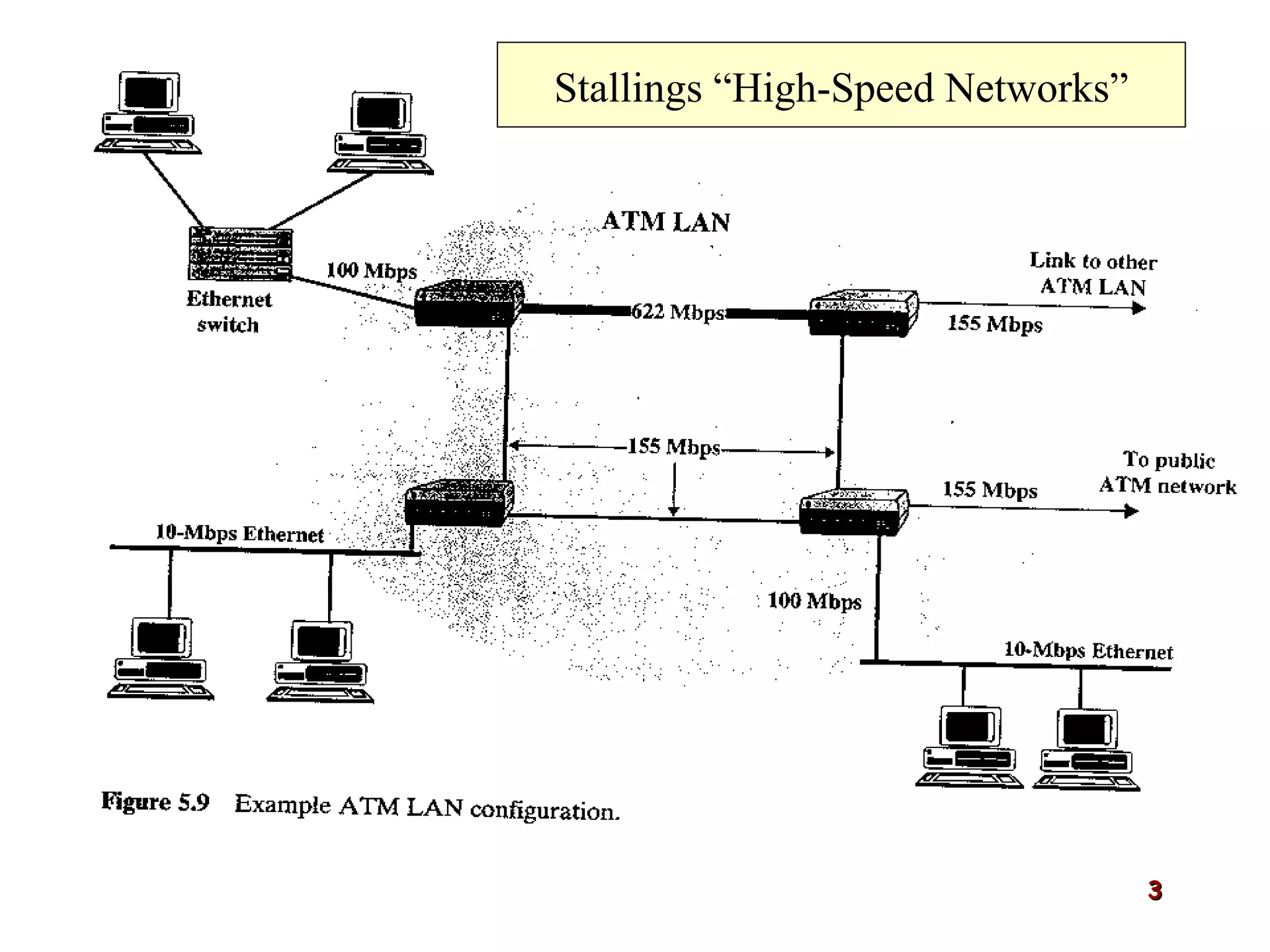
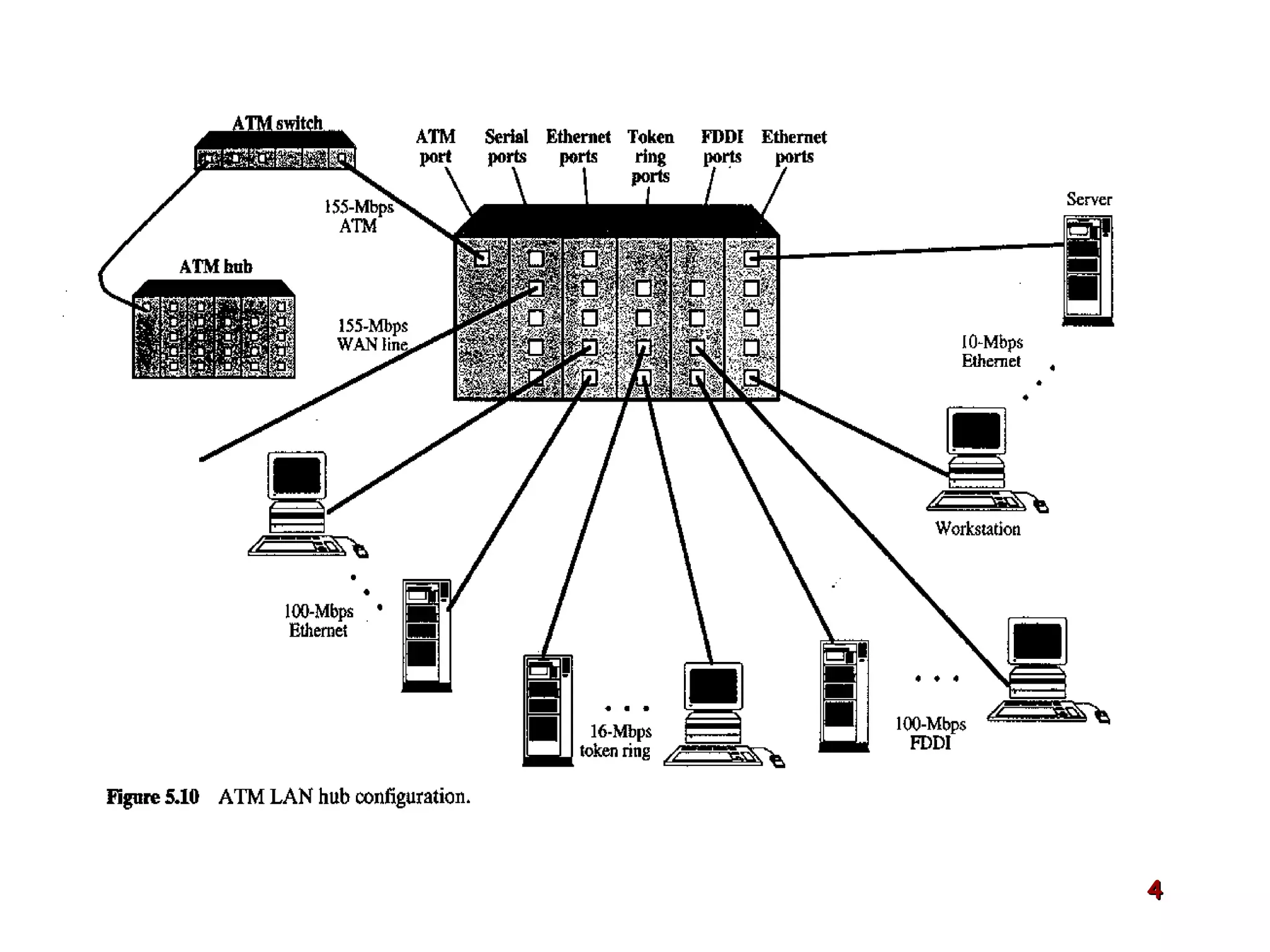
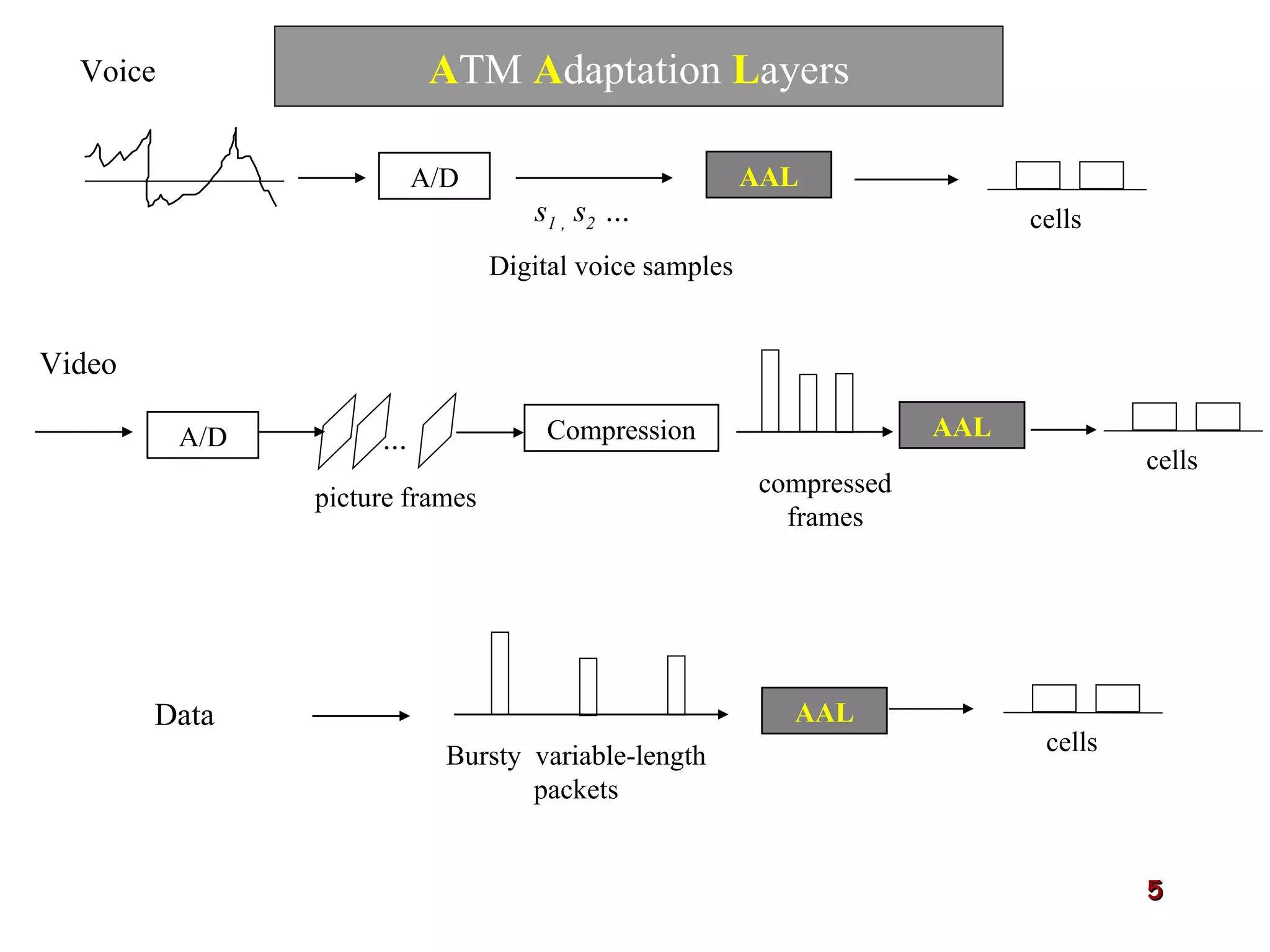
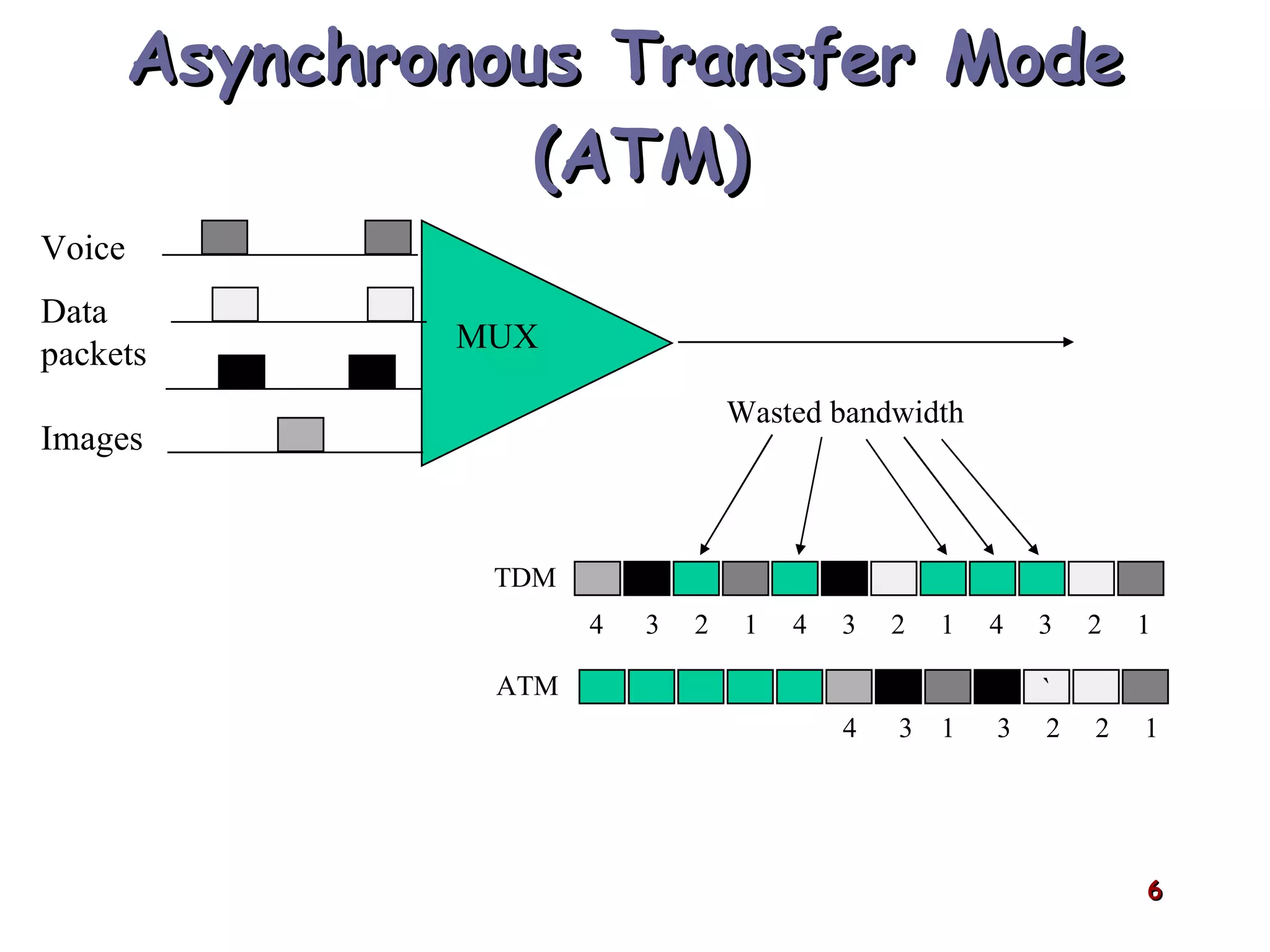
