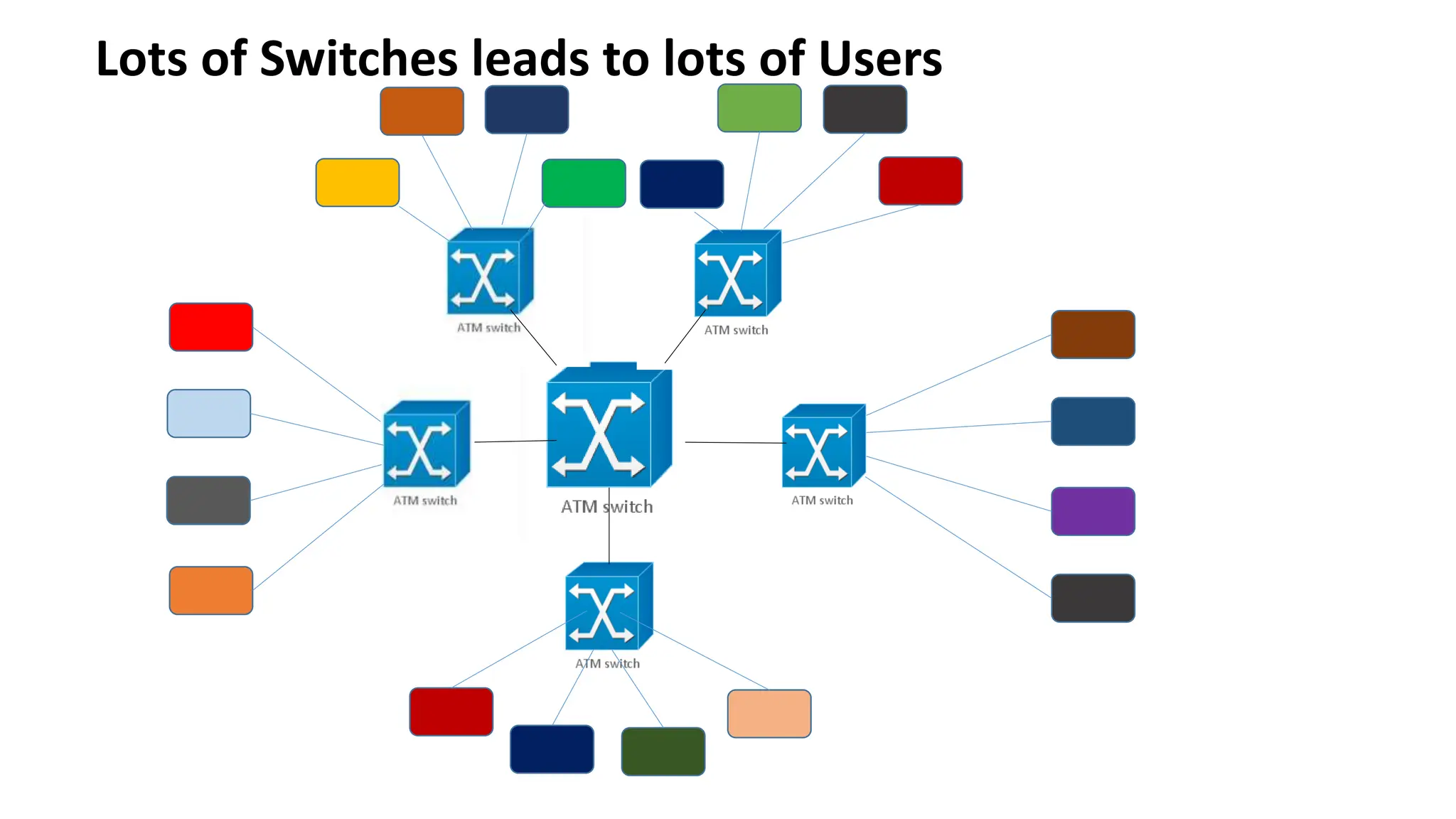
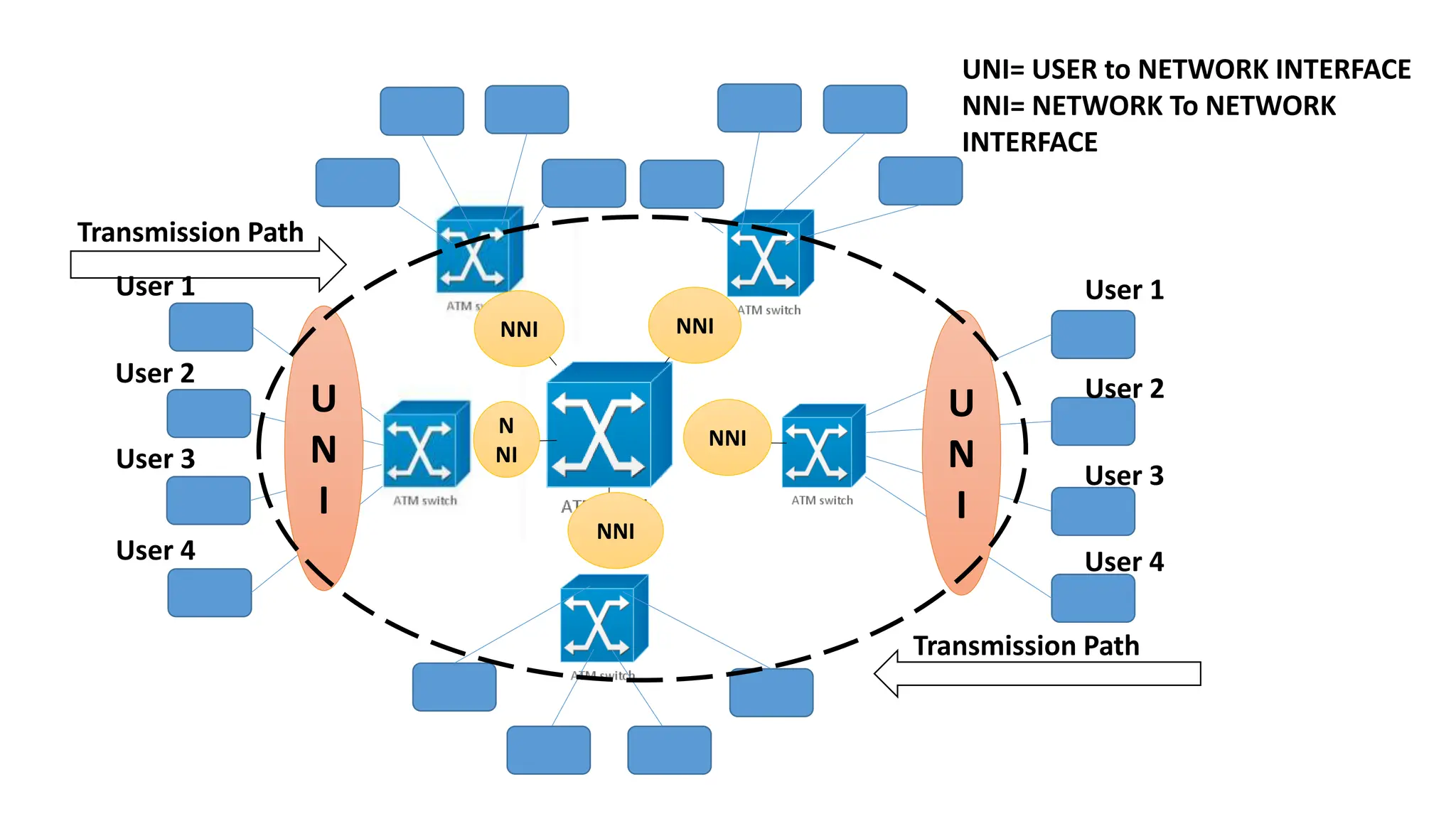
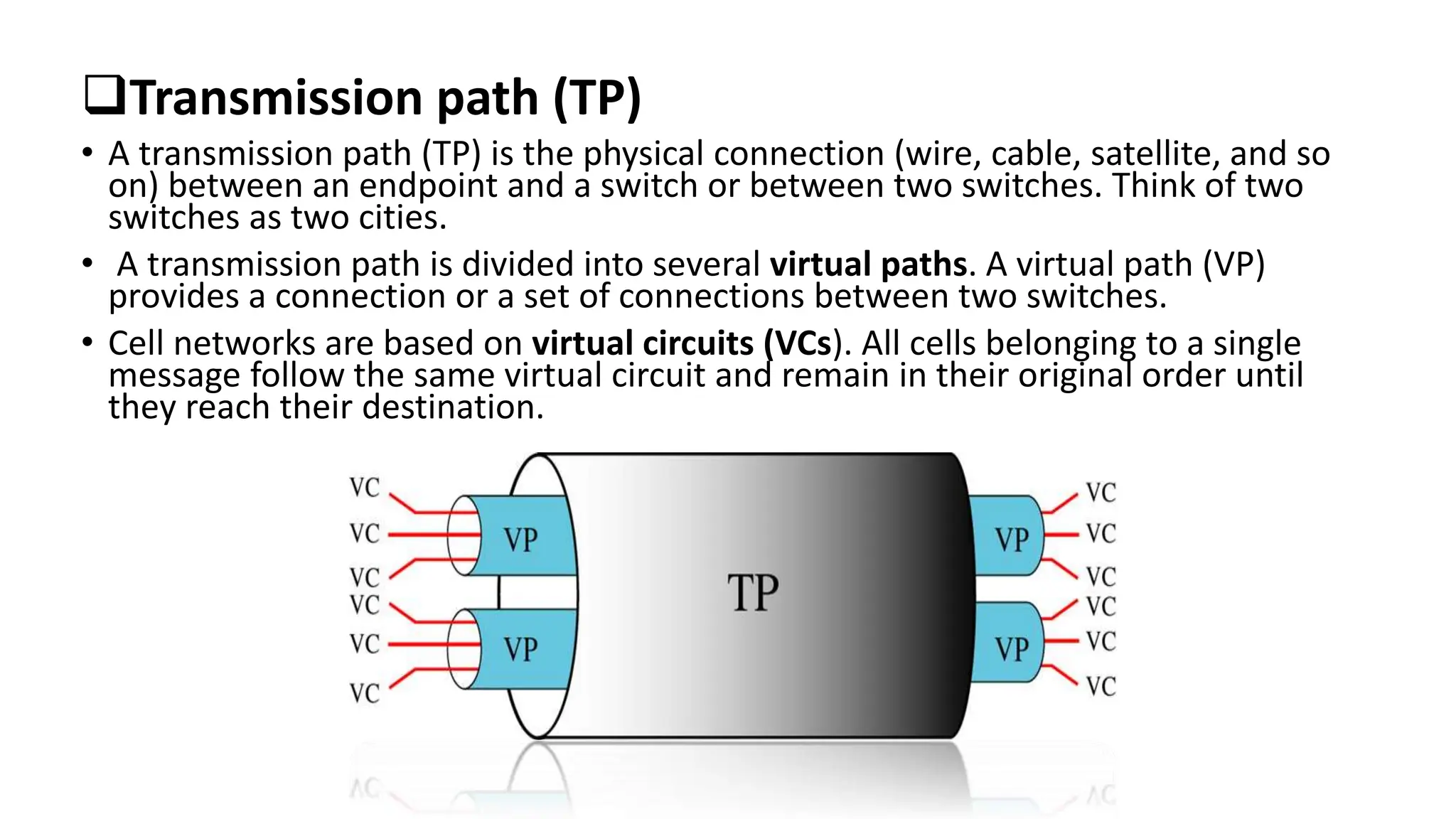
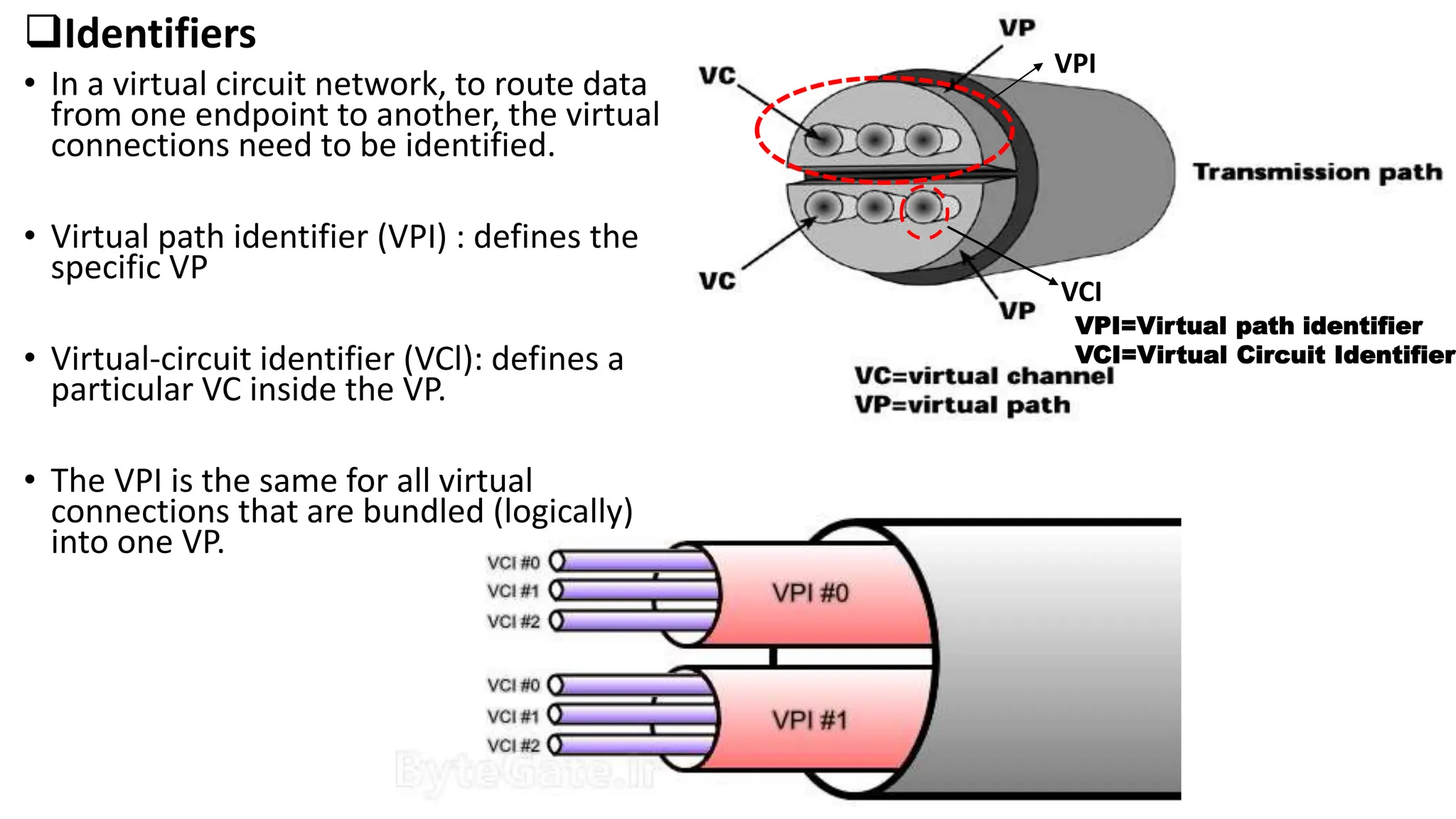
