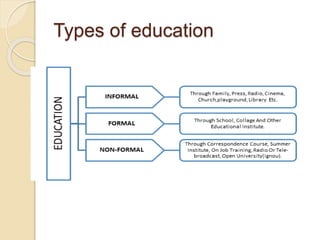
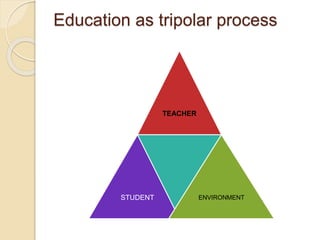
The document discusses the concepts of education and nursing education. It provides various definitions of education from different scholars such as Swami Vivekananda, M.K. Gandhi, Pestolozzi, and John Dewey. It describes nursing education as a professional education that aims for the harmonious development of students' physical, intellectual, social, emotional, spiritual and aesthetic abilities. The document also outlines the aims of general education and nursing education as well as the trends and evolution of nursing education in India from 1871 to 2001.