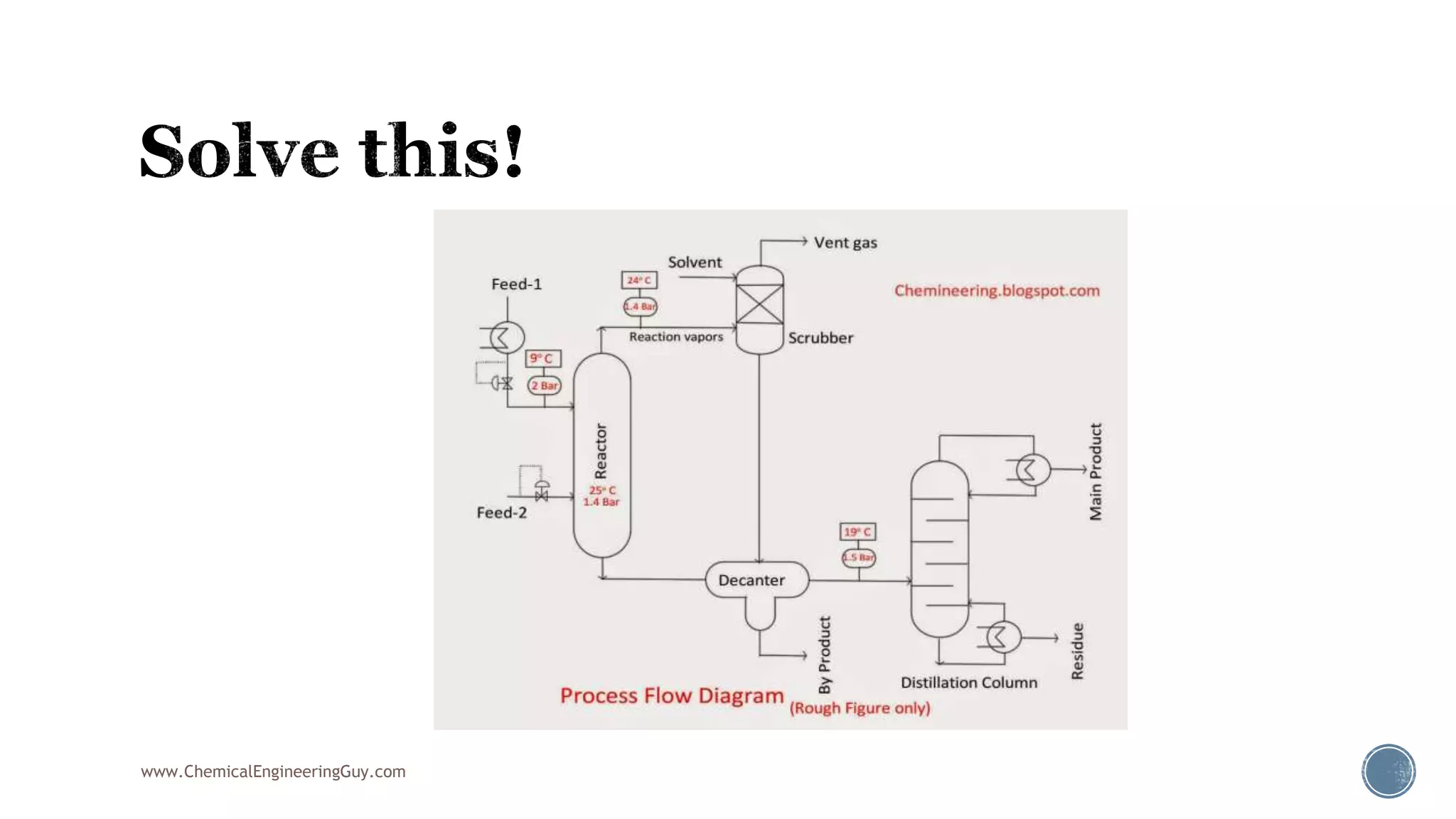
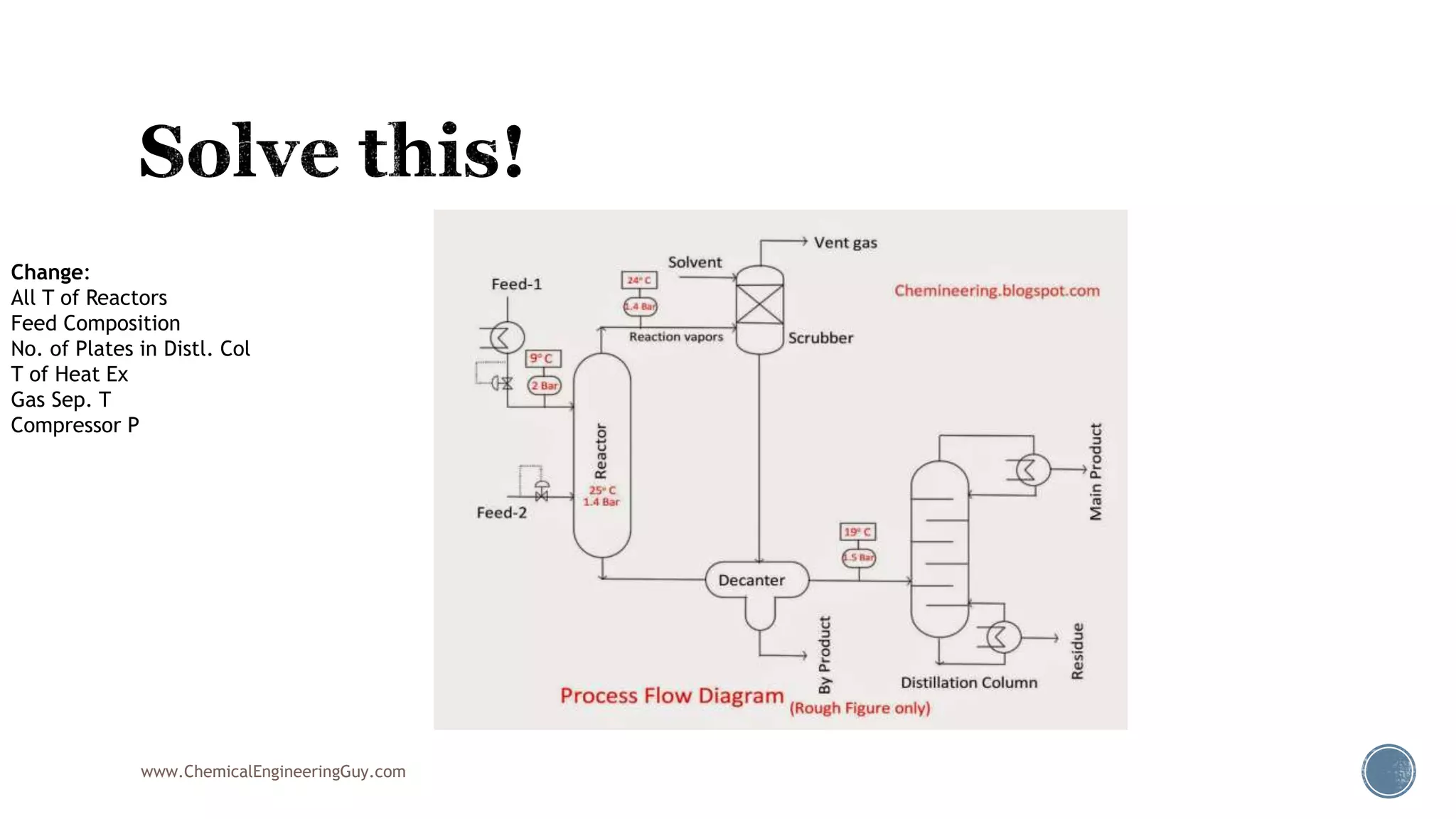
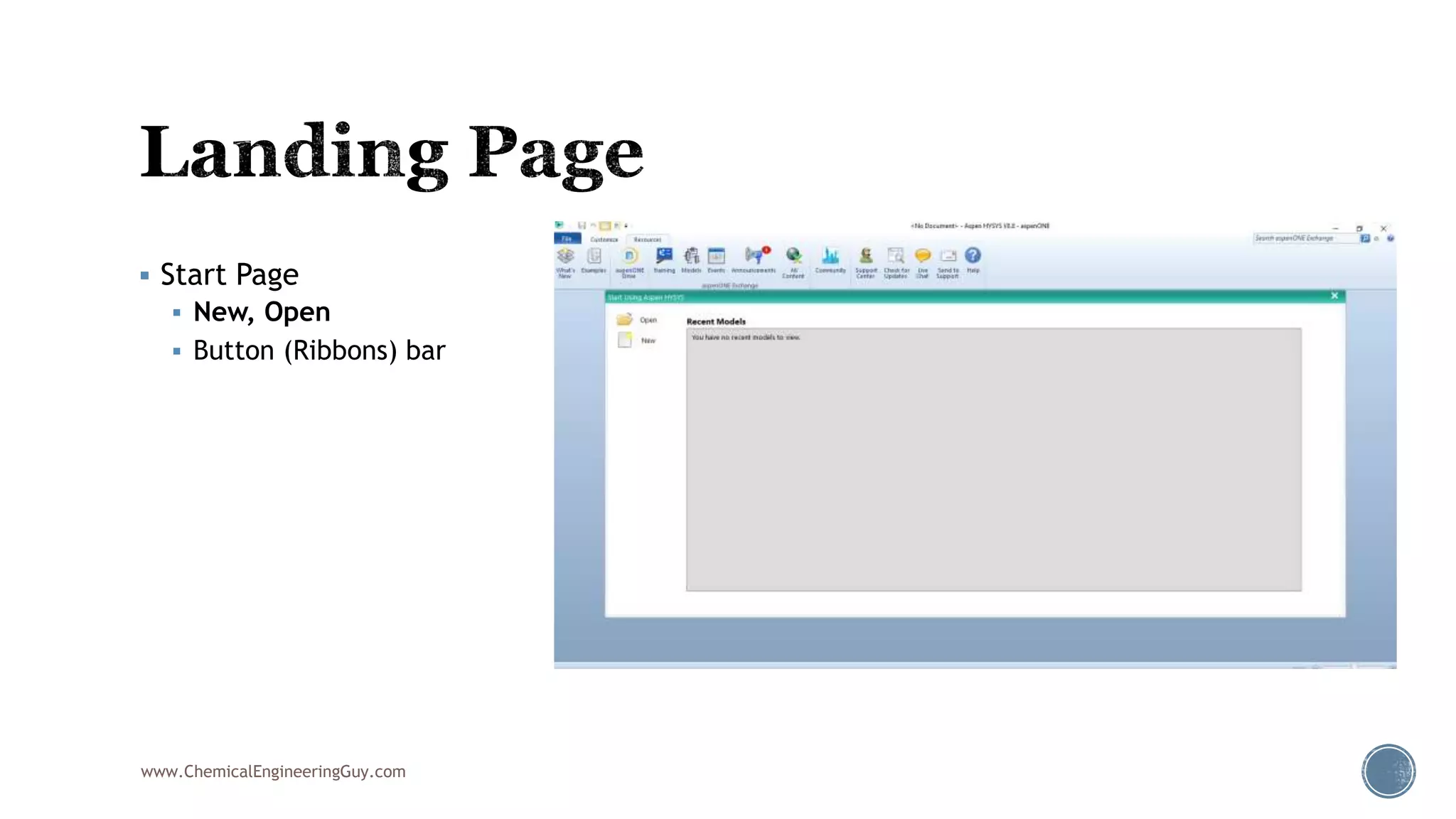
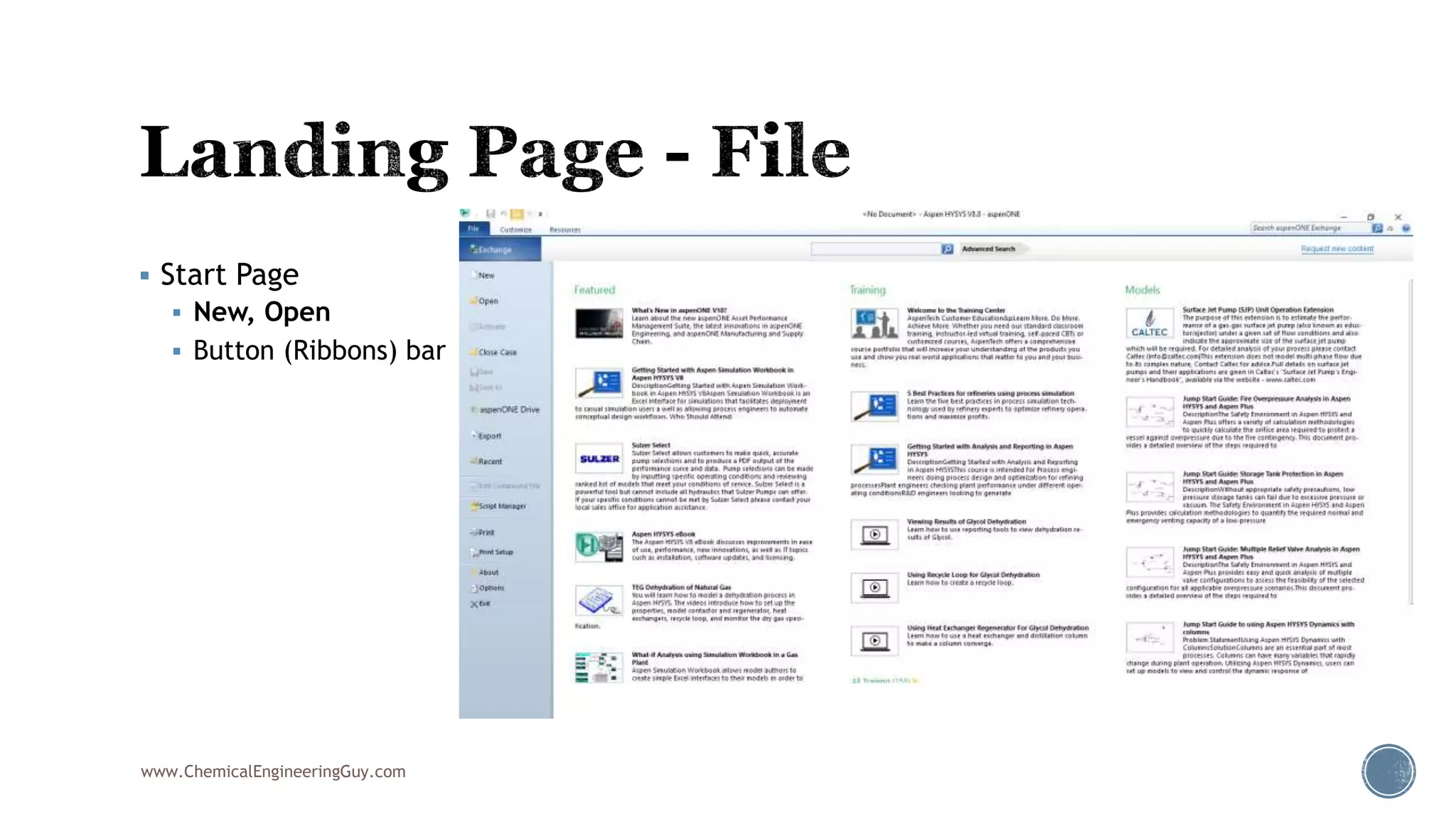
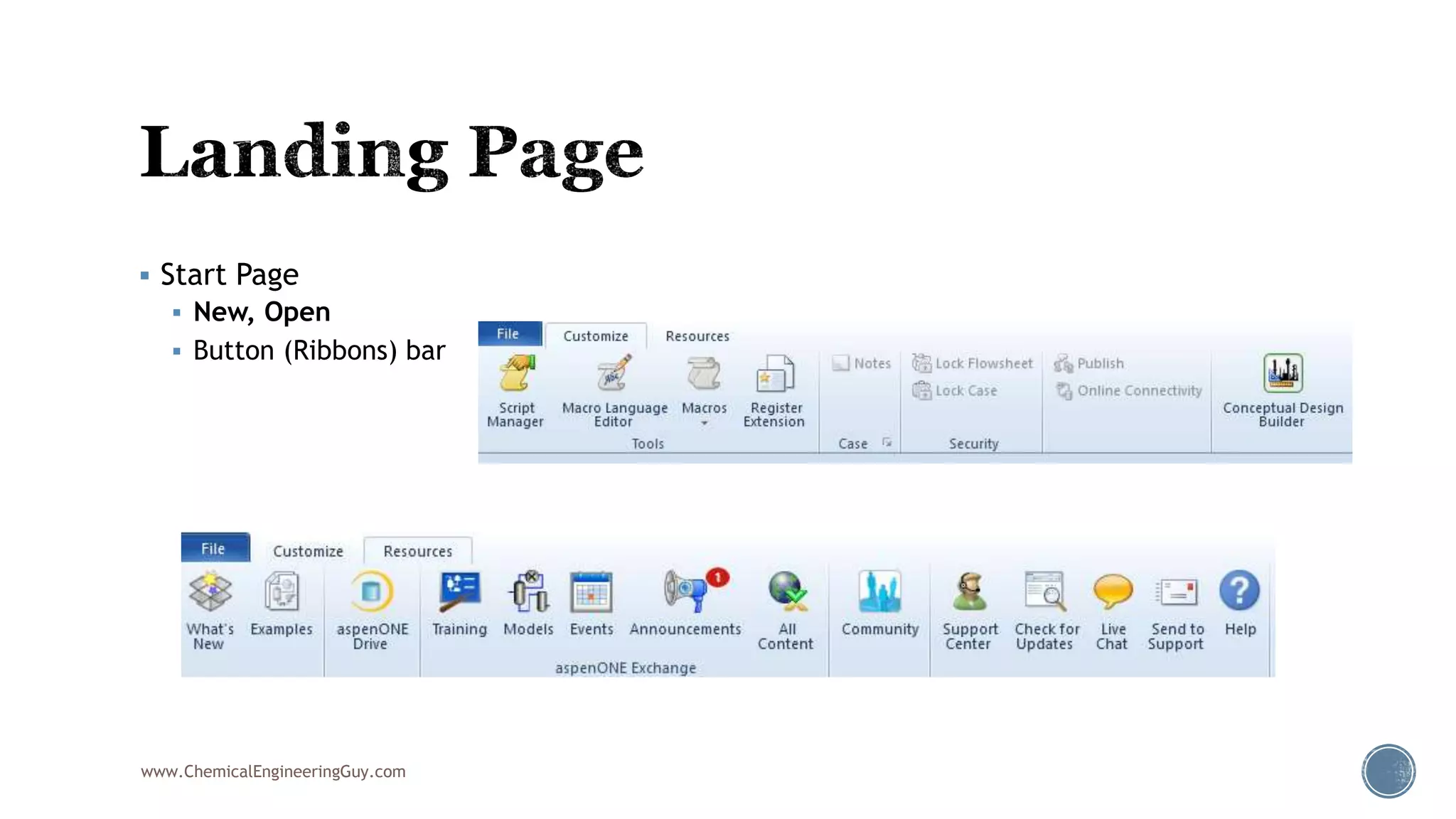
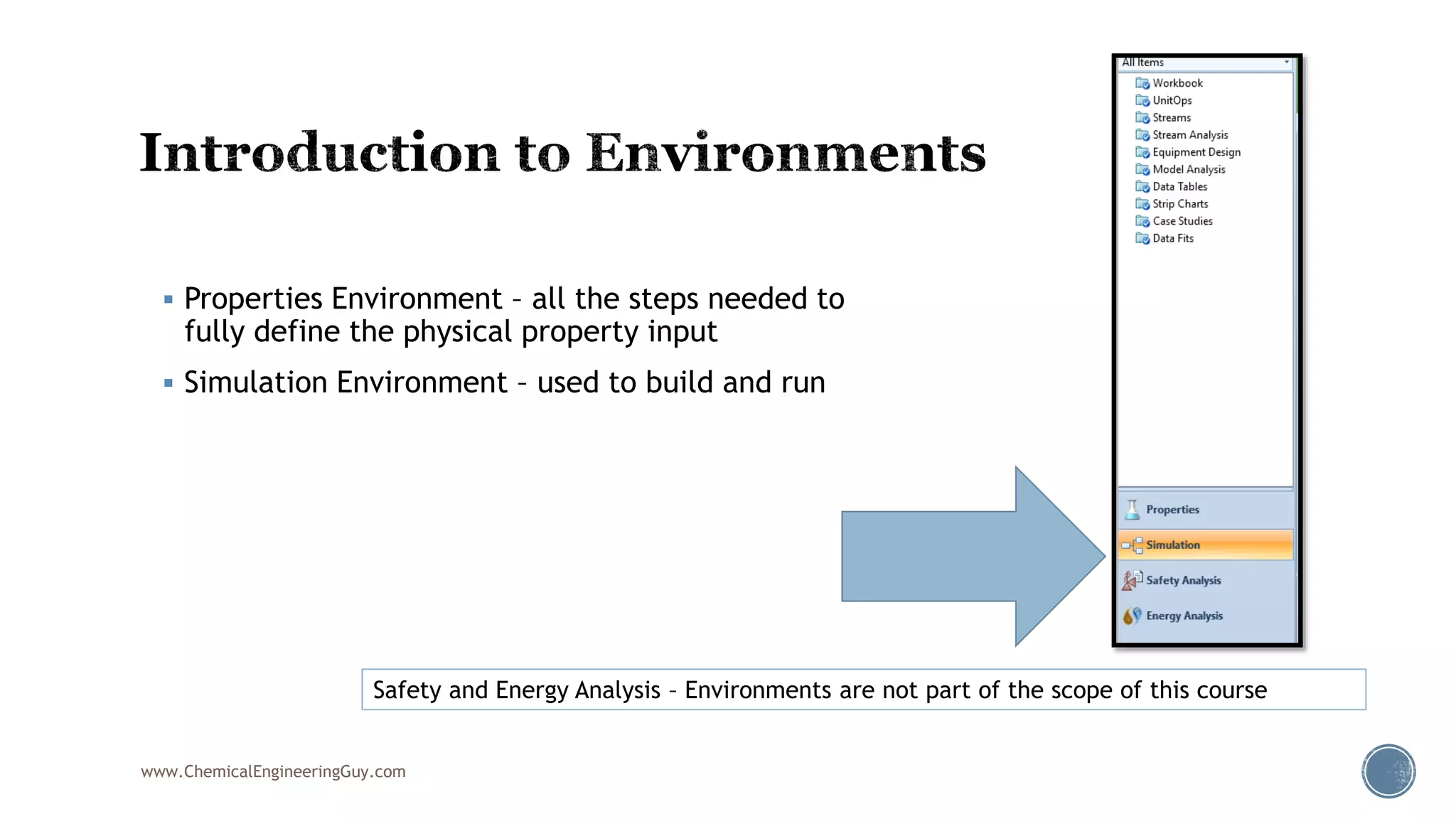
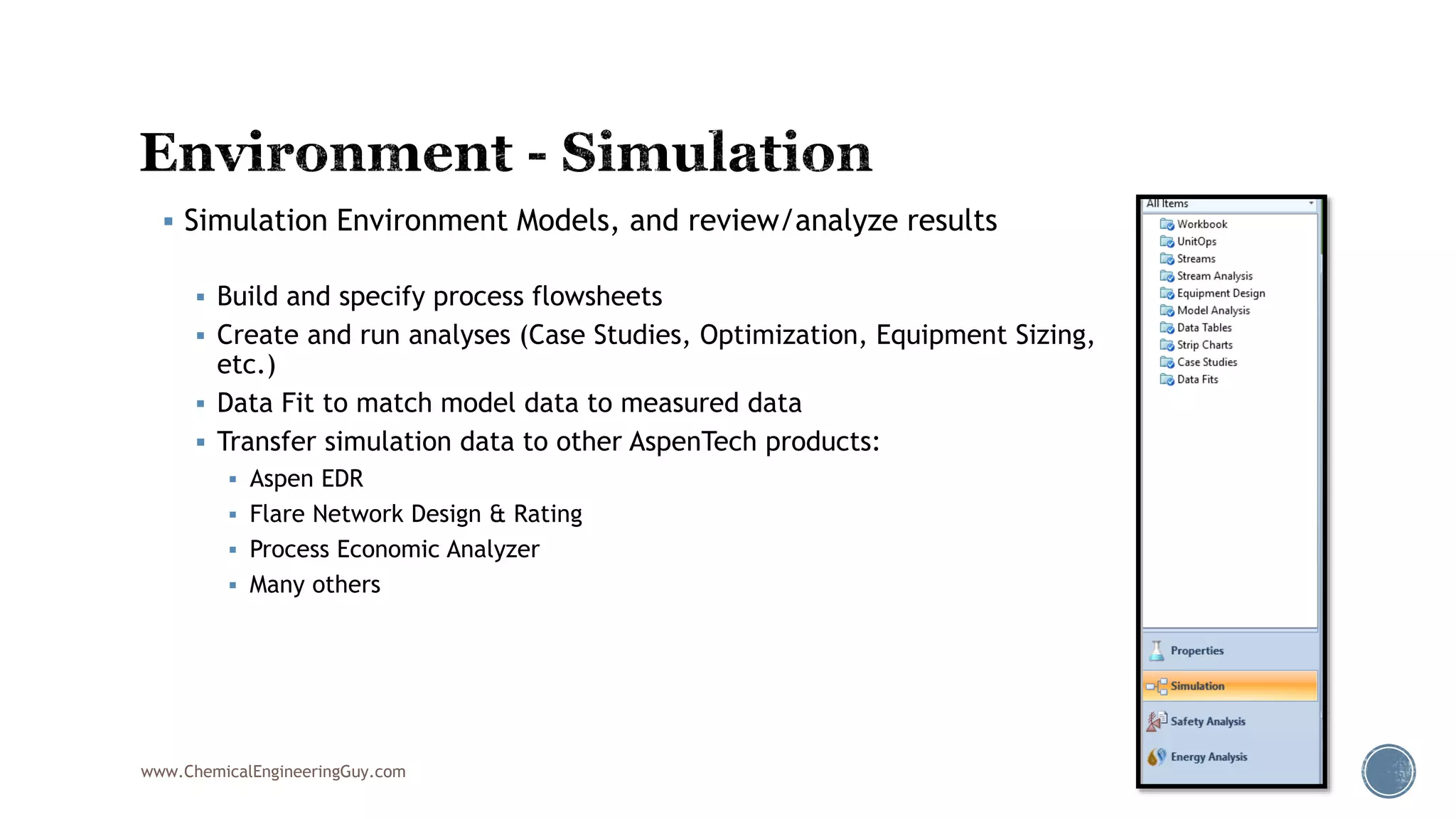