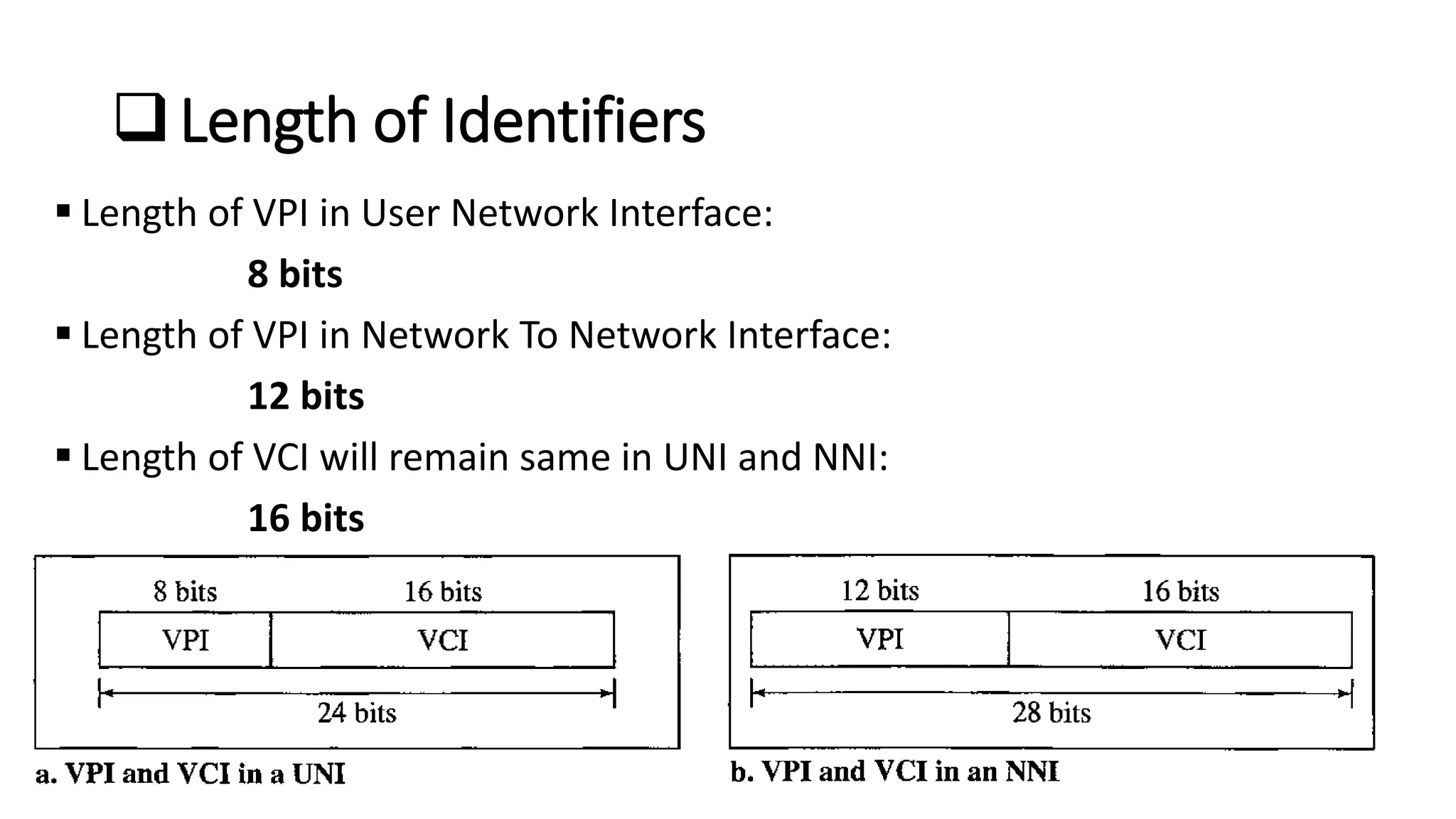
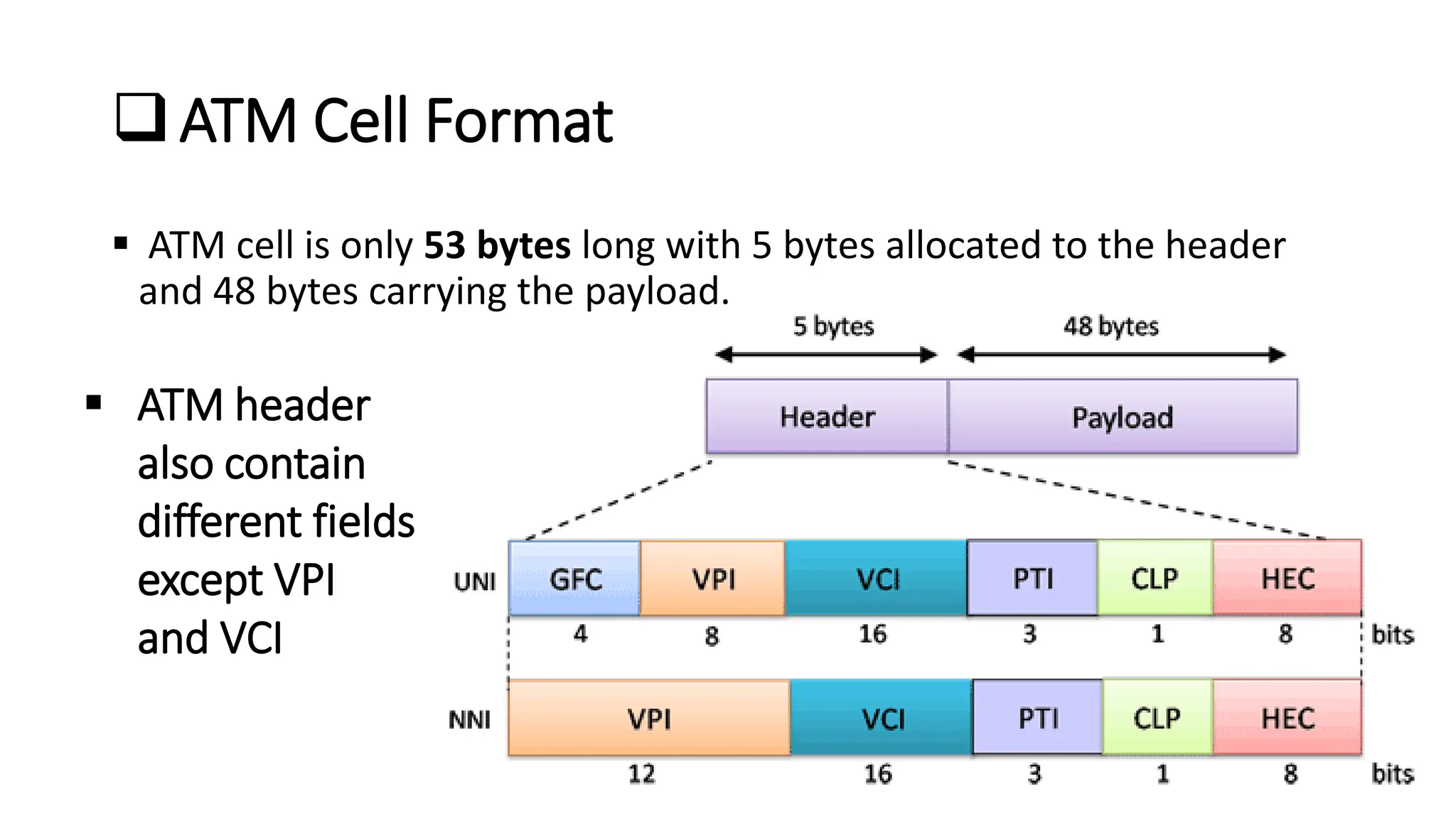
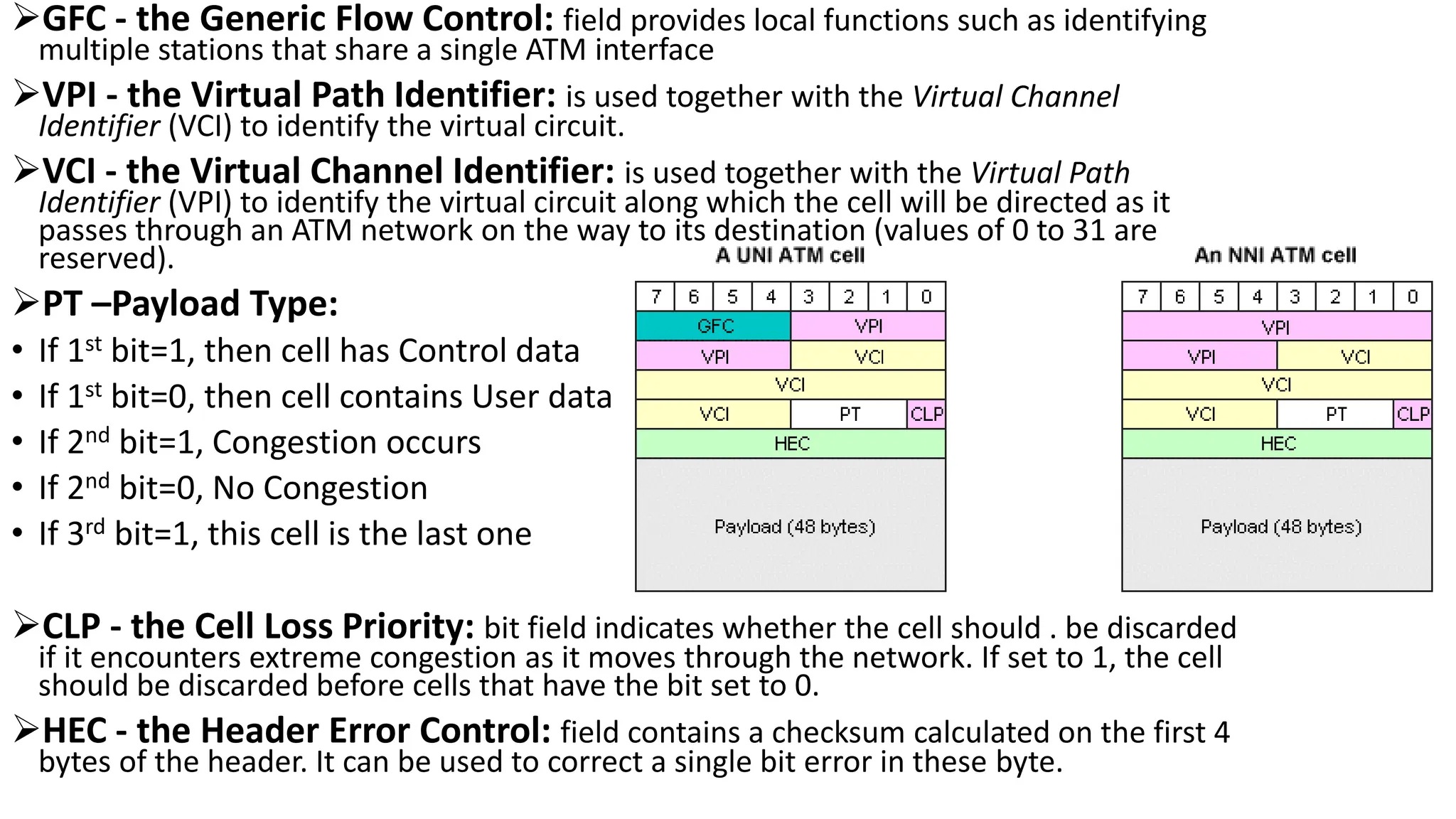
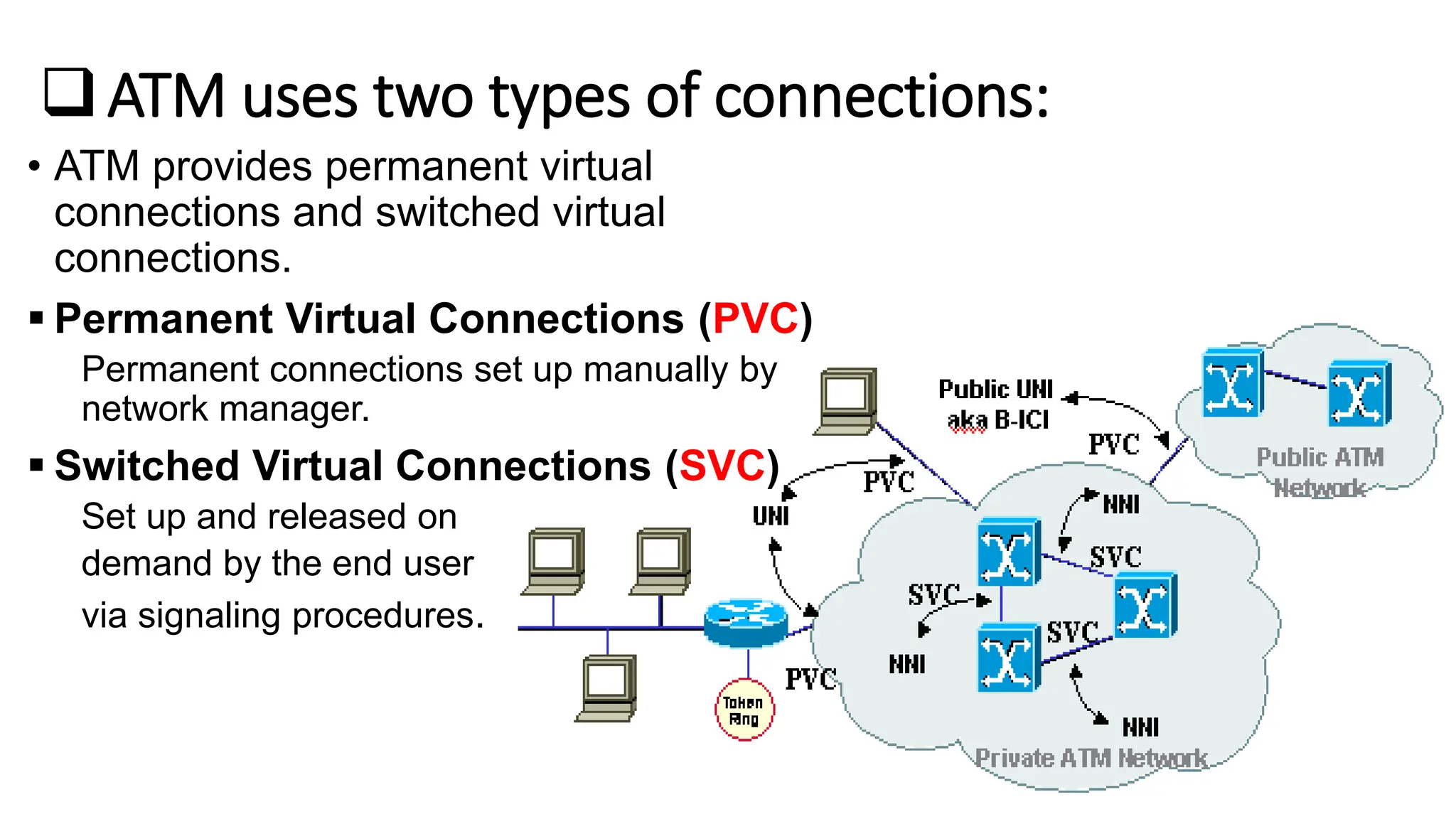
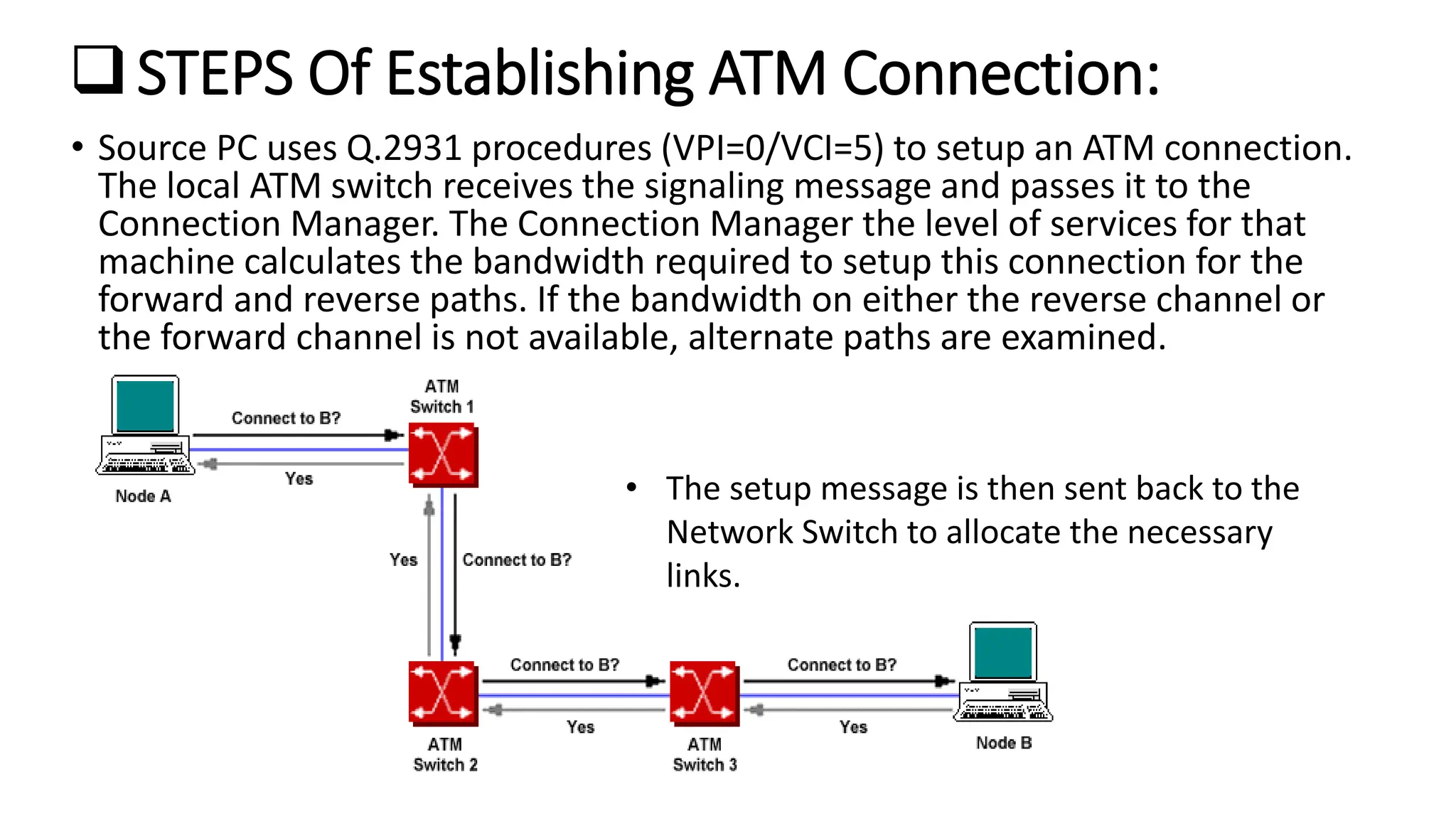