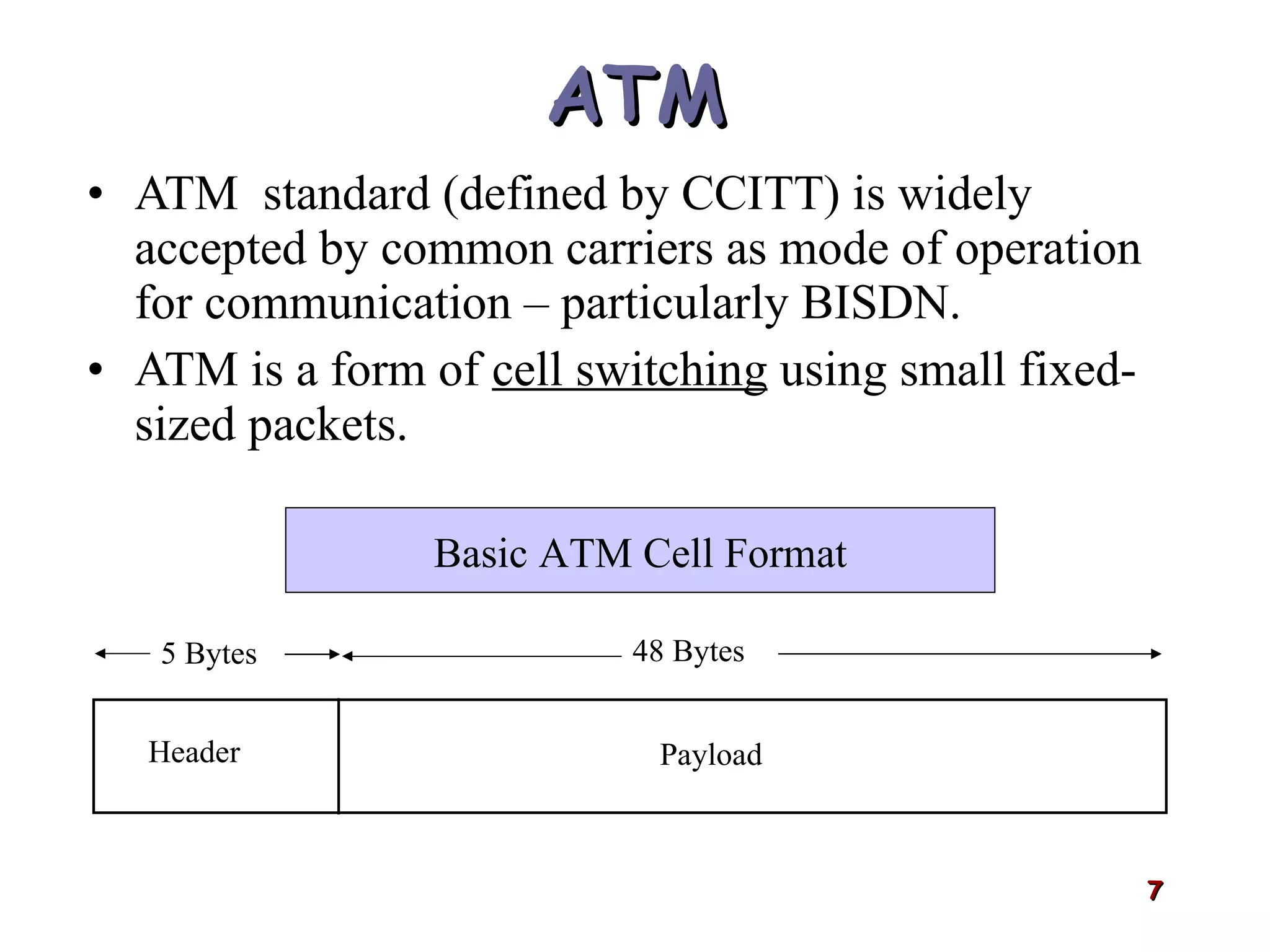
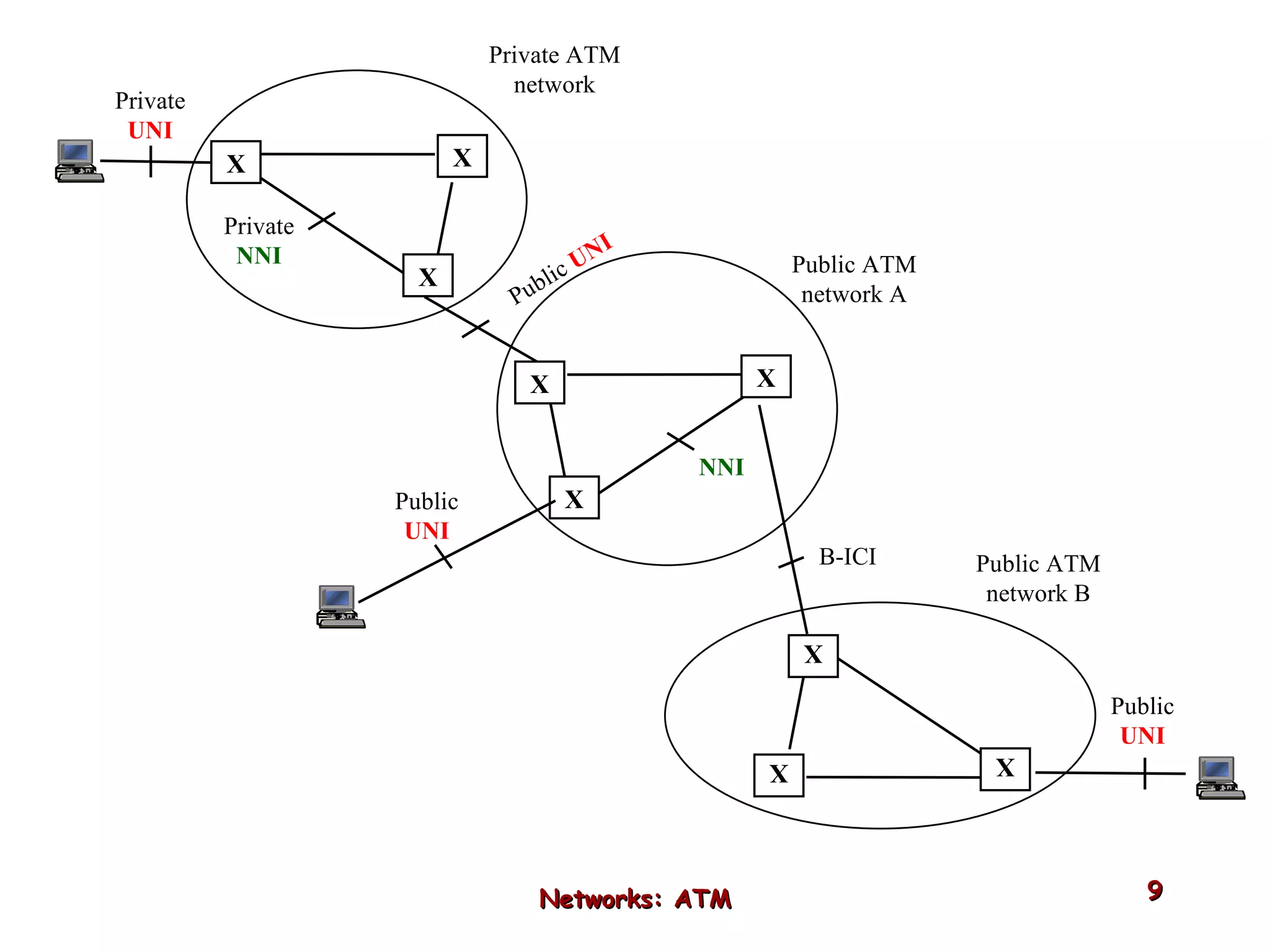
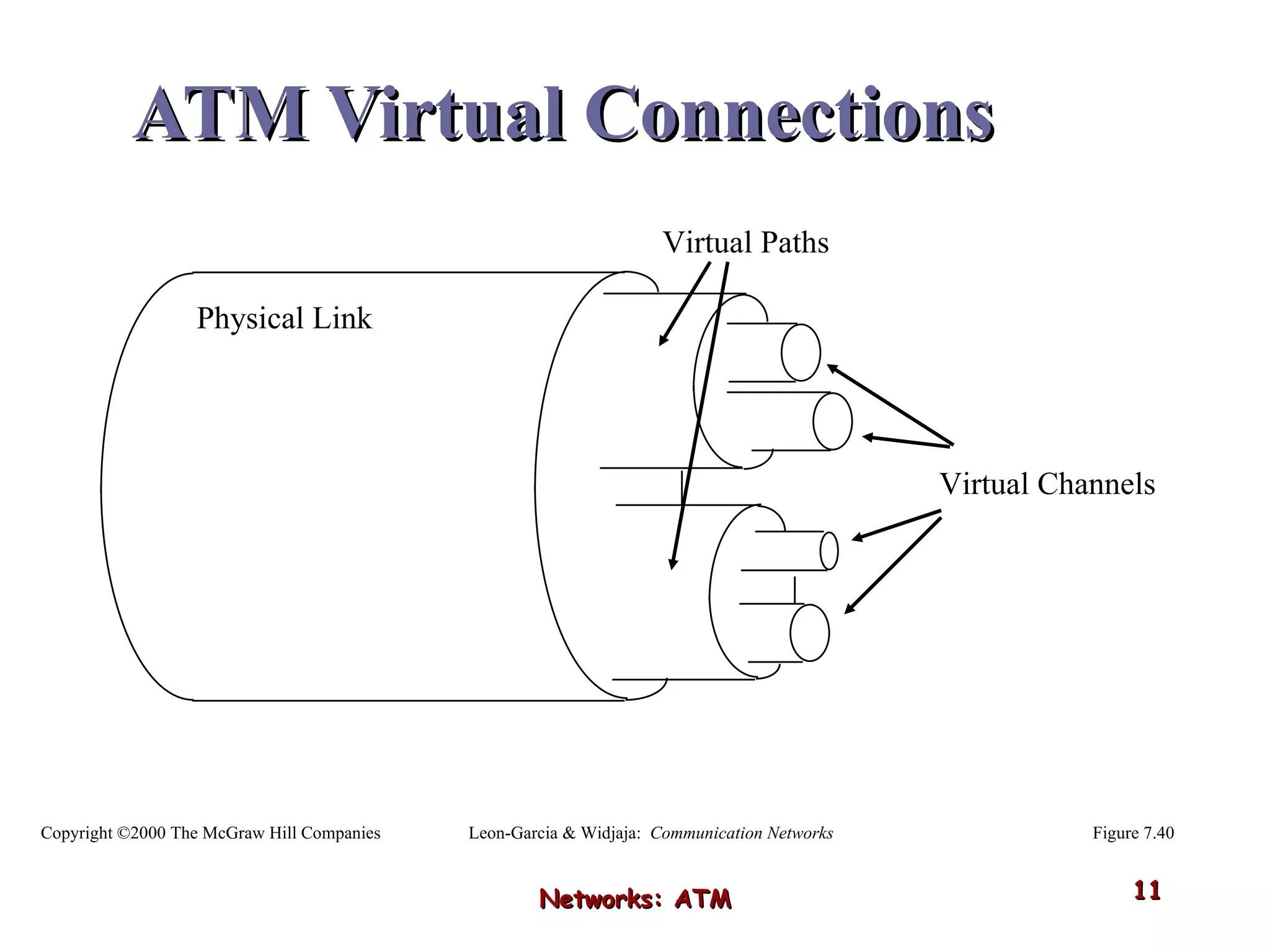
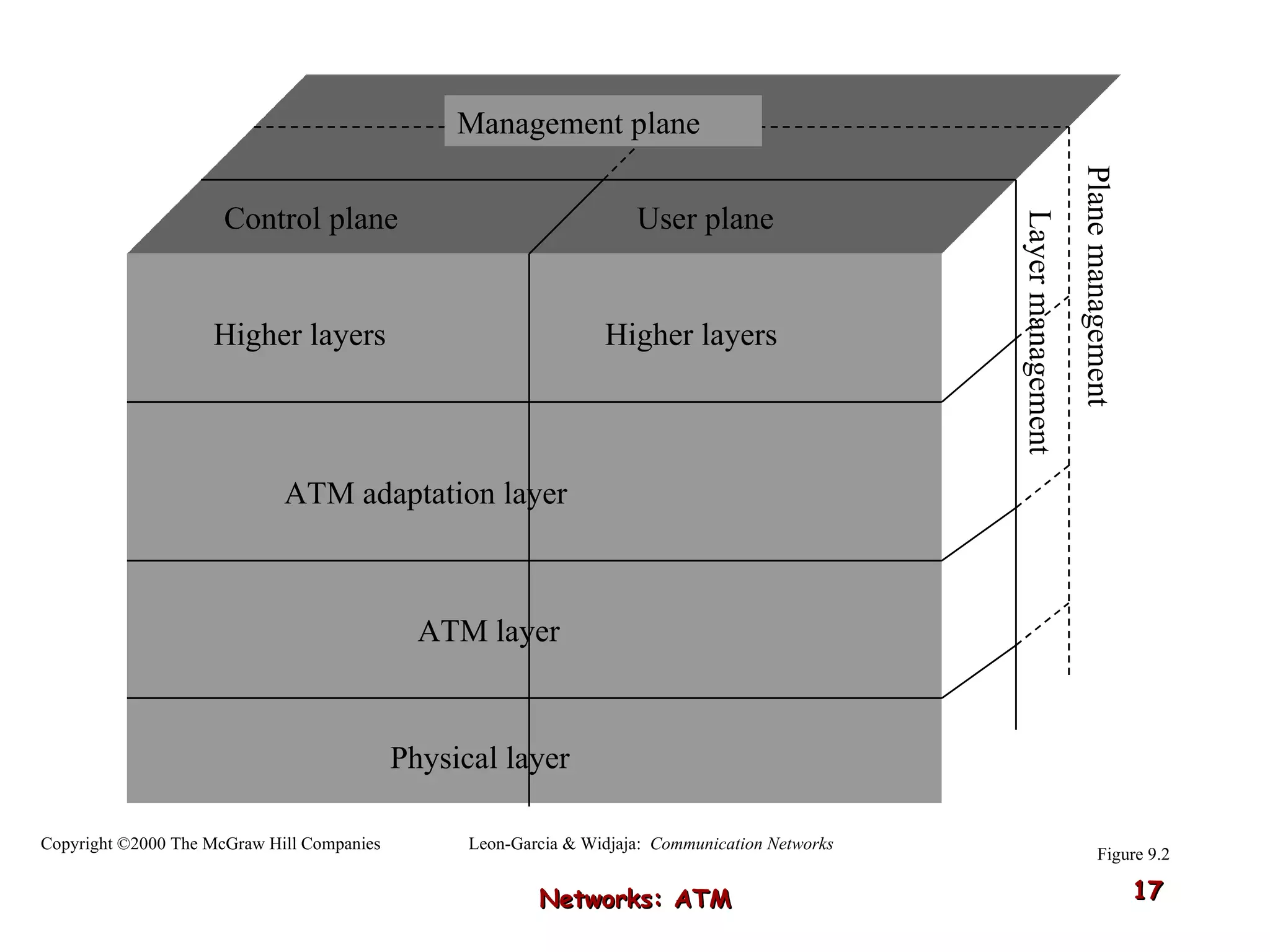
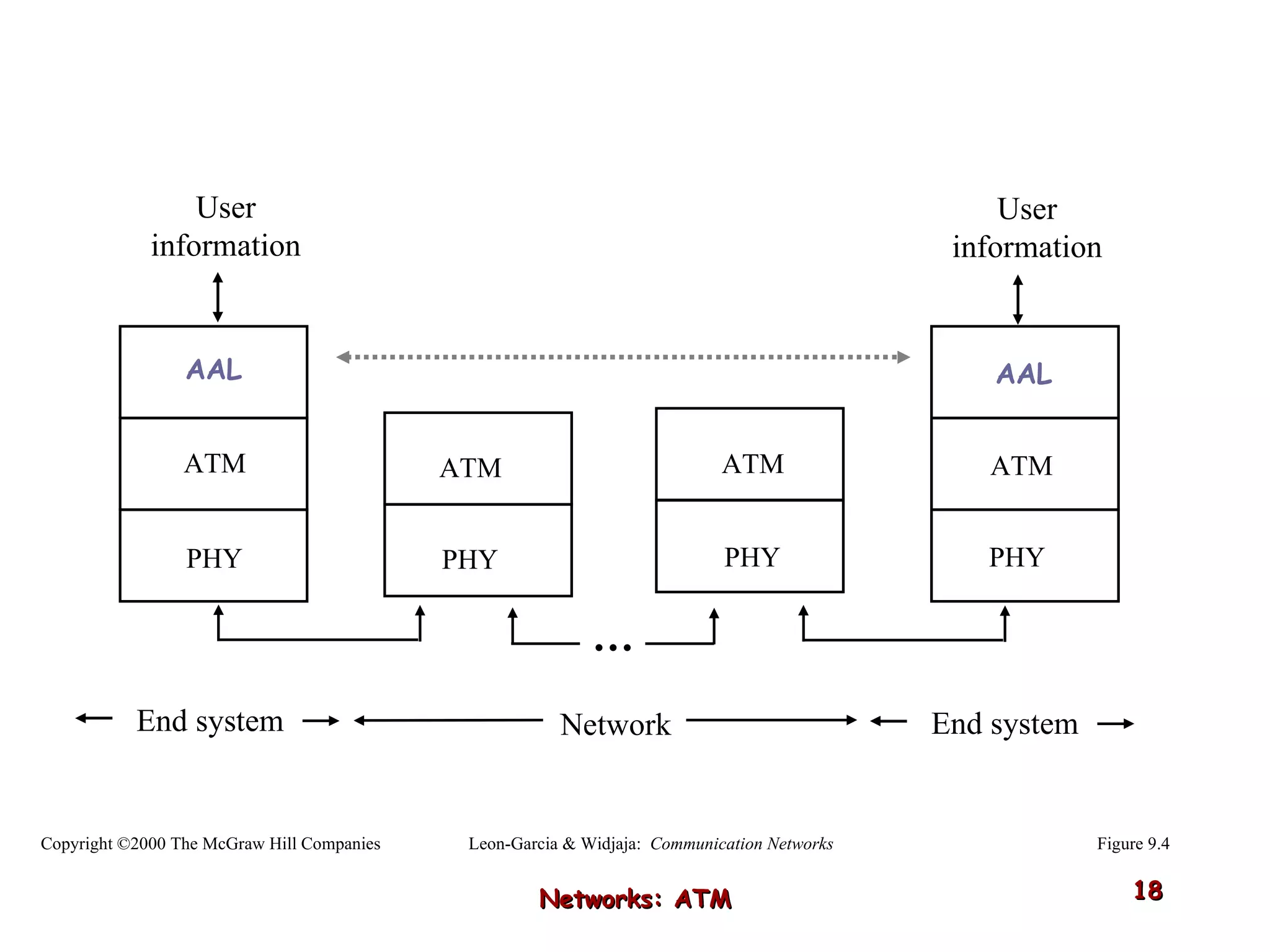
