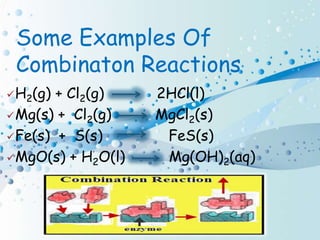
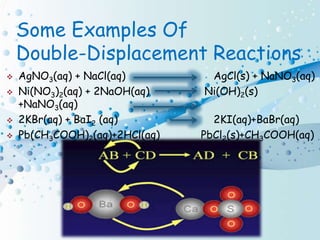
Chemical reactions involve the transformation of one or more substances into different substances. In a chemical reaction, the original substances are called reactants and the newly formed substances are called products. There are several types of chemical reactions including combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, and oxidation-reduction reactions. An oxidation-reduction reaction involves the loss or gain of oxygen, hydrogen, or electrons and can be classified as either an oxidation or reduction process.