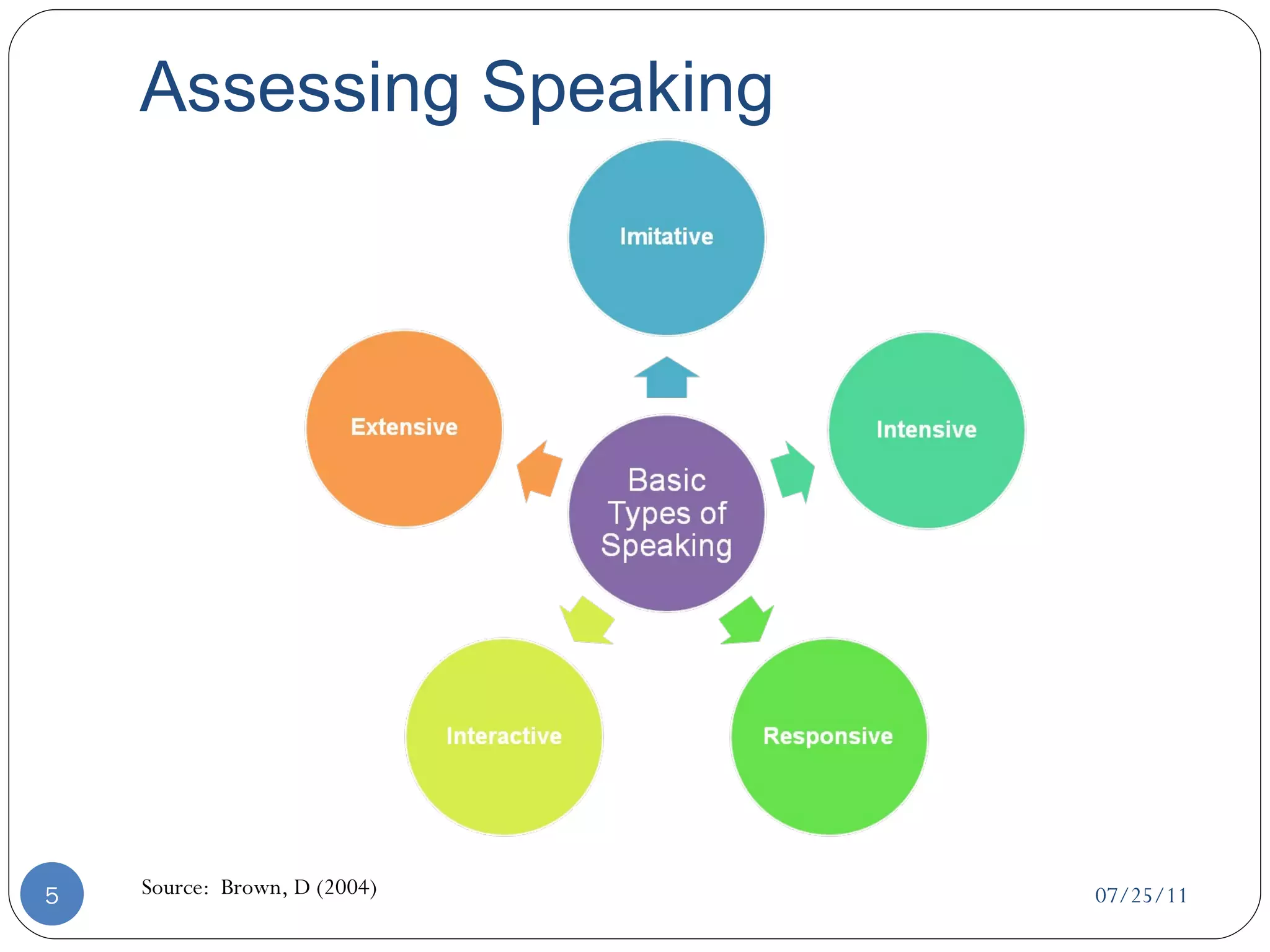
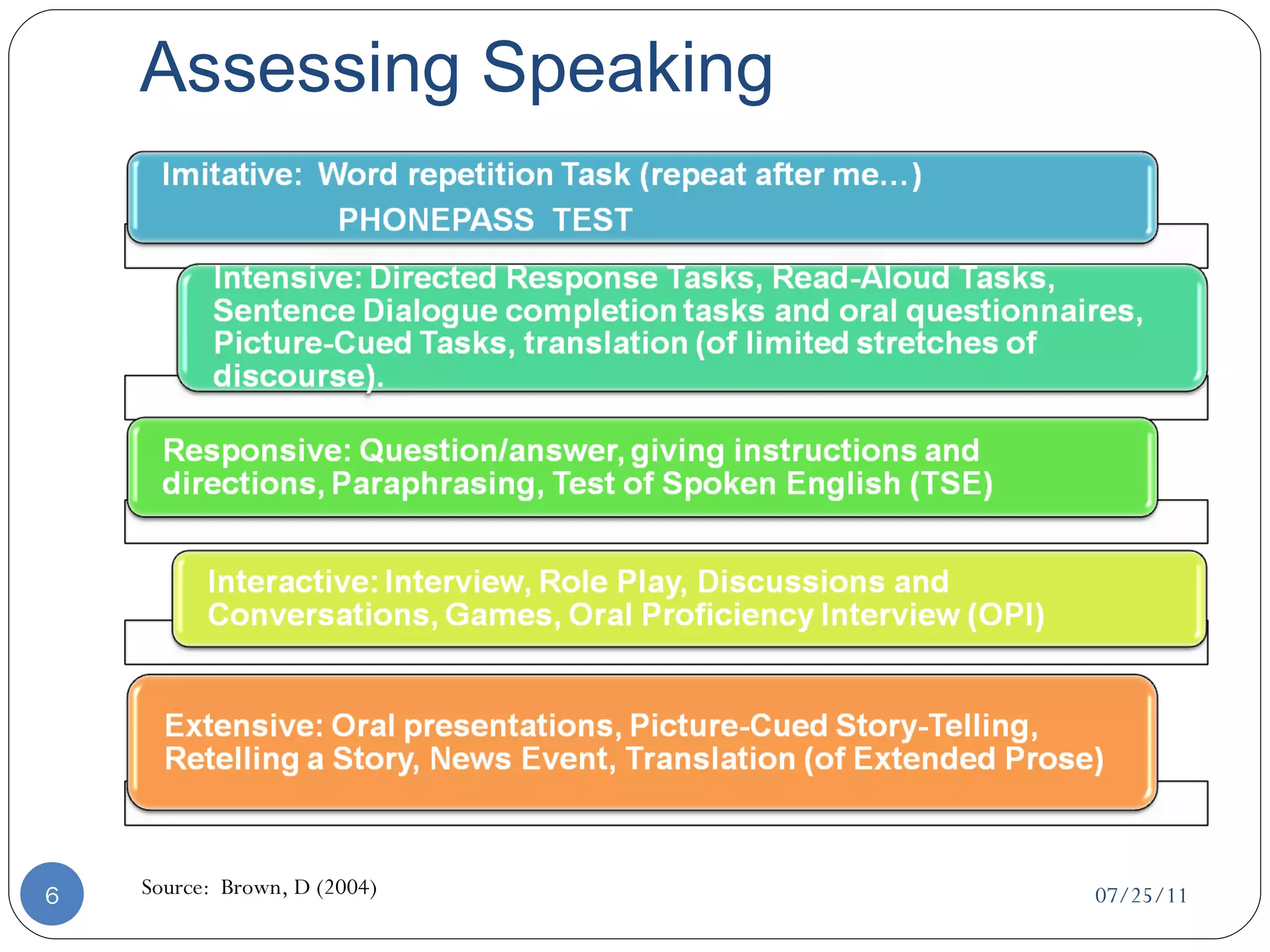
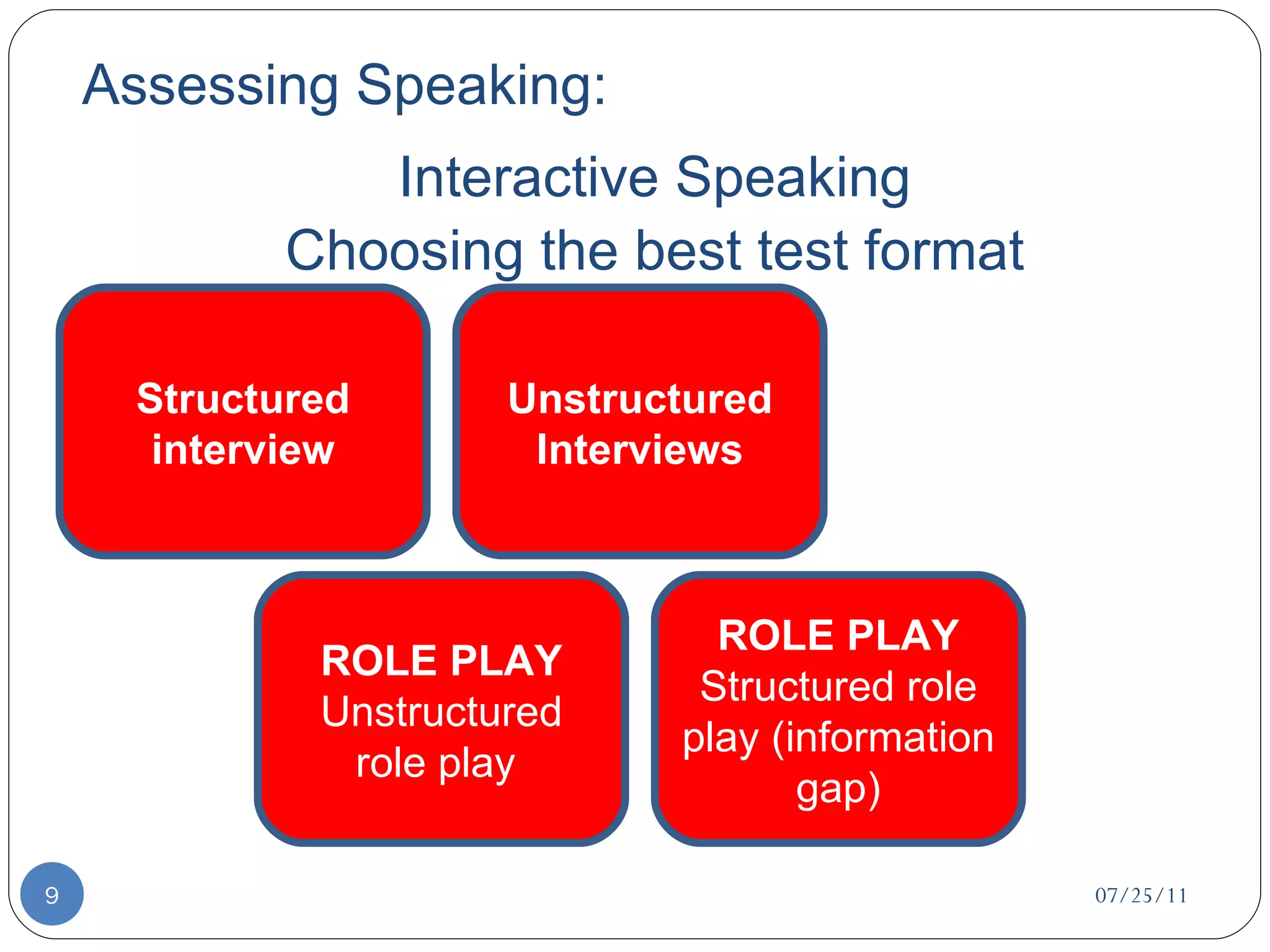