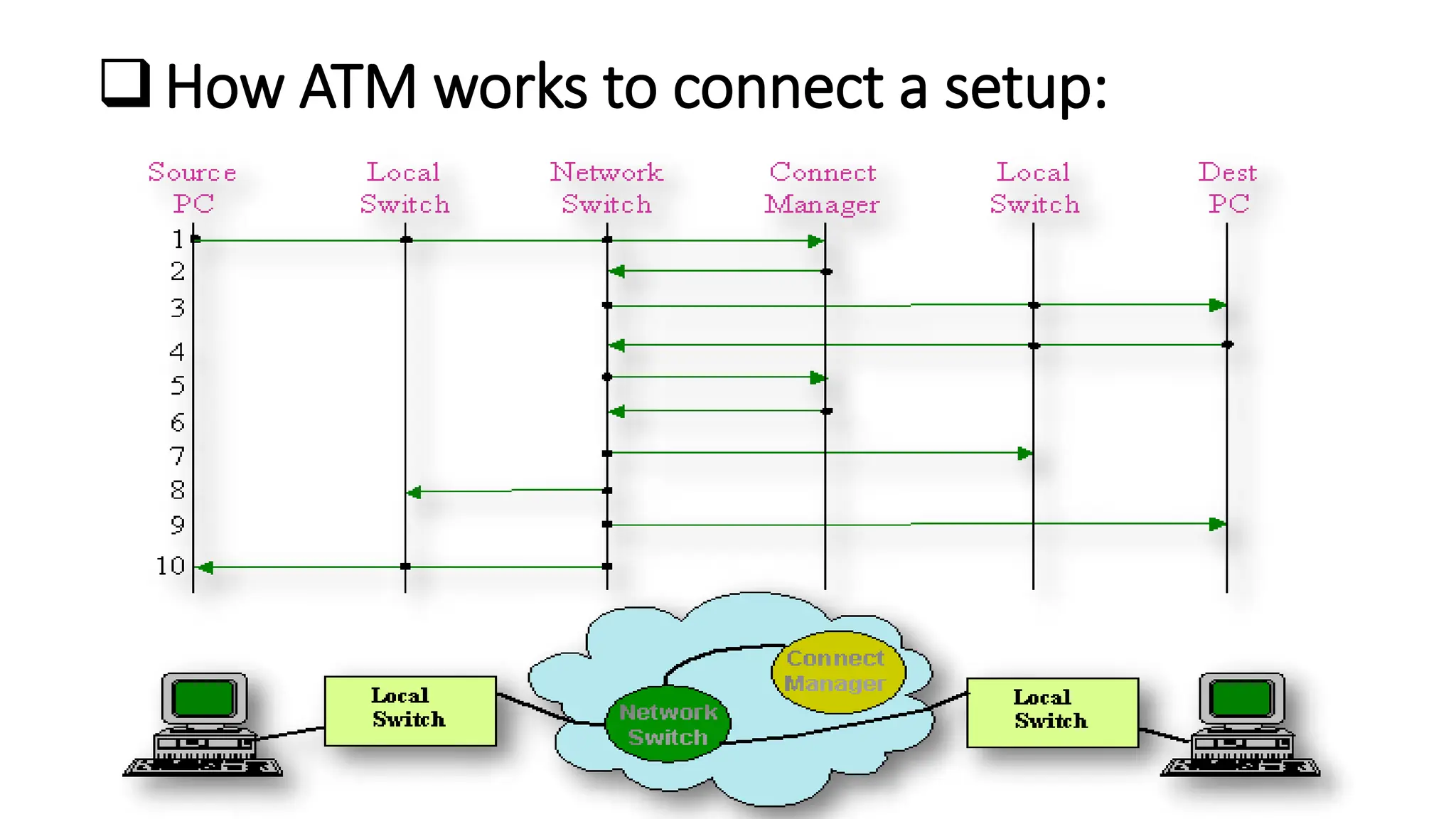
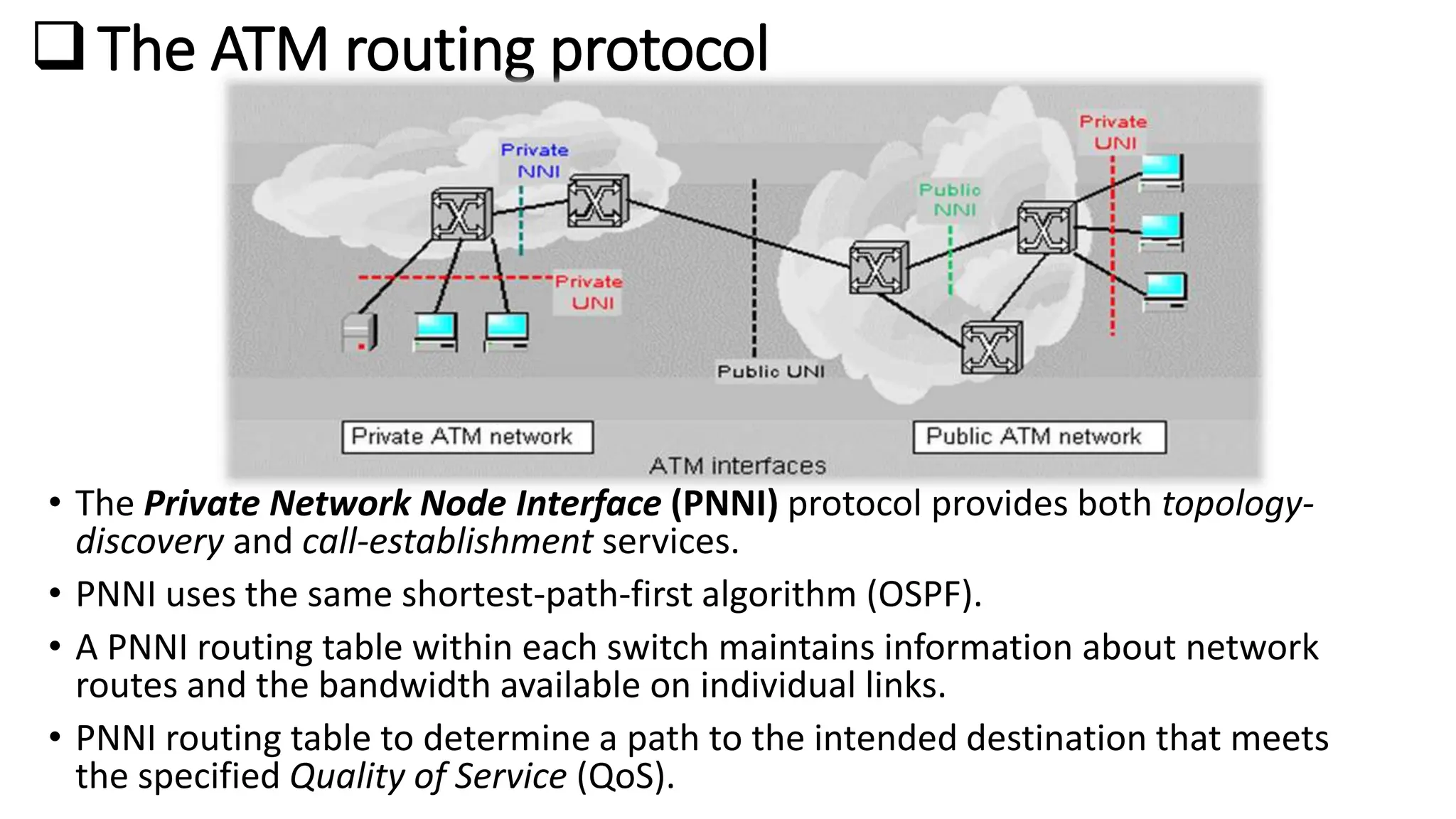
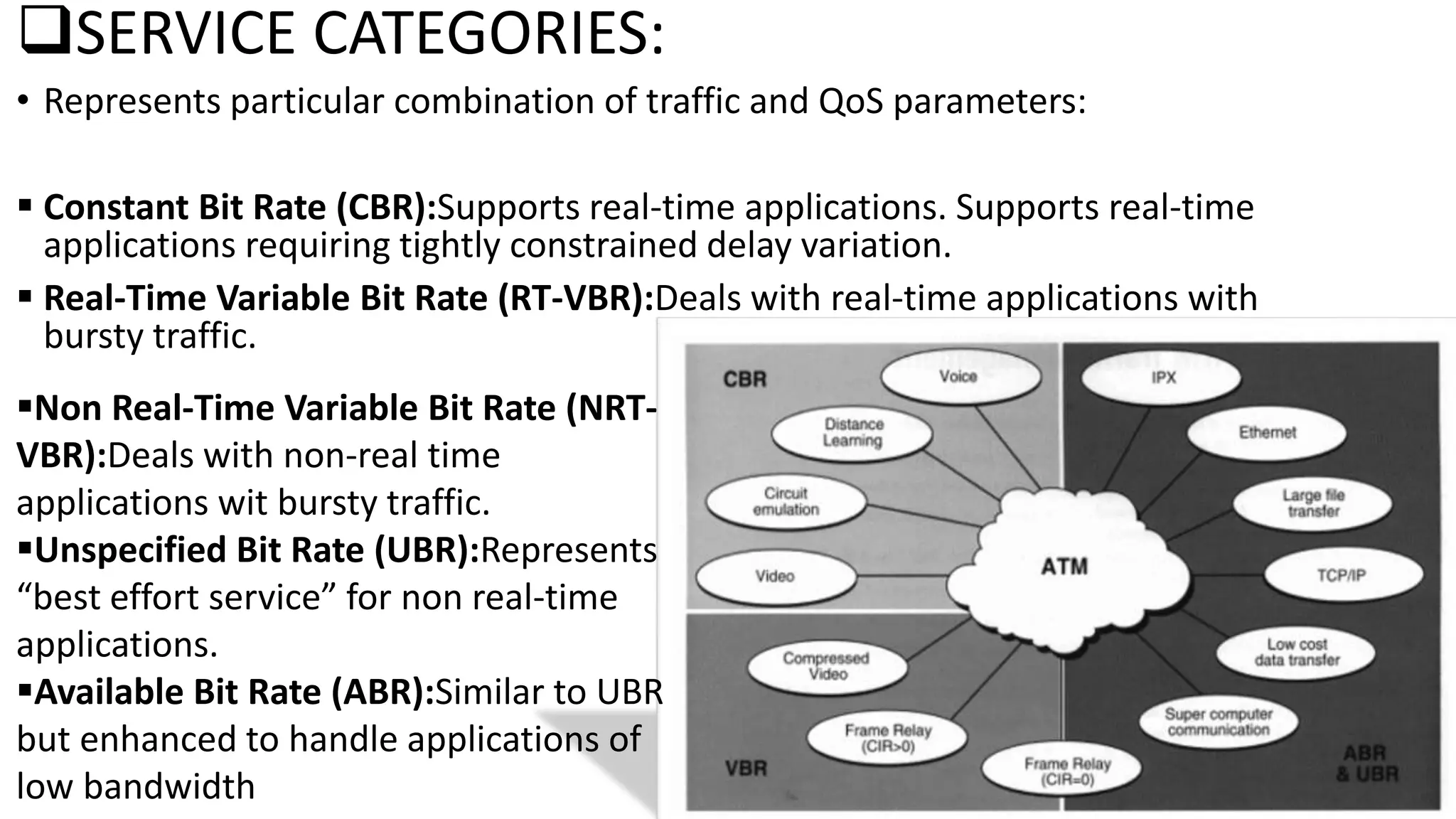
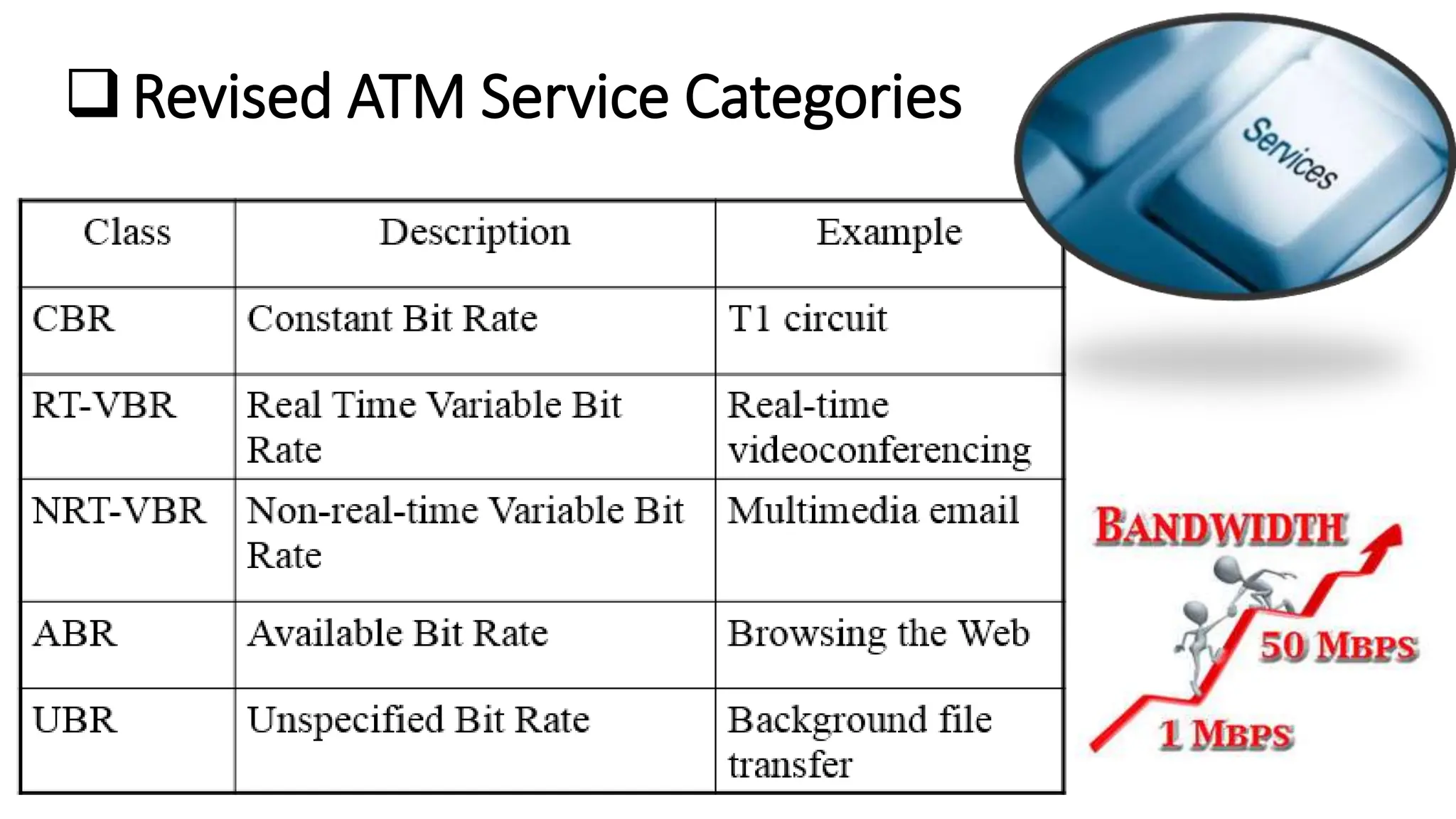