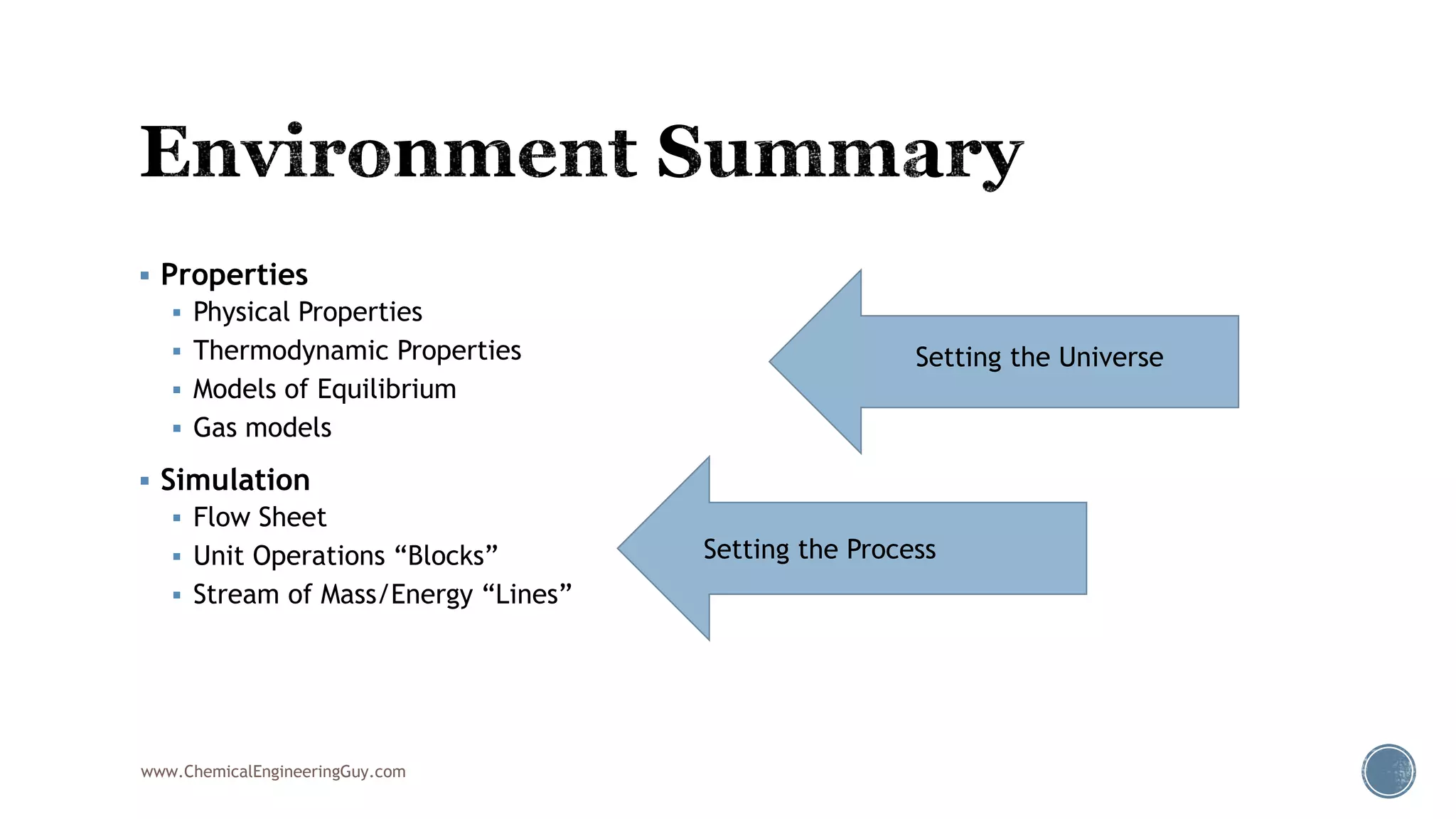
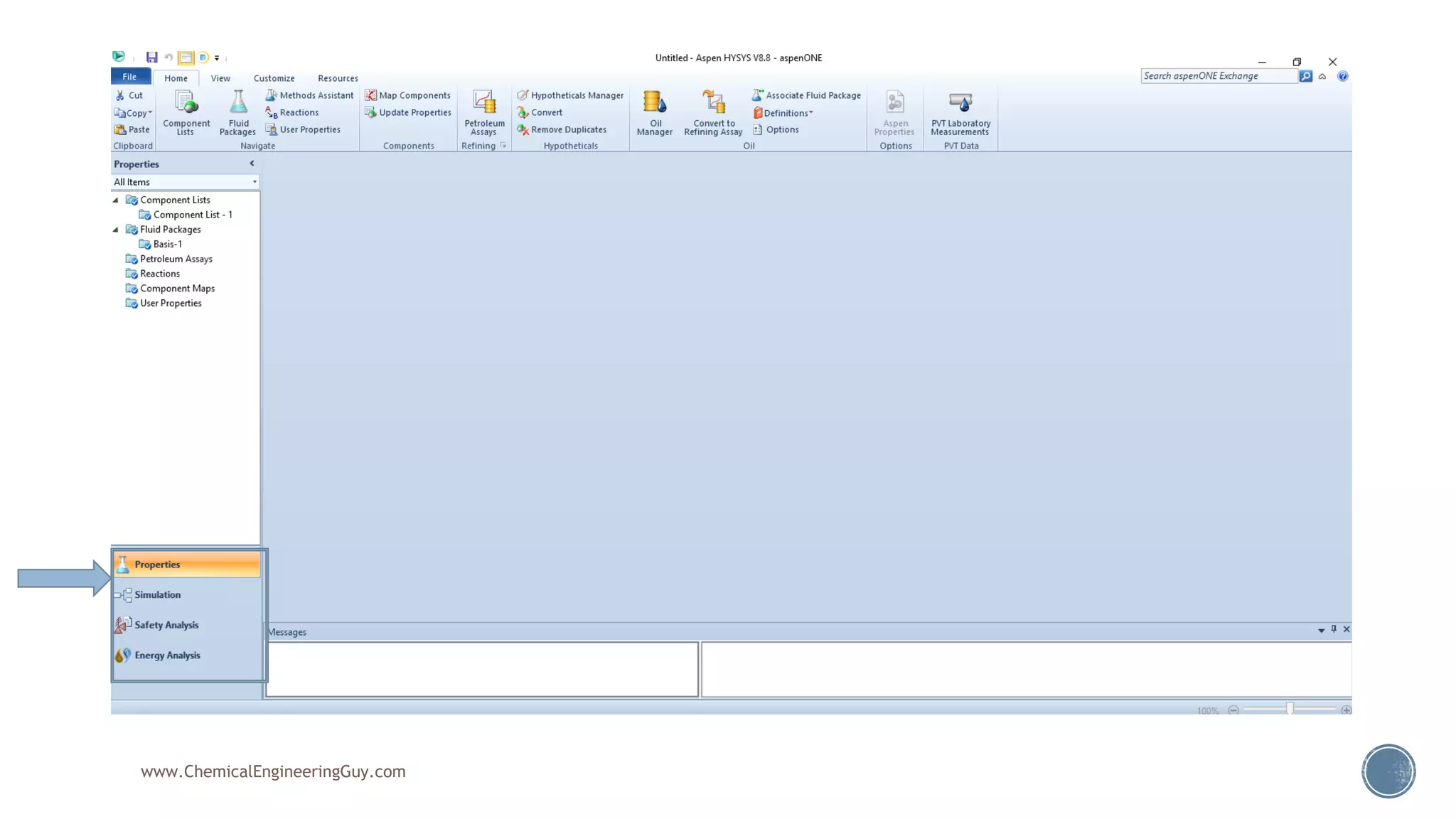
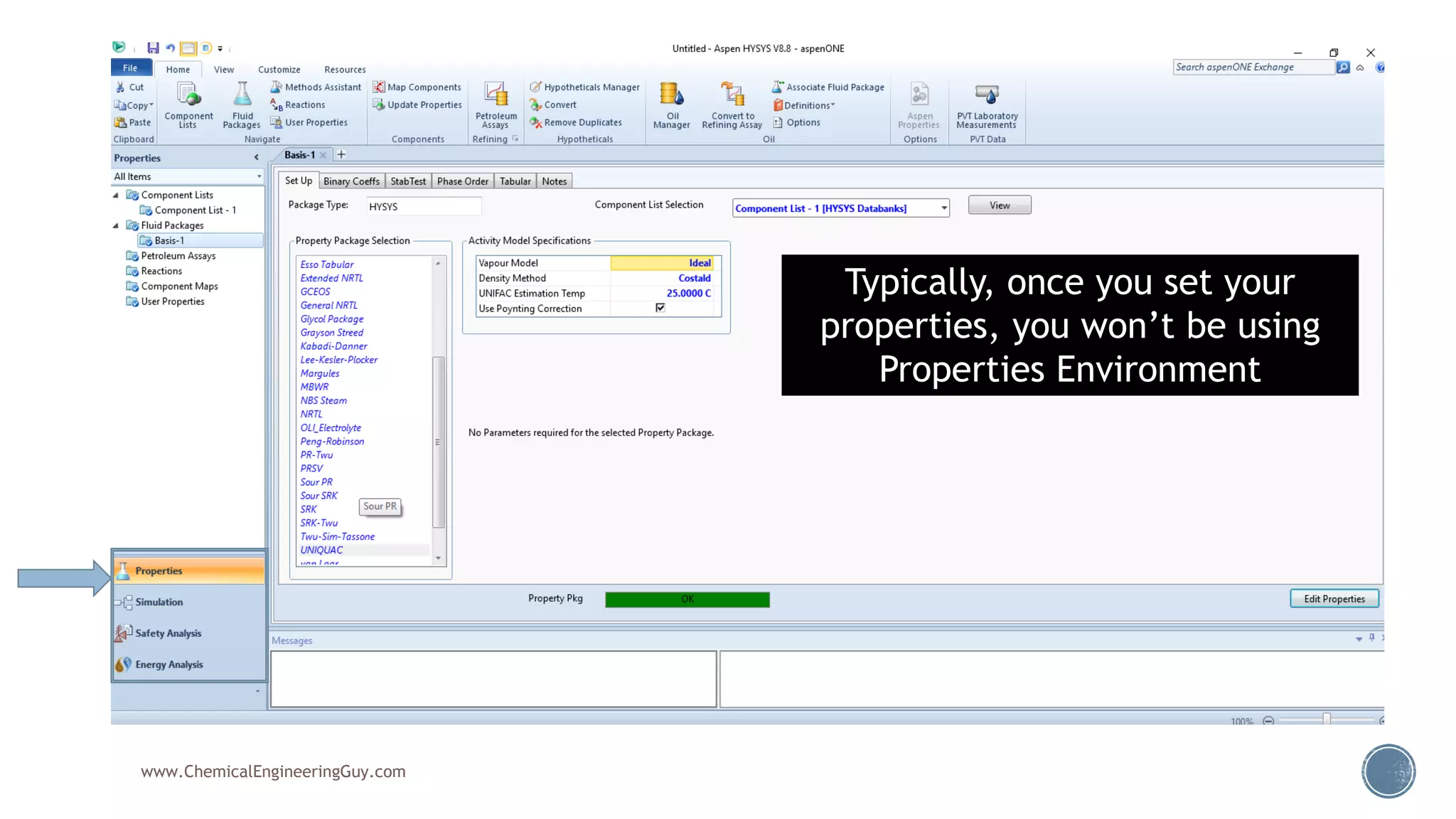
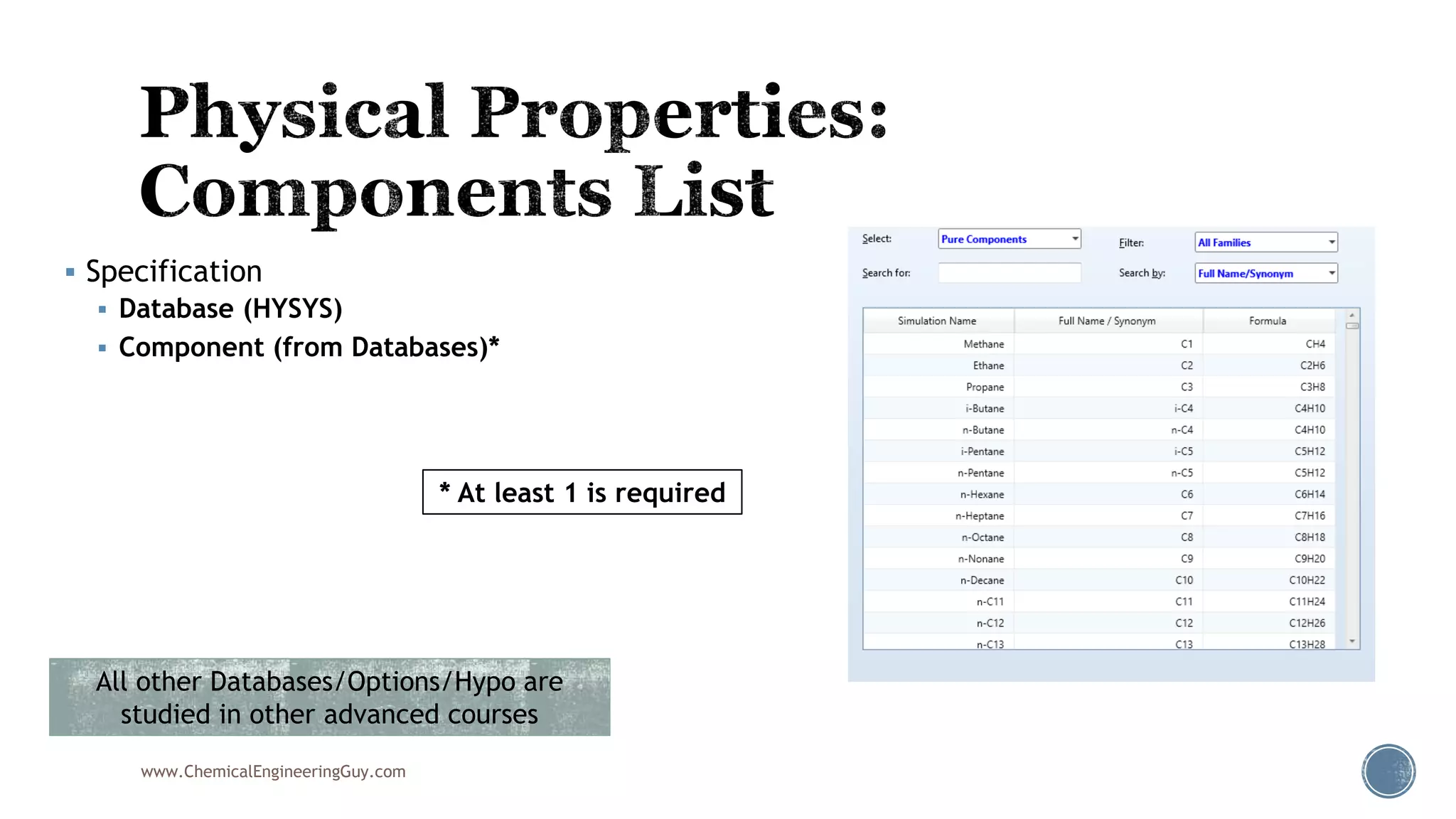
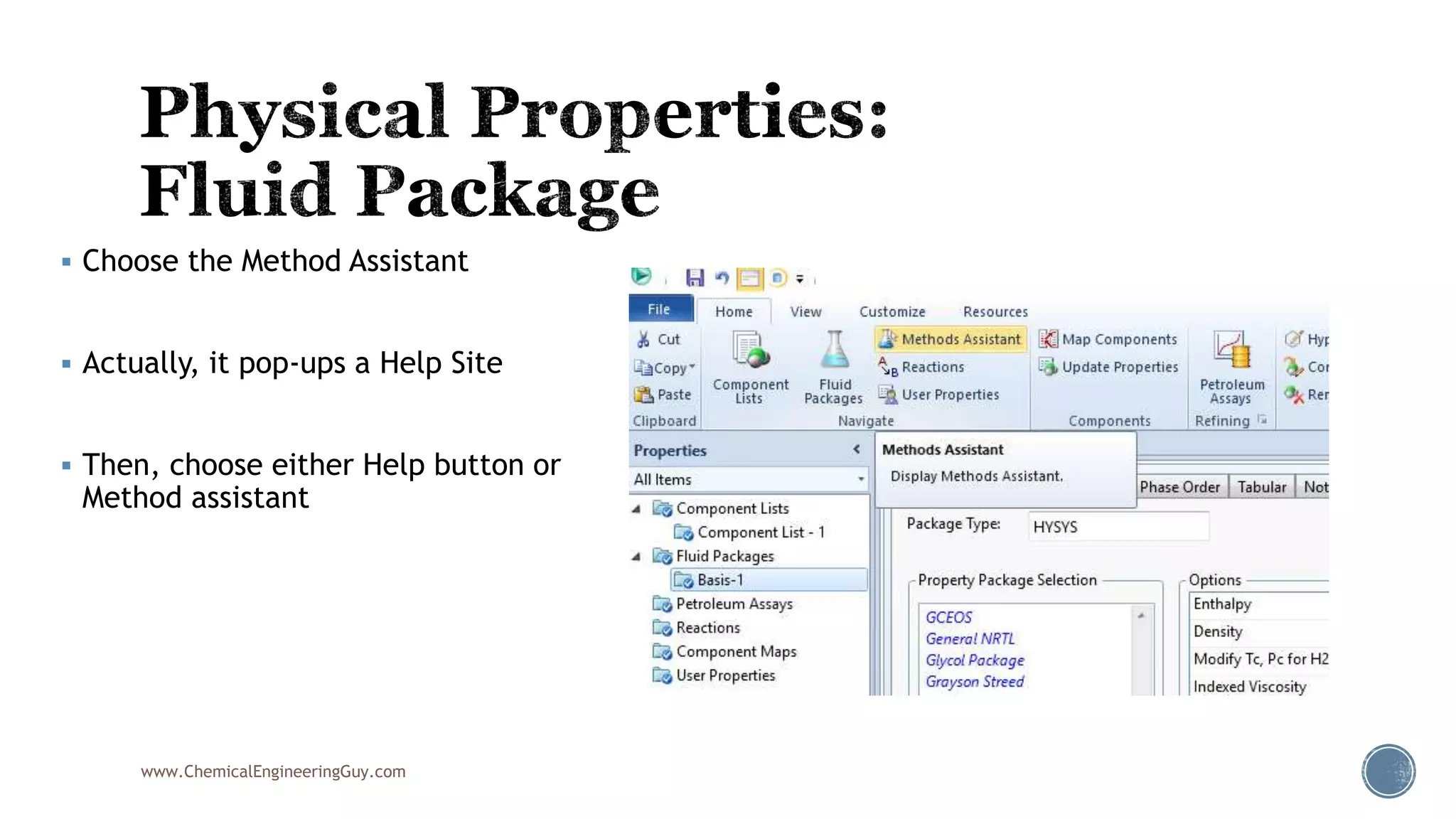
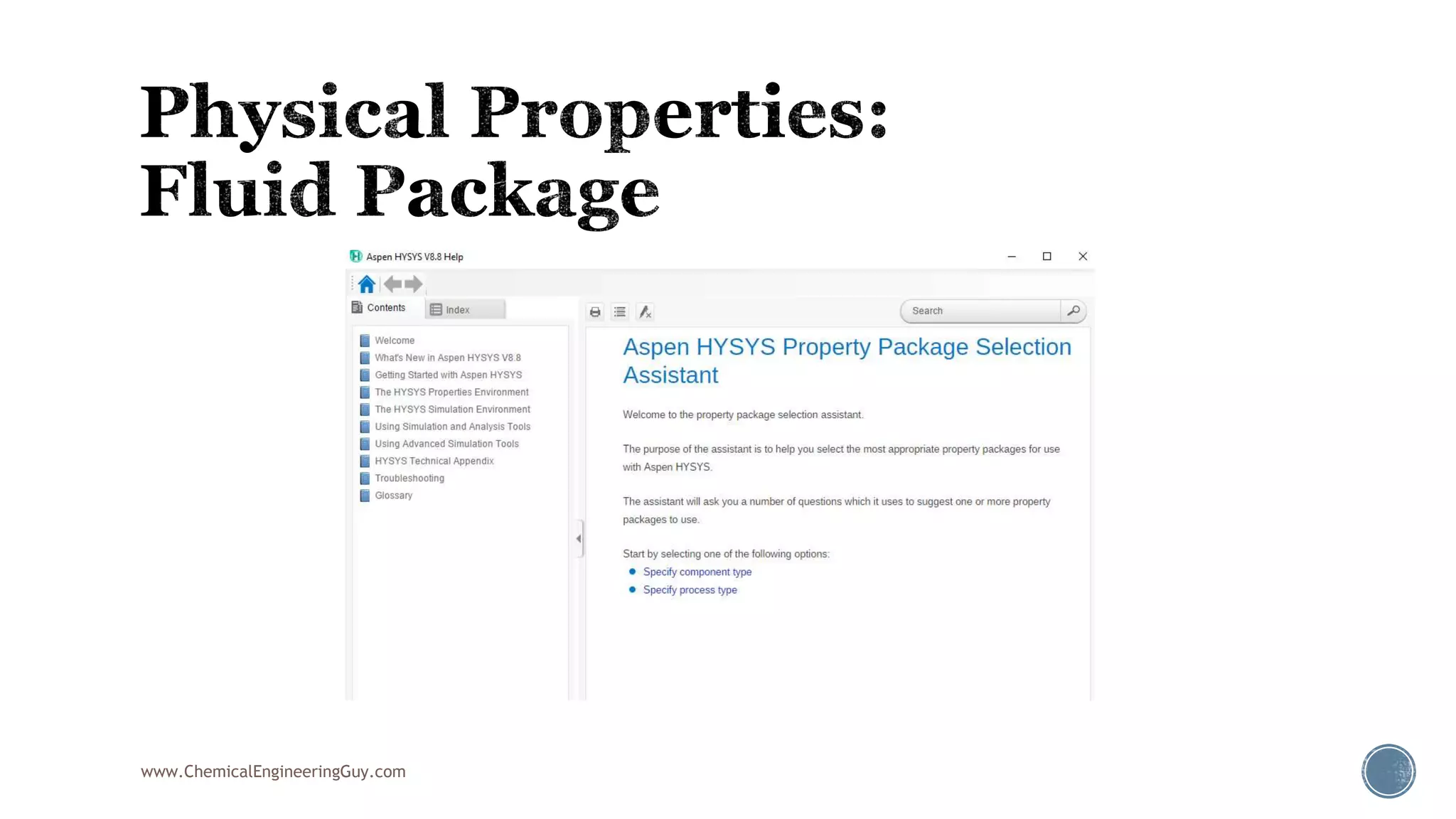
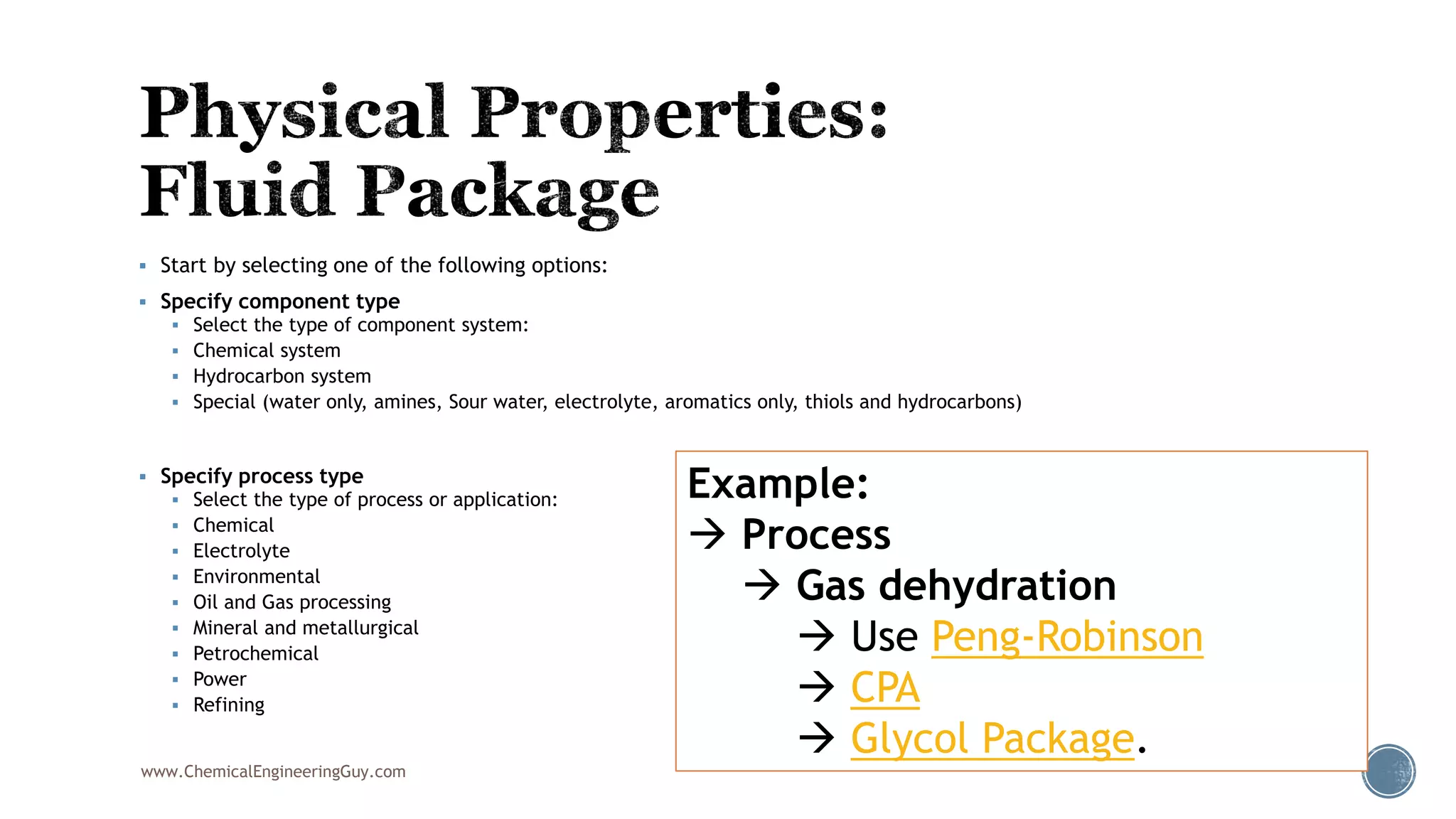
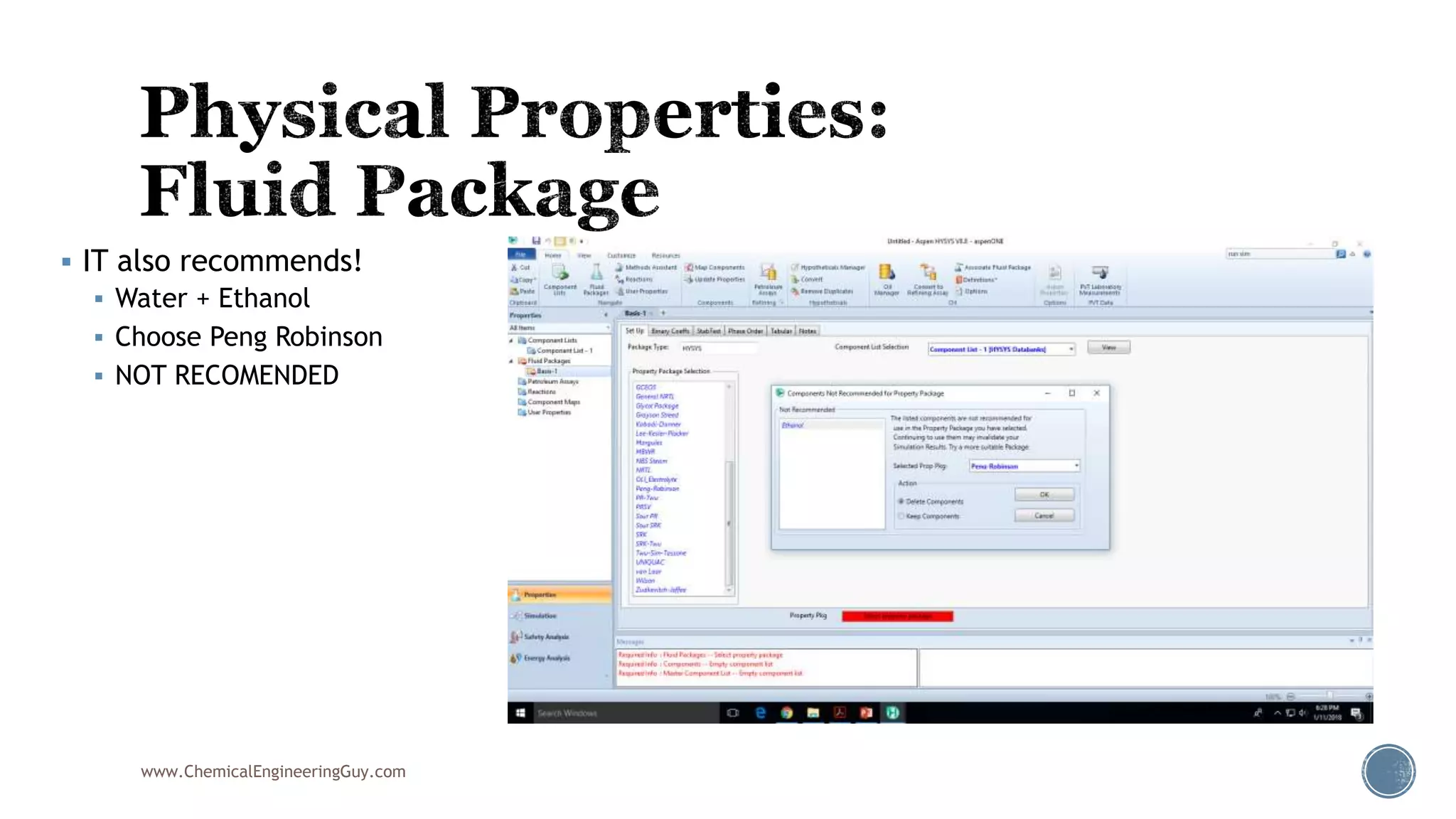