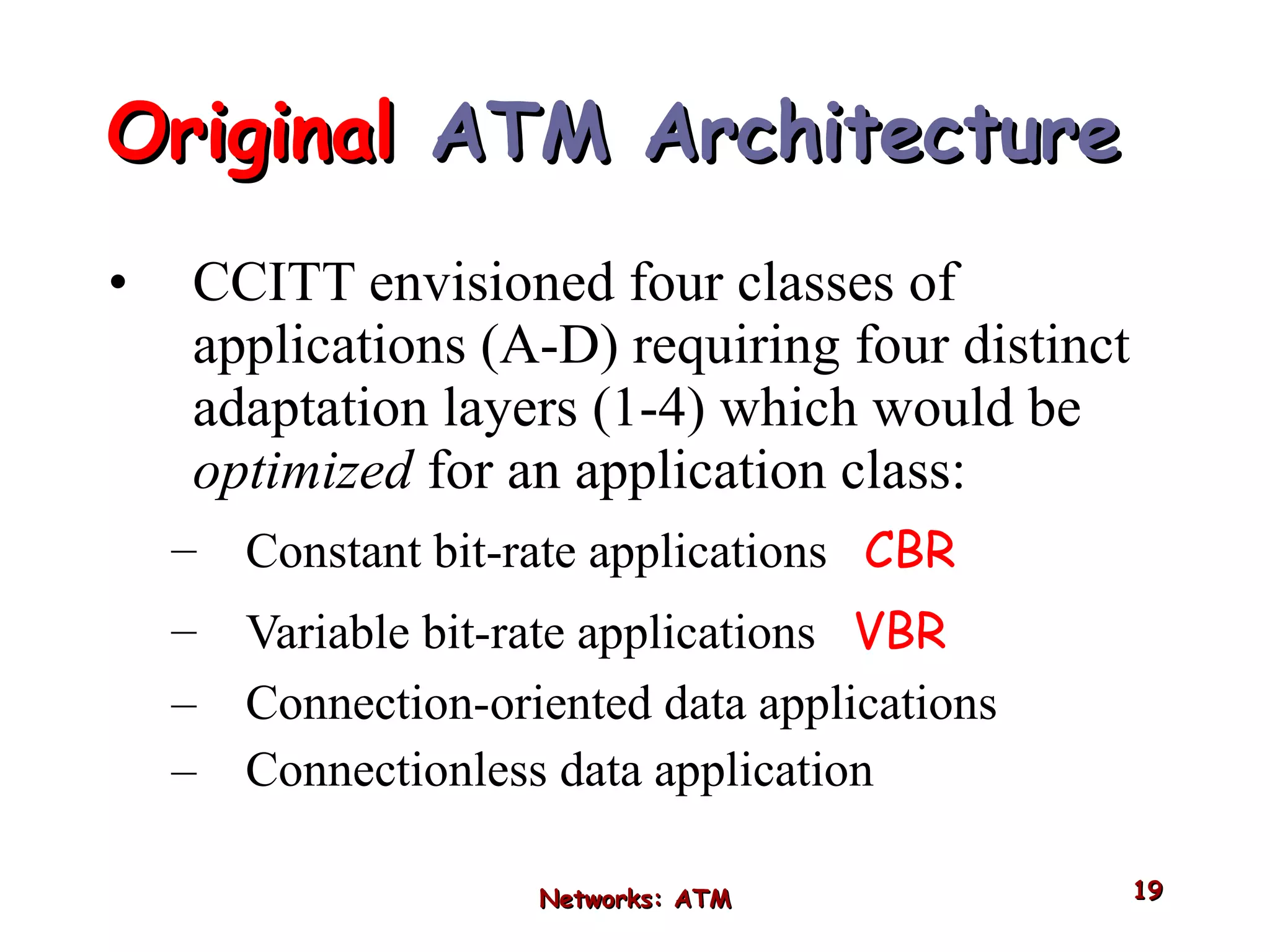
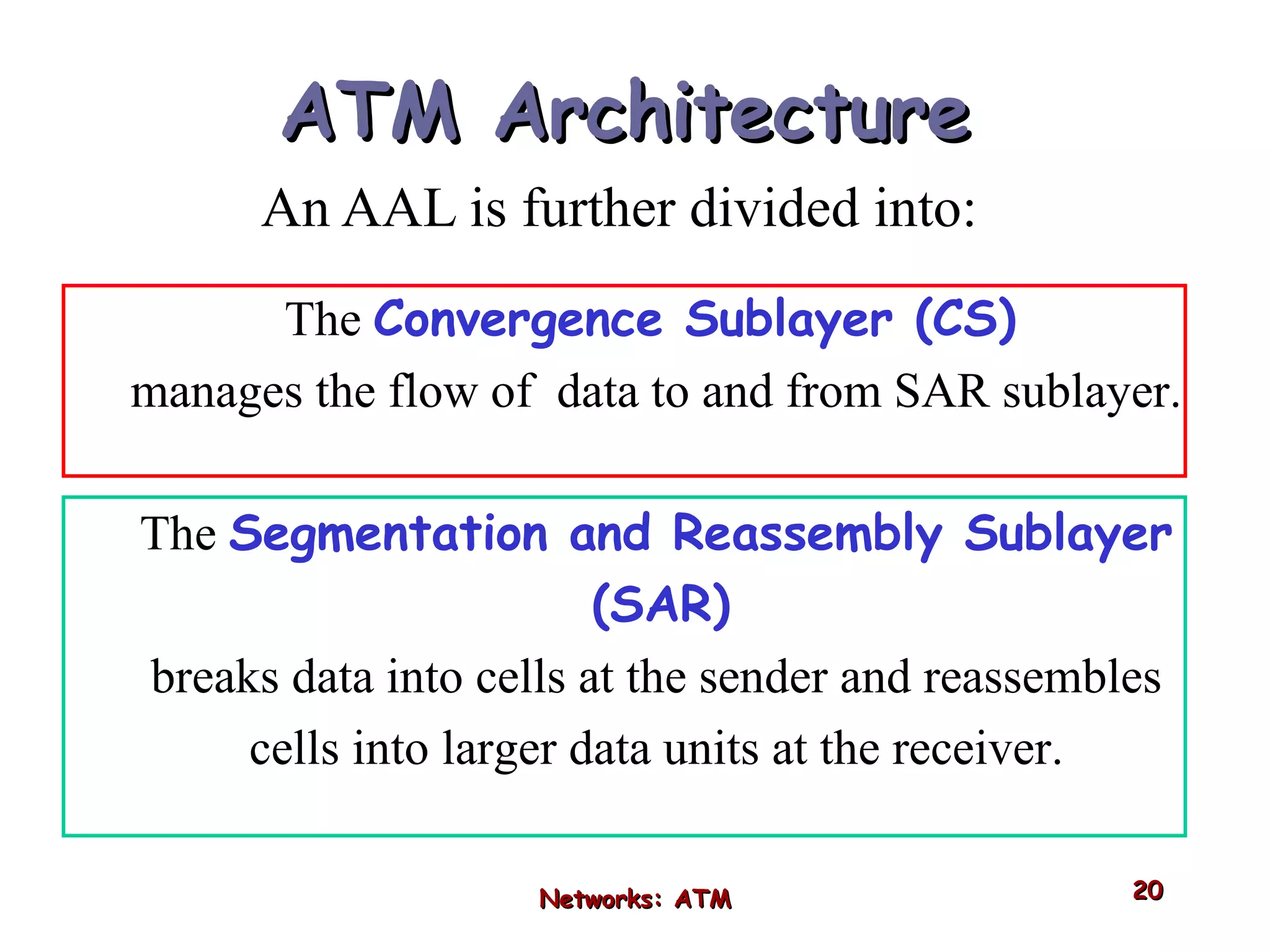
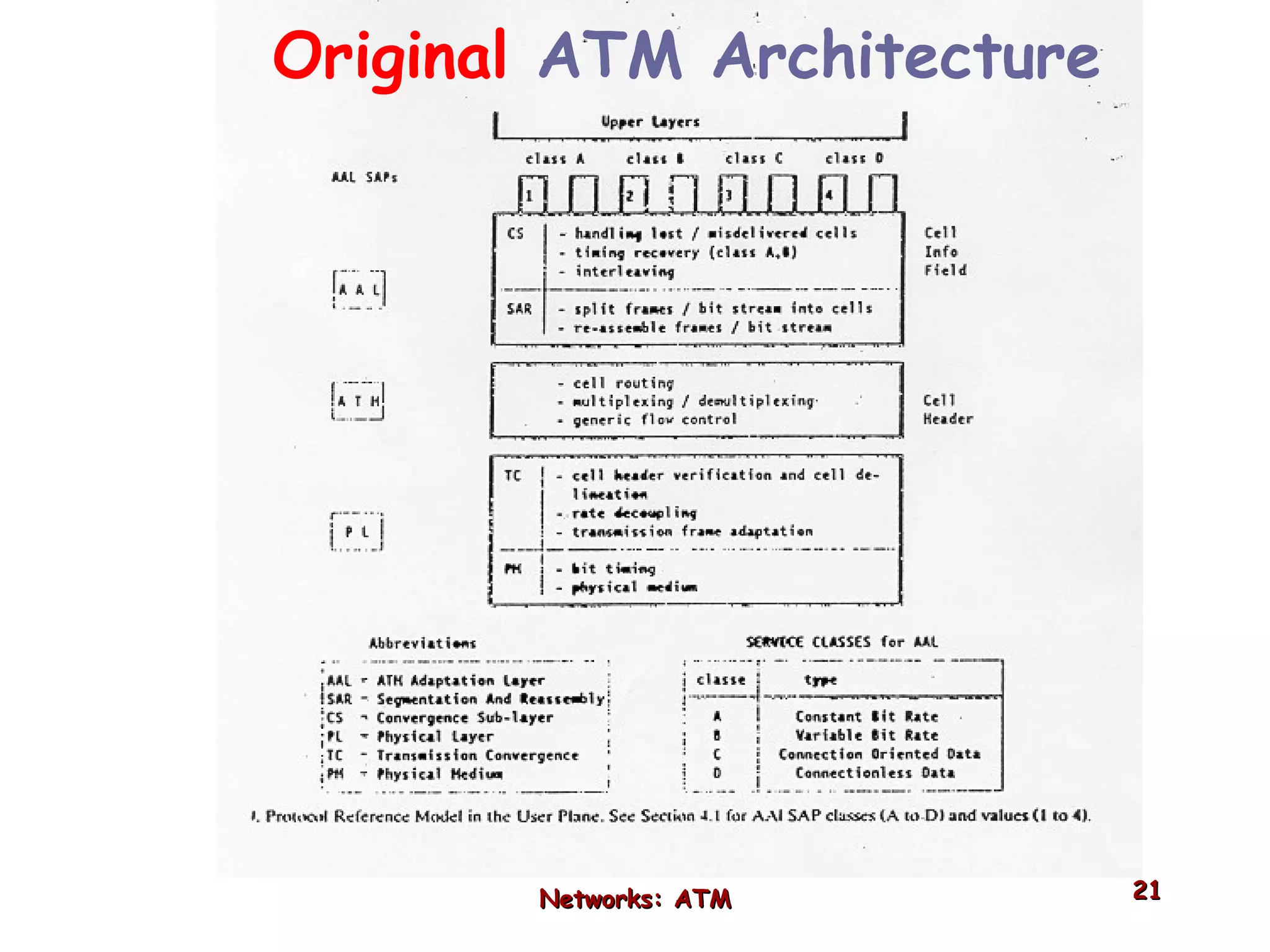
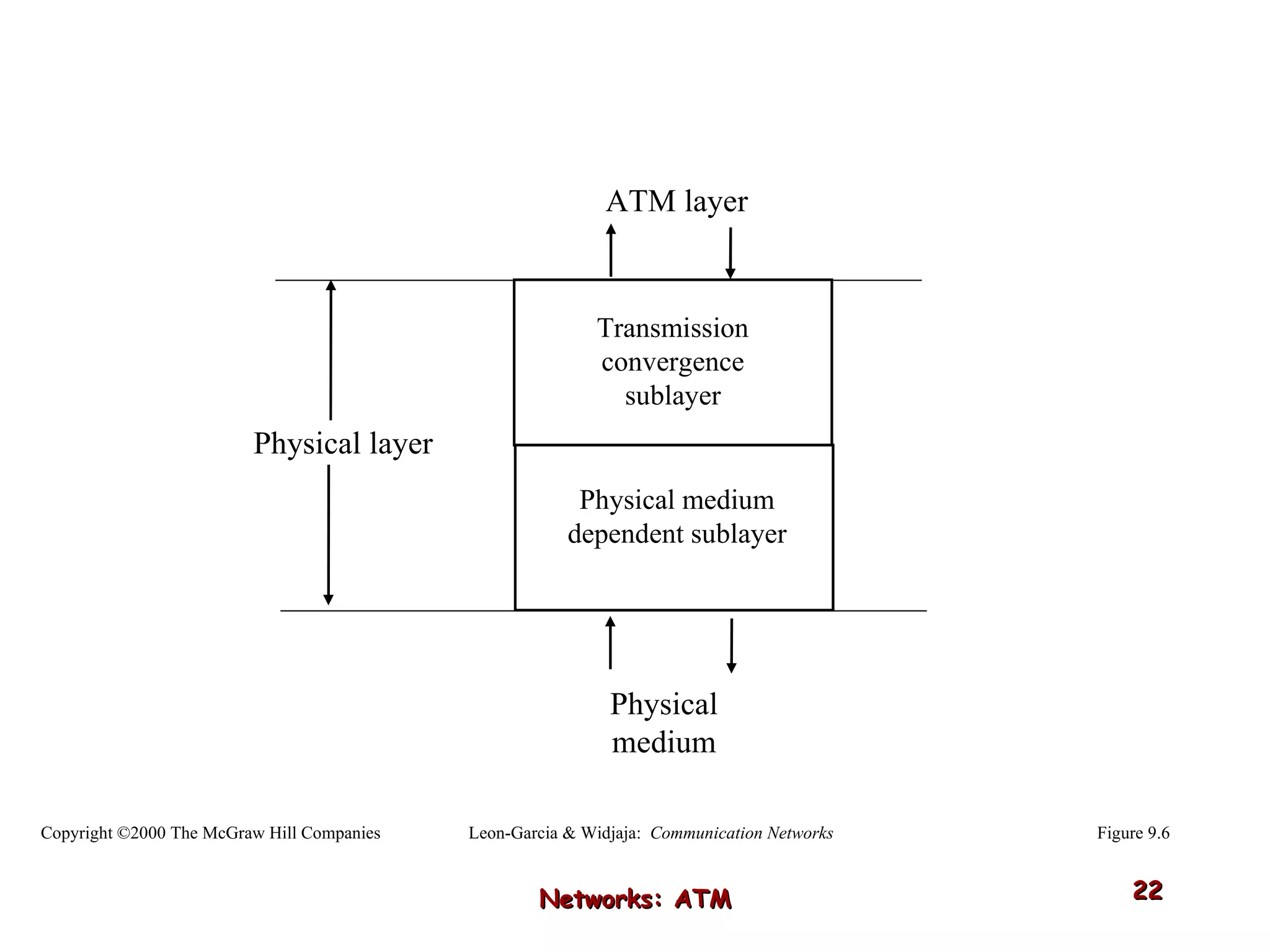
