Embed presentation
Downloaded 130 times



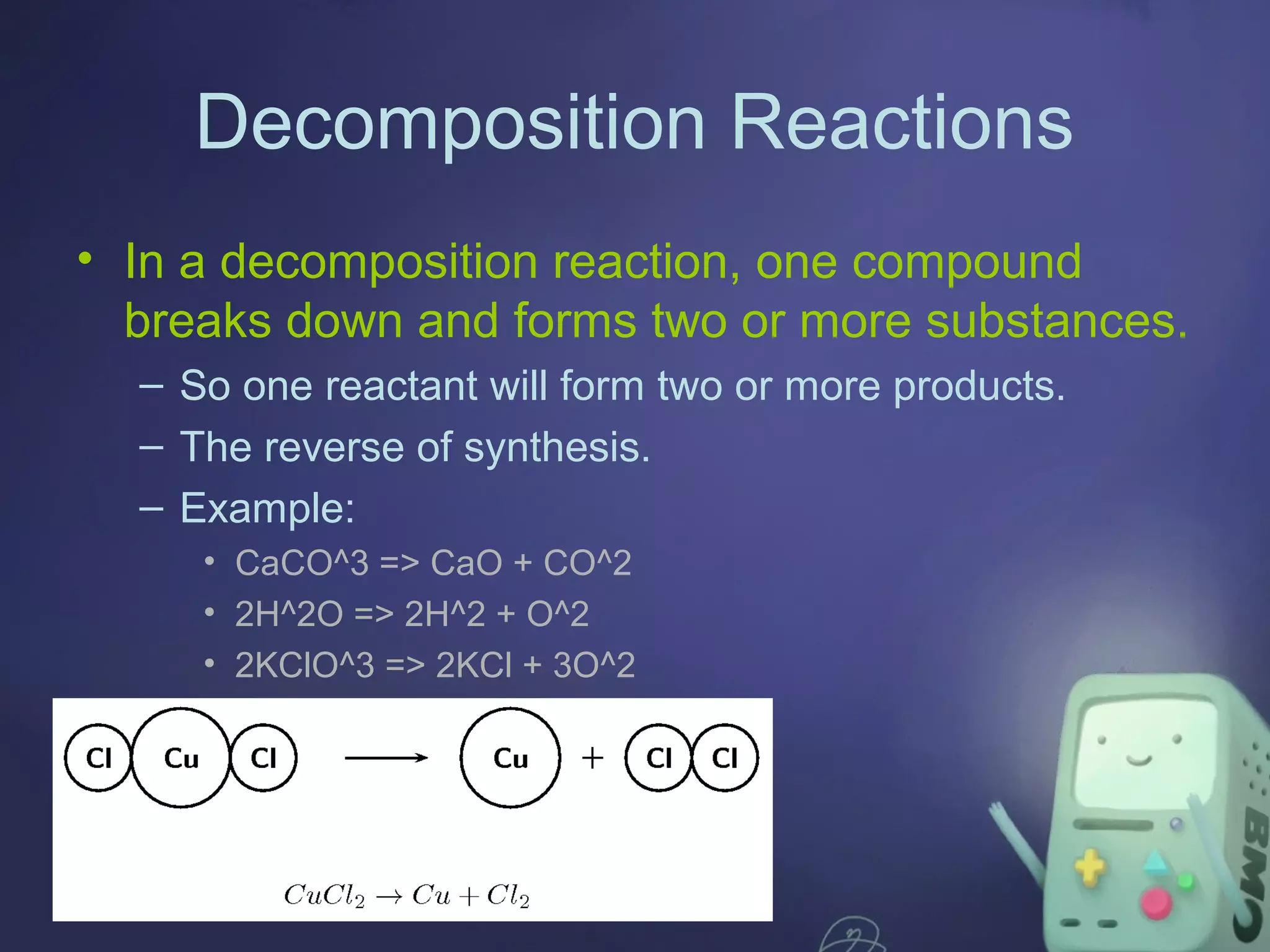
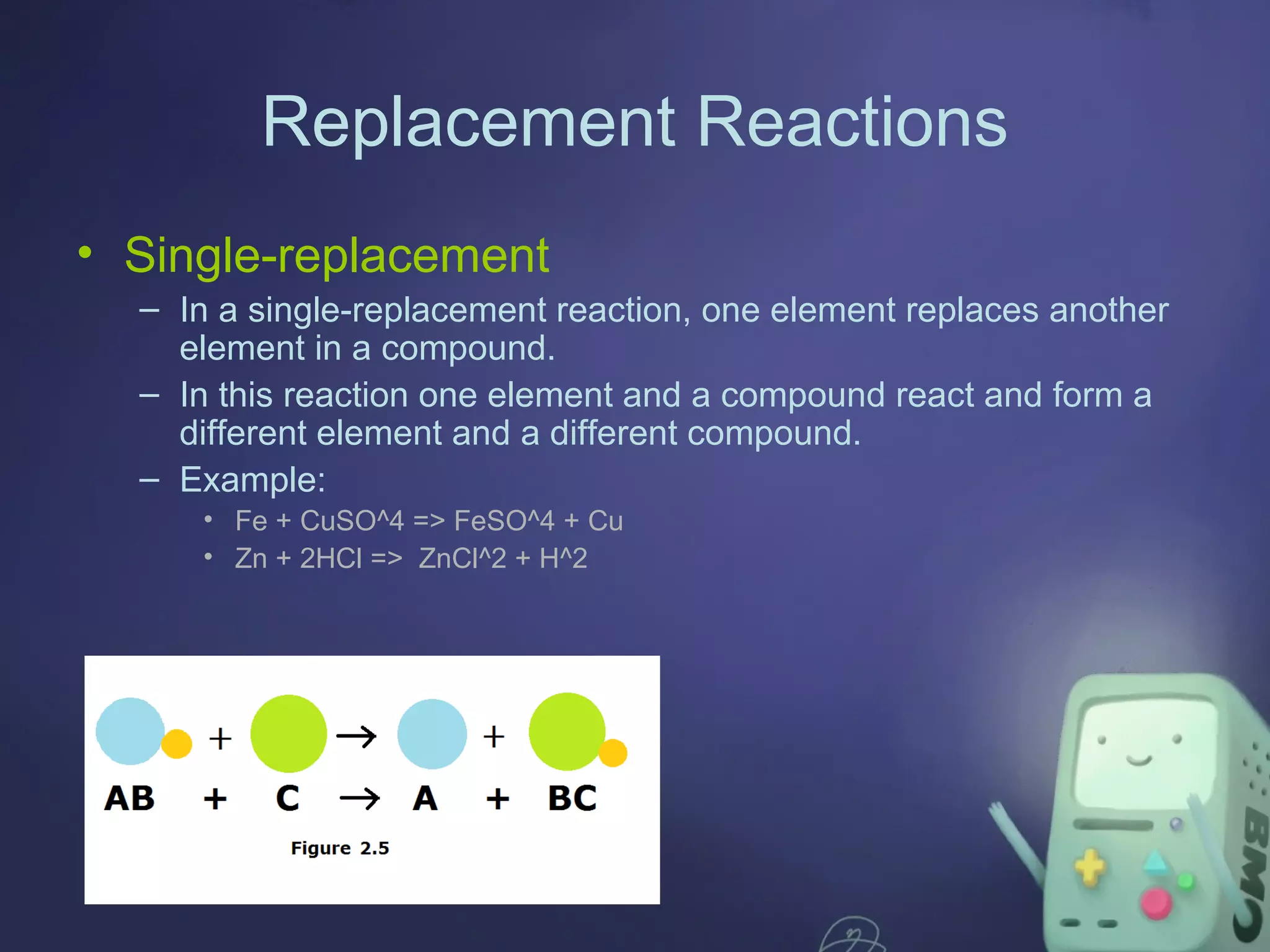