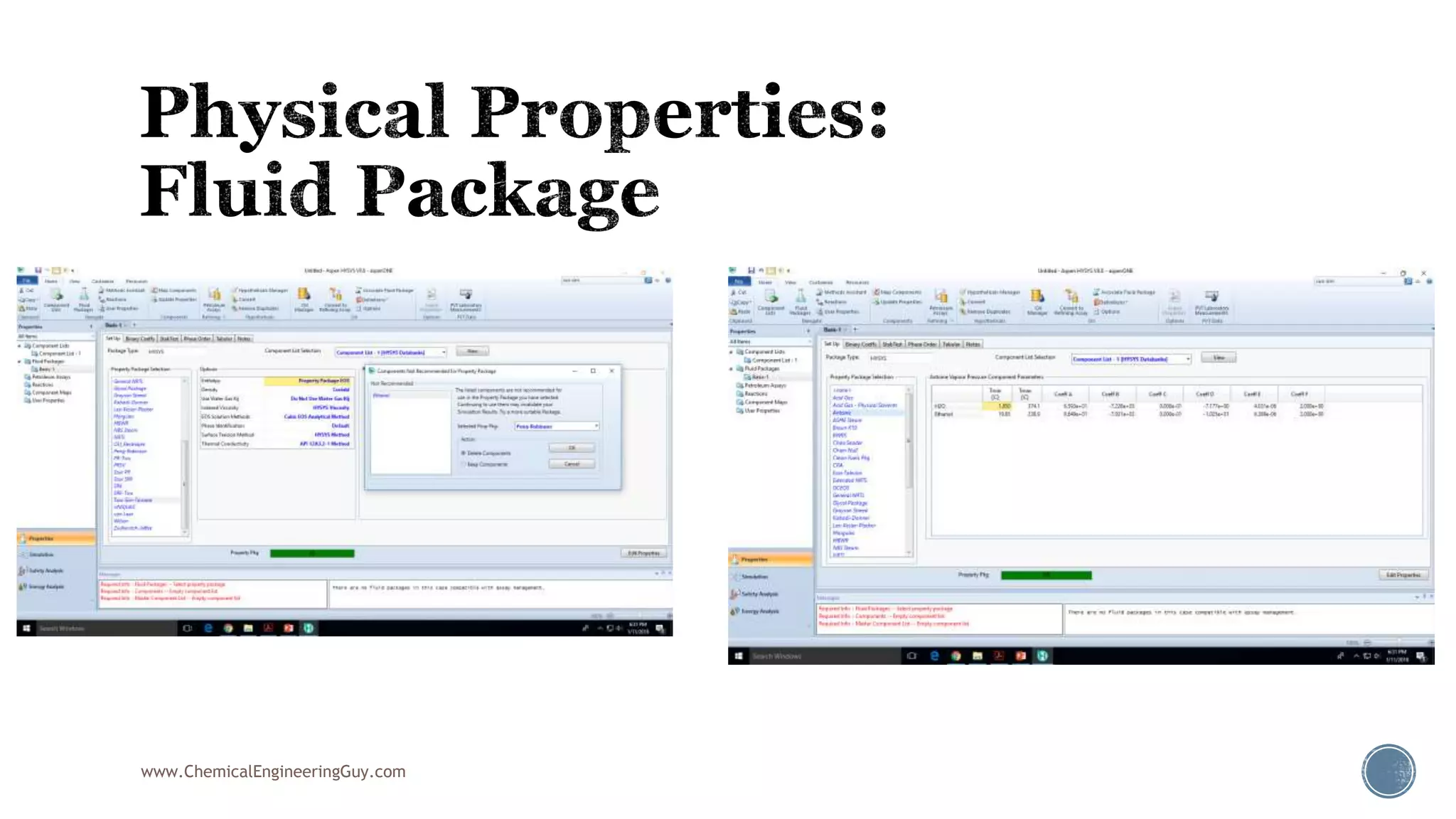
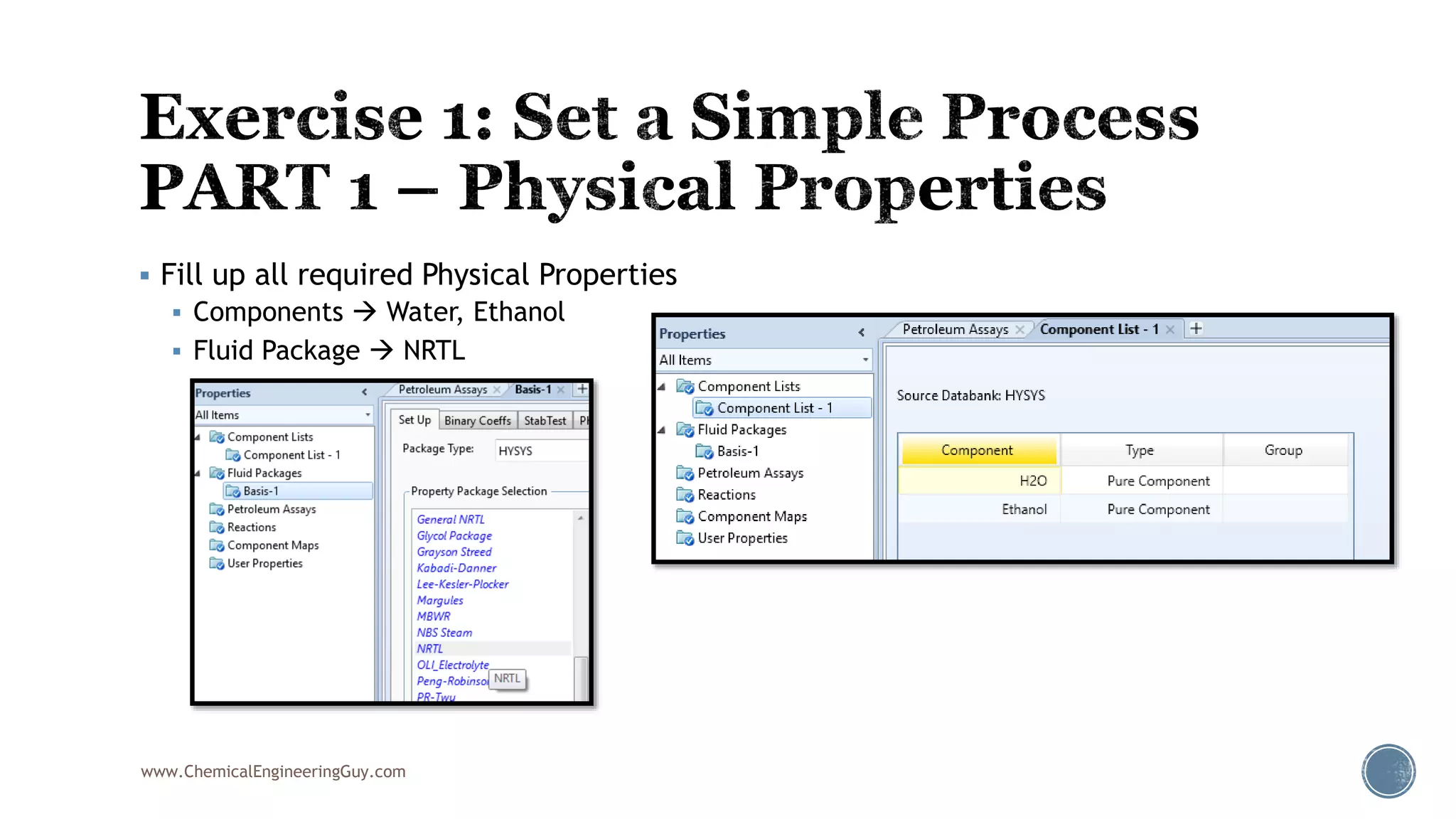
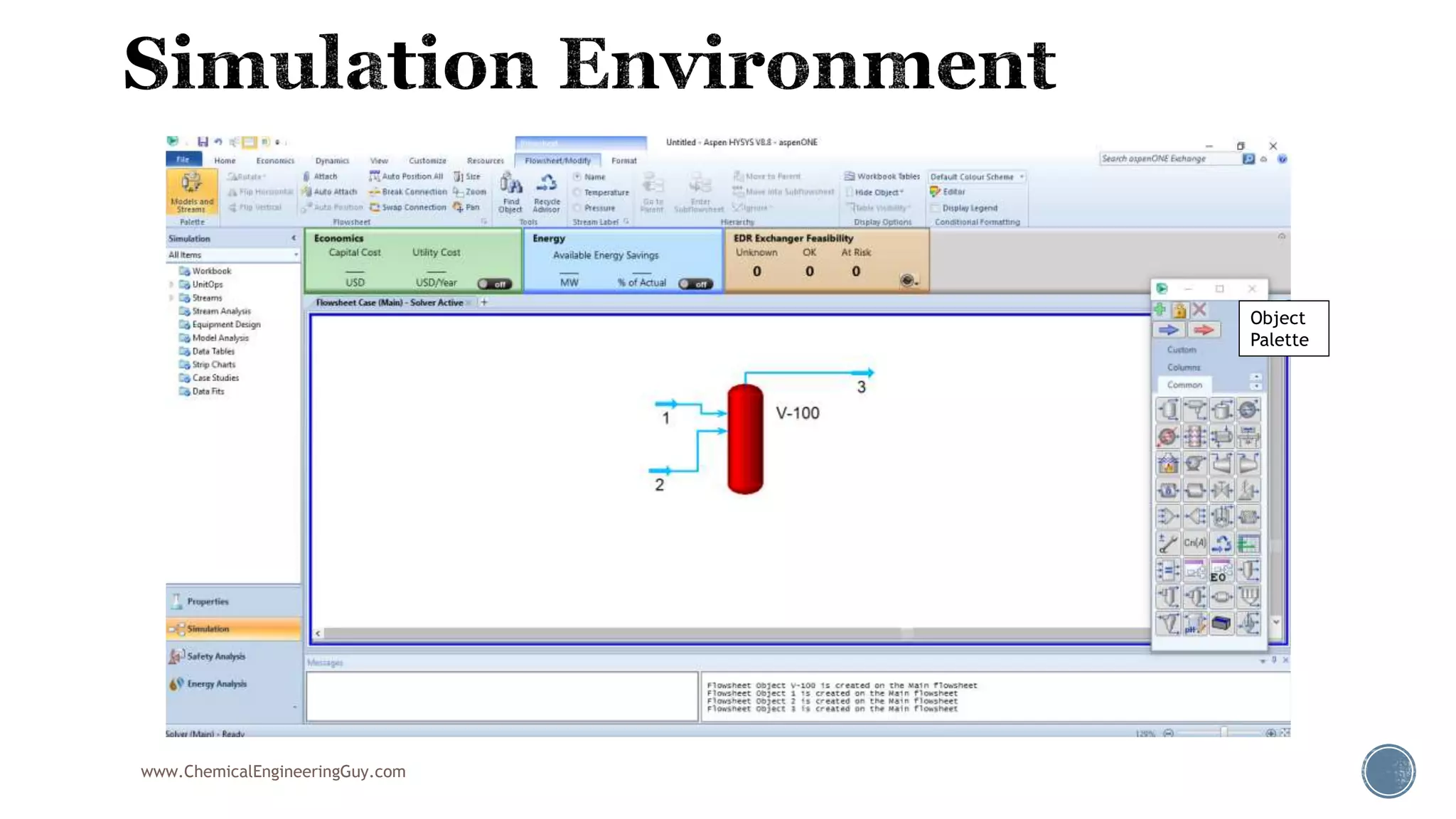
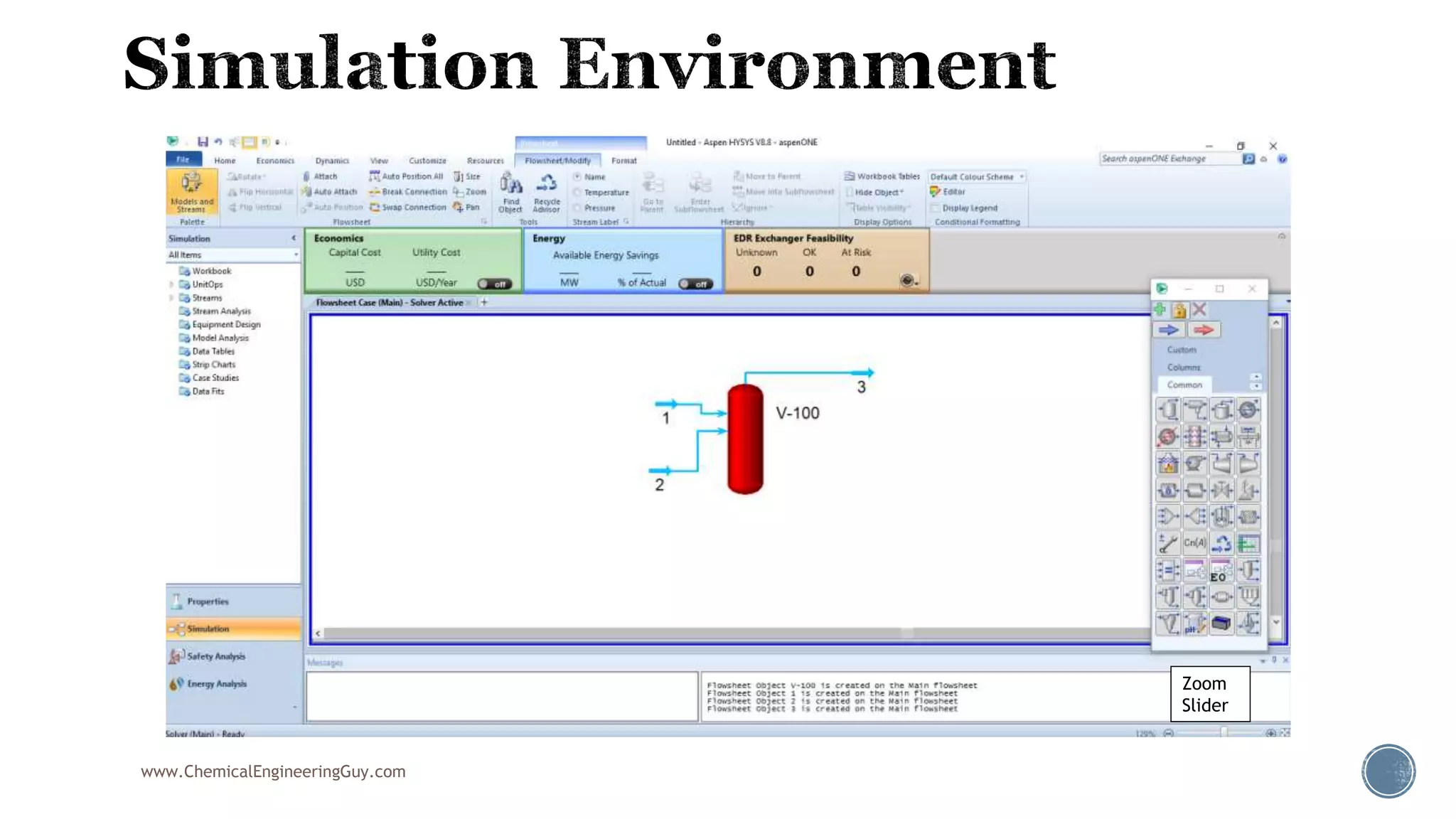
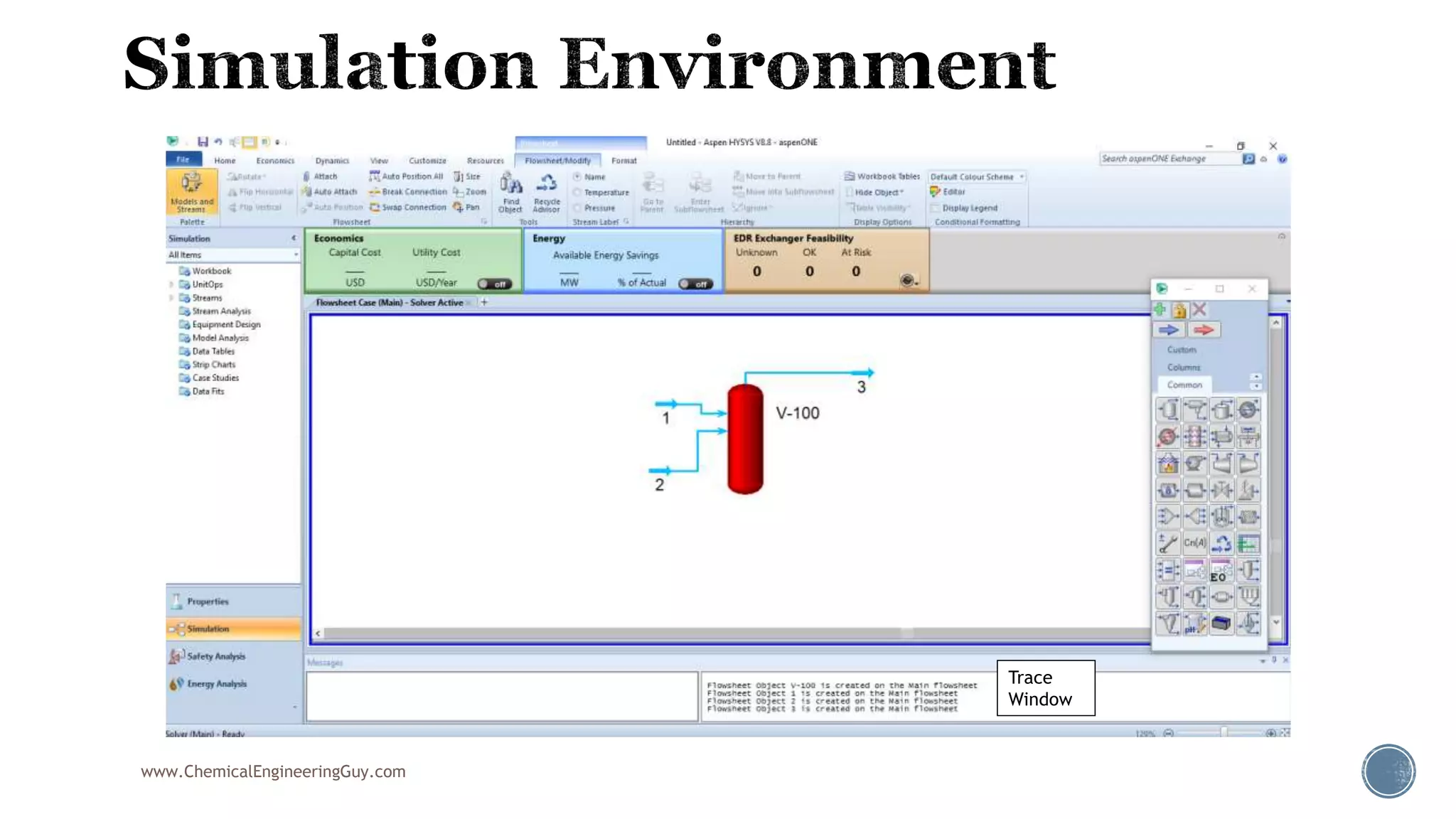
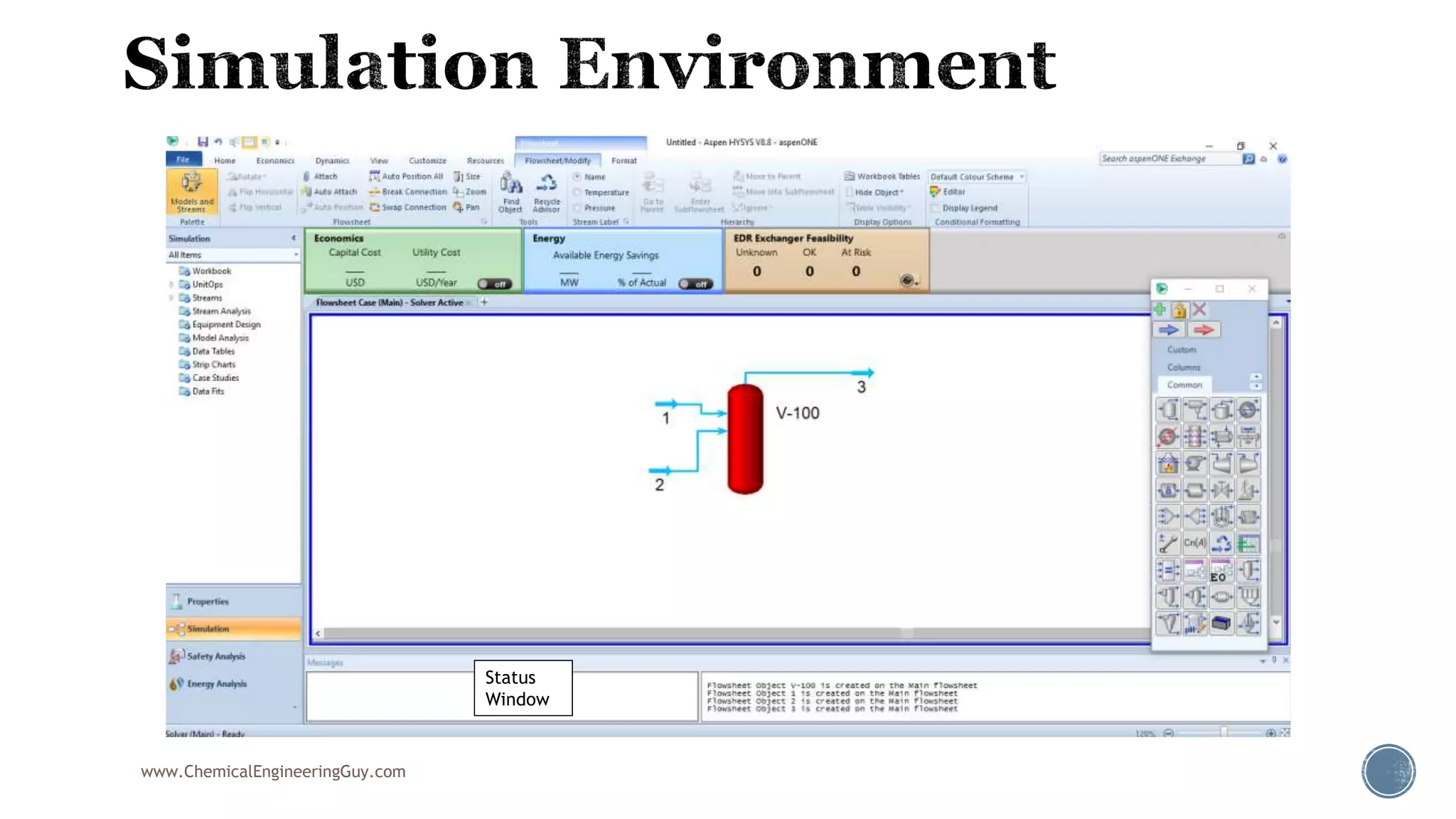
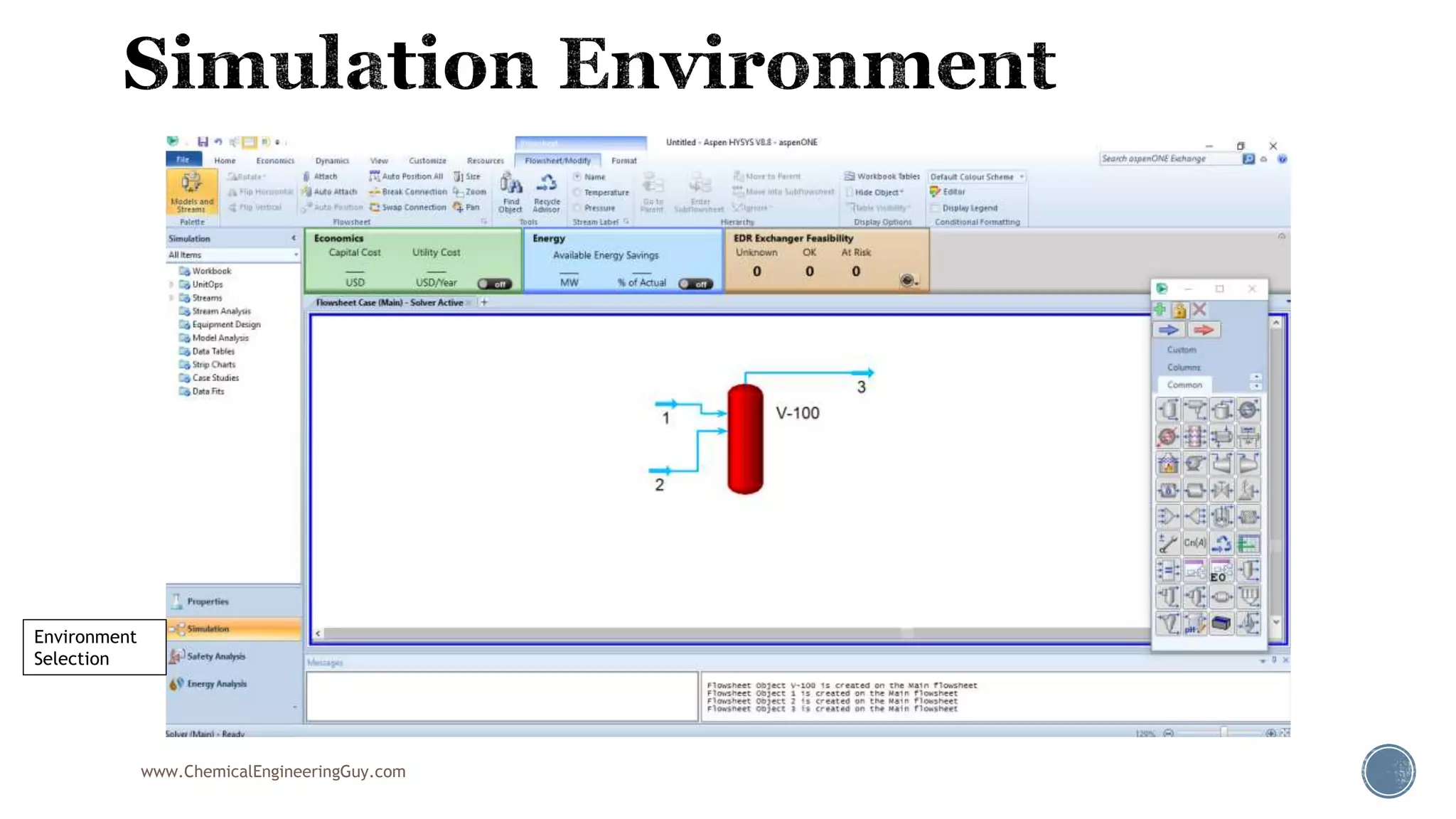