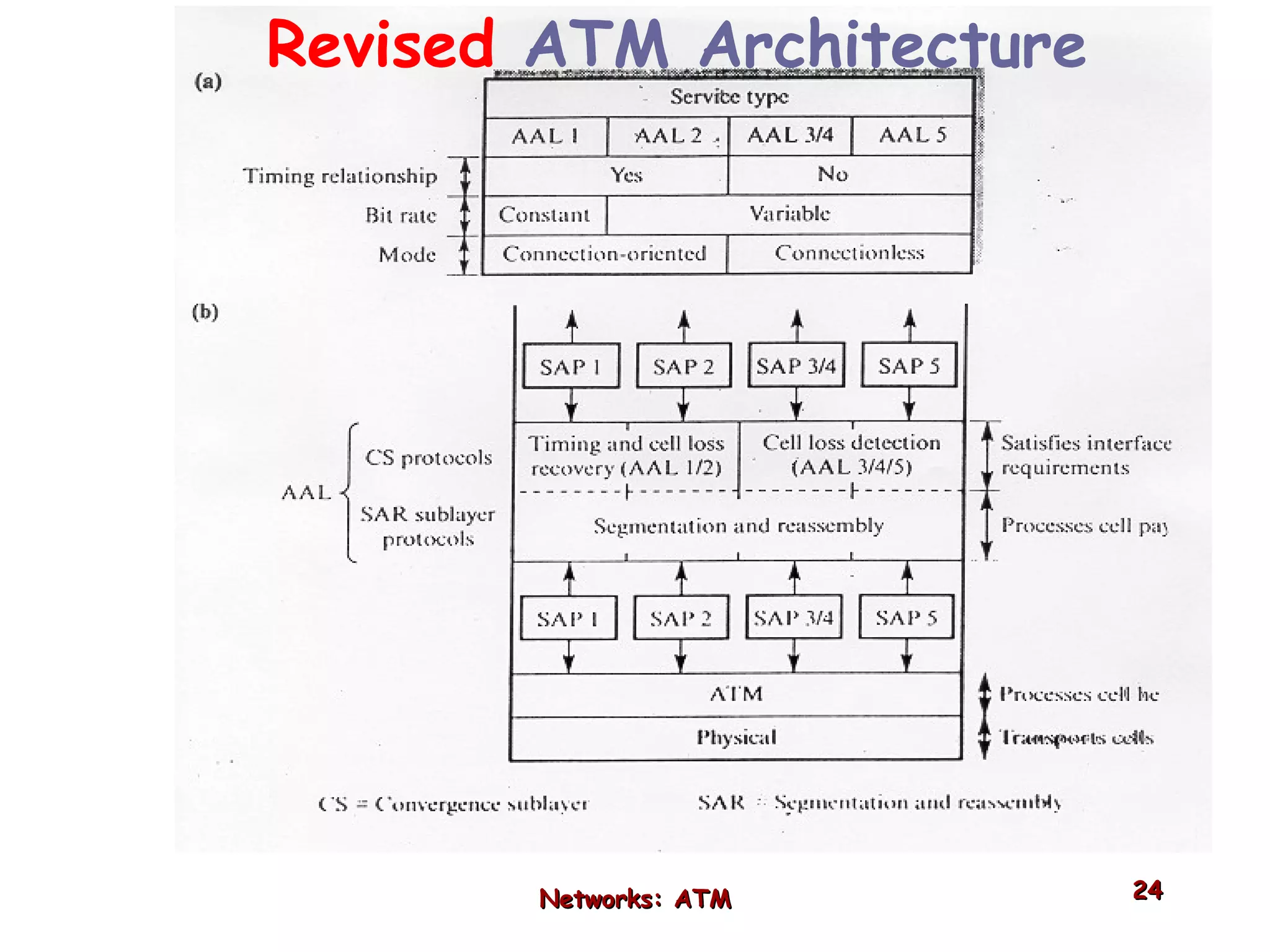
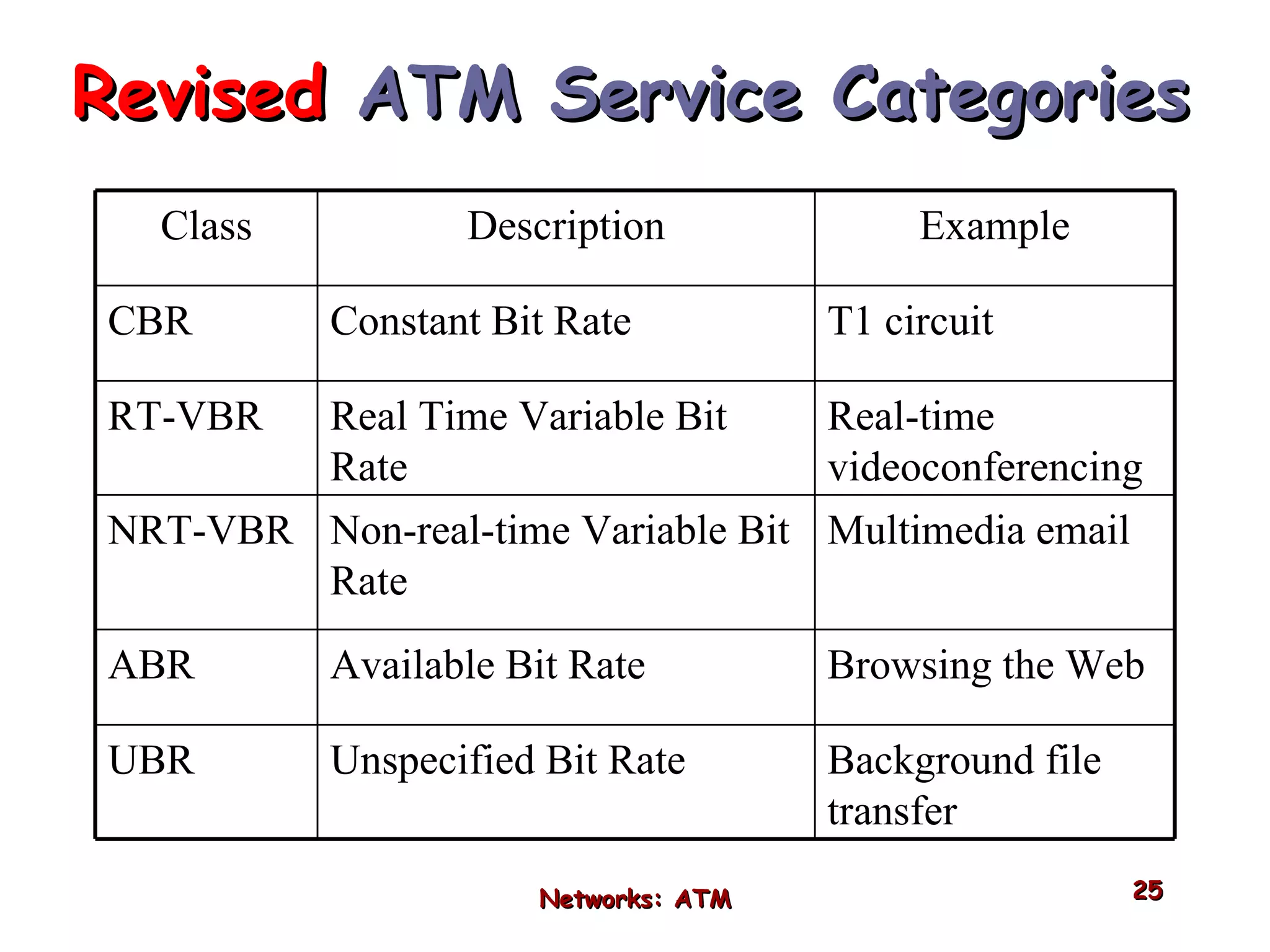
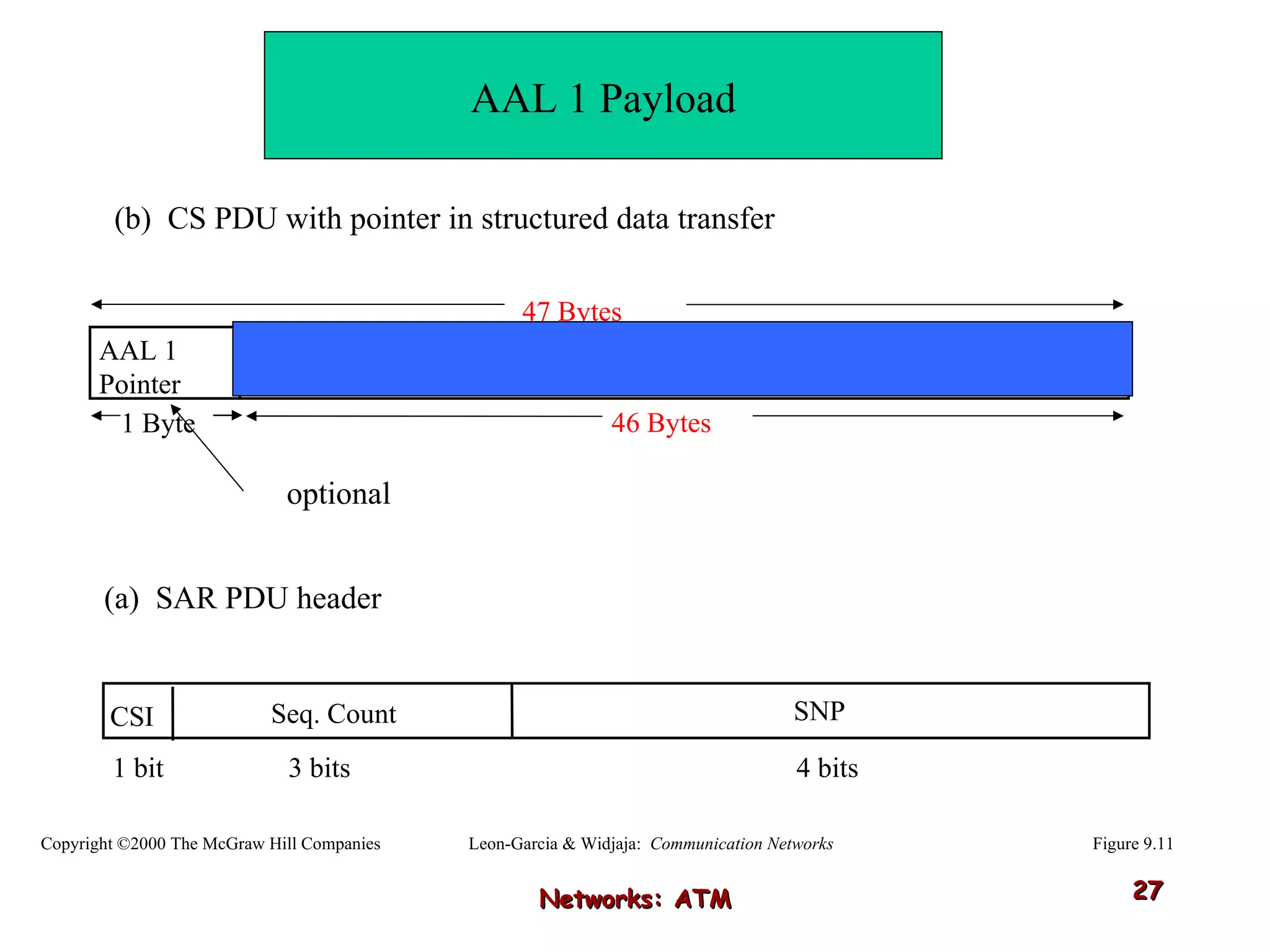
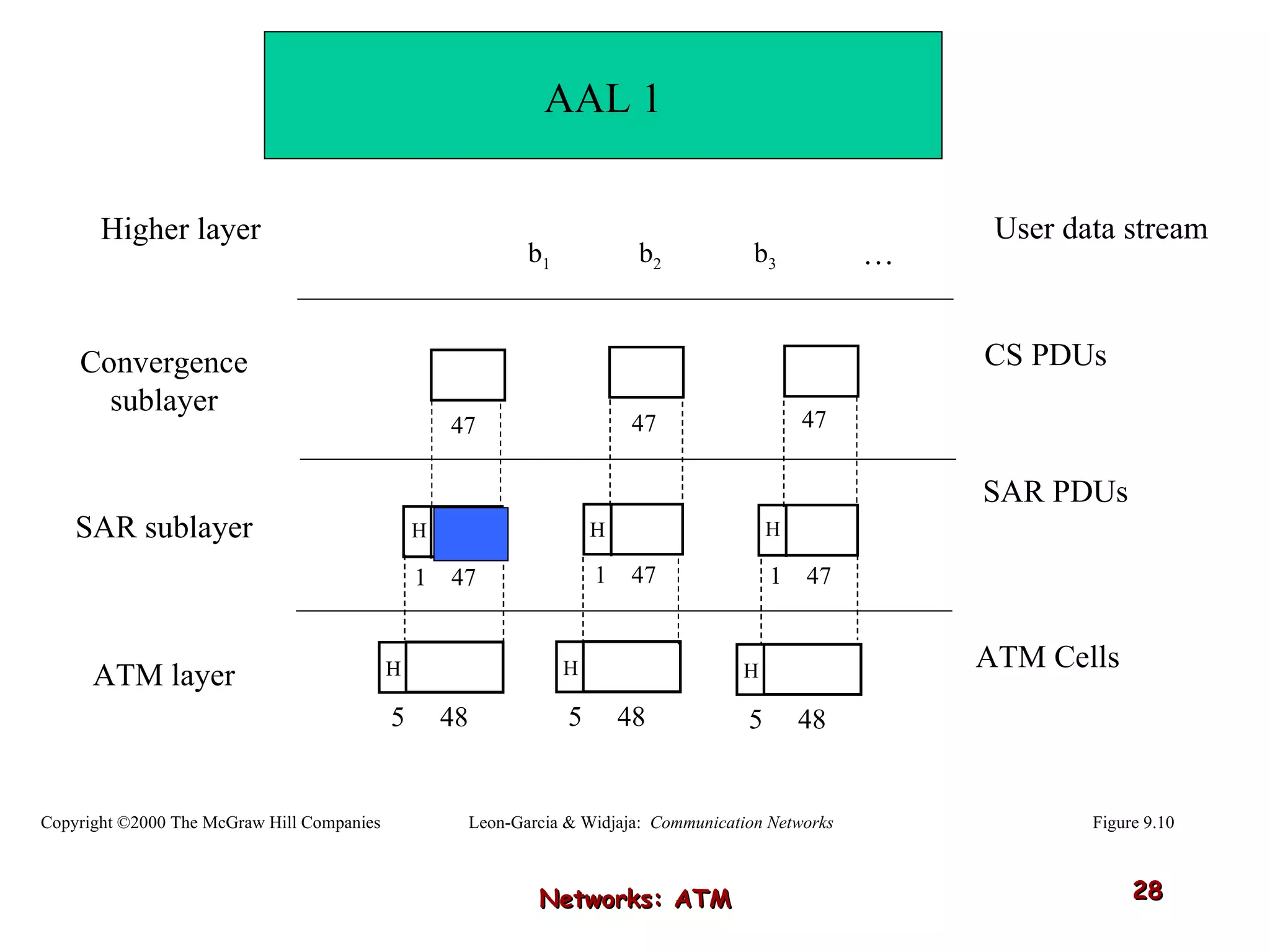
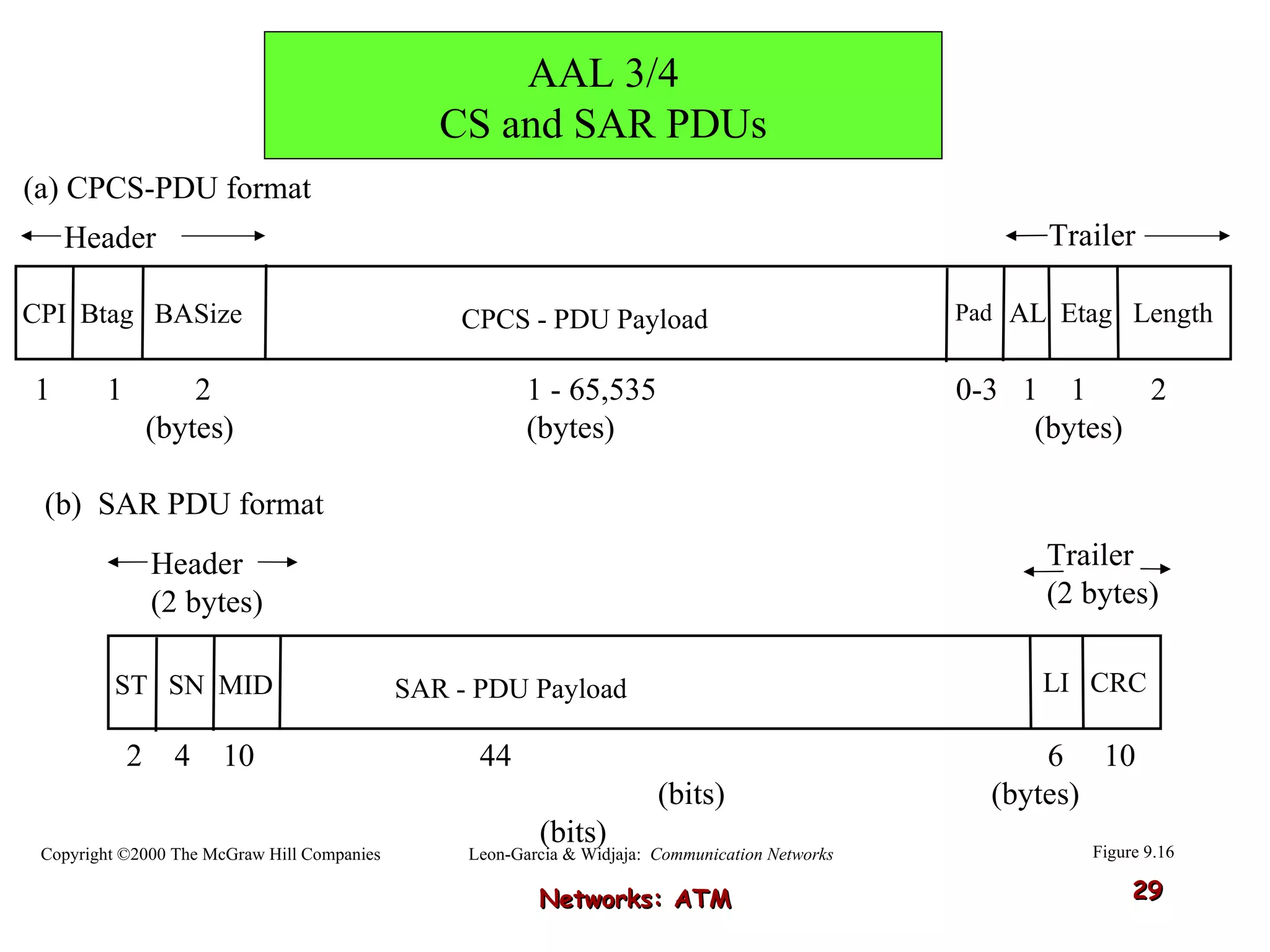