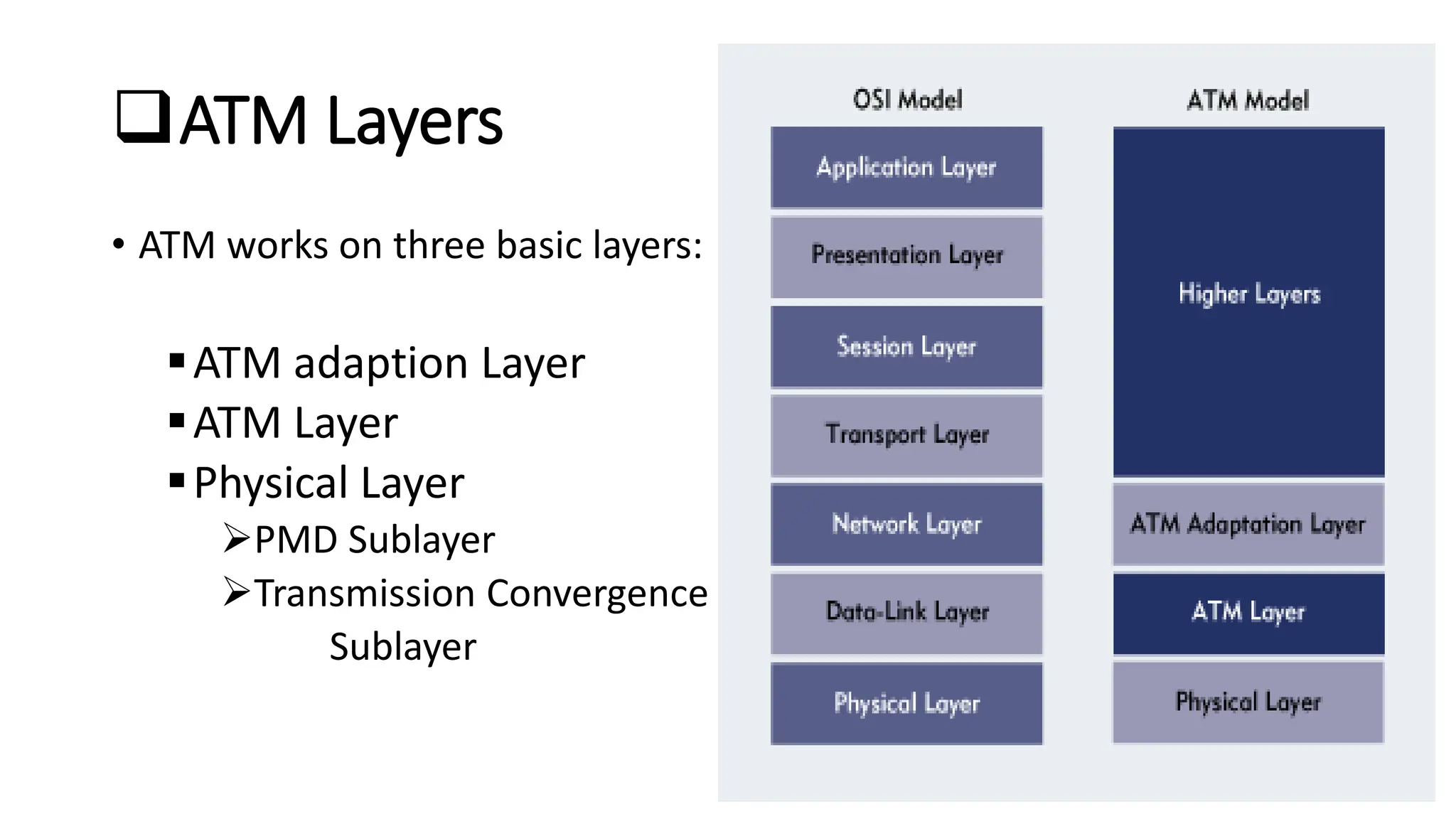
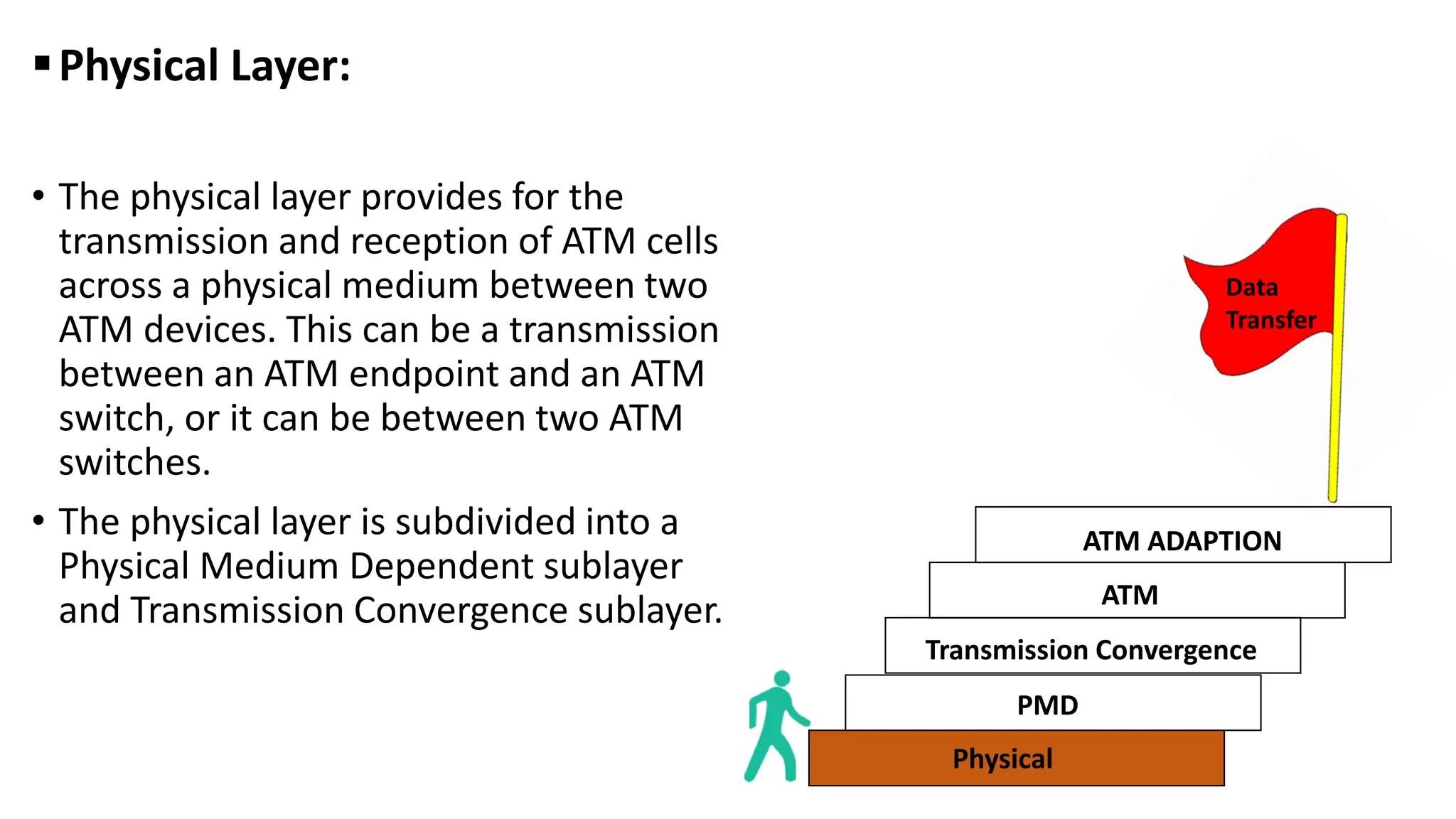
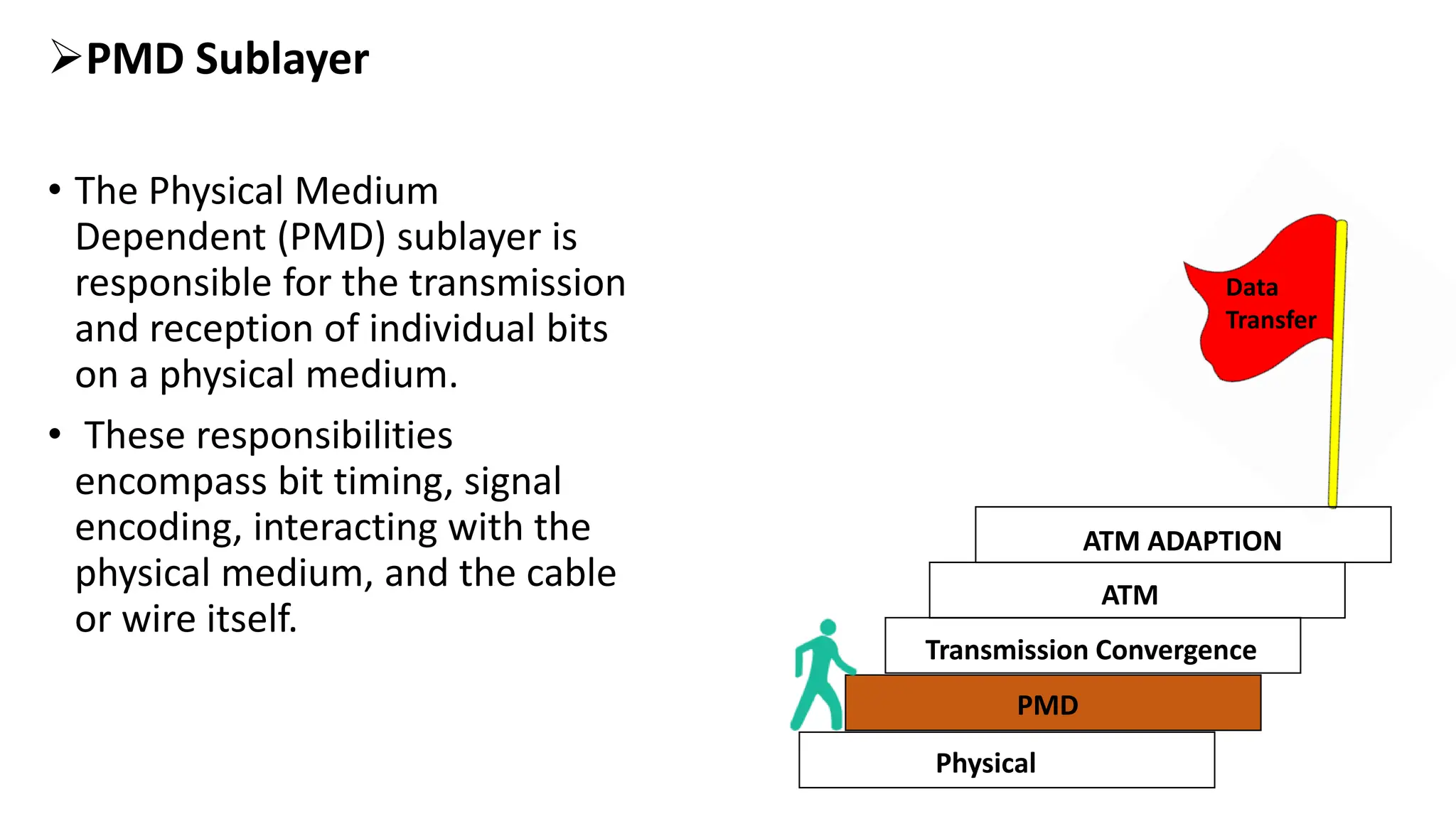
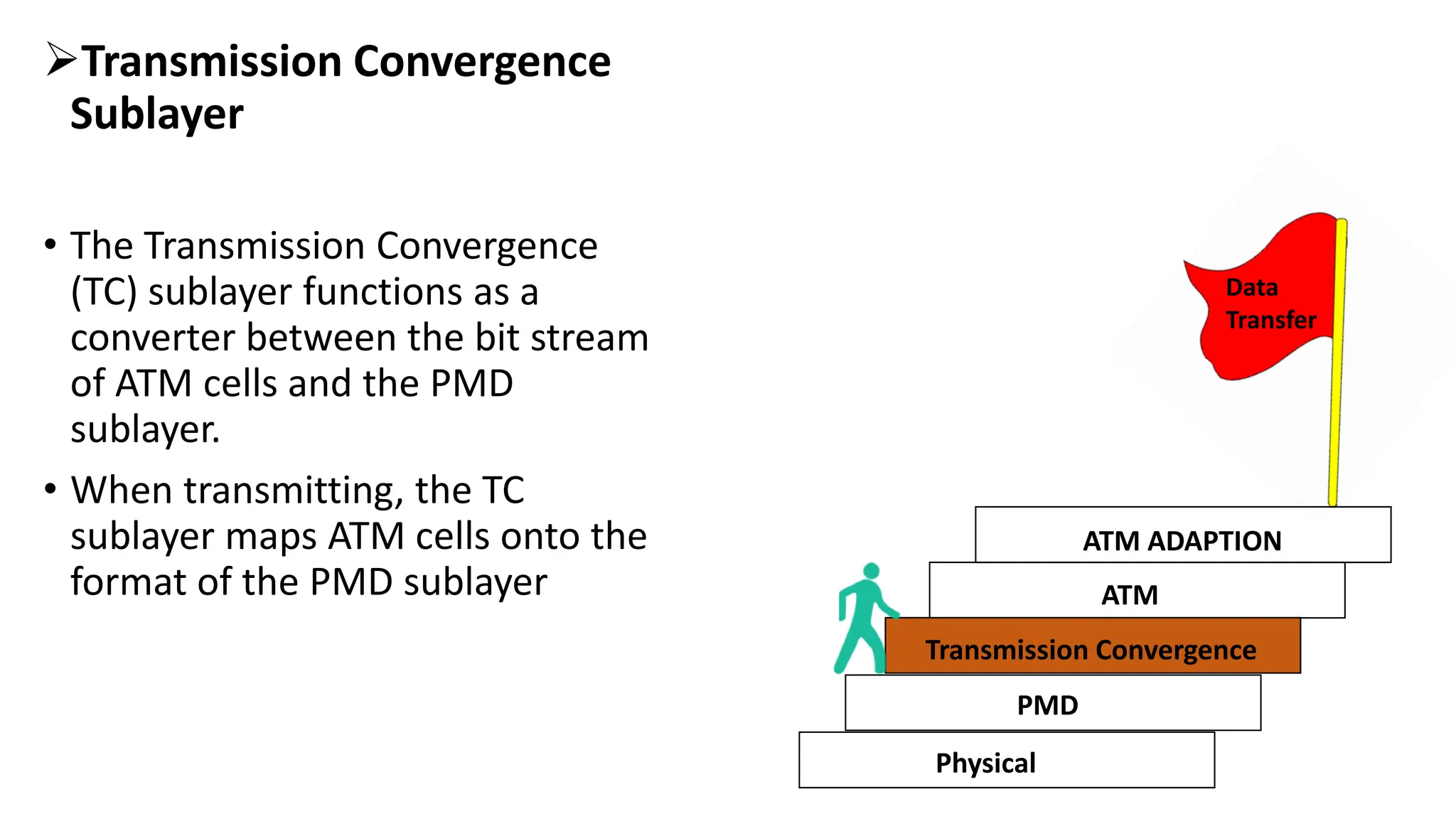