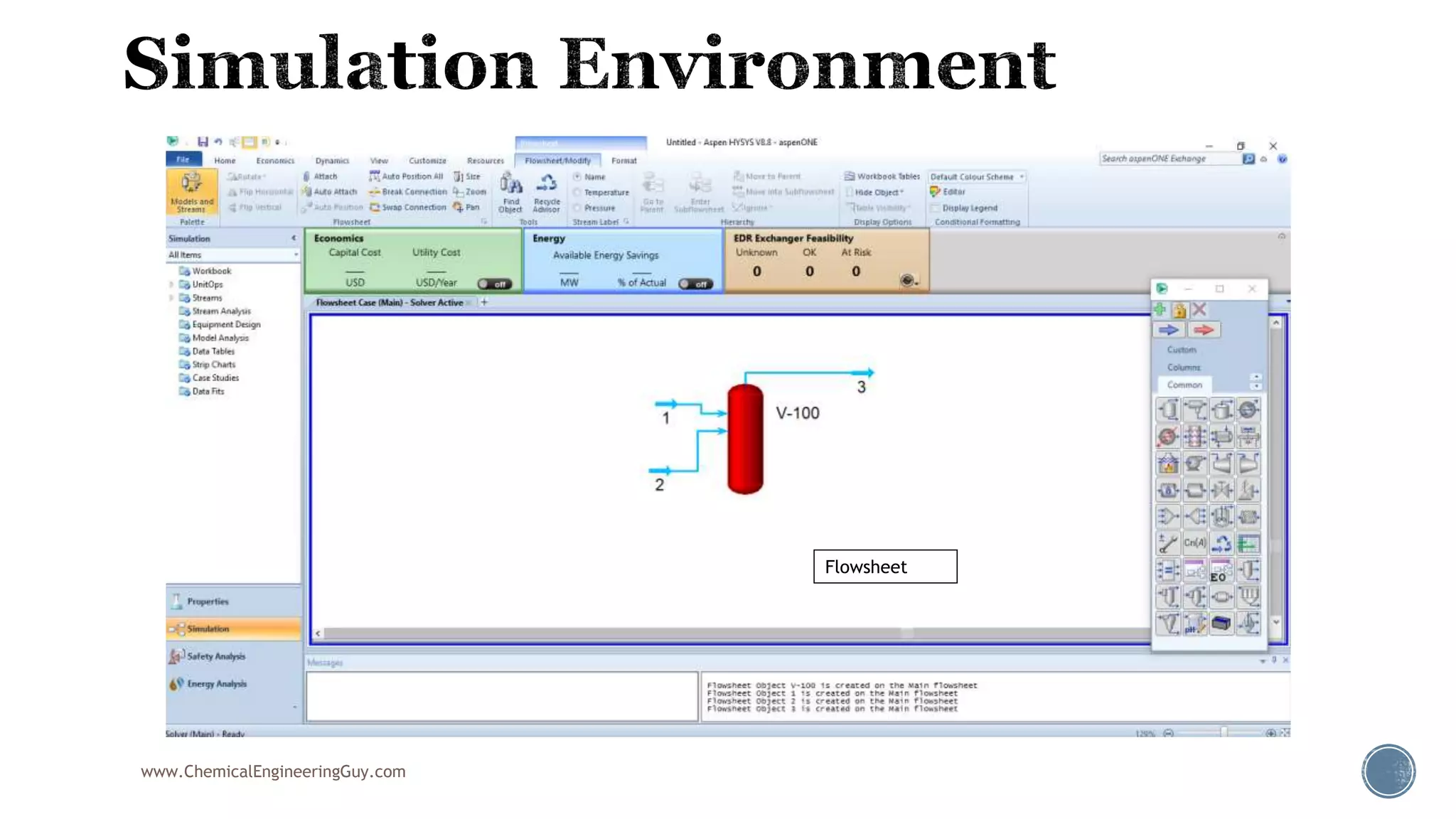
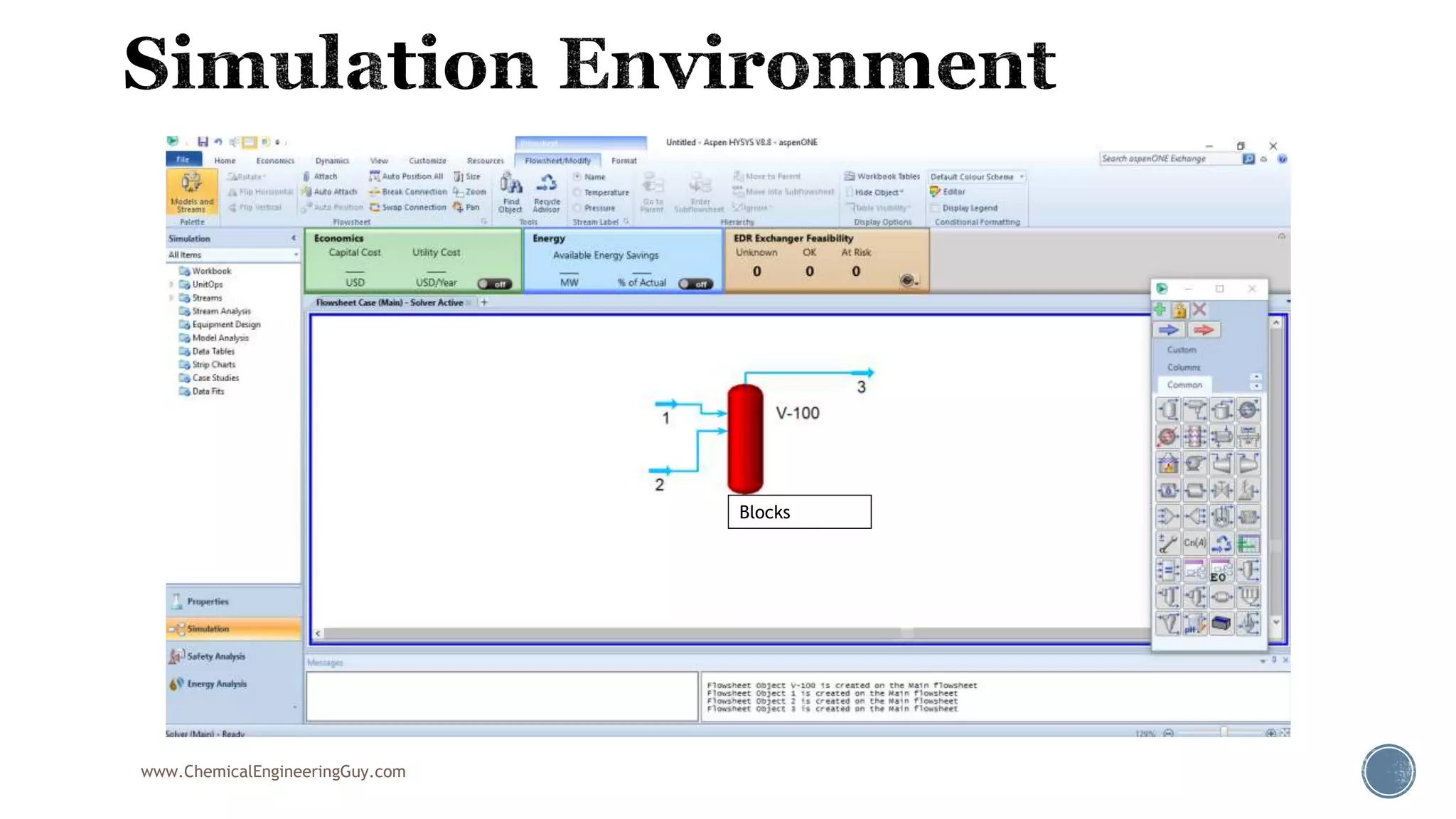
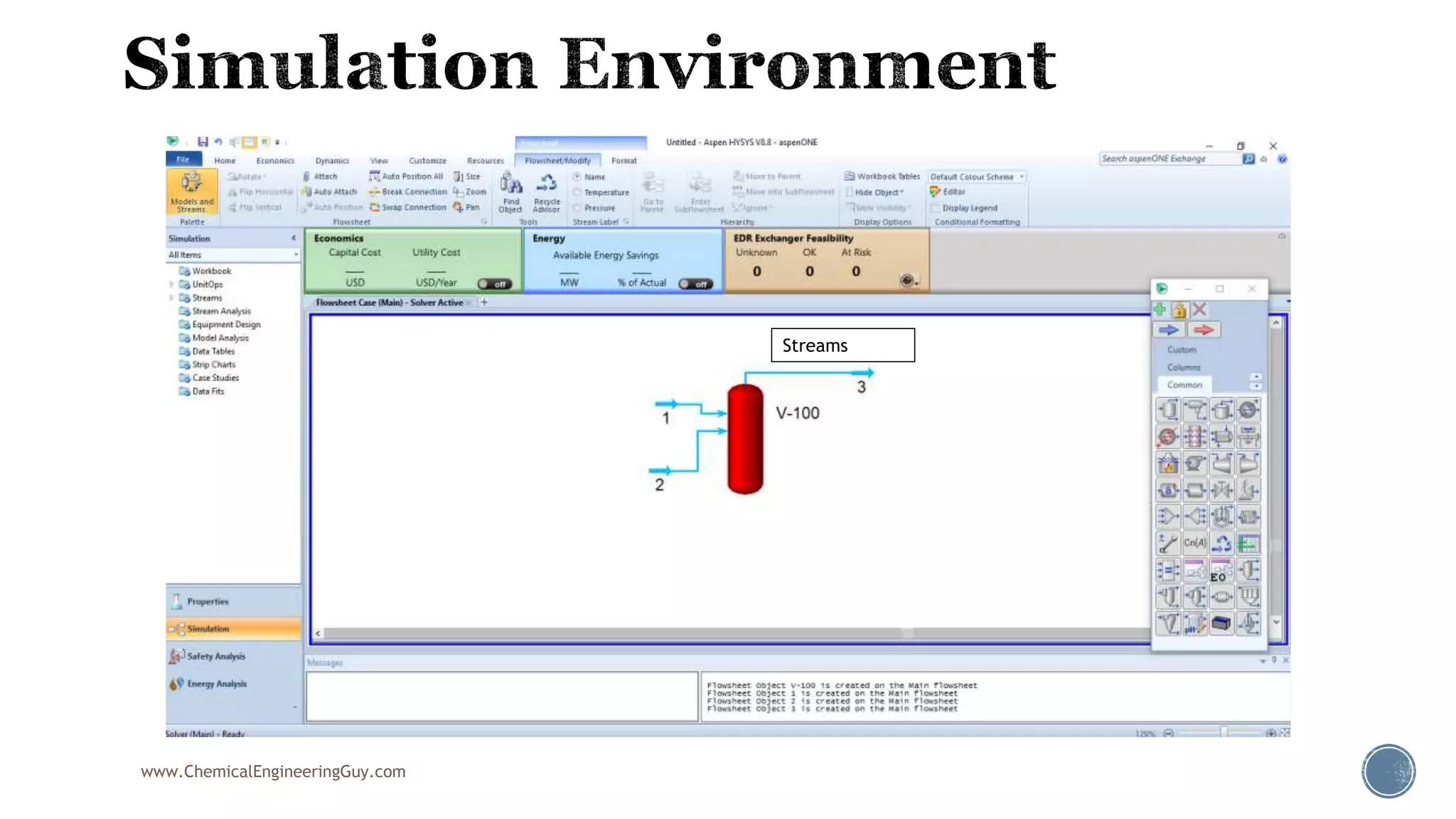
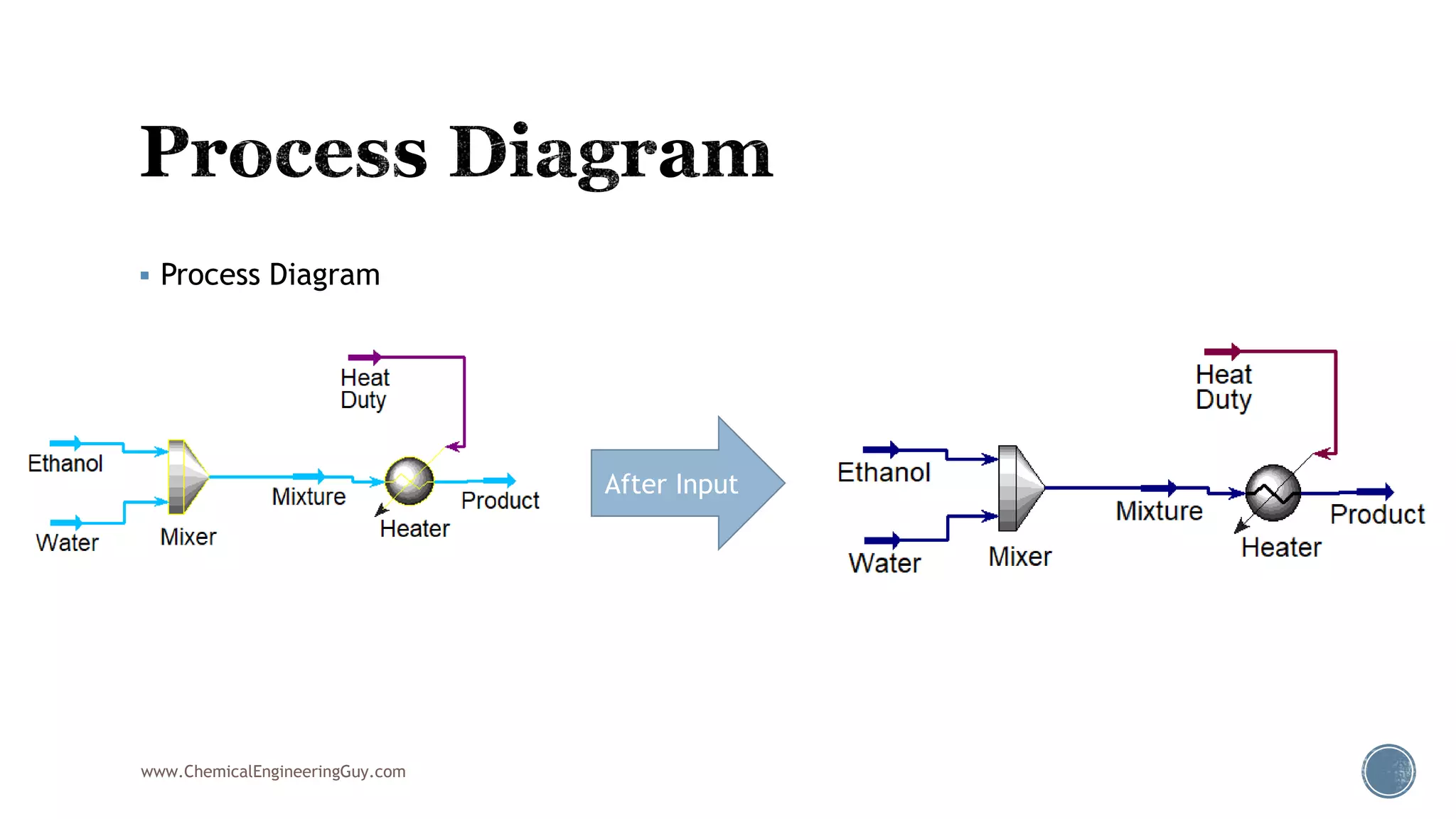
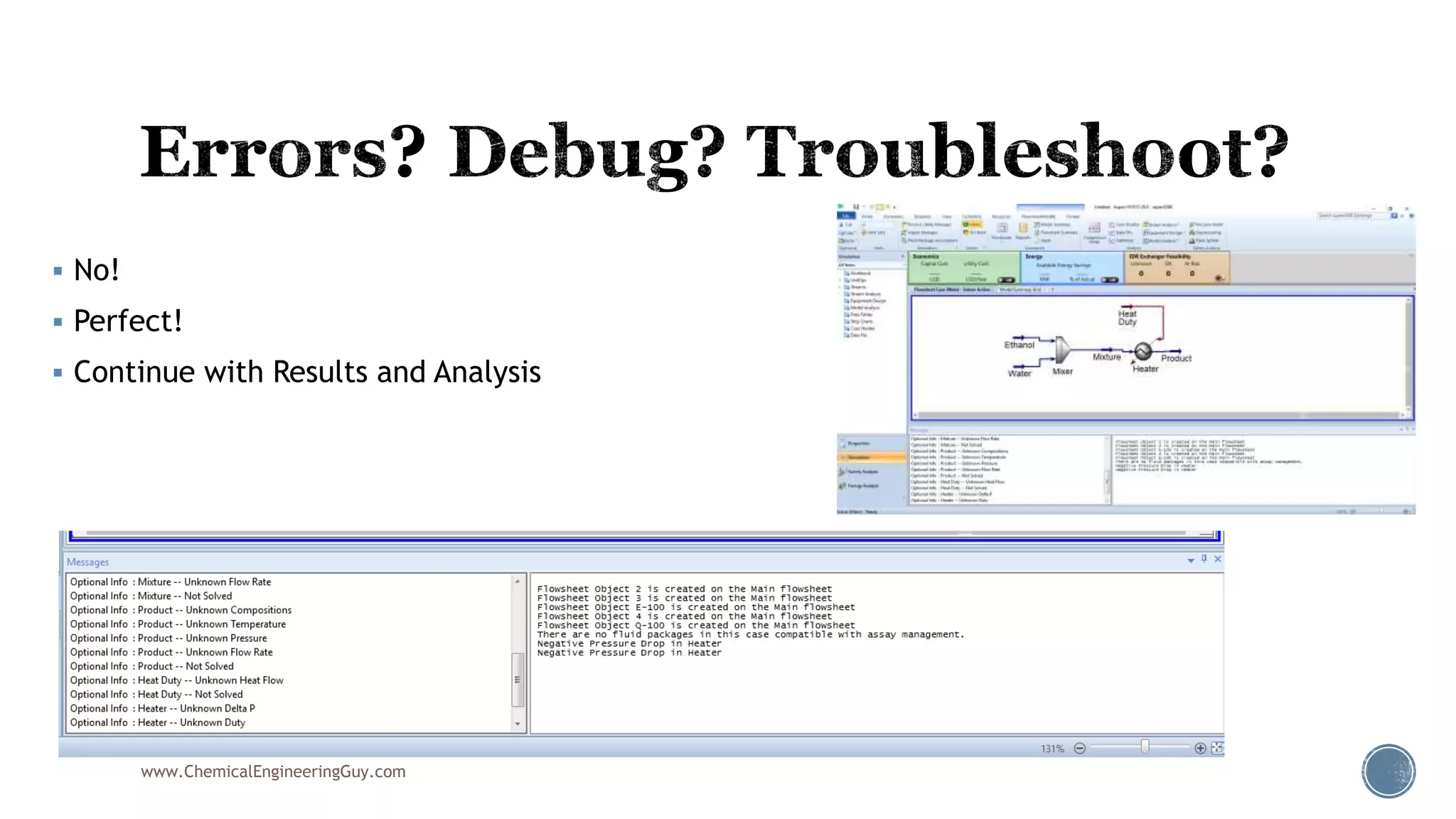
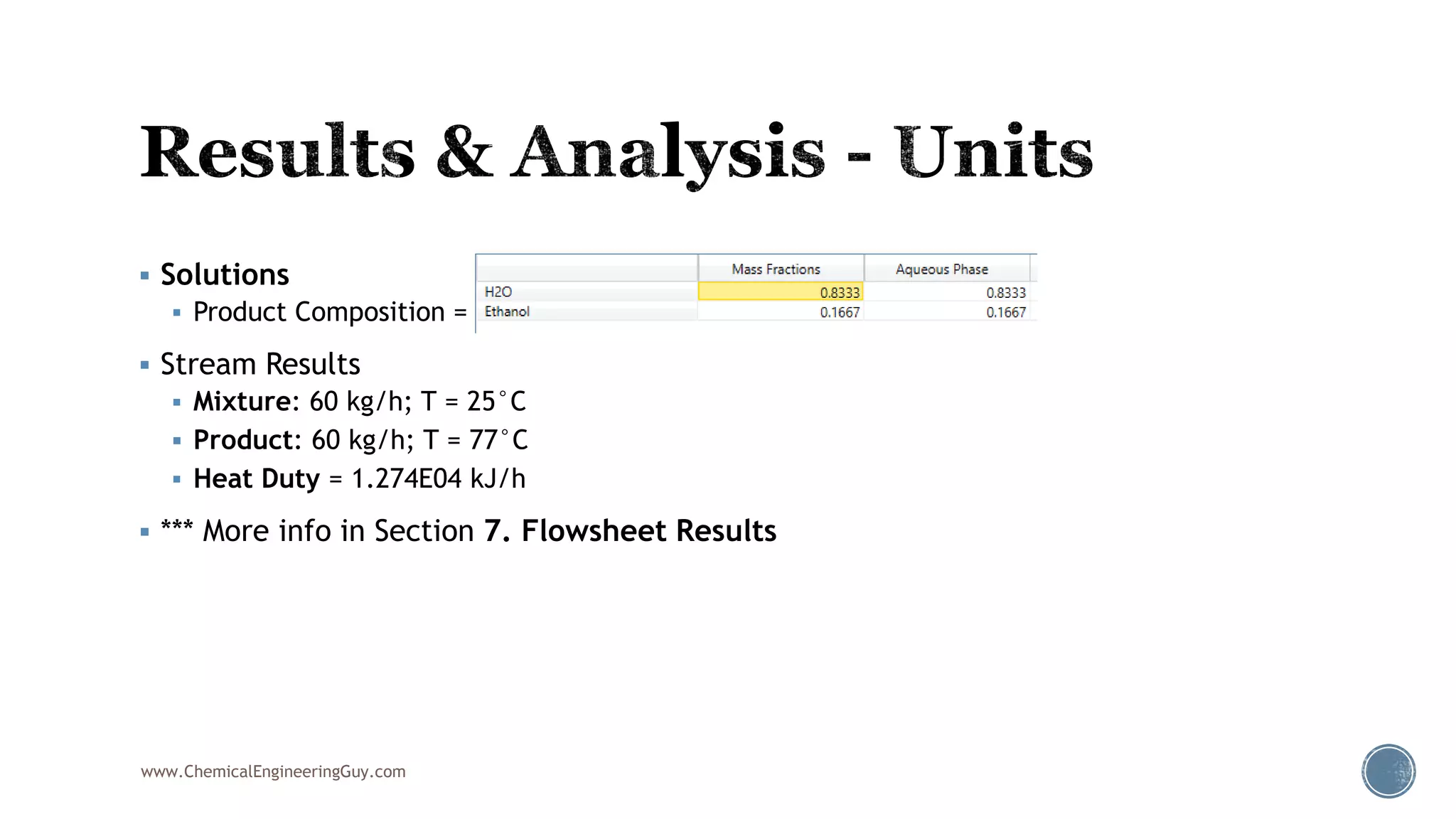
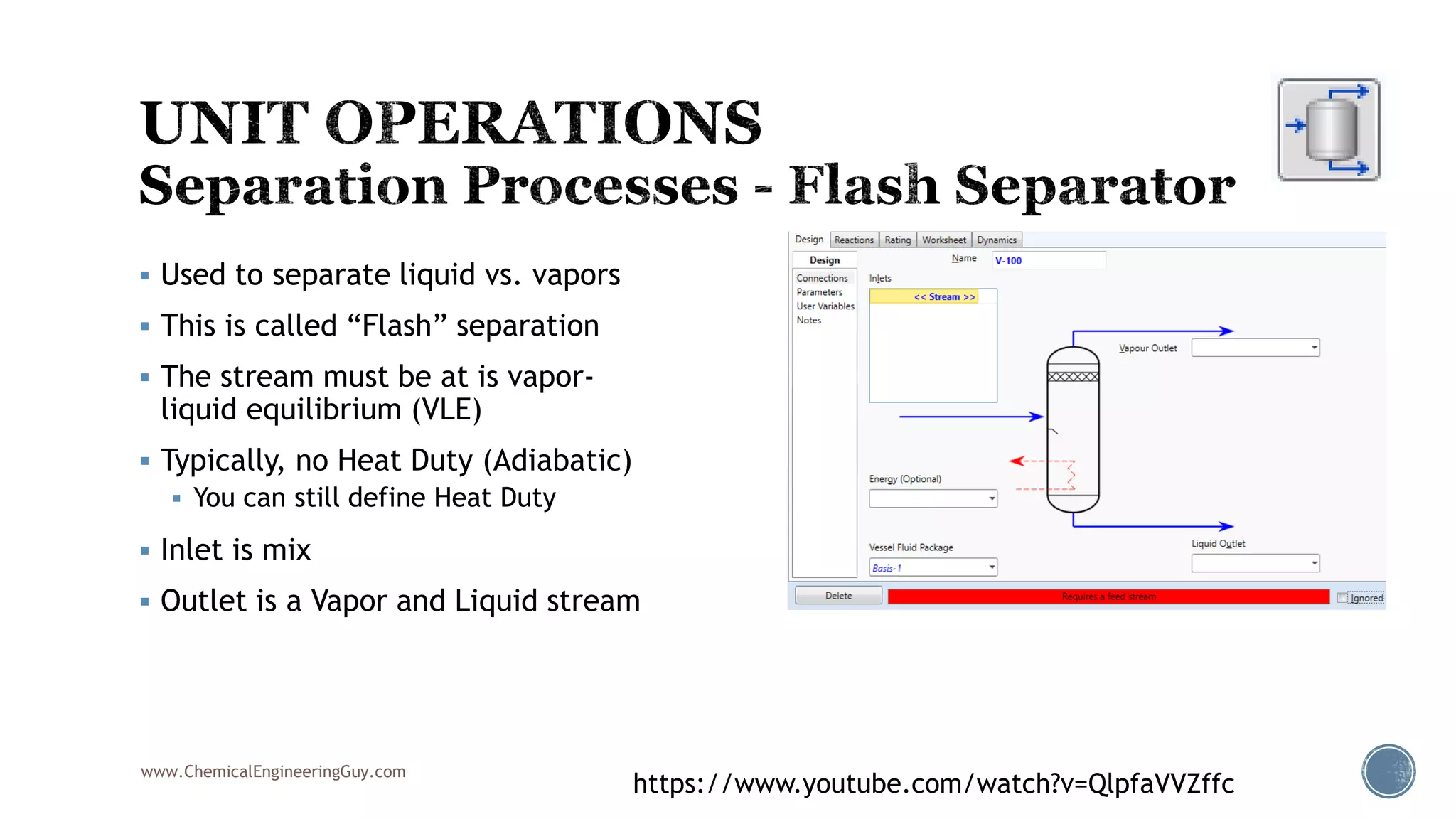