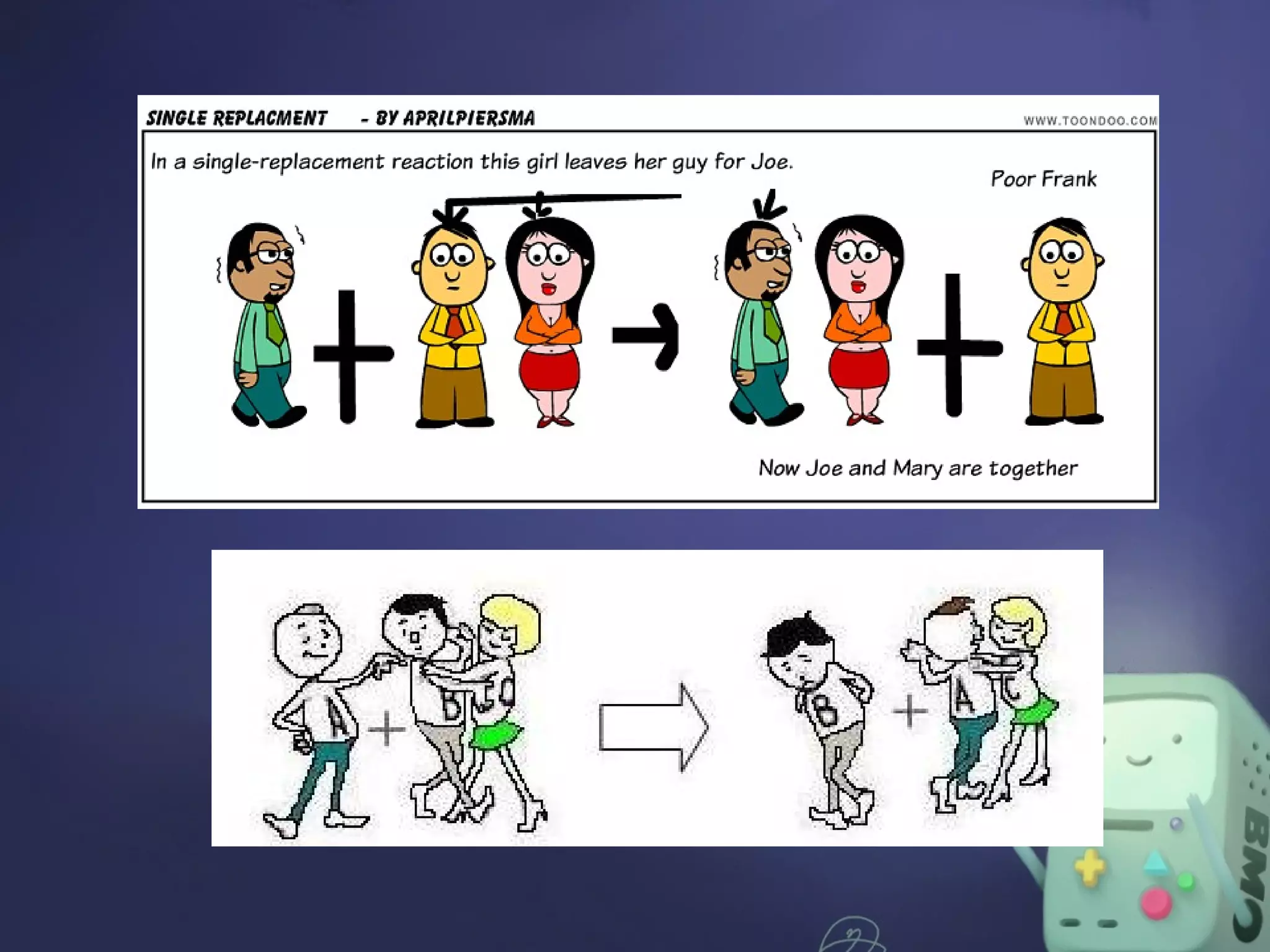
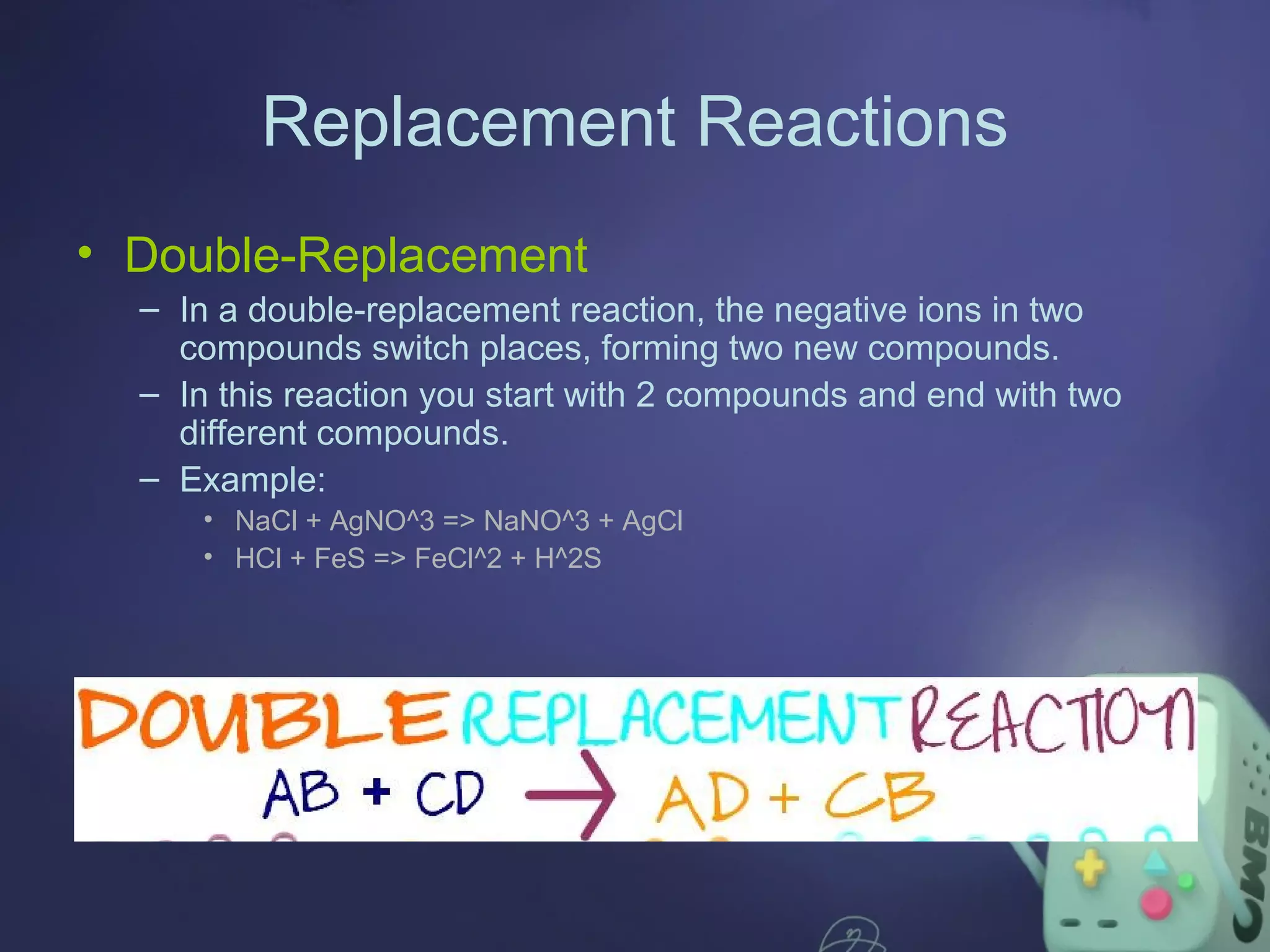
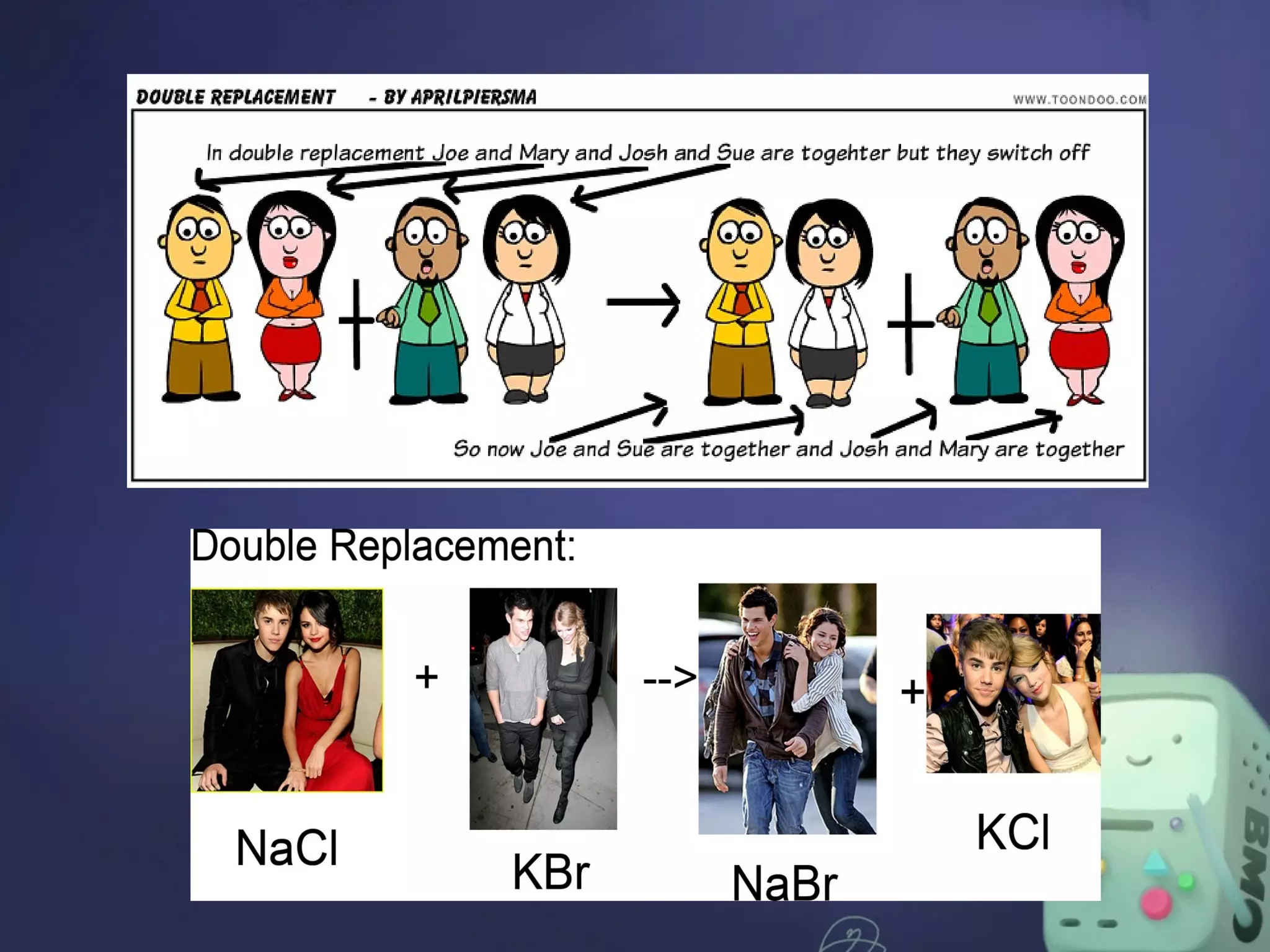

