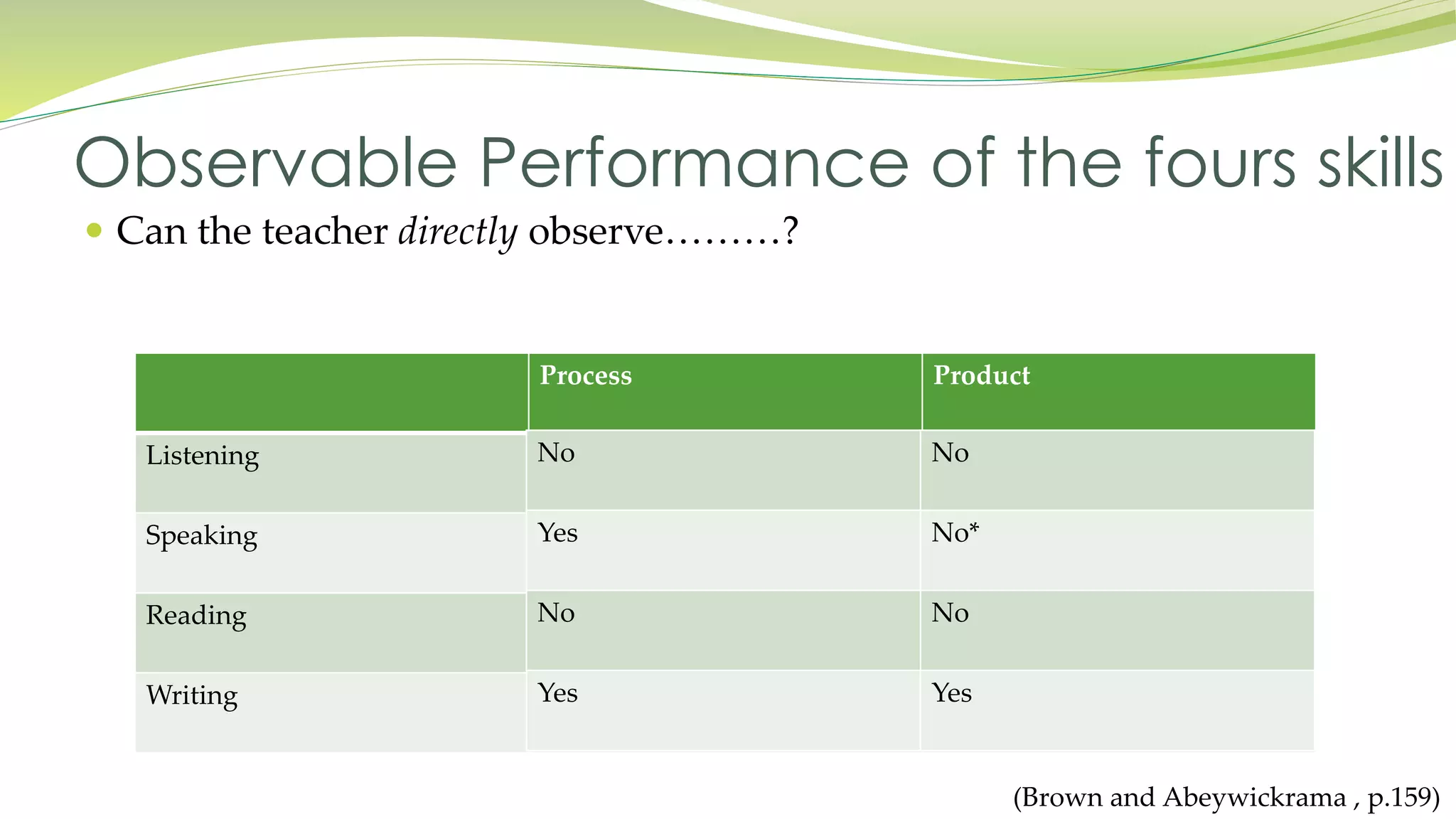
The document discusses reading assessment. It notes that reading overlaps with and is similar to the other language skills of listening, speaking and writing. Assessments also overlap these skills. Reading performance is classified into selective, extensive, and interactive types, mirroring classifications for listening and speaking. The document outlines numerous assessment tasks used to evaluate reading and the variations that exist. It concludes that isolating reading from the other skills is difficult as assessments overlap skills.