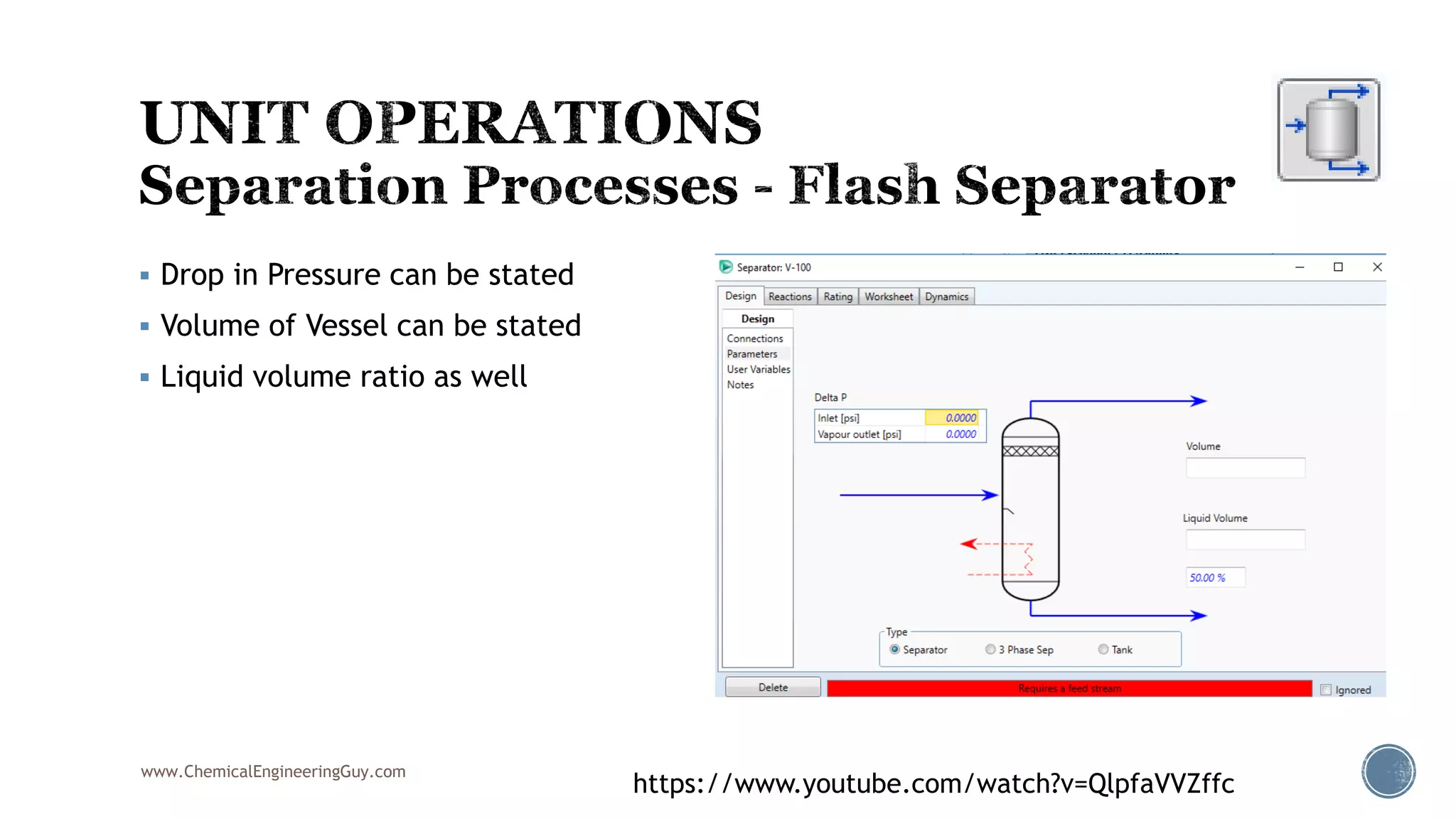
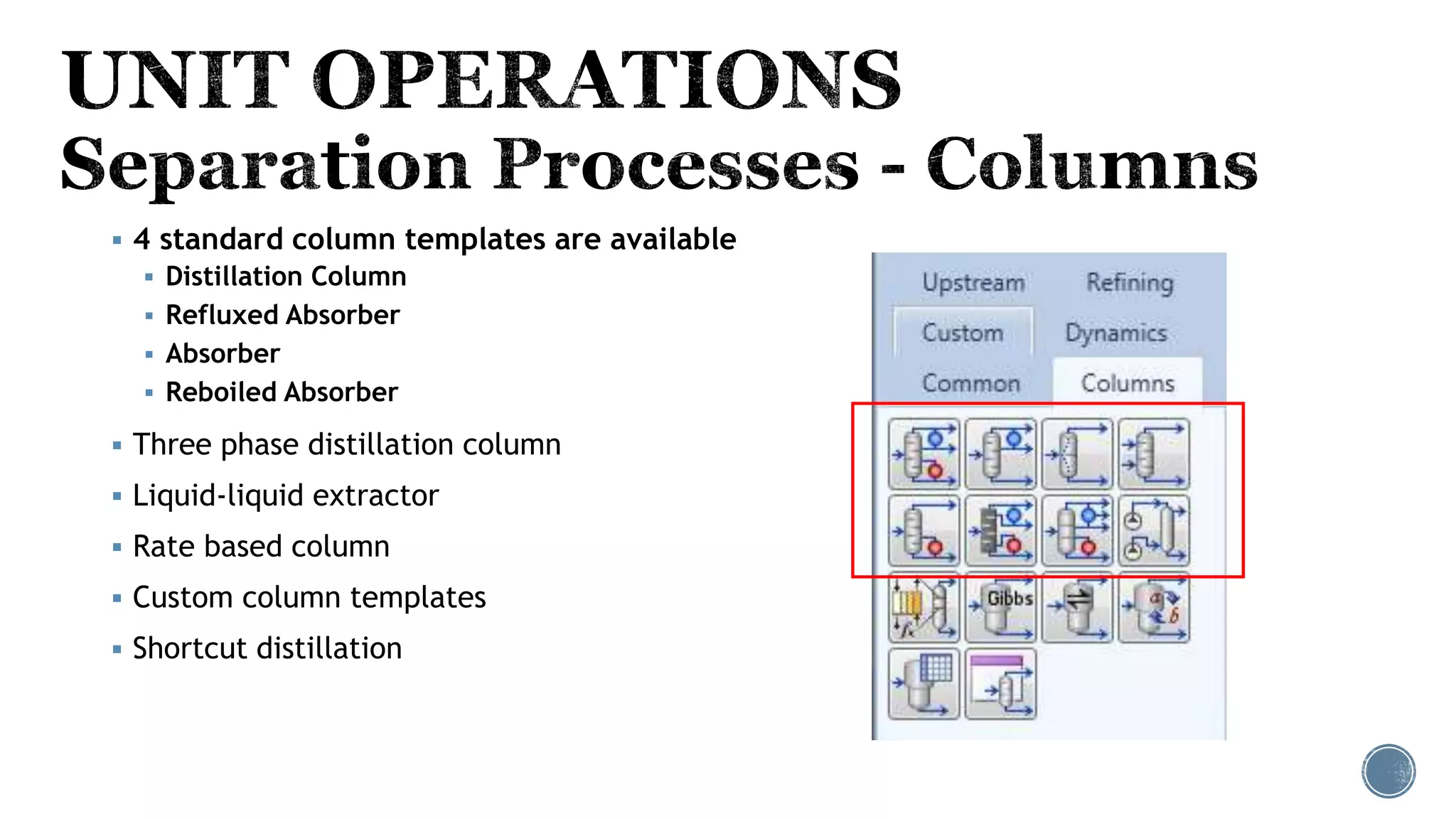
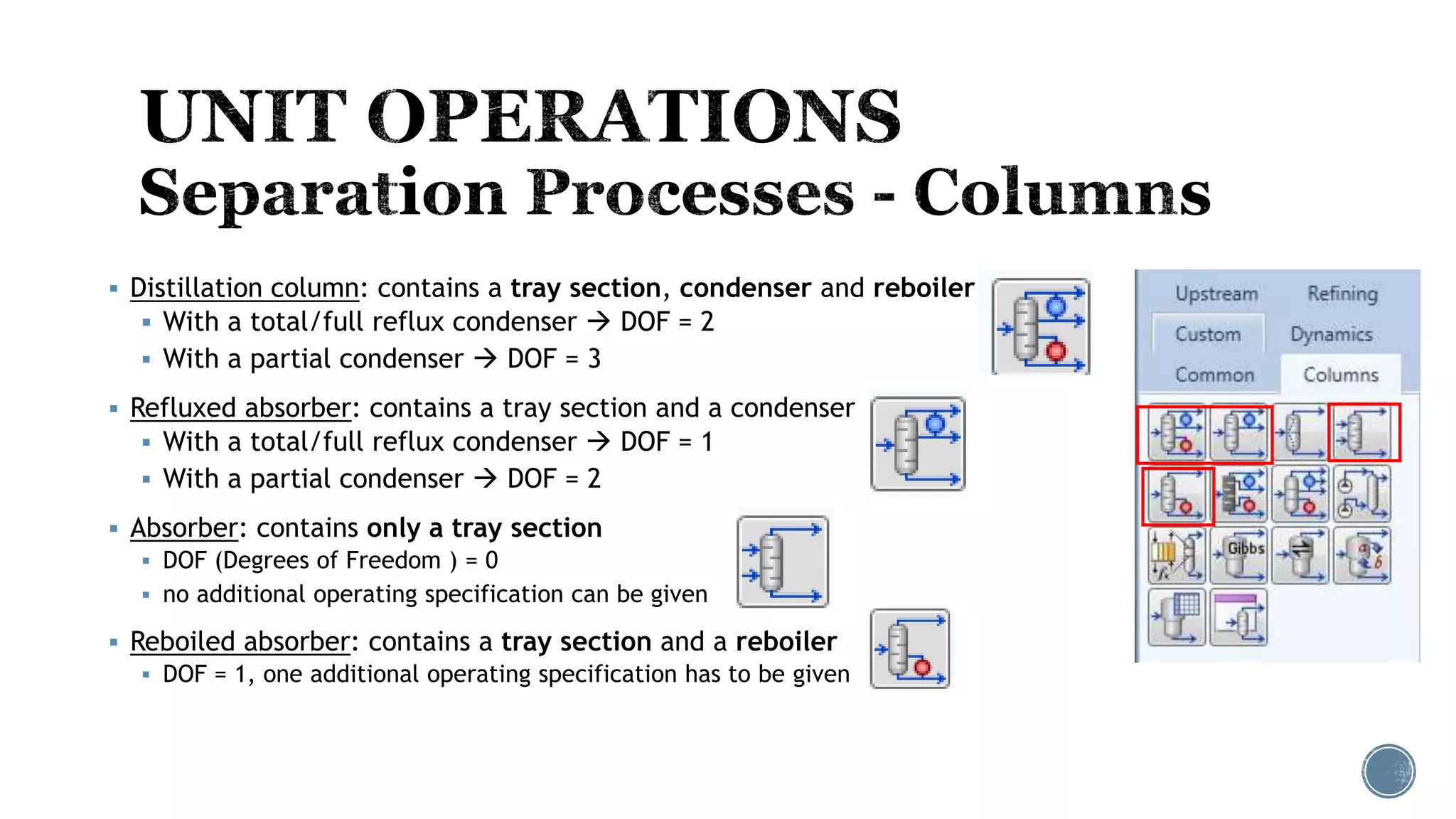
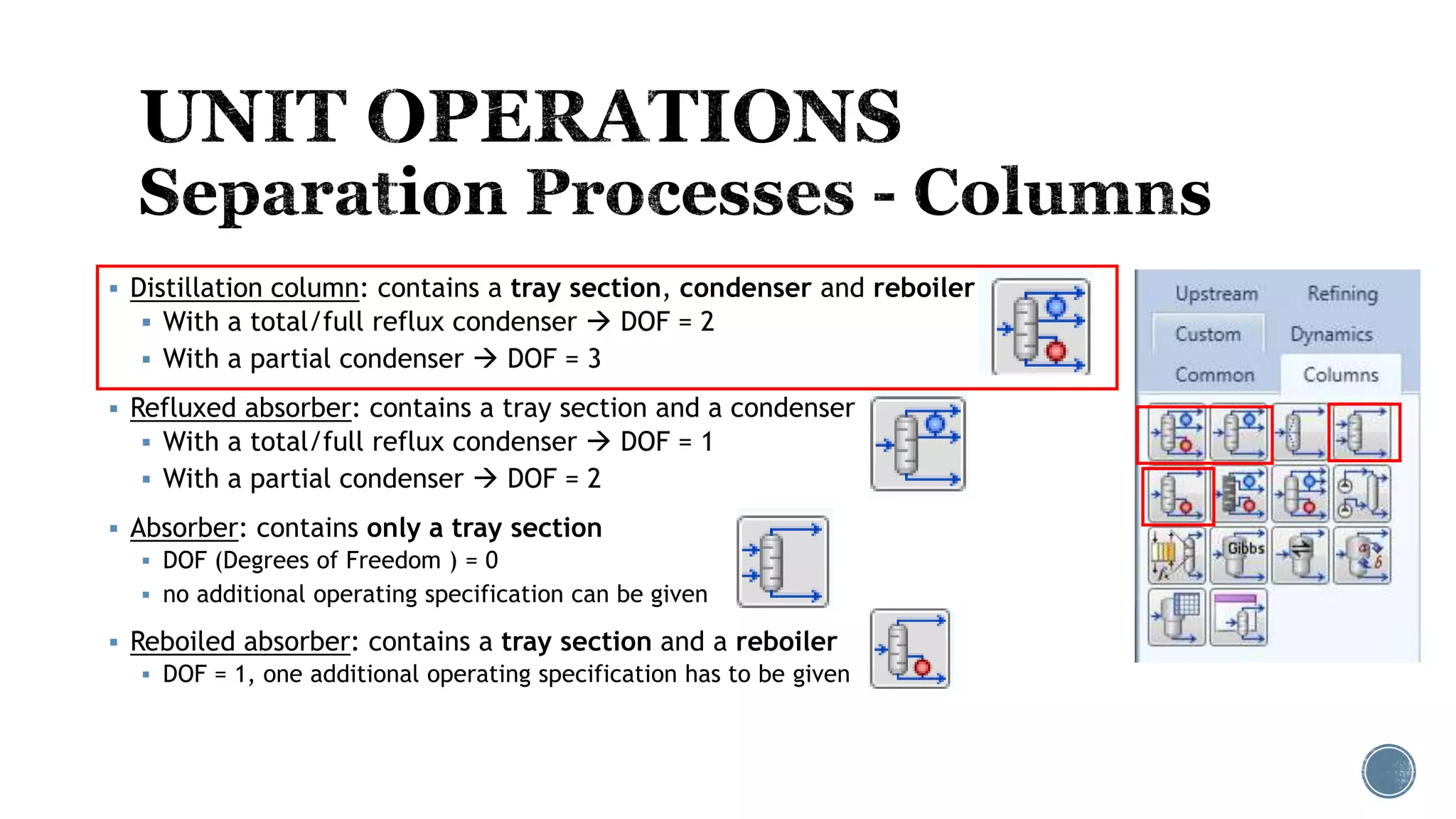
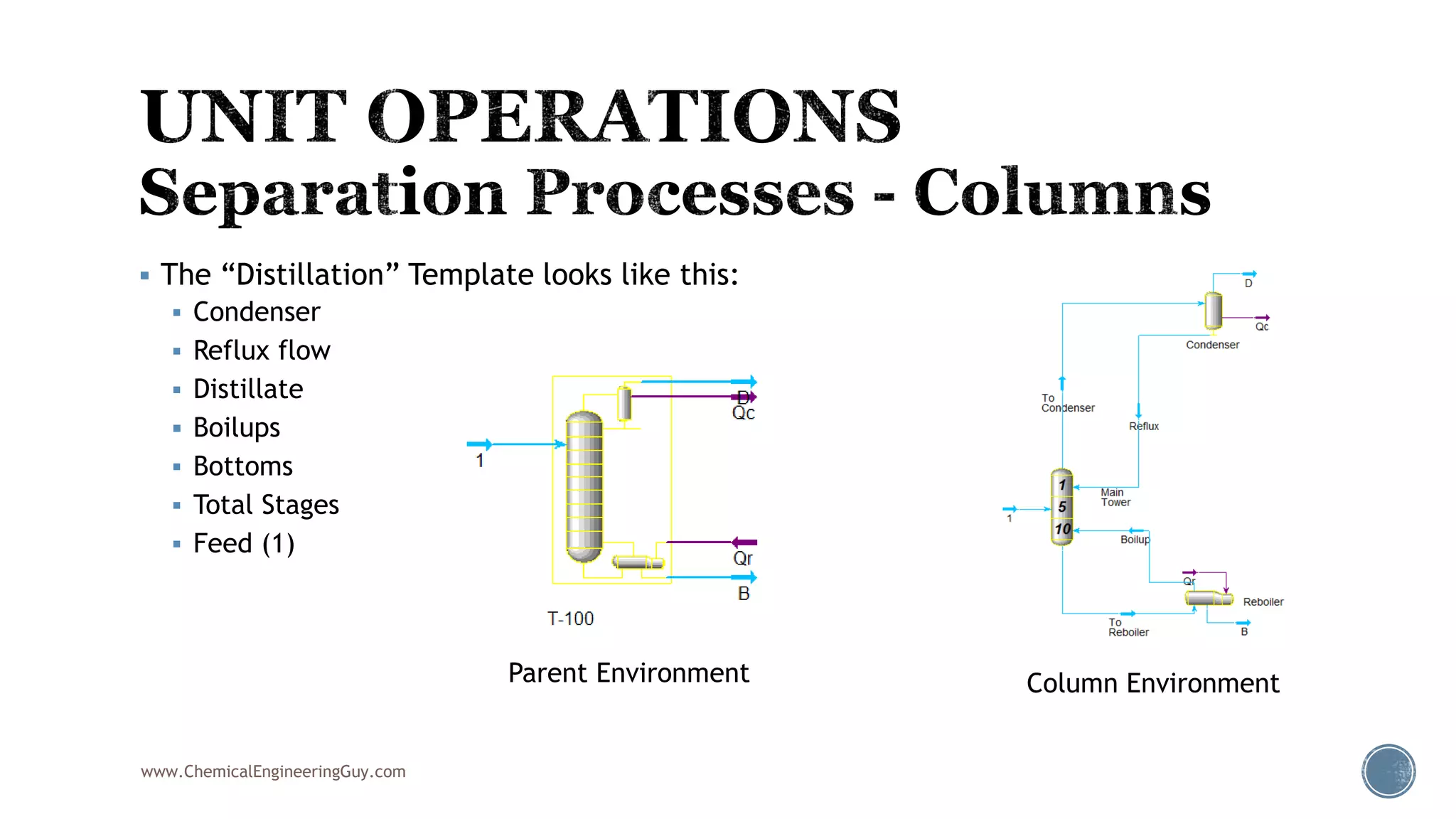
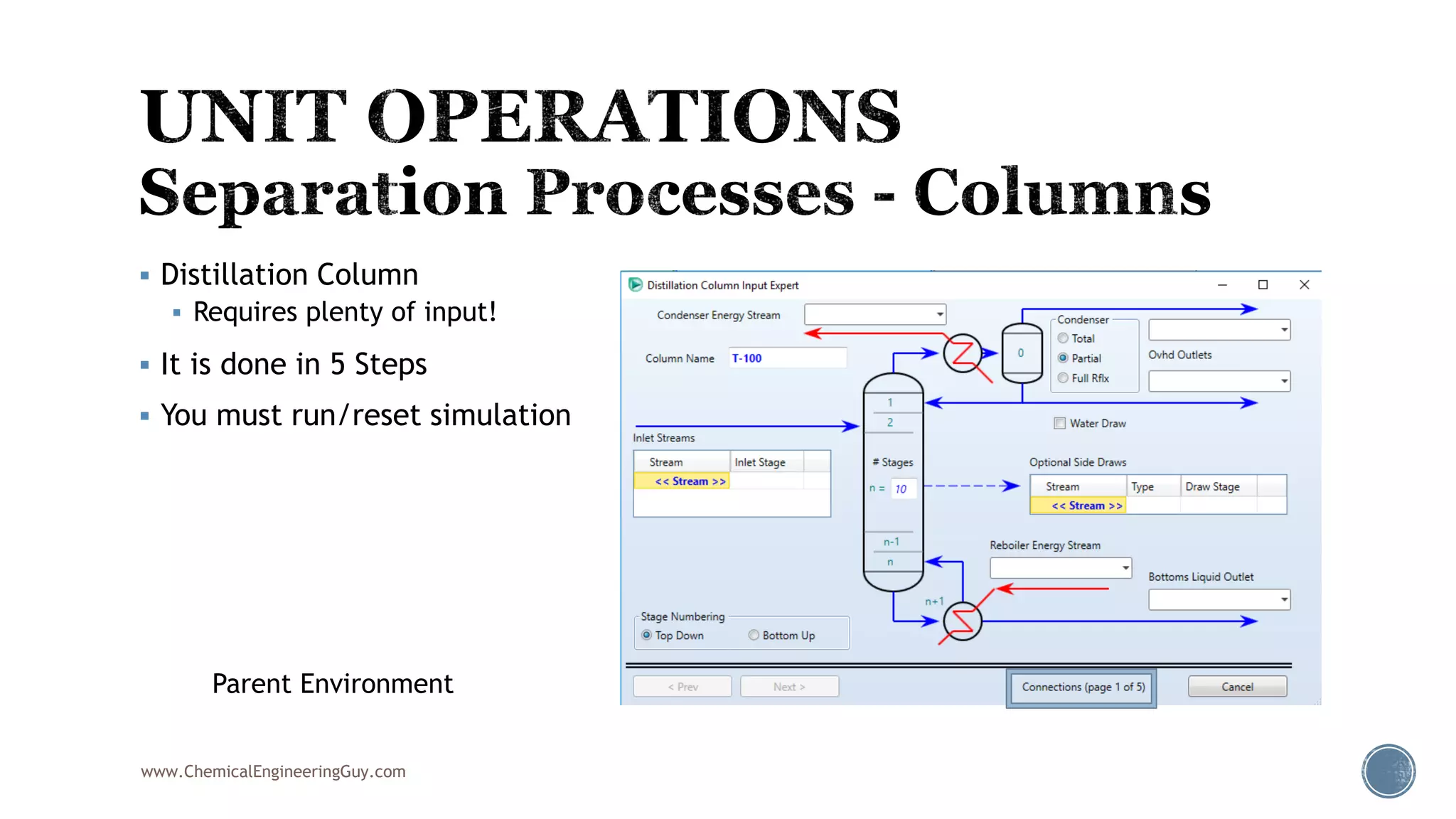
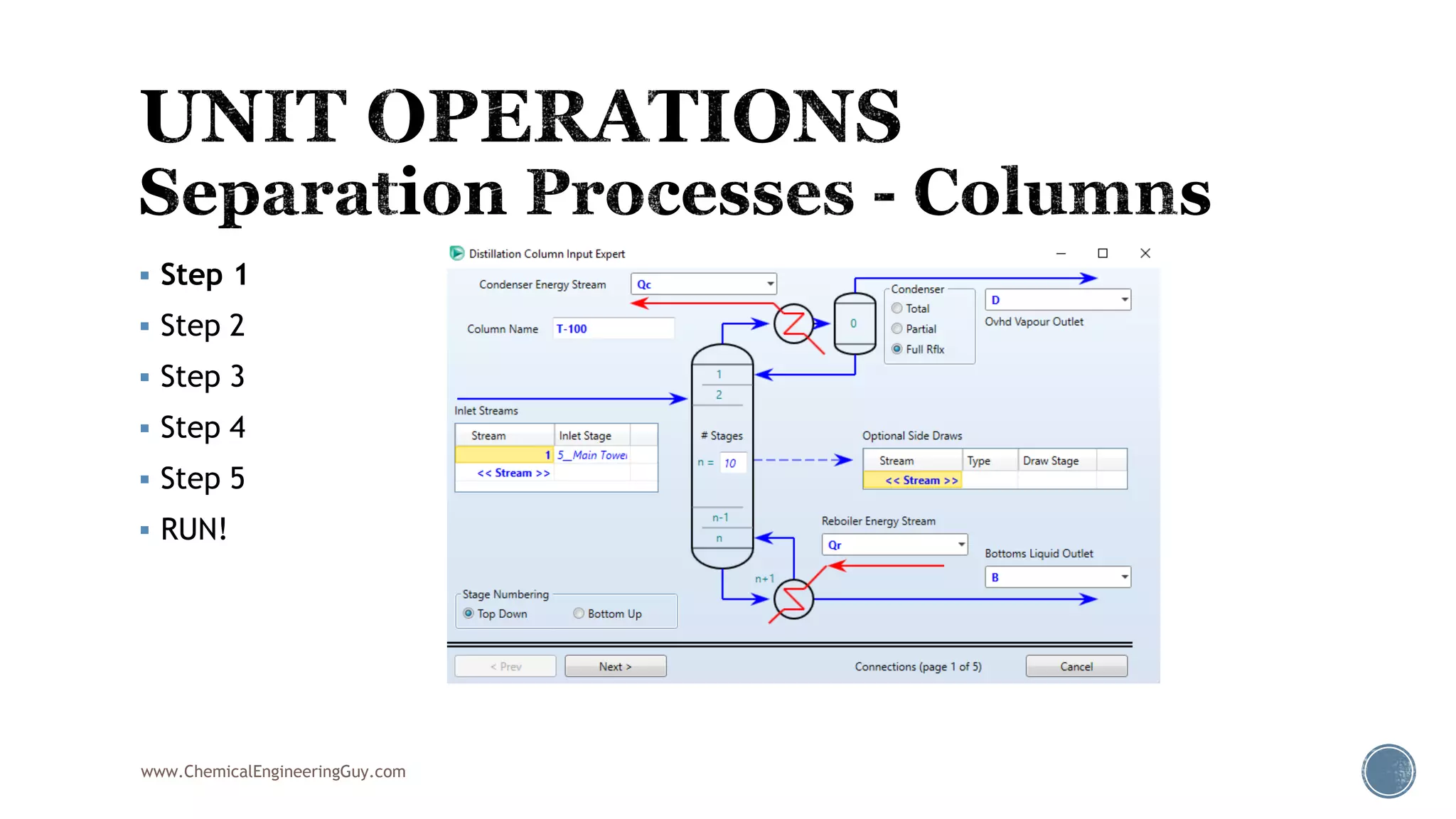
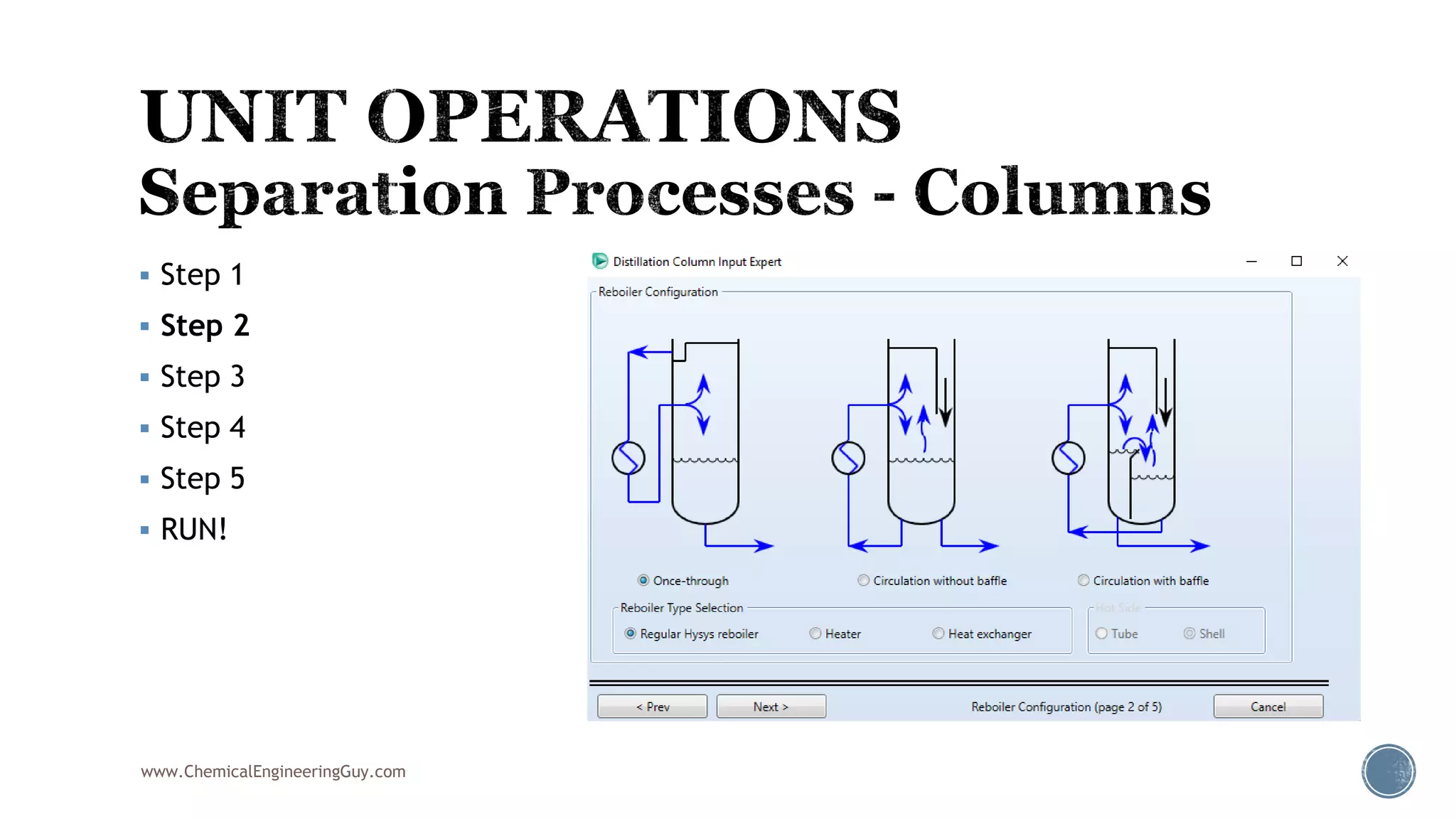