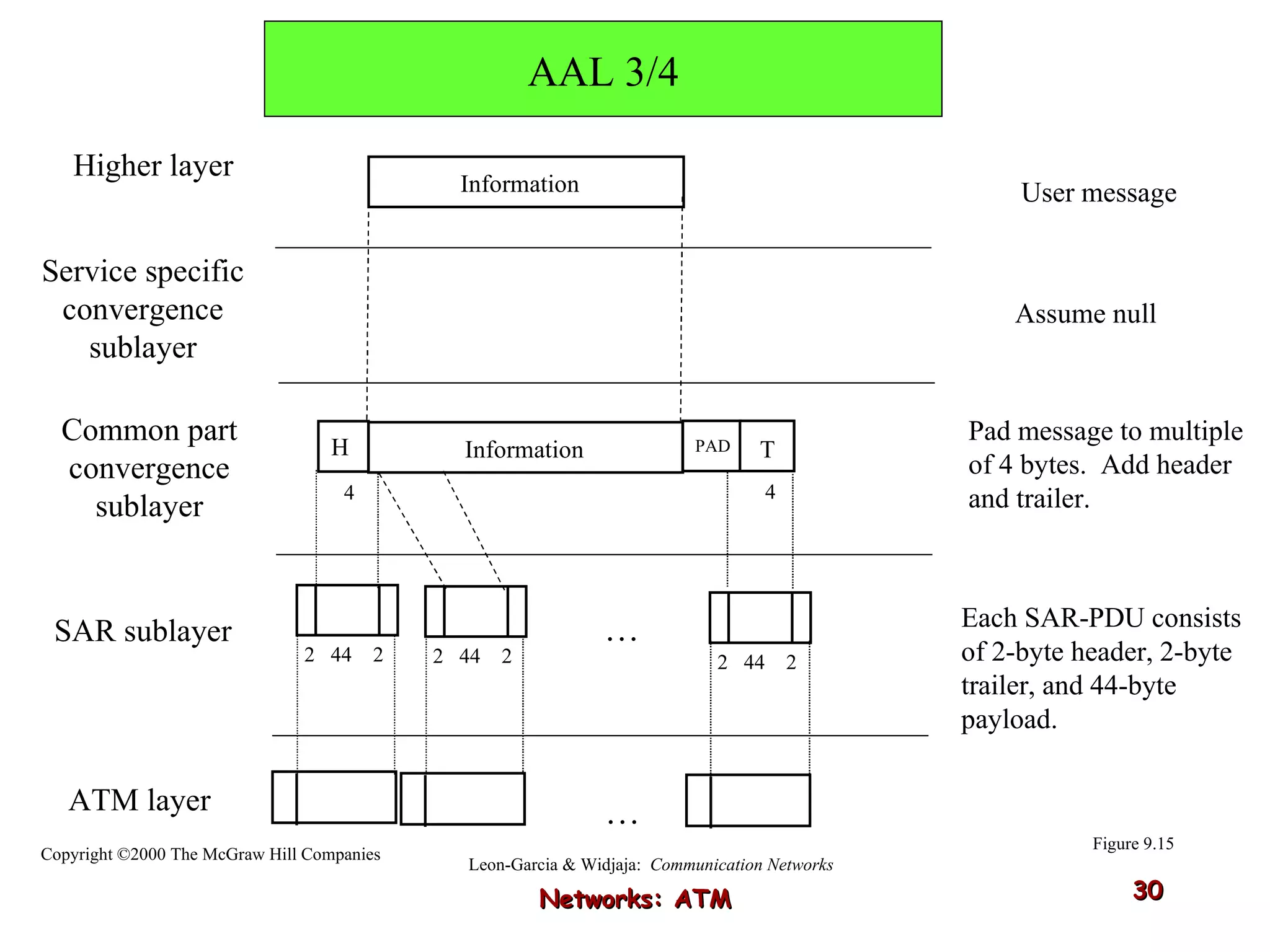
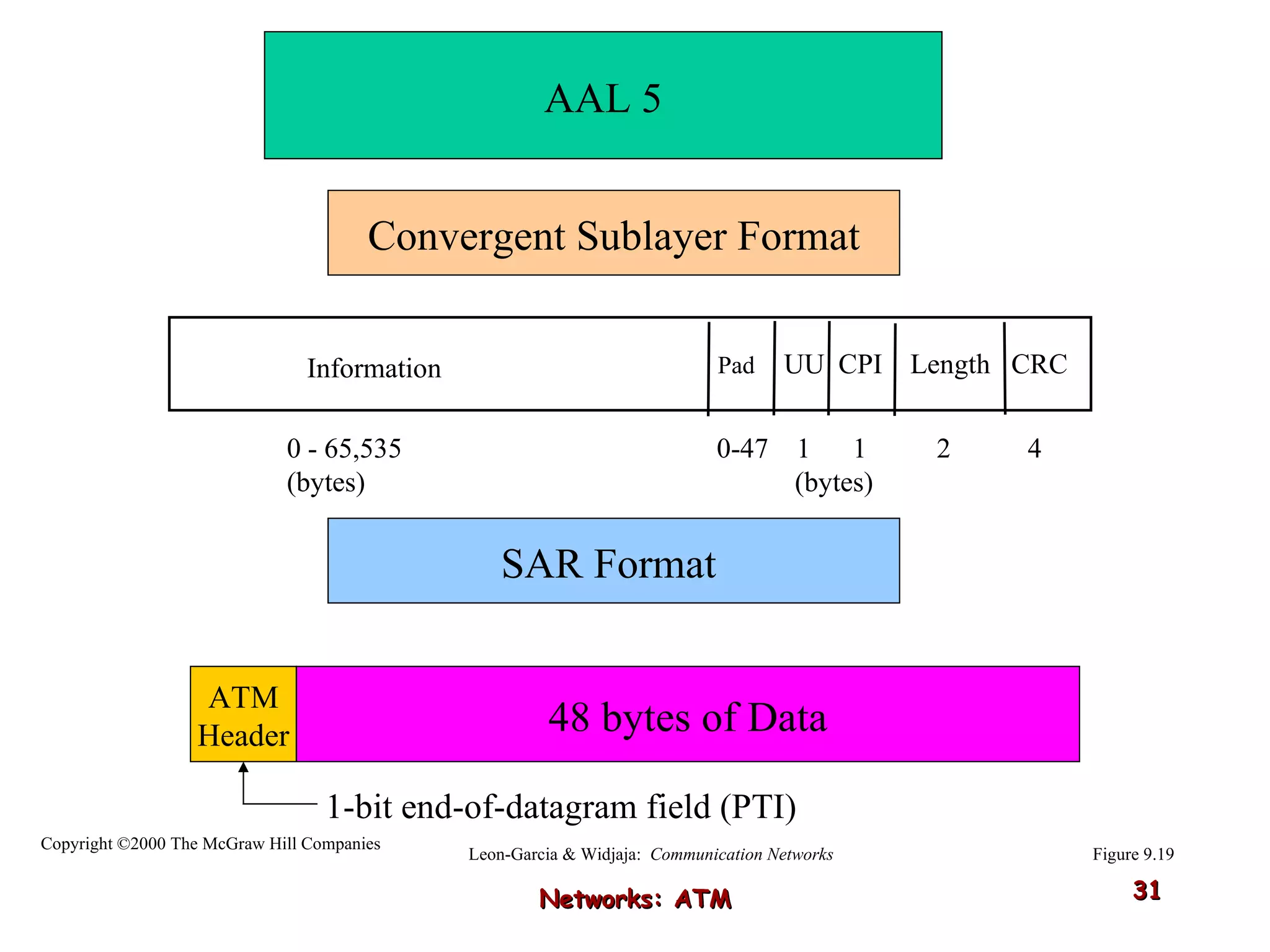
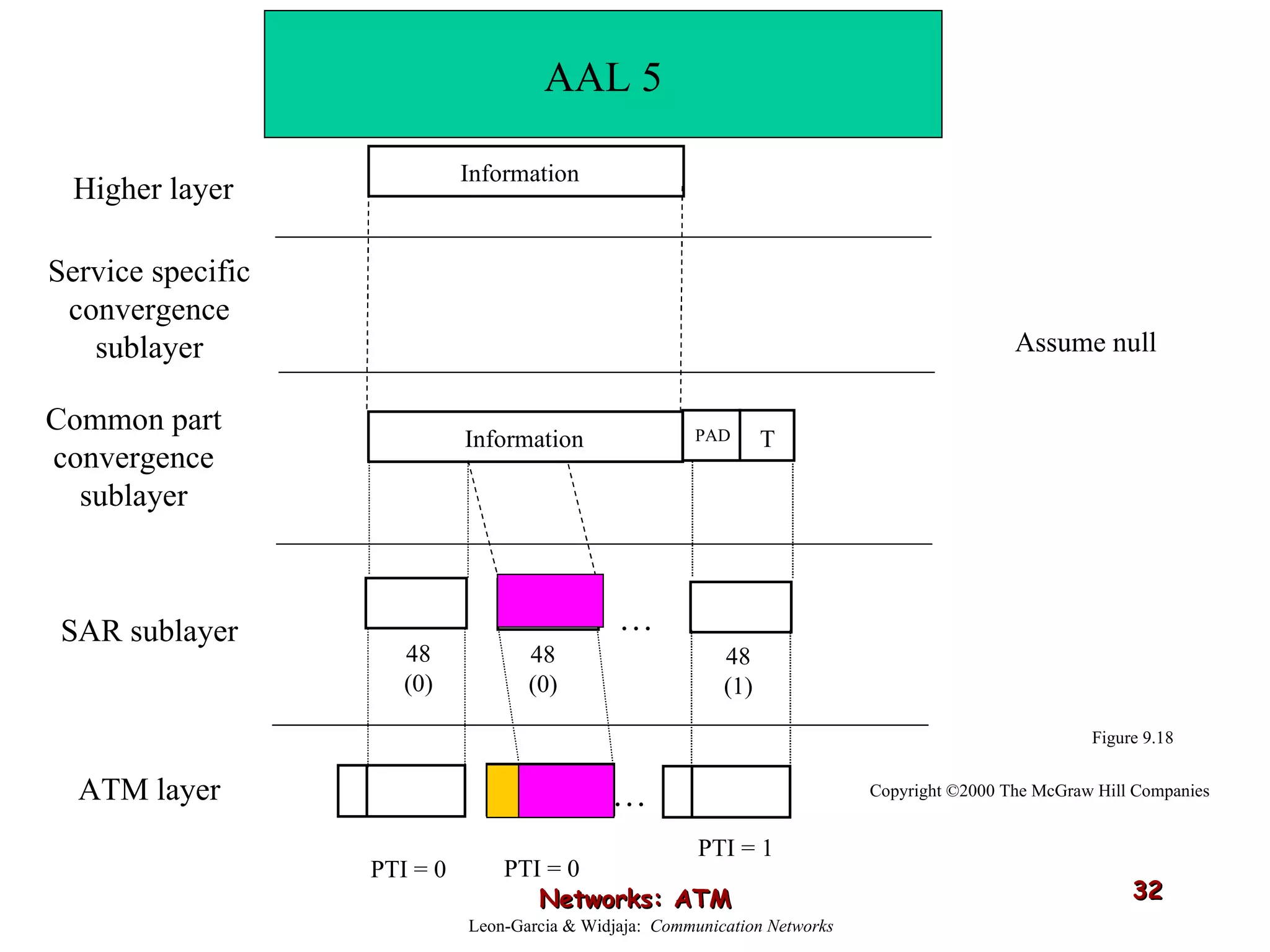
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) was developed to address issues with integrating different types of digital traffic such as voice, video, and data on local area networks. ATM uses fixed-size cells consisting of header and payload to efficiently transport variable bit rate traffic. The ATM architecture includes adaptation layers to segment higher-level data into cells and reassemble cells back into packets or frames. The architecture was refined over time to better support different traffic types through permanent and switched virtual connections.