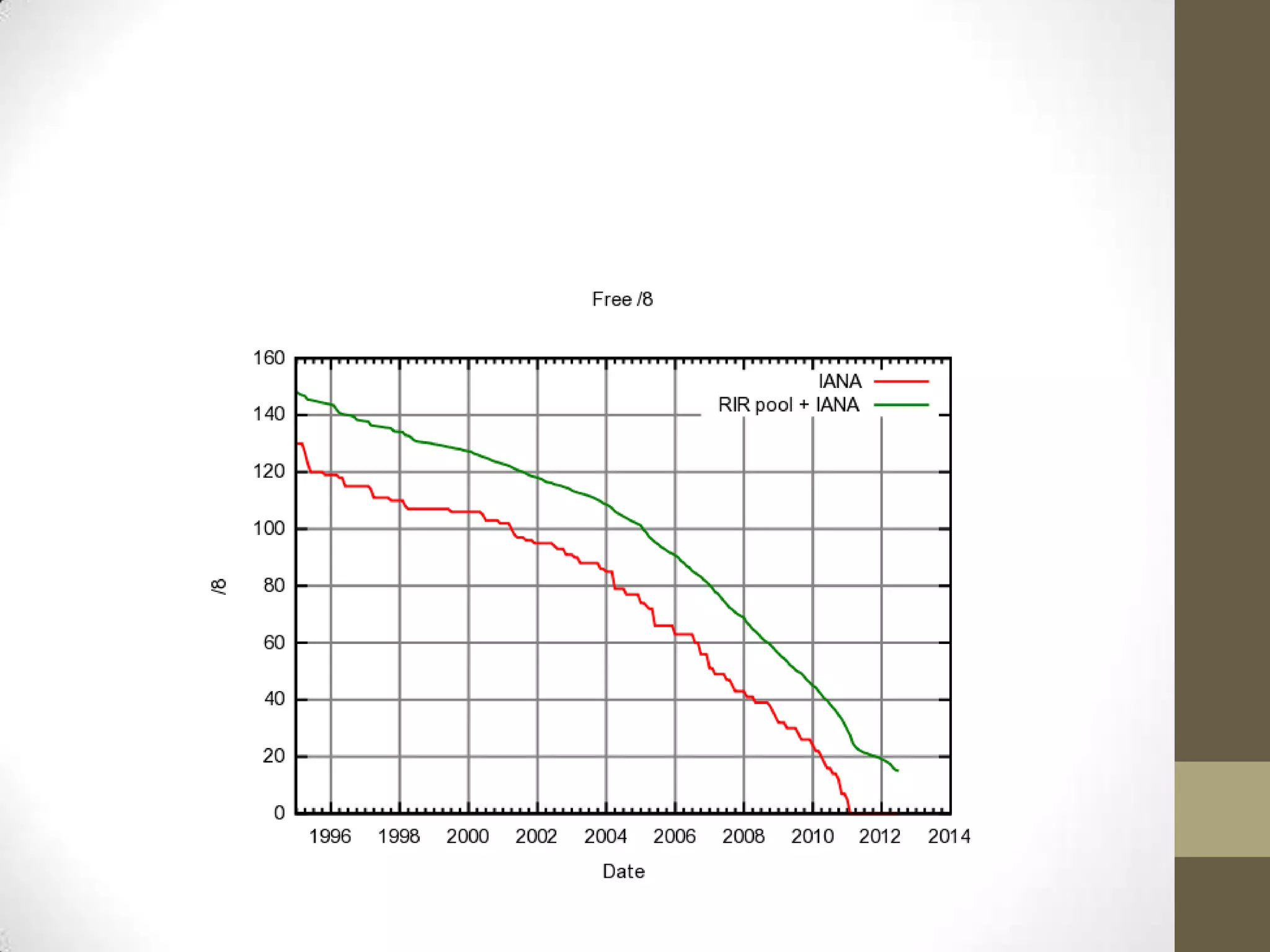
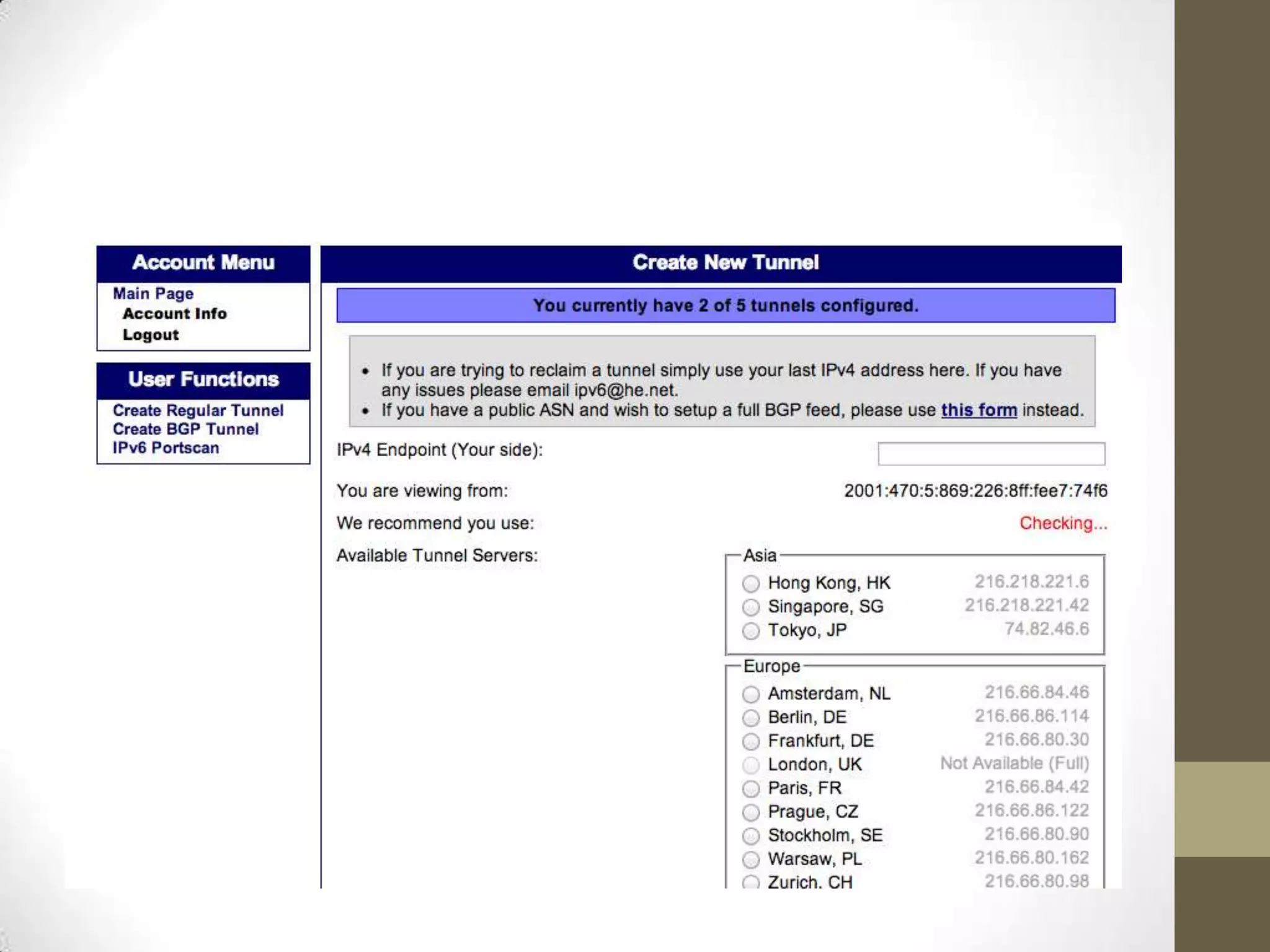
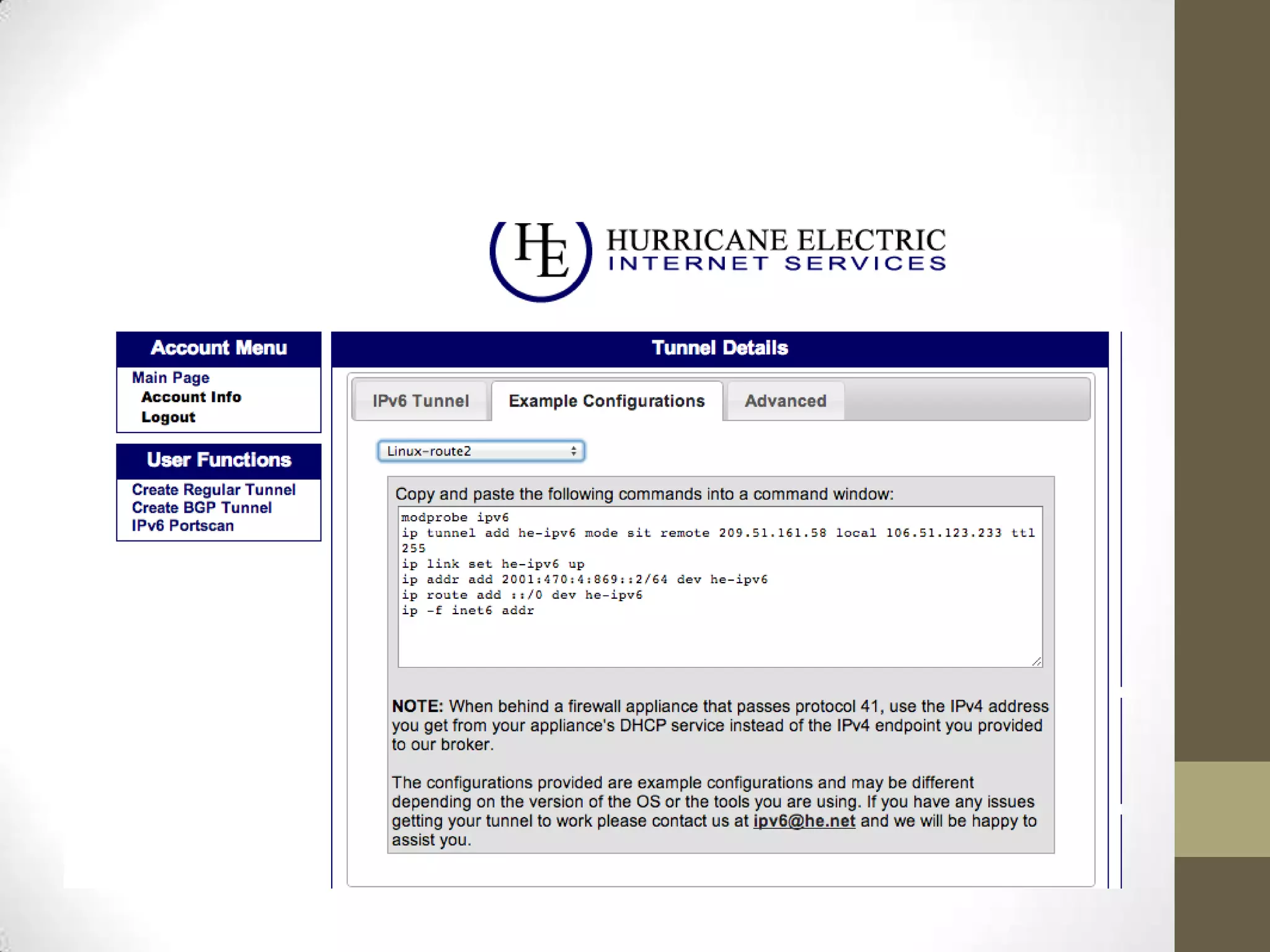
IPv6 is the successor to IPv4 and was developed to address the problem of IPv4 running out of addresses. IPv6 implements a new 128-bit addressing system that provides many more addresses than IPv4. Transitioning to IPv6 is important for businesses to allow for personalized content, targeted advertising, and to avoid issues with widespread network address translation. Individuals and organizations can obtain IPv6 access through their ISP's native implementation, by using tunneling services like Tunnelbroker.net, or via protocols like 6to4 and Teredo that tunnel IPv6 traffic over IPv4 networks.



![What is IPv6?