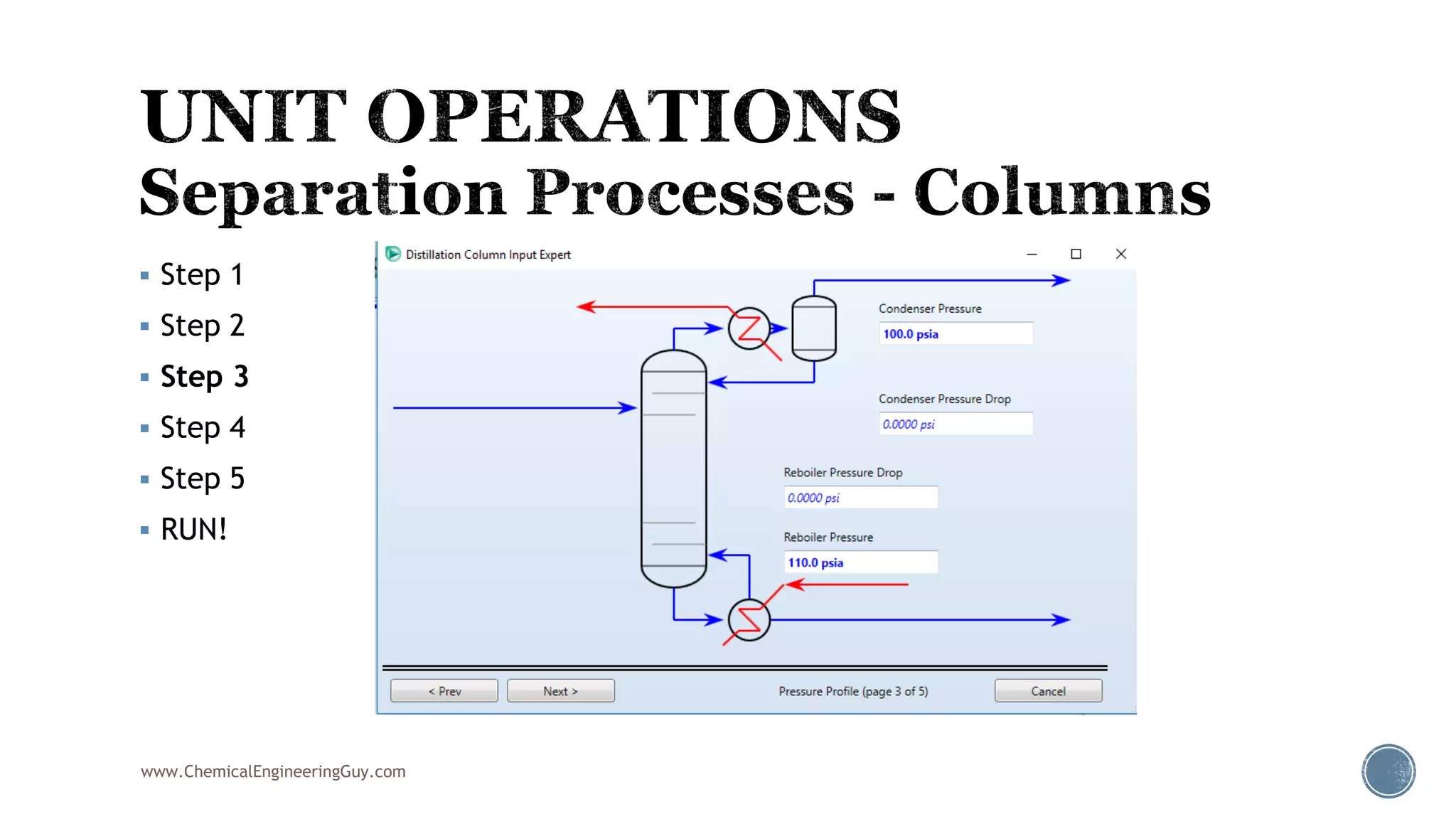
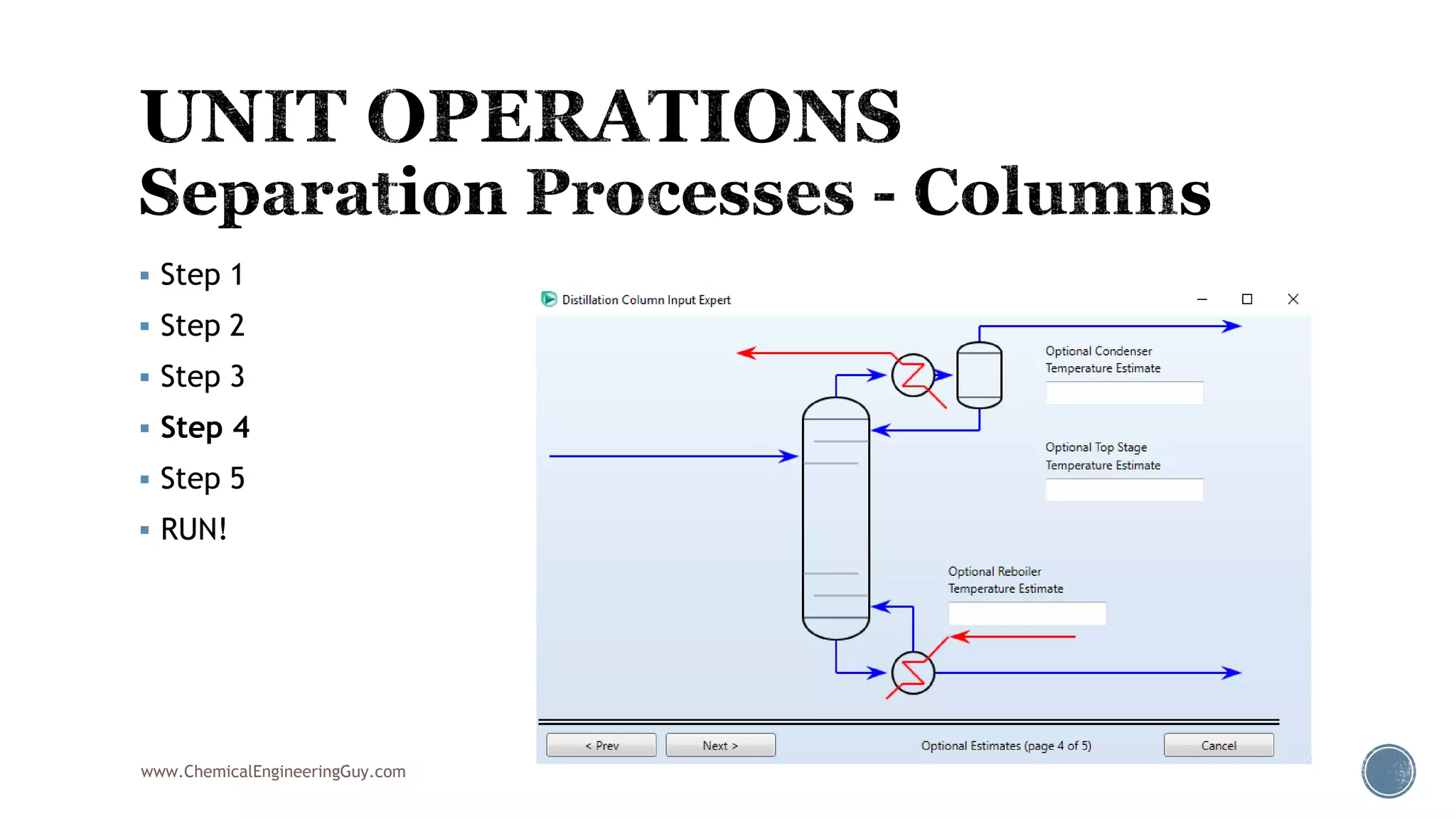
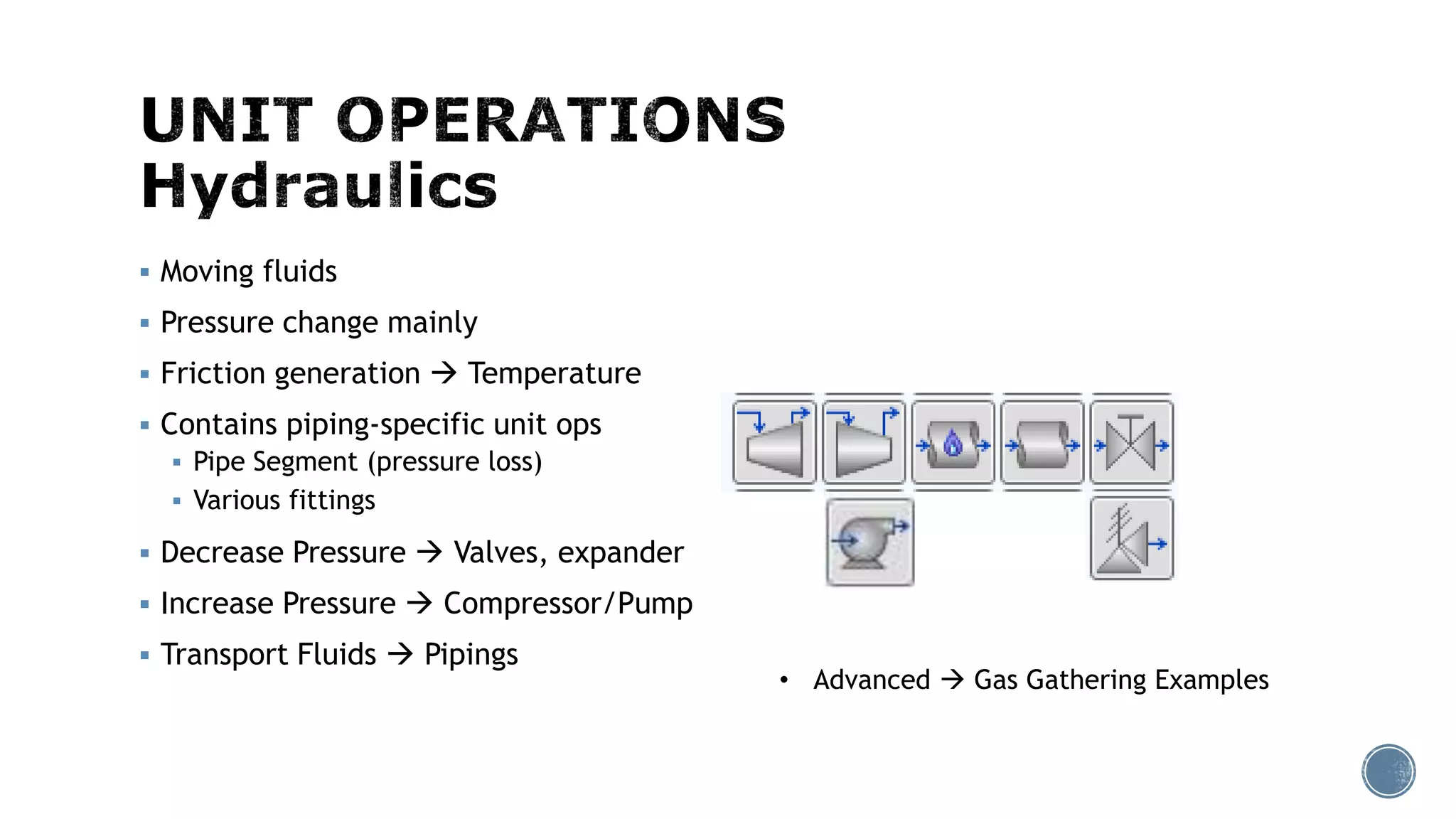
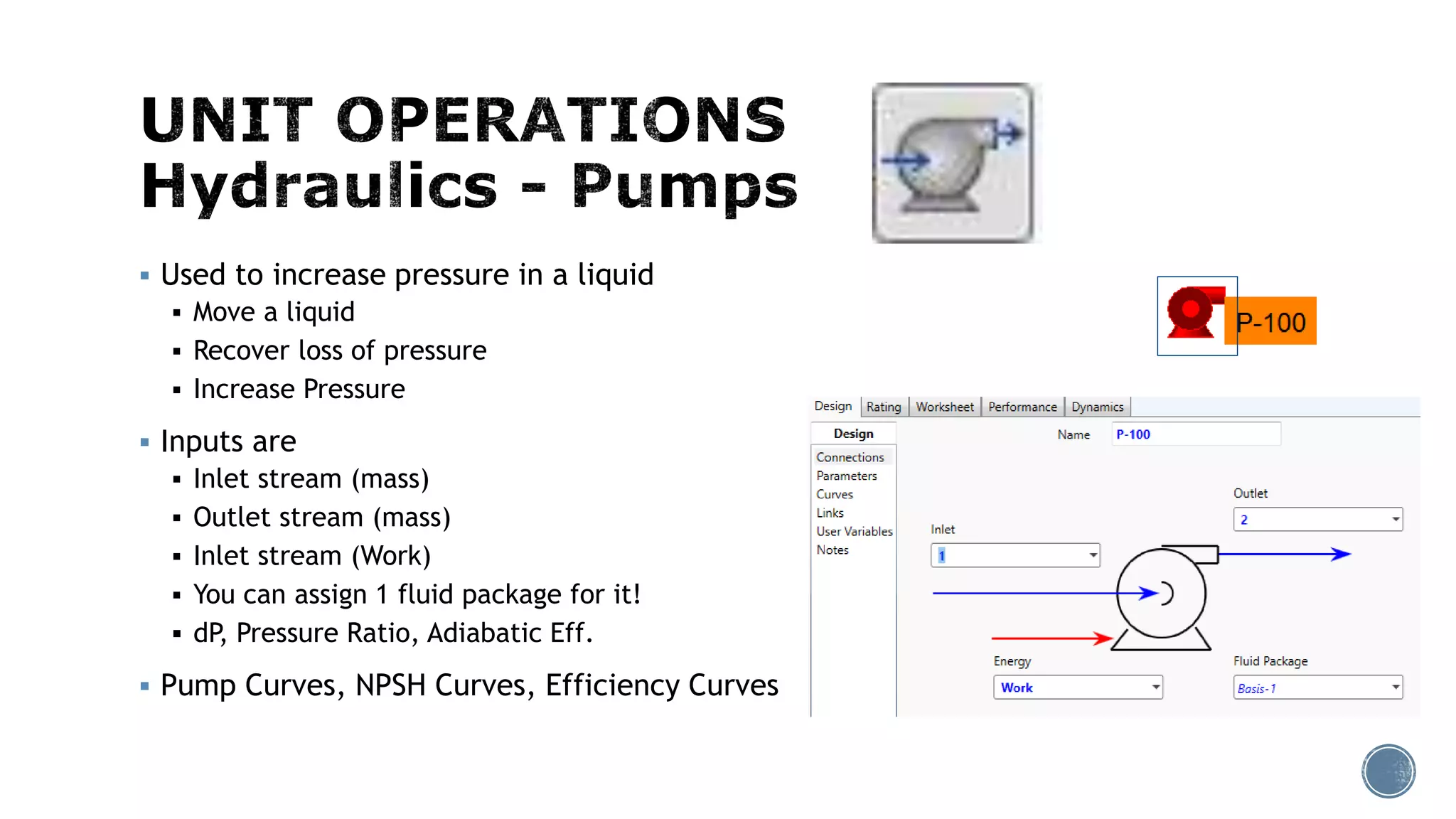
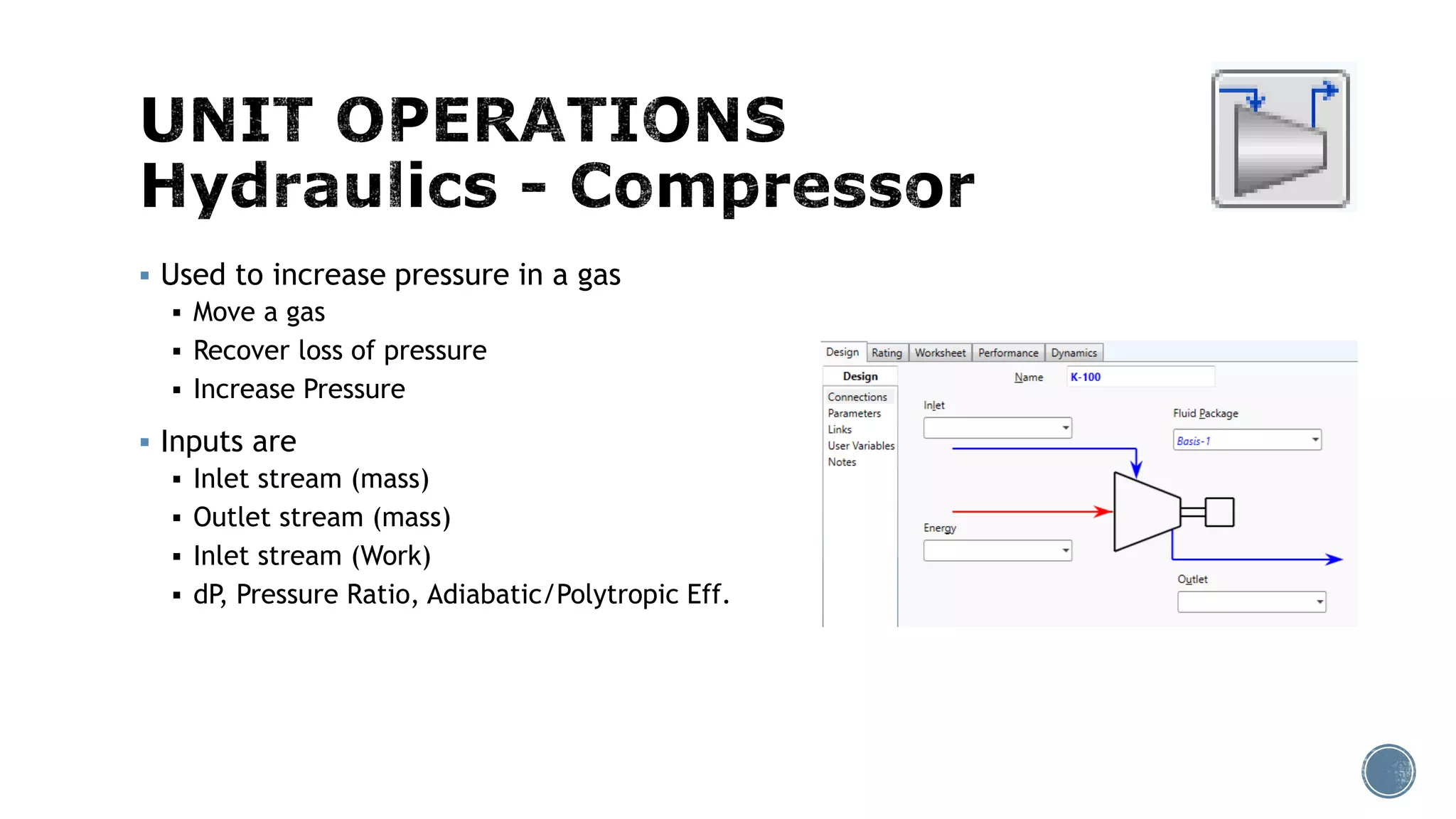
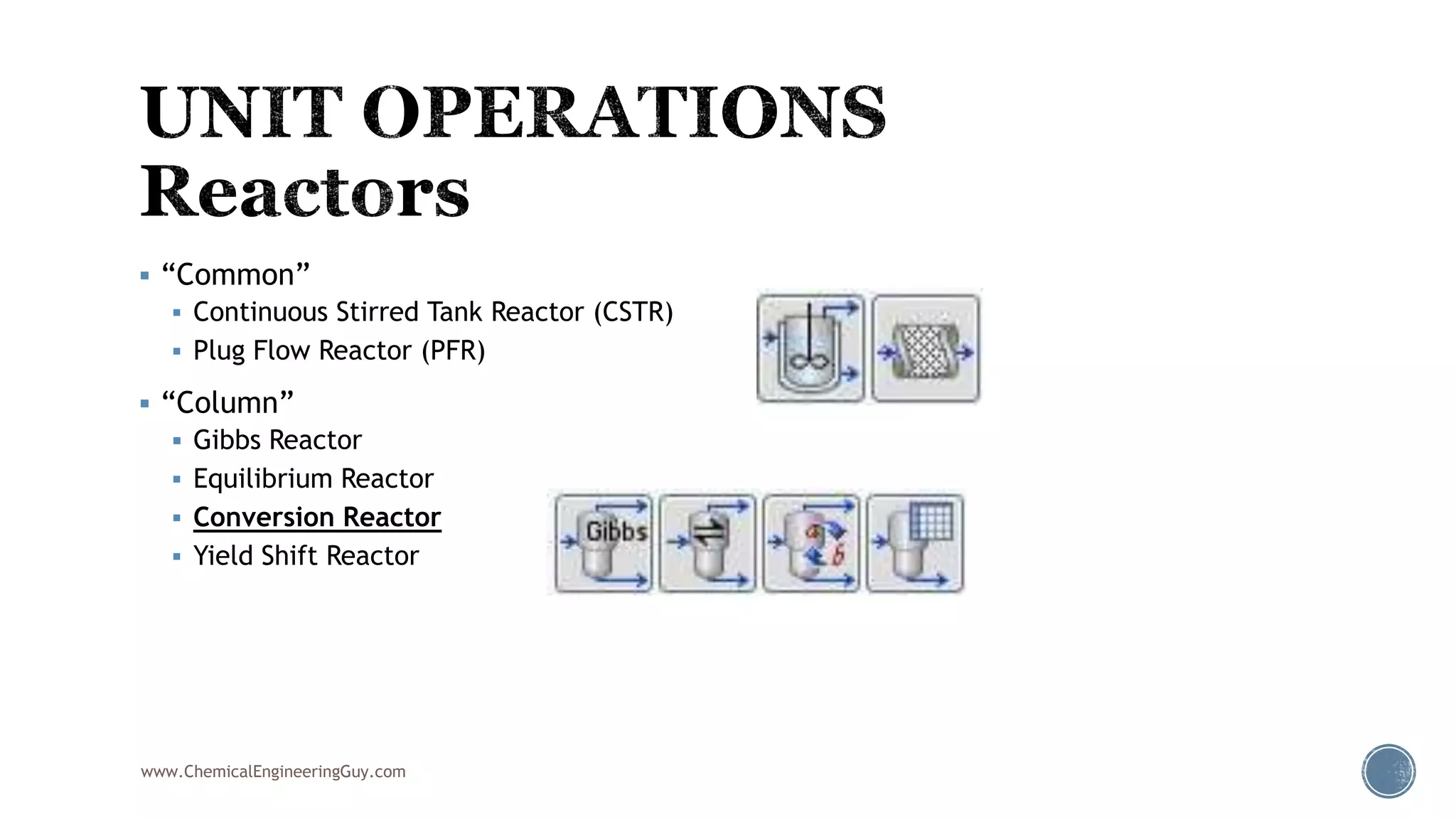
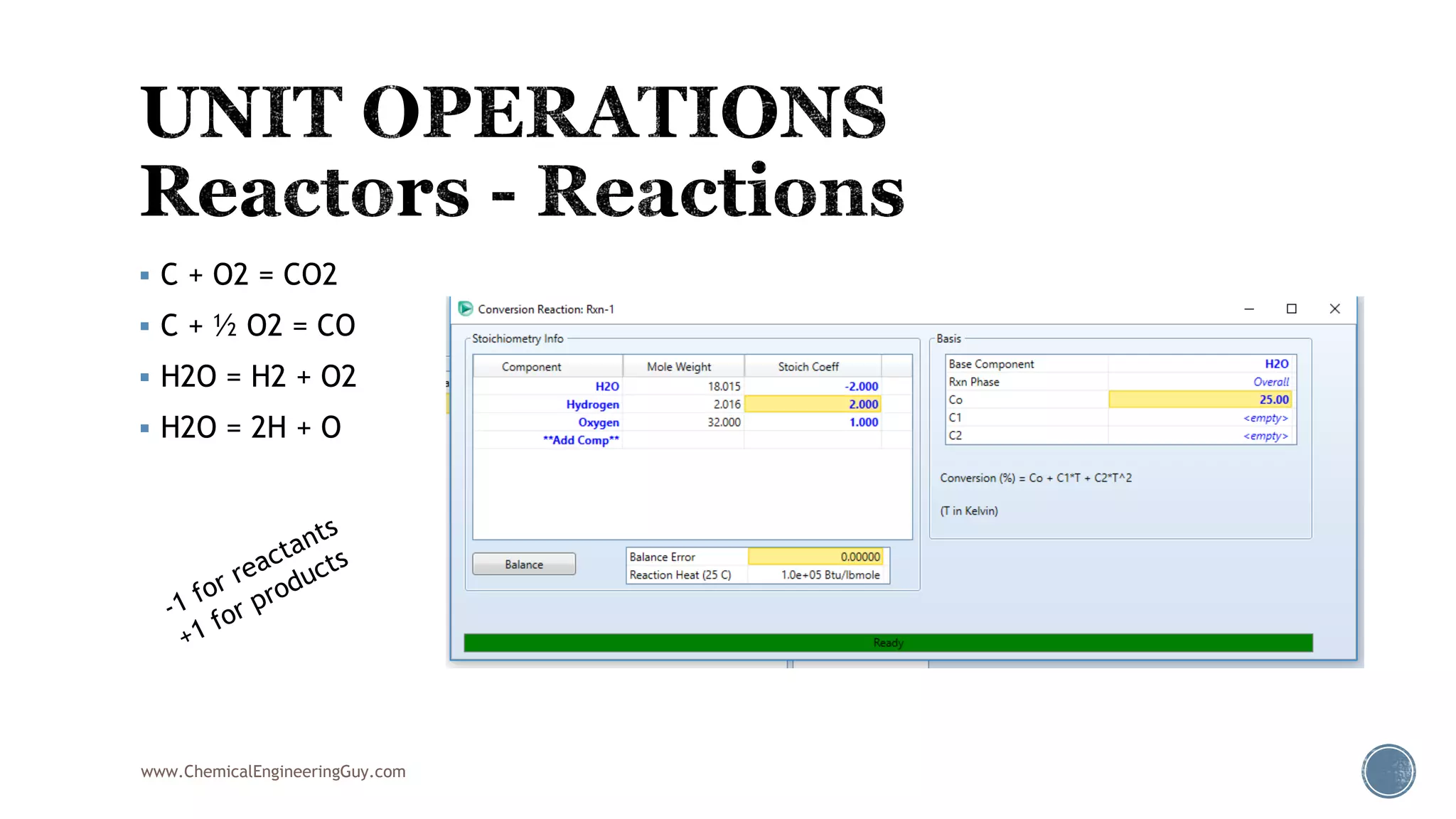
