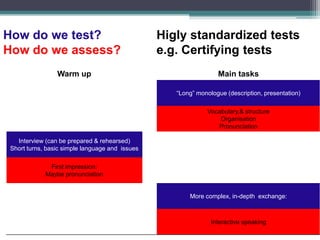
The document outlines the challenges and importance of testing speaking skills in language learning, emphasizing the need for fair assessments that provide meaningful feedback to learners. It discusses different aspects of speaking to be tested and the use of standardized tests, including various assessment methods and documentation issues. Additionally, it references the Common European Framework of Reference (CEFR) and various bibliographic sources for further reading.



![Why test language learning? (1)
‘Tests are also important instruments of public
policy. National examinations, for example, are
used to ensure that learners at educational
institutions across the country are held to the
same standards.’
Douglas, D. [2010:2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingspeaking-121019072038-phpapp02/85/Testing-speaking-4-320.jpg)
![Why test language learning? (2)
‘Tests also allow other stakeholders, including
programme administrators, parents, admissions
officers and prospective employers, to be assured
that learners are progressing according to some
generally accepted standard or have achieved a
requisite level of competence in their second
language’.
Douglas, D. [2010:1-2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingspeaking-121019072038-phpapp02/85/Testing-speaking-5-320.jpg)
![Why test language learning? (3)
‘Perhaps the most important reason is fairness.
We like to make sure all students are treated the
same, to give each of them equal opportunity to
show us what they’ve learned and what they can
do with the language they’ve learned. Tests allow
us to present all our students with the same
instructions and the same input under the same
conditions.’
Douglas, D. [2010:1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingspeaking-121019072038-phpapp02/85/Testing-speaking-6-320.jpg)