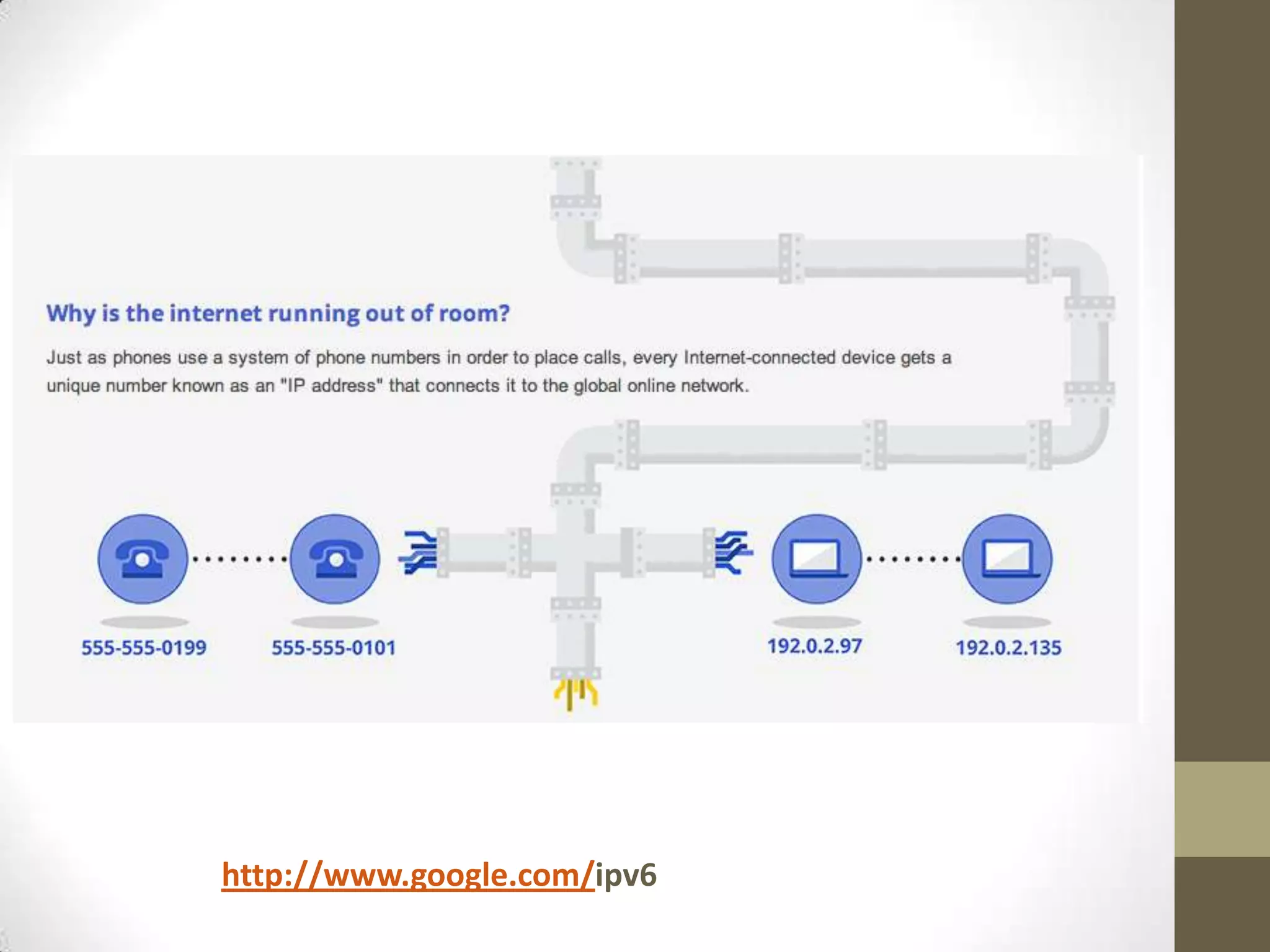
What is IP?!
IP address!
Internet Protocol address.
Your address on the internet.