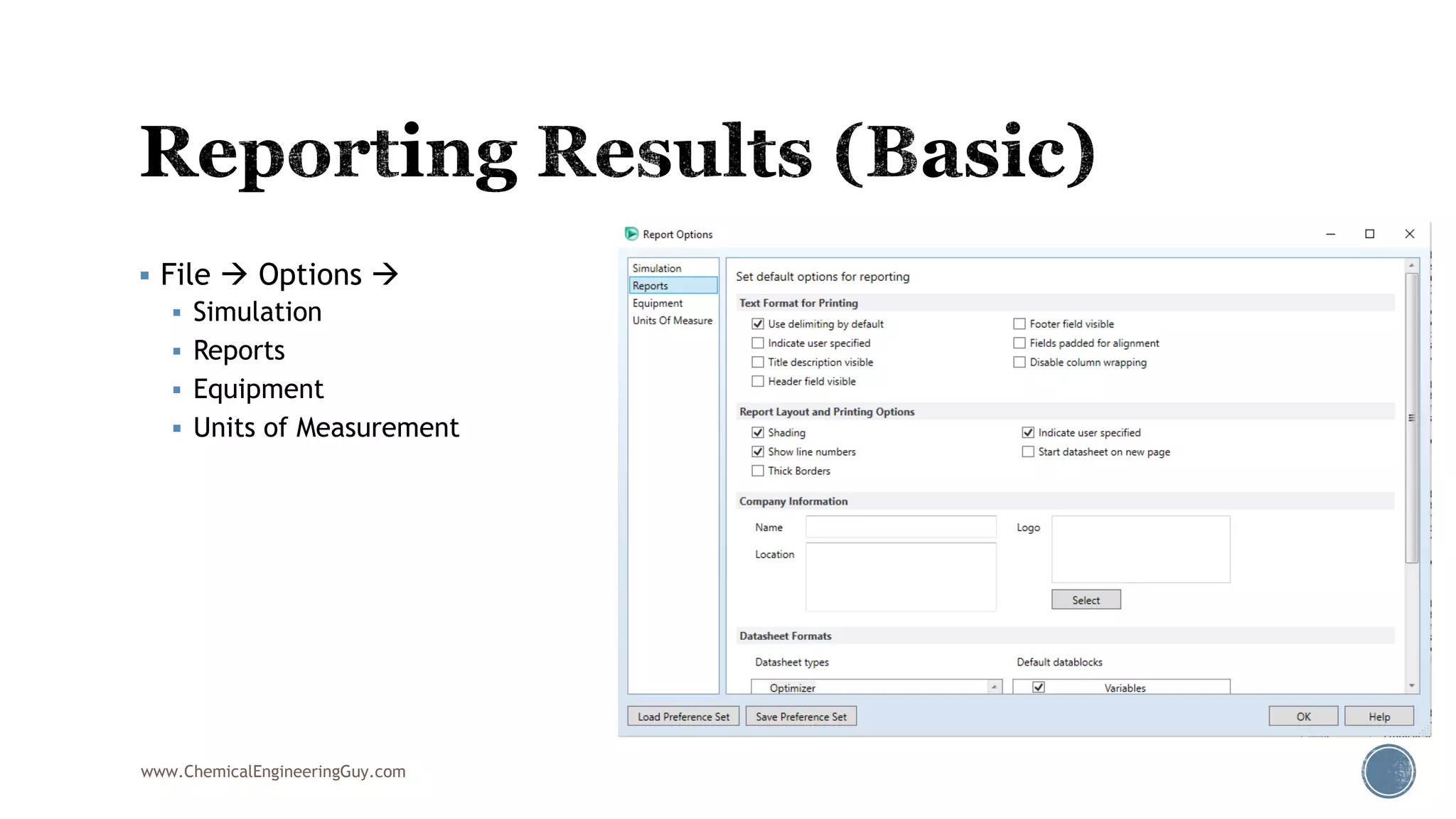
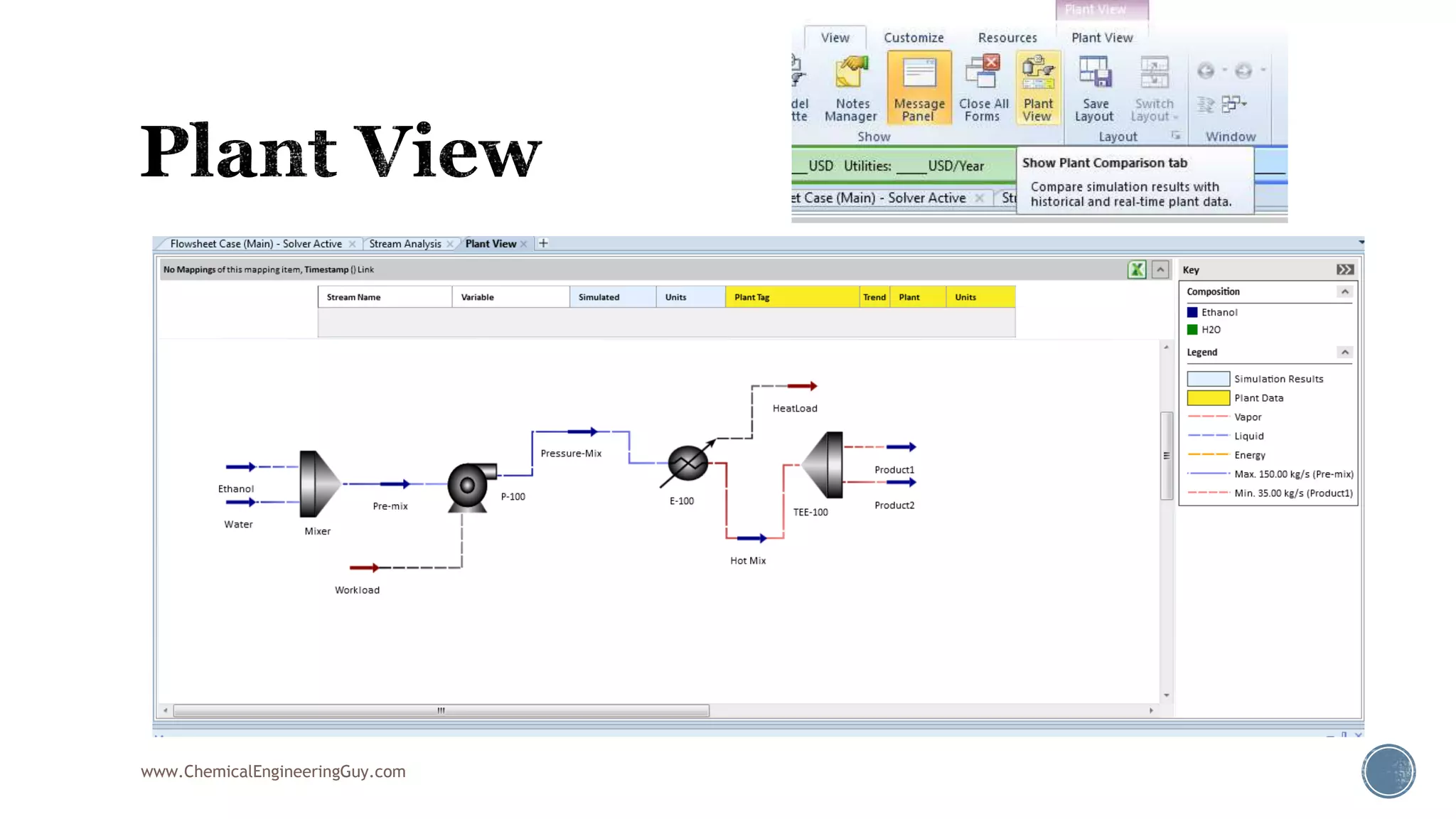
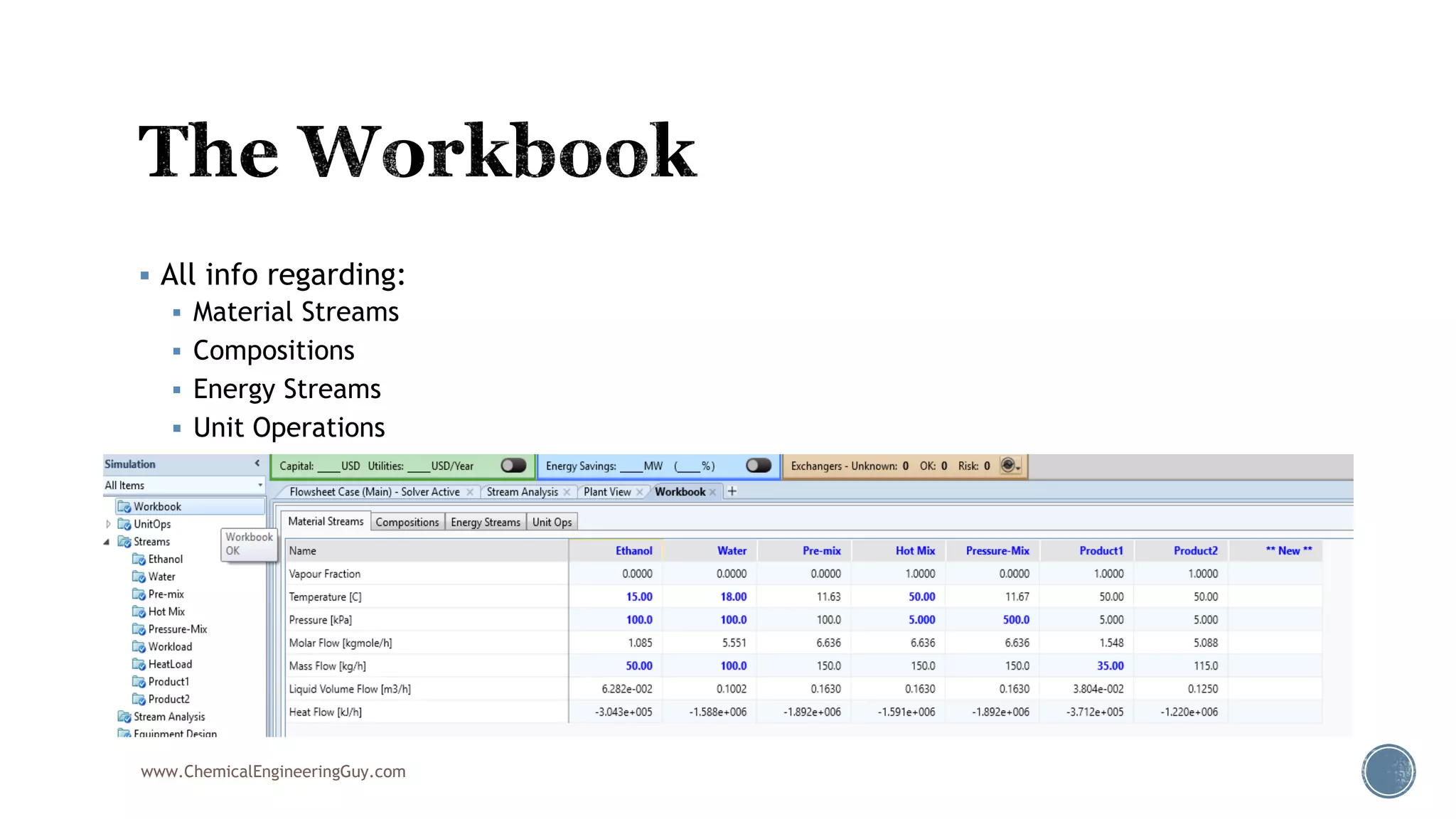
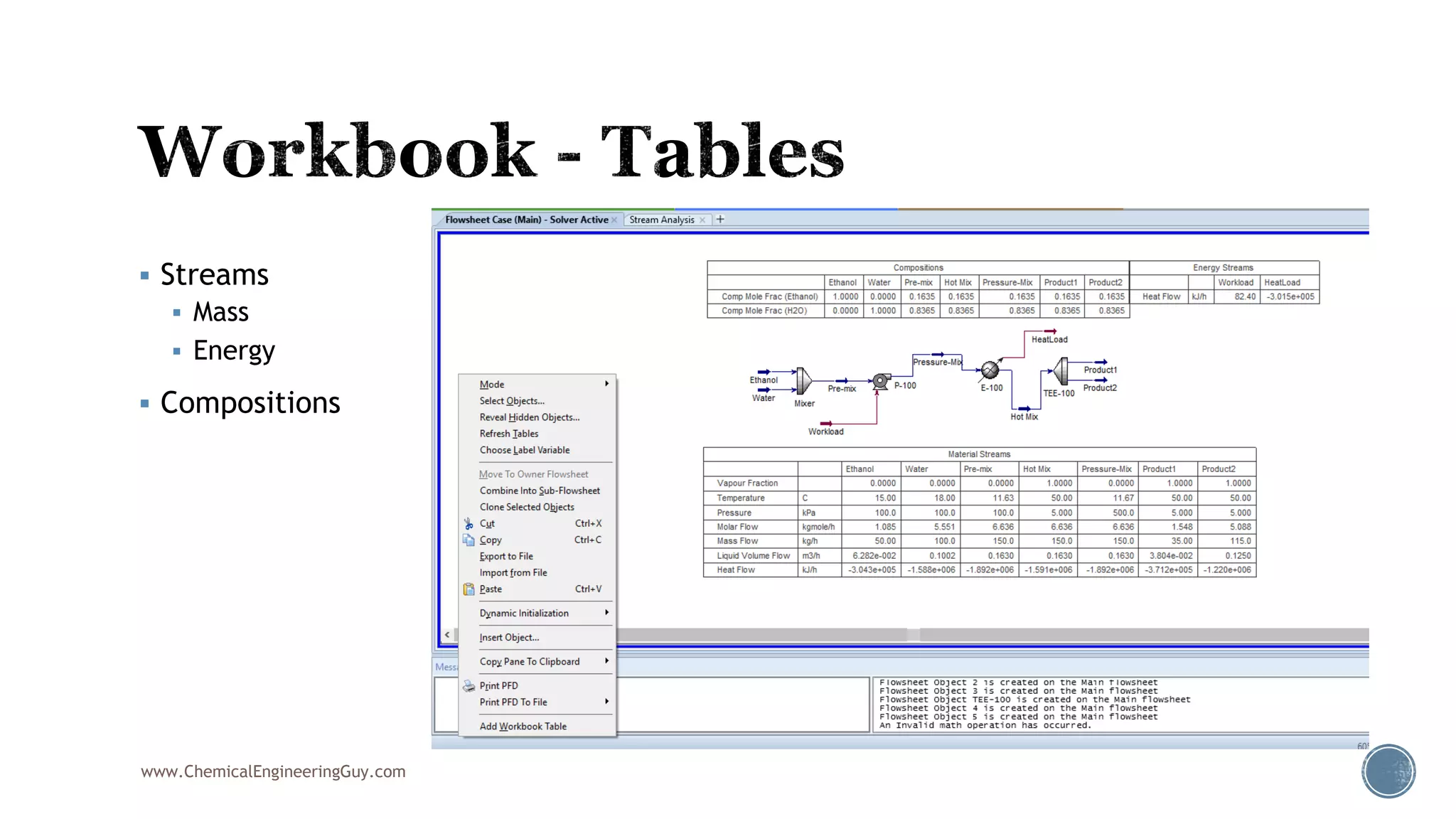
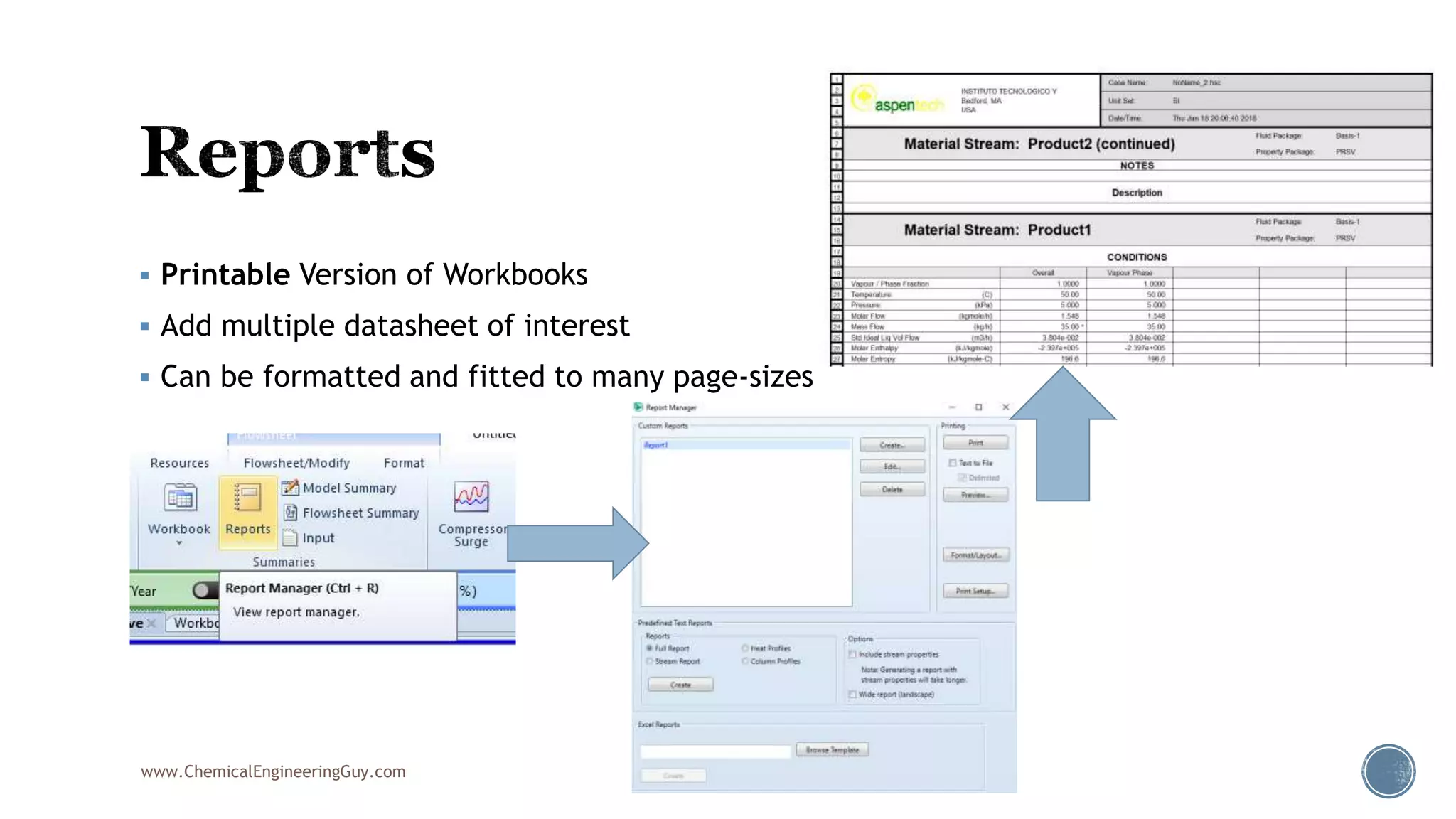
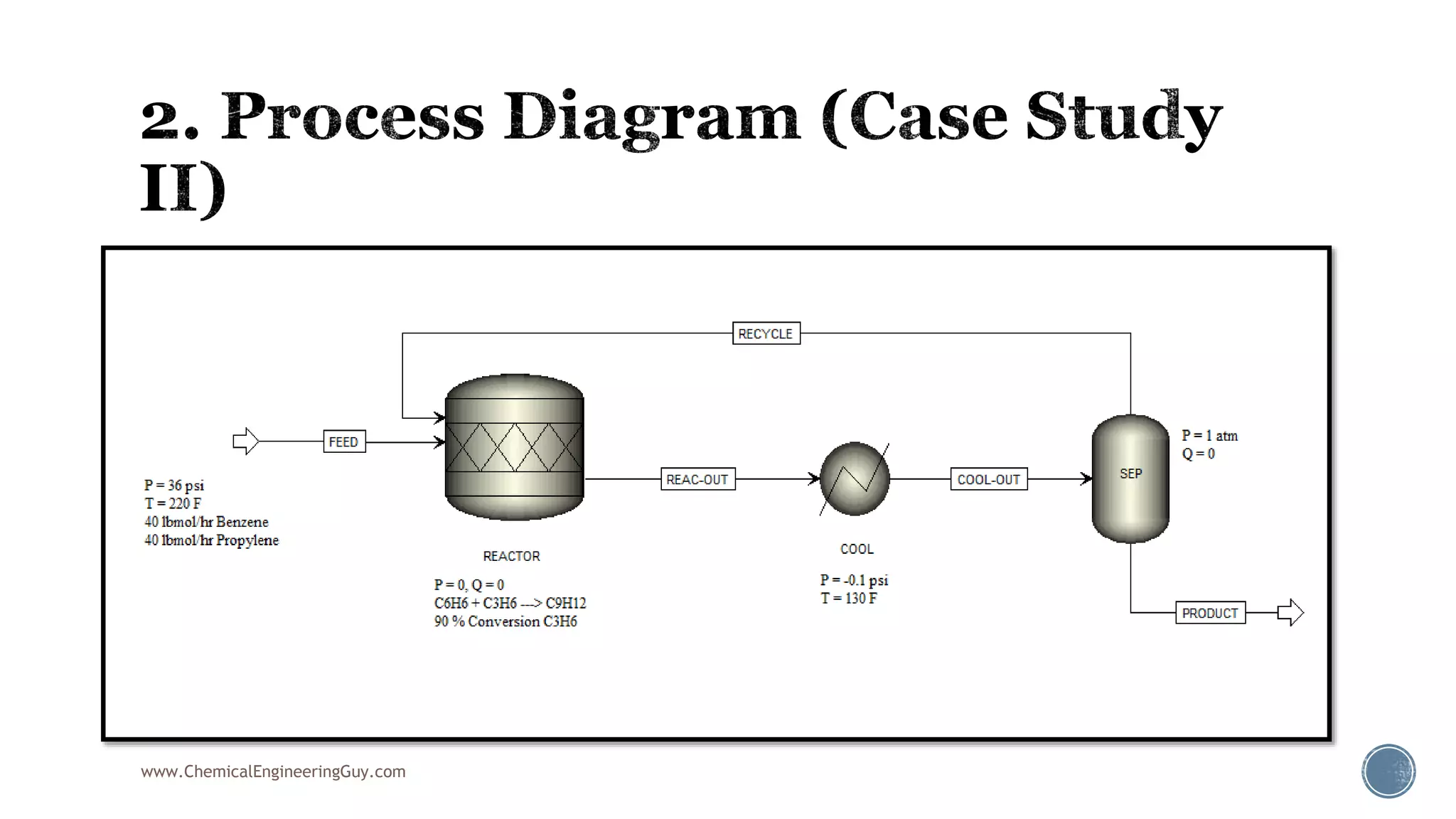
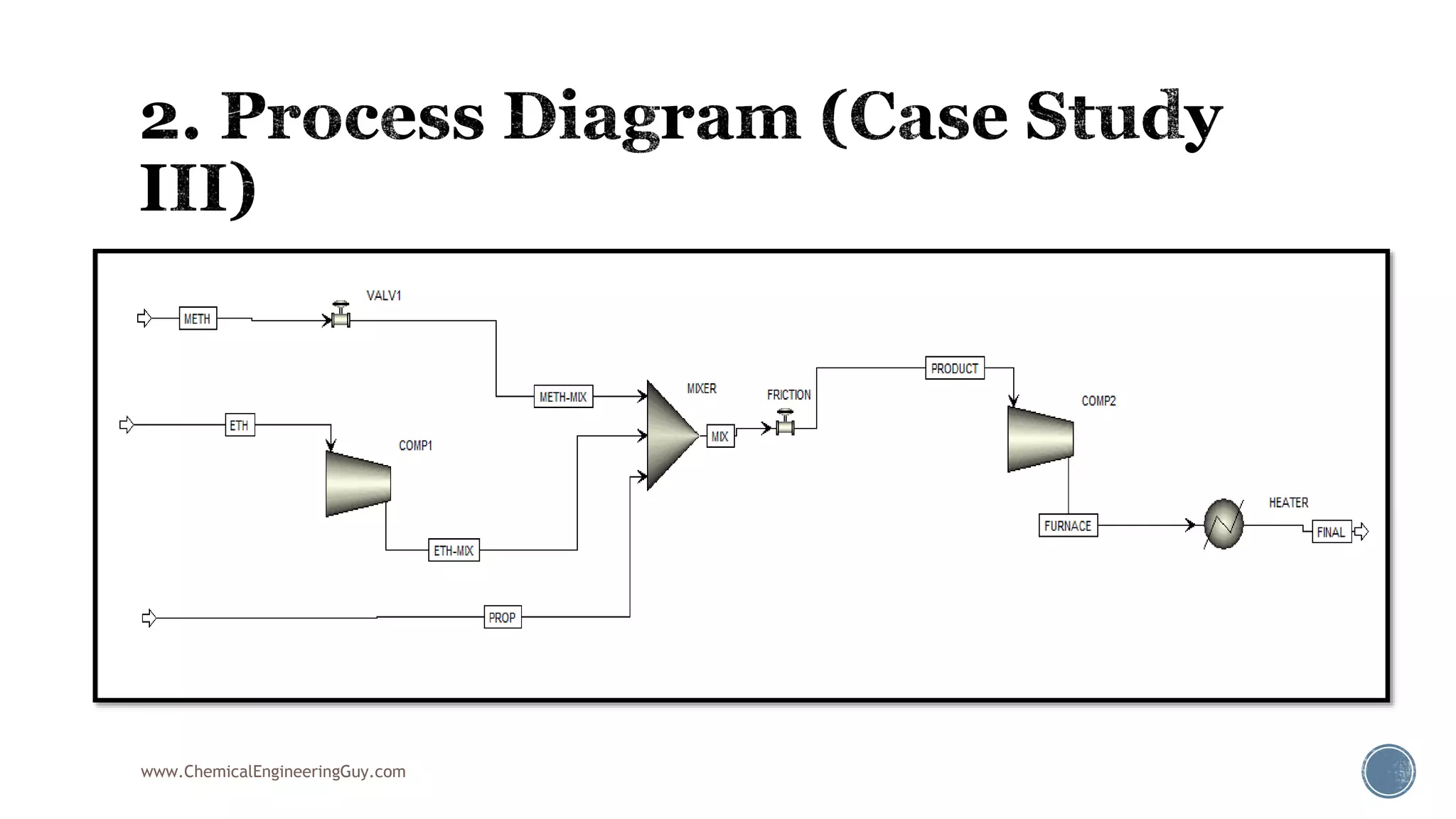
