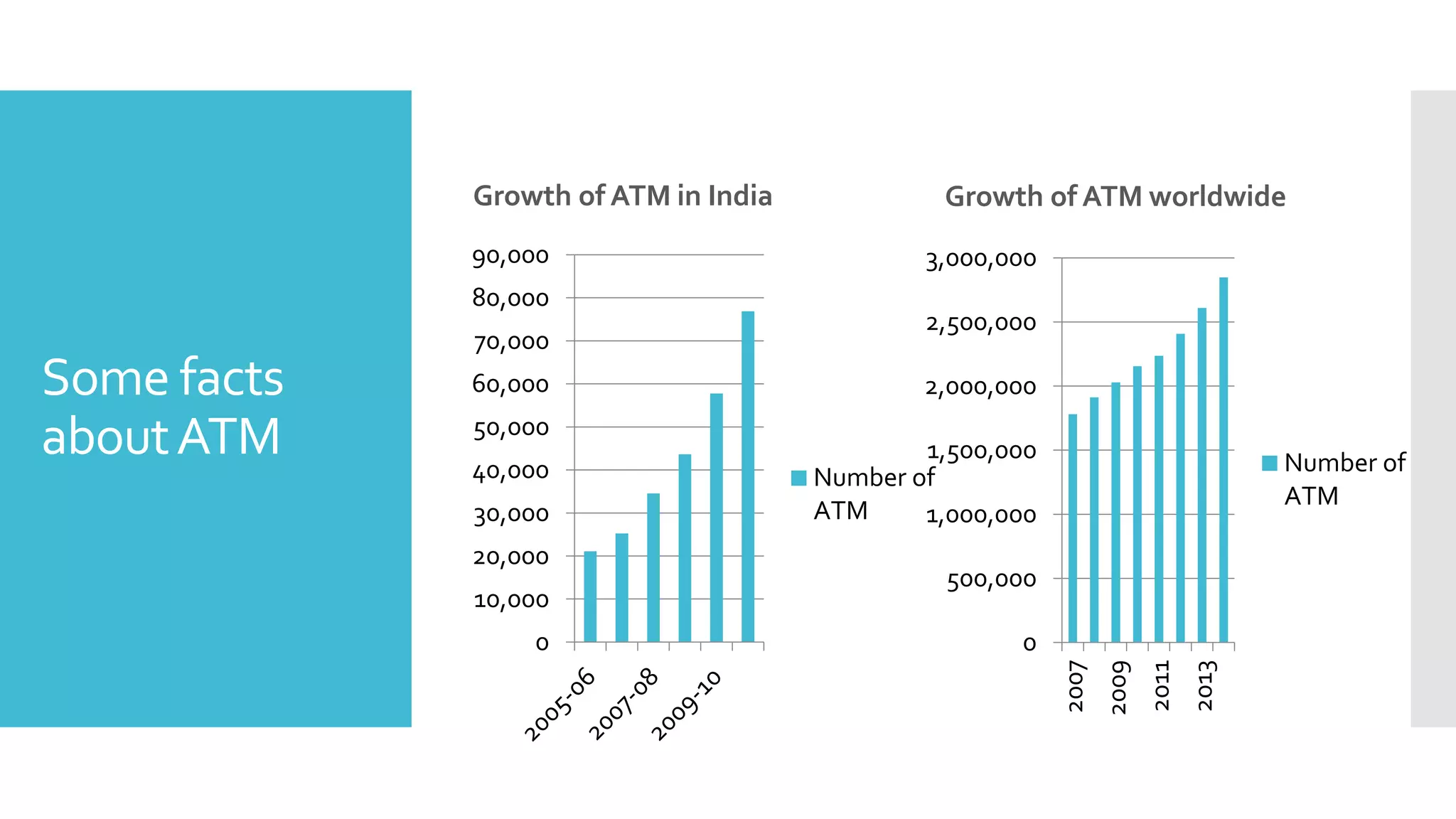
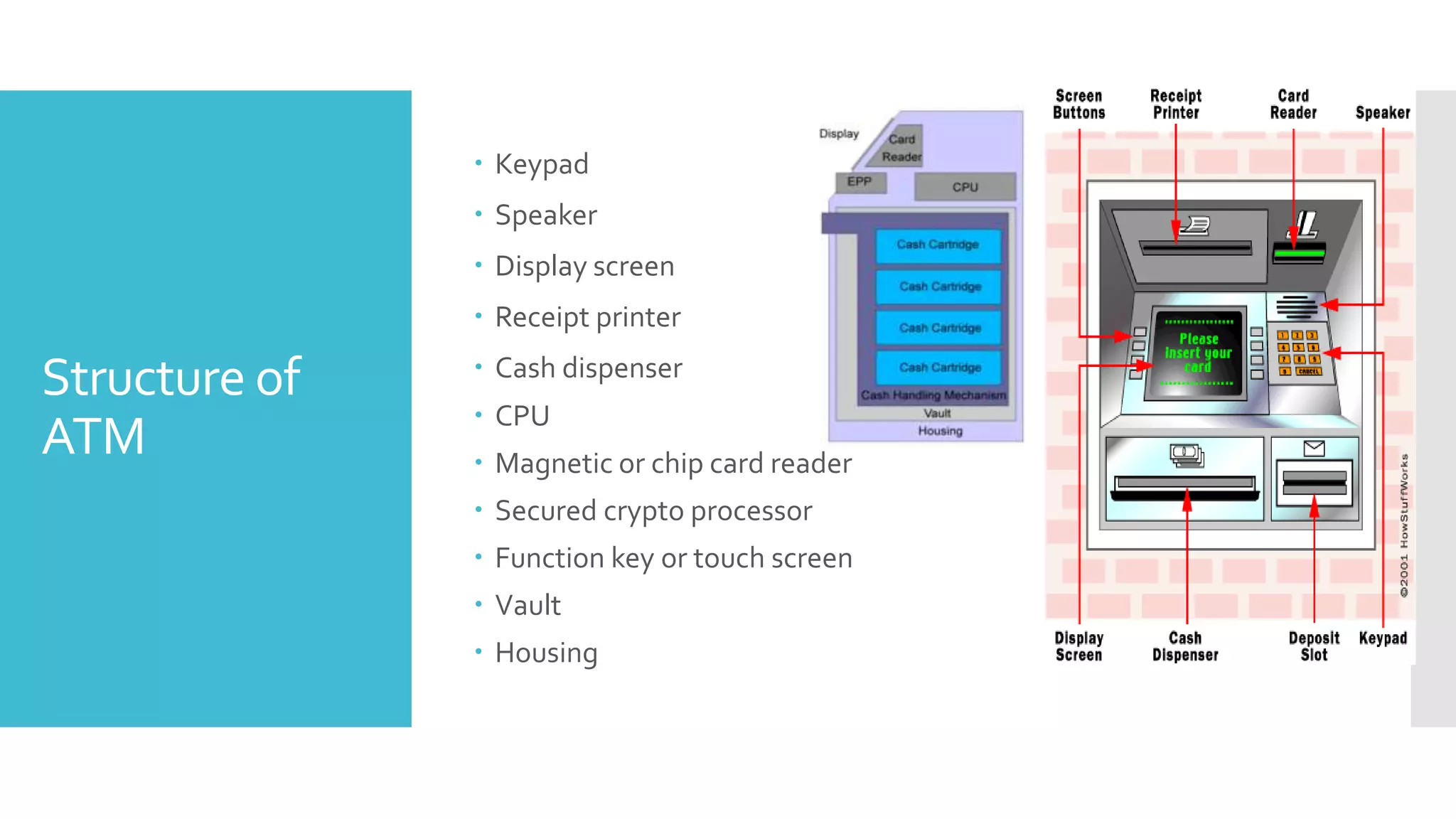
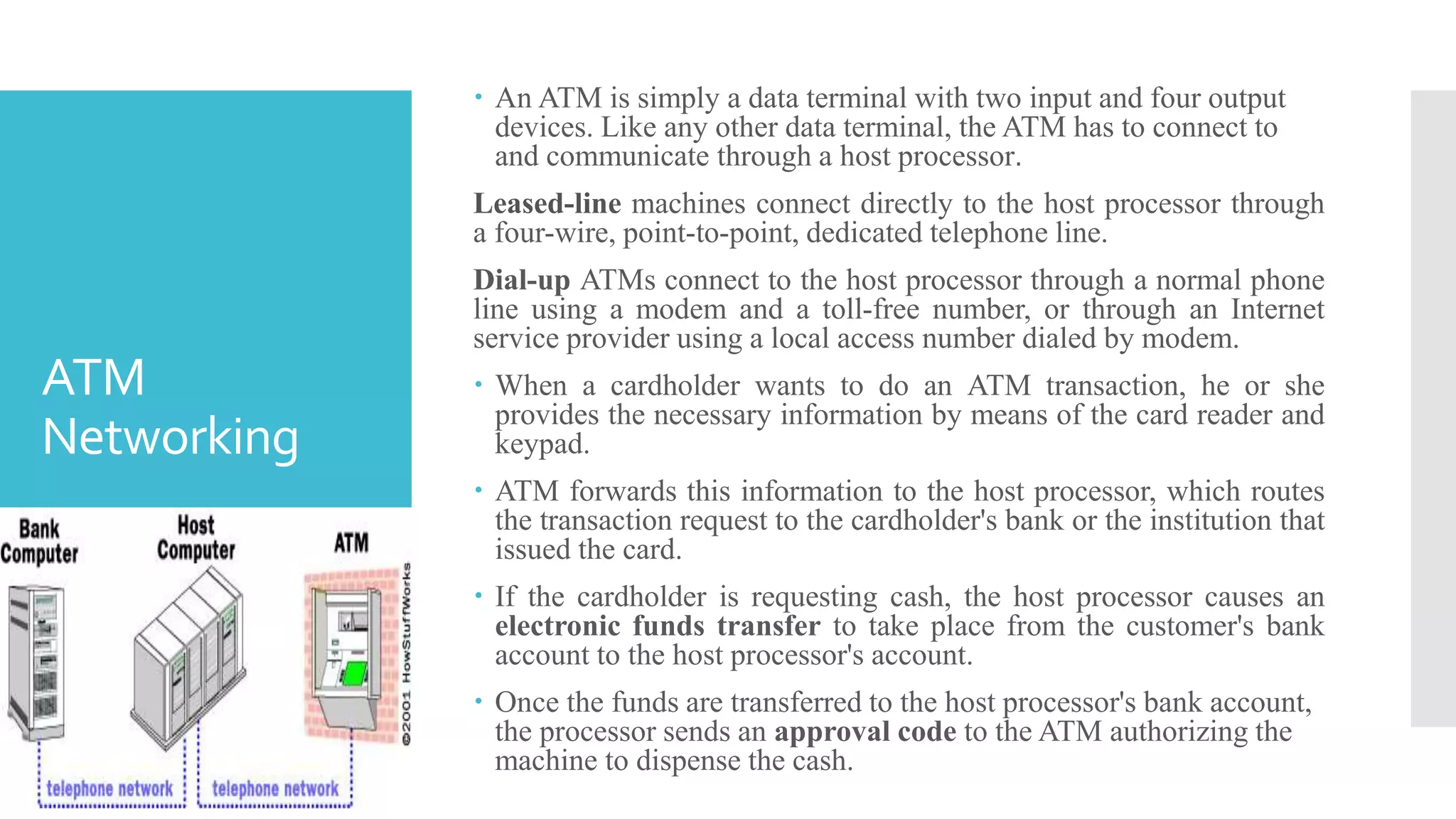
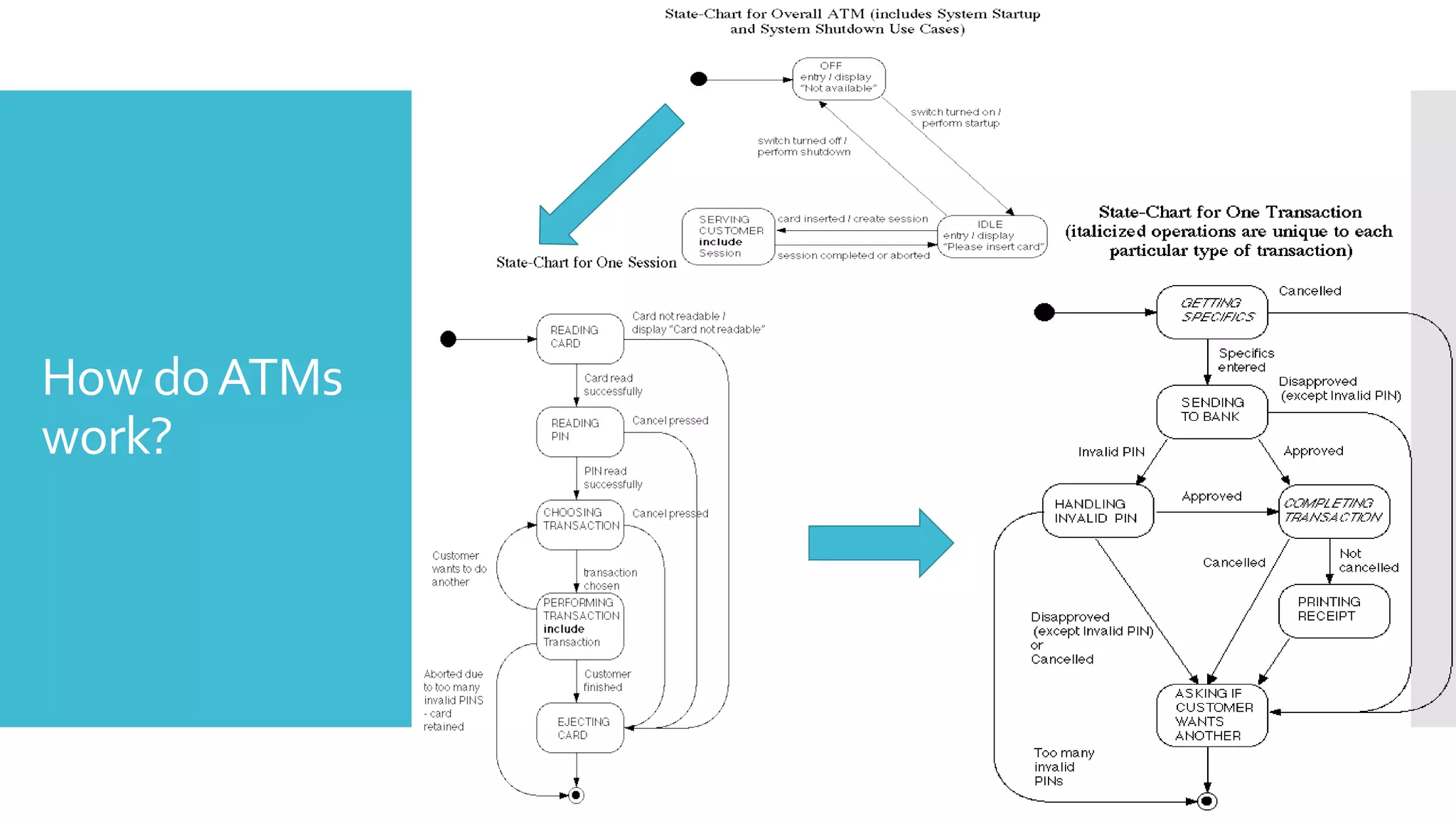
The document provides an overview of automated teller machines (ATMs). It discusses what an ATM is, the history and growth of ATMs, their functions and structure. Key points covered include that an ATM allows customers to access financial transactions without a human clerk, the first ATM was installed in 1967 in London, and ATMs now number in the millions worldwide. Functions of ATMs include withdrawing cash, checking balances, paying bills and transferring funds. Common ATM components are also outlined such as card readers, displays, cash dispensers and receipt printers.