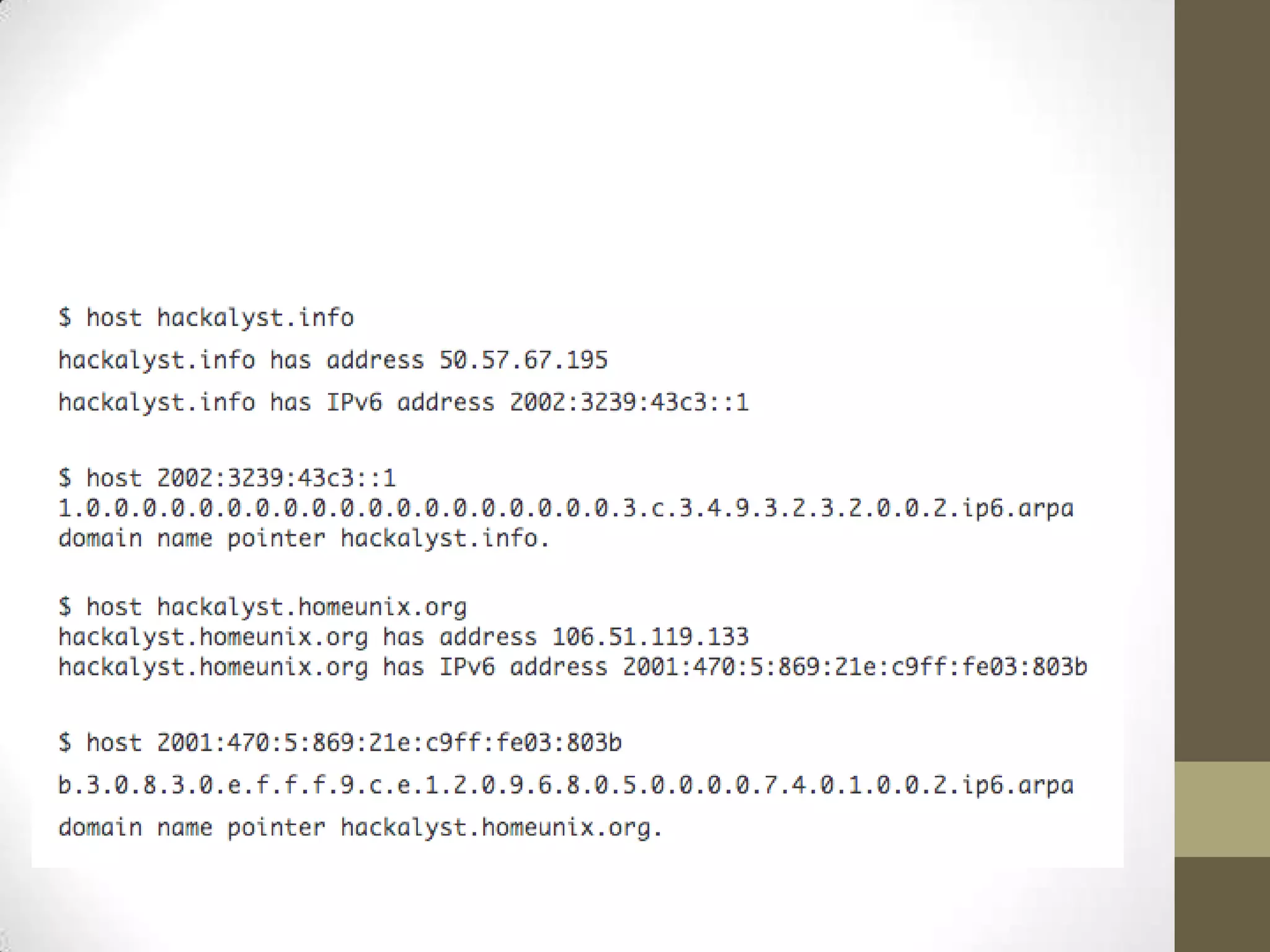
[anshup@mouthwa ~]$ host barcampbangalore.org
barcampbangalore.org has address 69.194.227.195
[anshup@mouthwa ~]$ host hackalyst.info
hackalyst.info has address 50.57.67.195
hackalyst.info has IPv6 address 