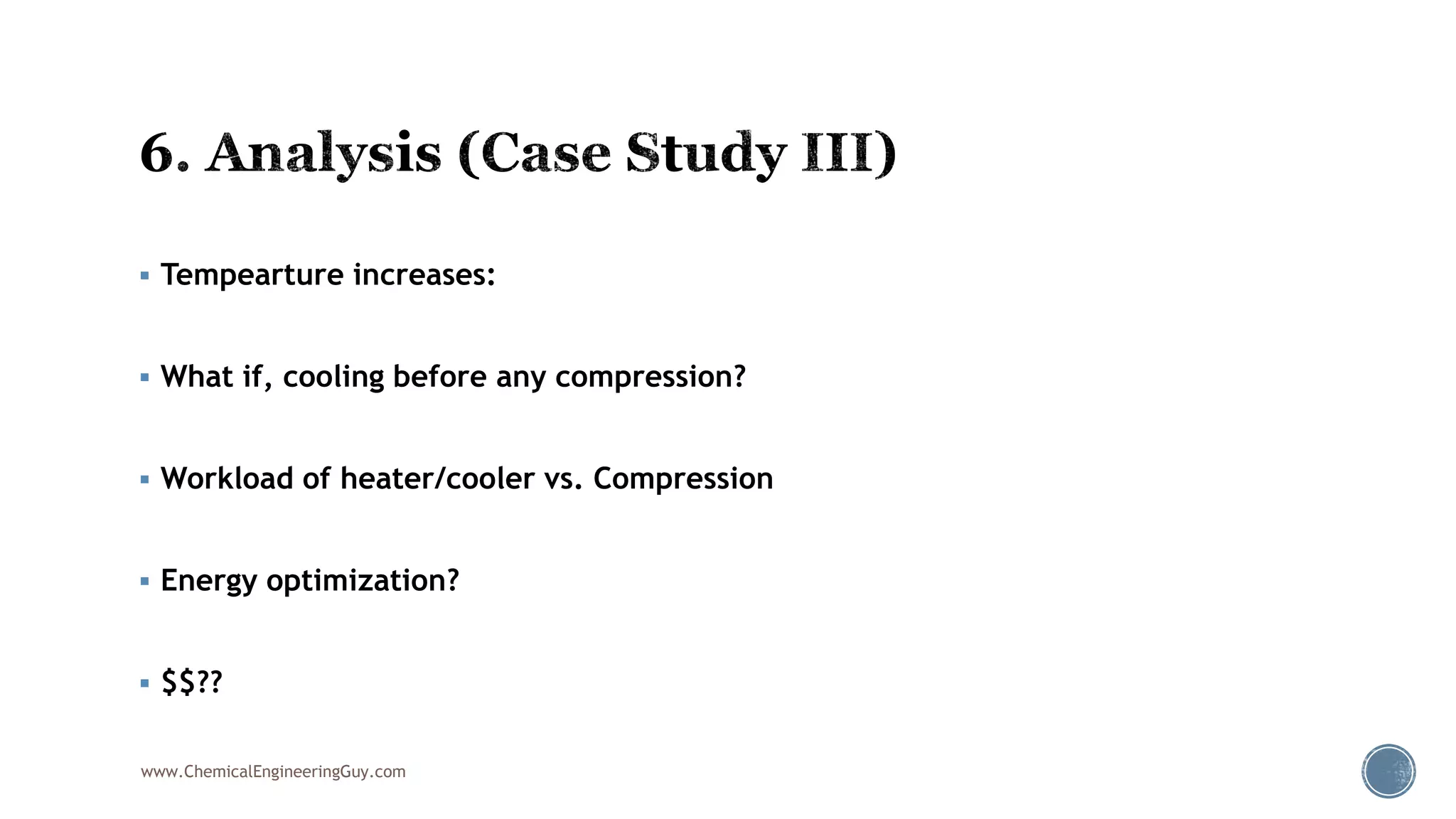
Based on the information provided, a hydrocarbon system and petroleum refining process type have been selected. The recommended property package is NRTL.
Does this help summarize the recommended package? Let me know if you need any clarification or have additional questions!