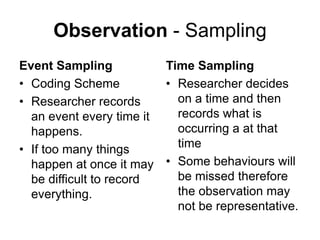
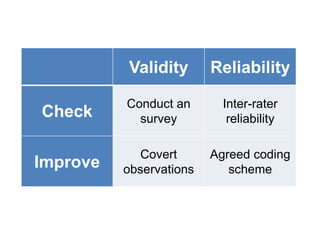
The document discusses the observational method of research. It defines different types of observational studies such as participant observations, non-participant observations, disclosed observations, and undisclosed observations. It also discusses structured observations using coding schemes and unstructured observations. The document notes some challenges with observational studies, such as issues with objectivity for participant observations and ethics concerns for undisclosed observations. It emphasizes the importance of reliability and validity in observational research.