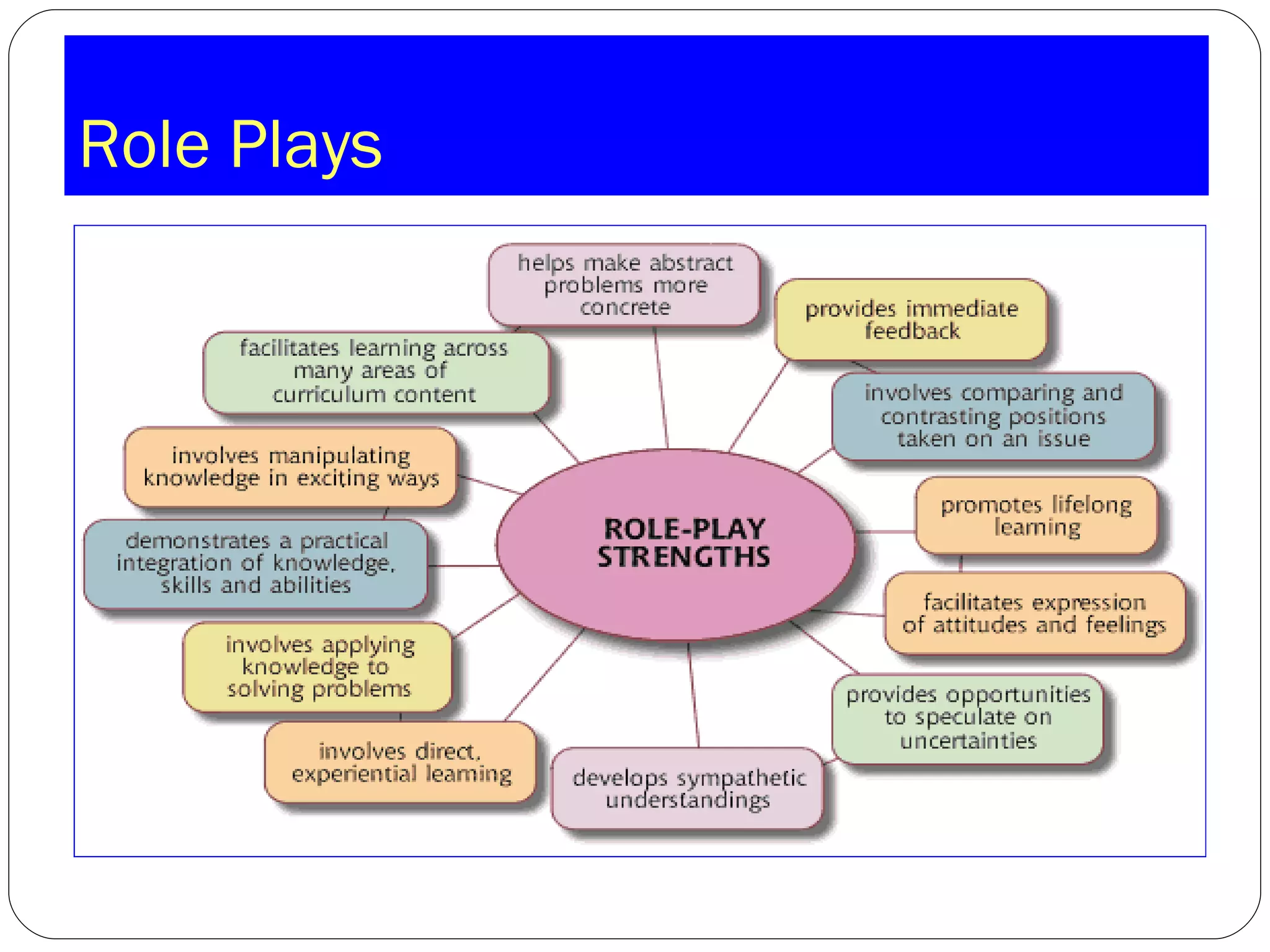
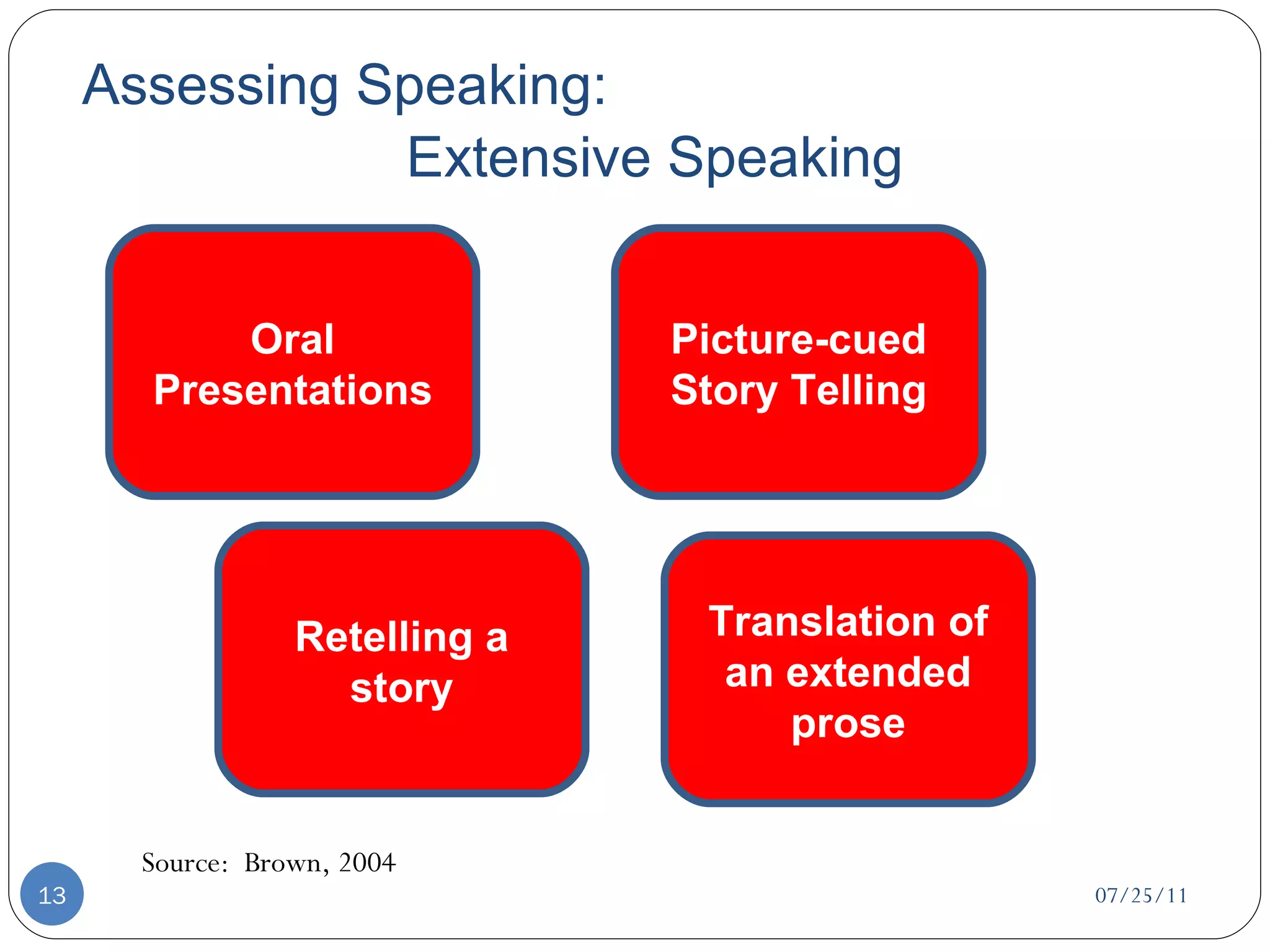
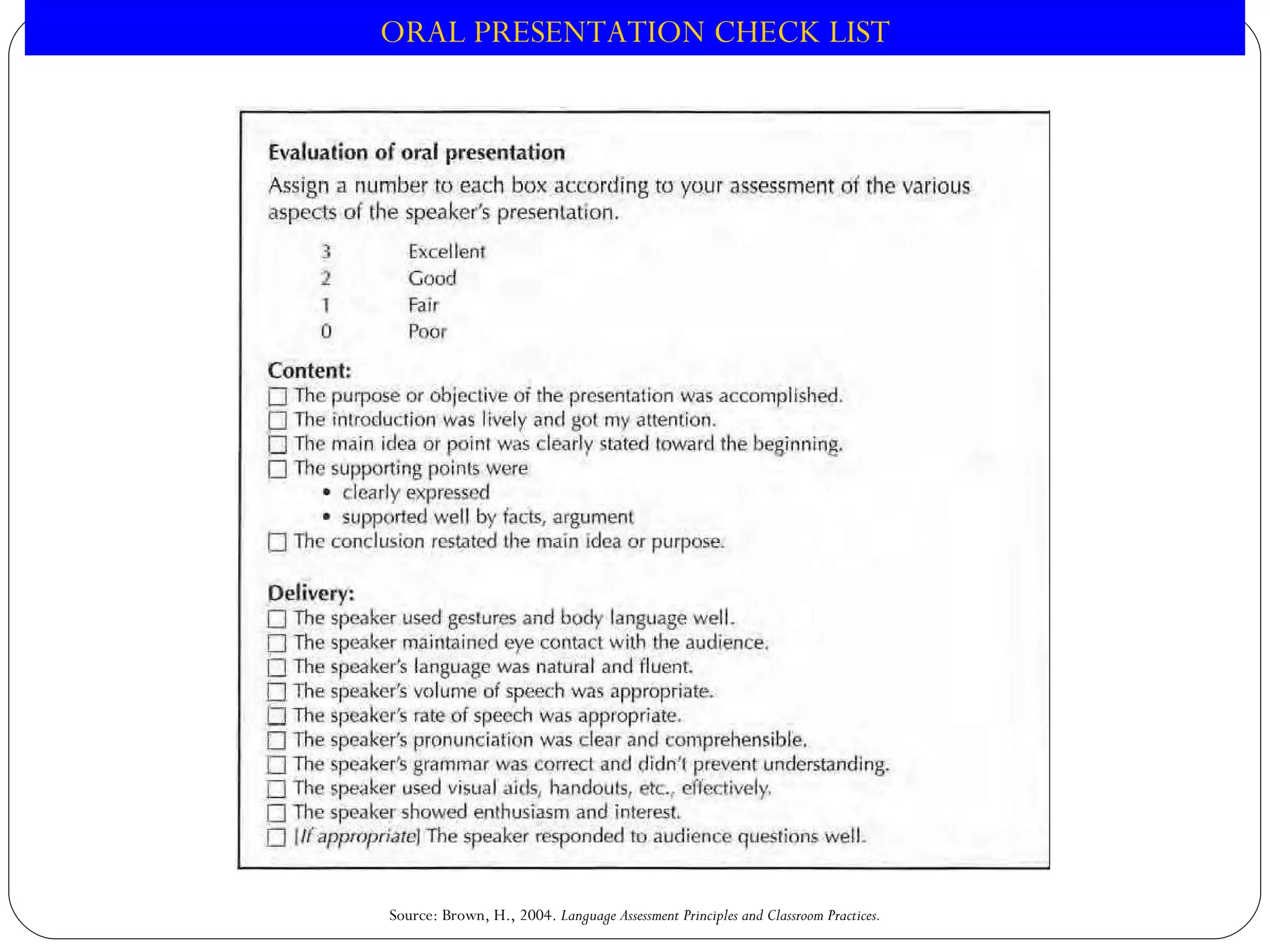
This document discusses strategies for assessing speaking skills in a second language. It describes the characteristics of spoken language, such as variation in speed, loudness, gestures, intonation, stress, rhythm, and pausing. It presents several methods for assessing speaking, including role plays, interviews, oral presentations, picture-cued story telling, and translations. Role plays can be structured or unstructured. Interviews involve warming up, level-checking, probing, and winding down. It's important to determine the appropriate criteria and tasks for assessing fluency versus accuracy in speaking.