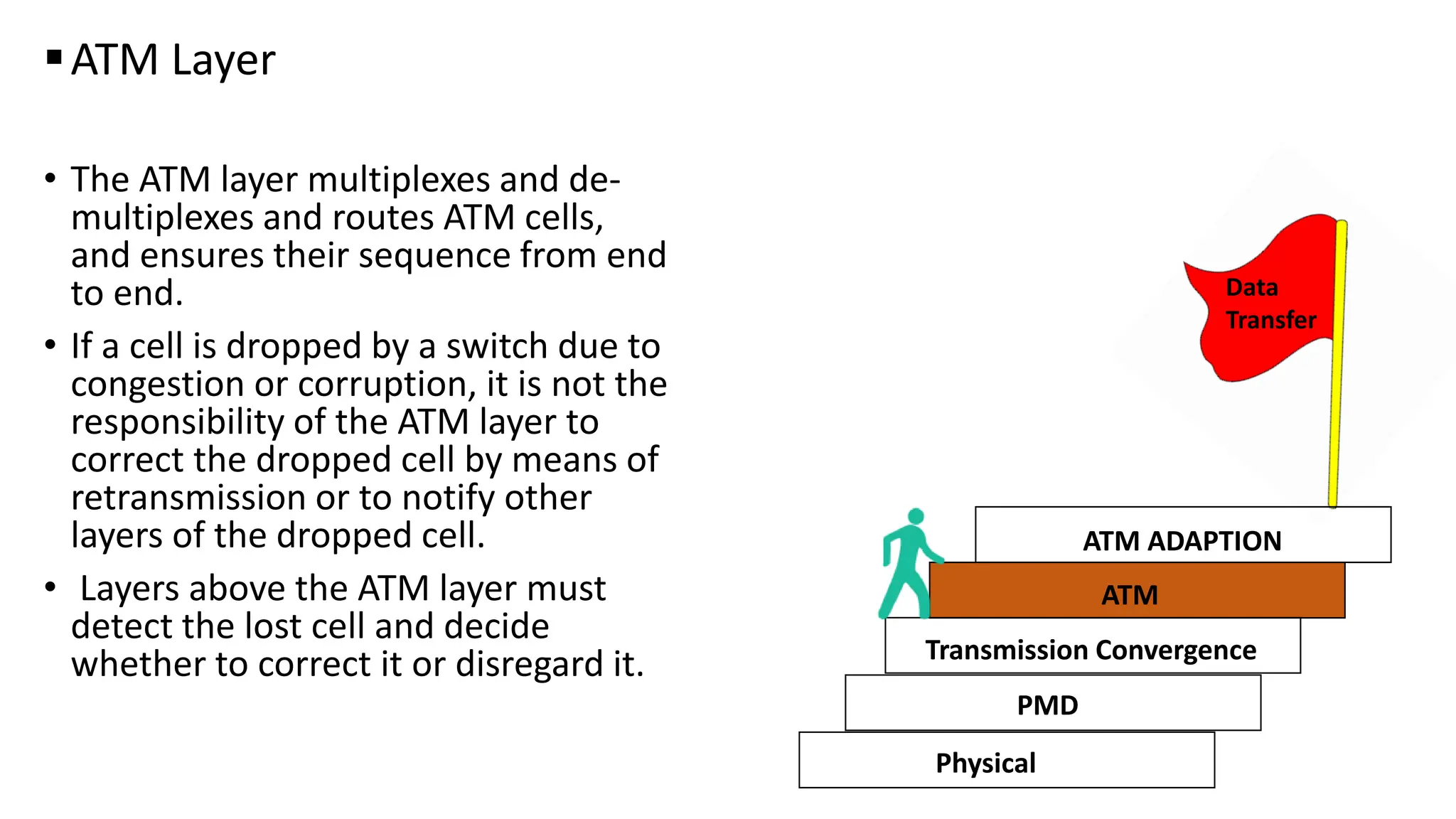
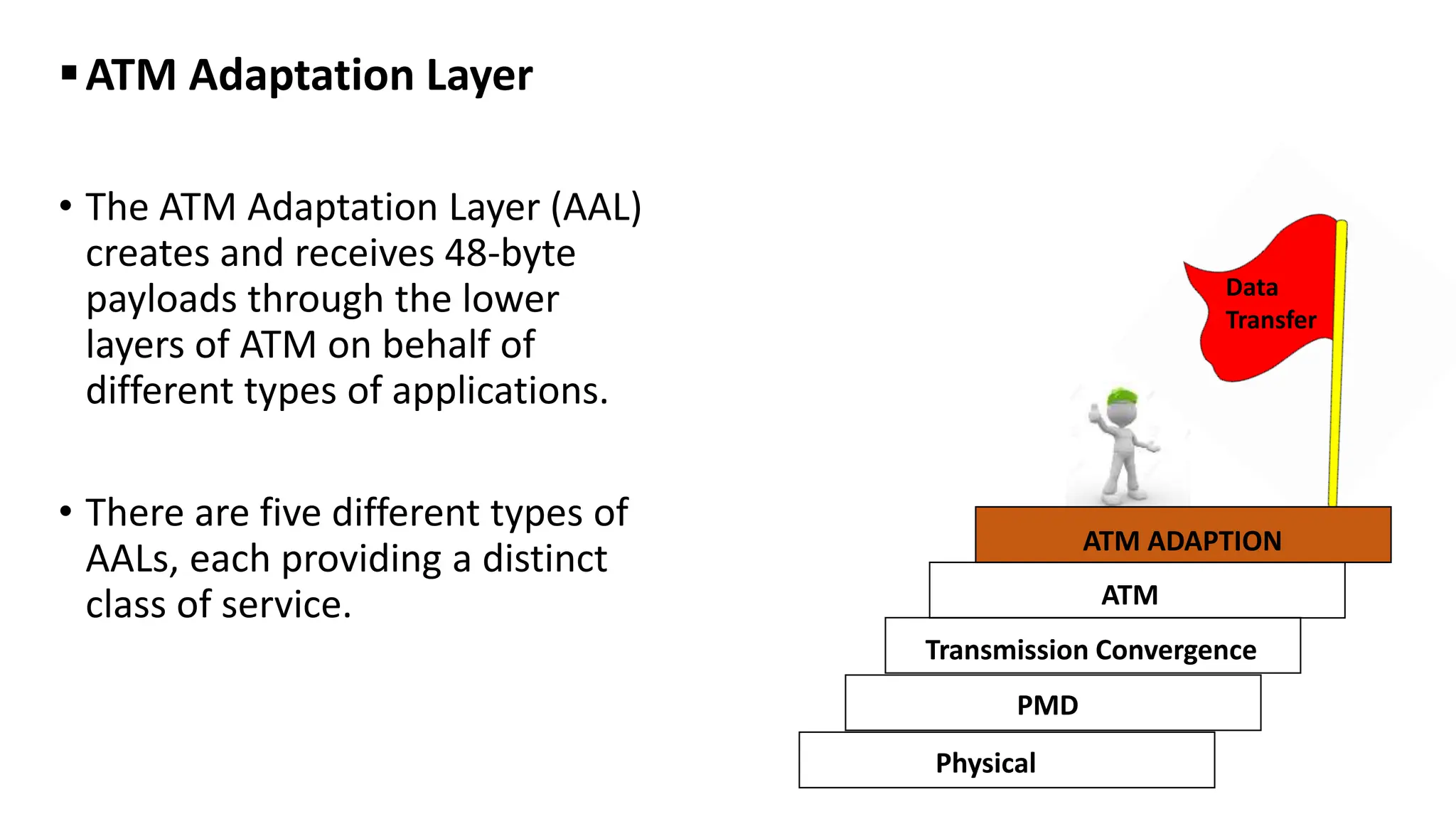
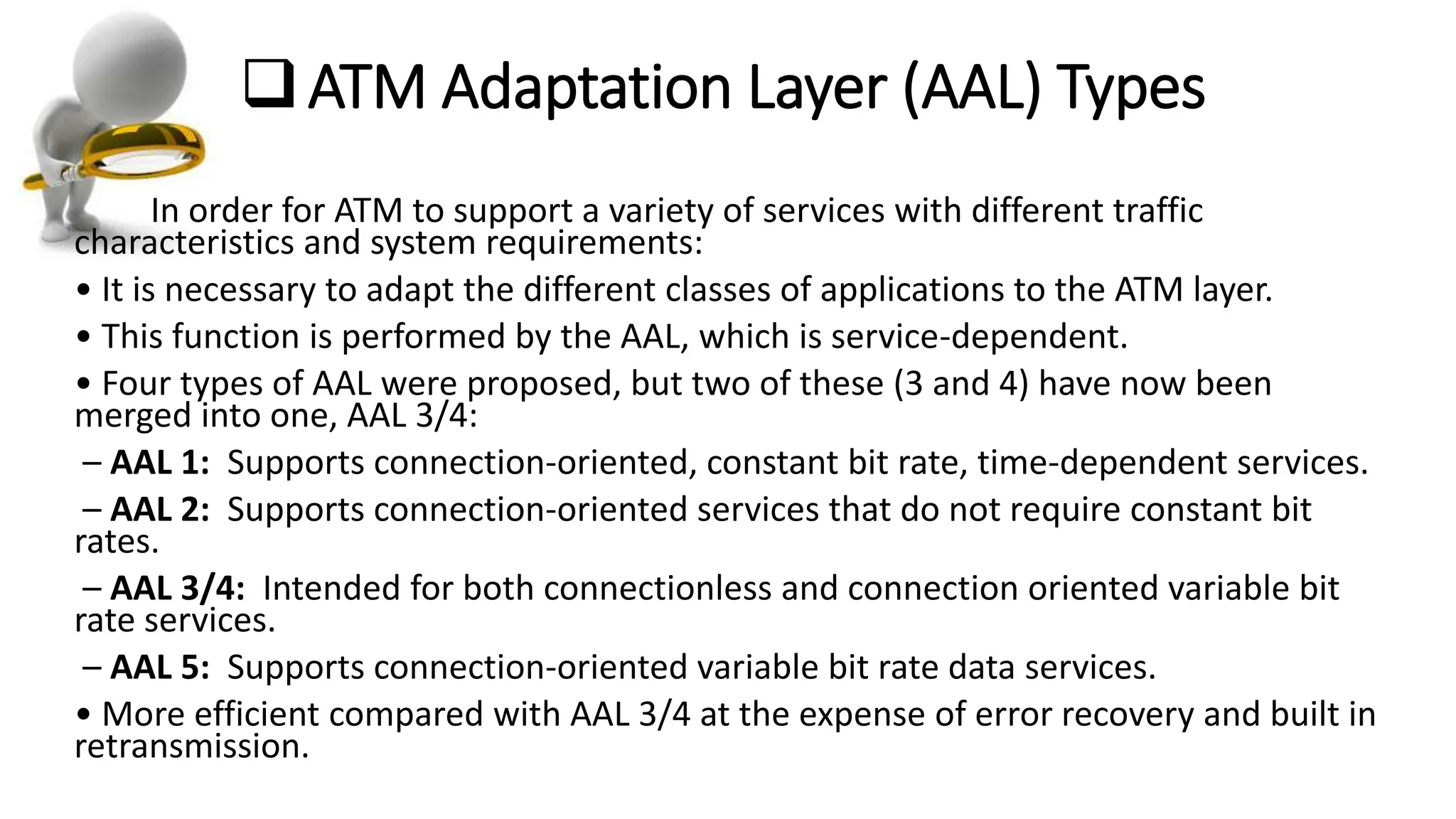
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a connection-oriented, high-speed switching and transmission technology that utilizes fixed-size packets, known as cells, to transport information efficiently across broadband networks. ATM resolves issues related to varying frame sizes and unpredictability in data communication by standardizing a small, uniform data unit for reliable transmission. Additionally, it offers guaranteed quality of service, low latency, and high-capacity switching, making it suitable for various applications including voice, video, and data traffic.