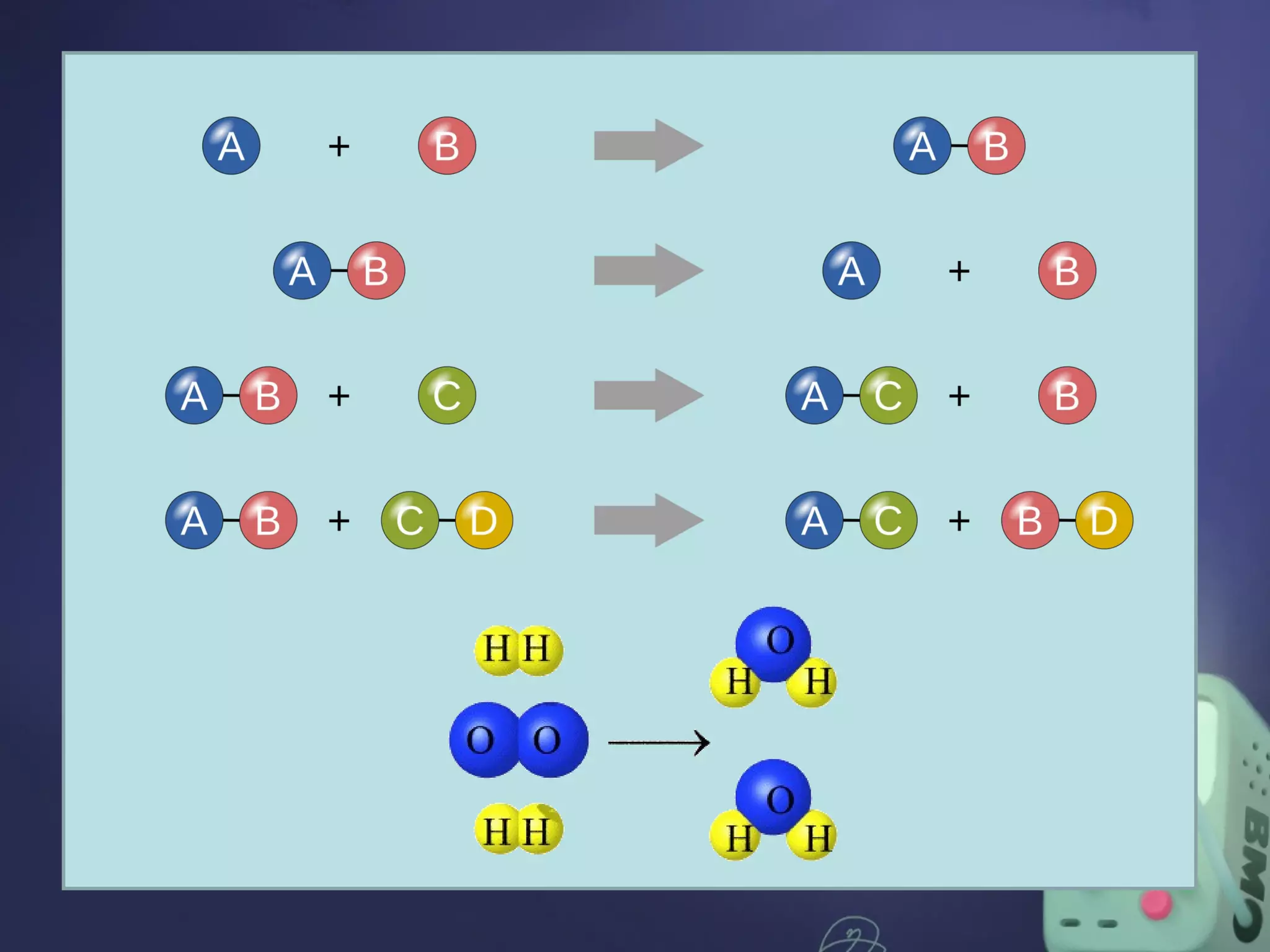

The document outlines four major types of chemical reactions: synthesis, decomposition, replacement, and combustion. Synthesis involves combining substances to form one compound, while decomposition breaks down a compound into multiple substances. Replacement reactions include single and double-replacement, and combustion refers to reactions where a substance combines with oxygen, typically releasing energy.











