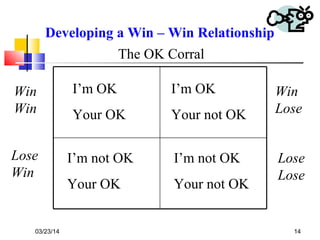
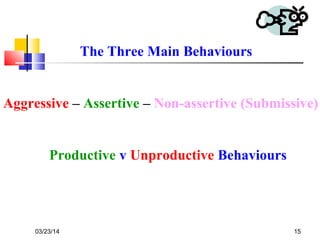
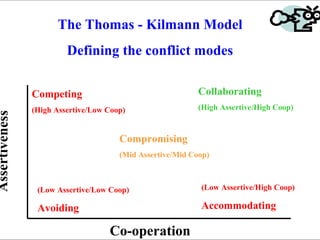
This document outlines the learning outcomes and content of an assertiveness training course. By the end of the course, students will gain knowledge and skills related to assertive communication, dealing with difficult people and situations, identifying personal rights, developing a "win-win" mentality, and changing unproductive habits. The course will cover topics like listening skills, questioning techniques, identifying different types of behaviors, and models for conflict resolution.