2002:3239:43c3::1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/barcamp2012ipv6-120824155536-phpapp02/75/what-why-how-of-IPv6-2002-3239-43c3-1-4-2048.jpg)






























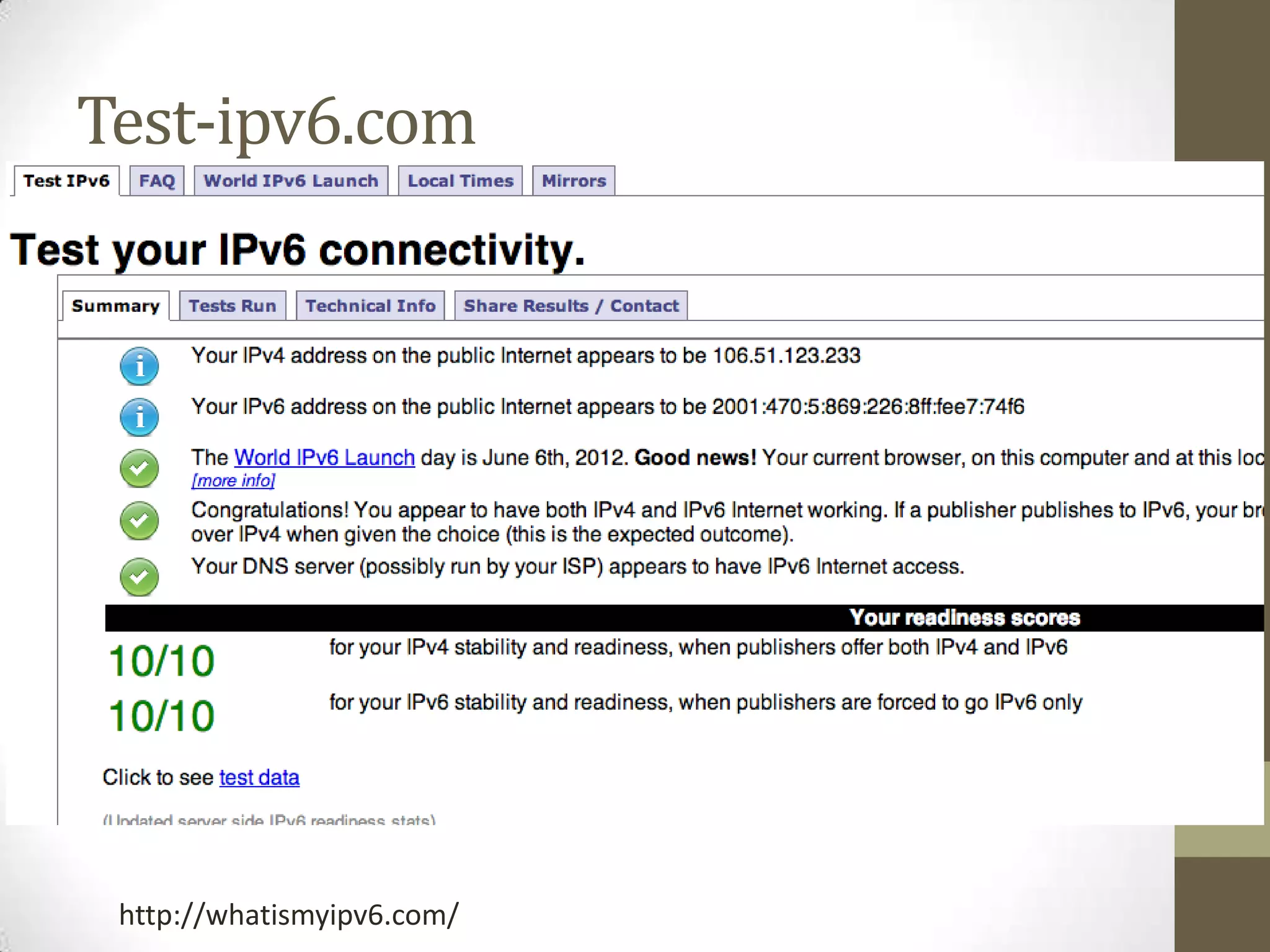
![What about DNS?!
Dns.he.net
Dyndns.com
2001:4860:4860::8888
2001:4860:4860::8844
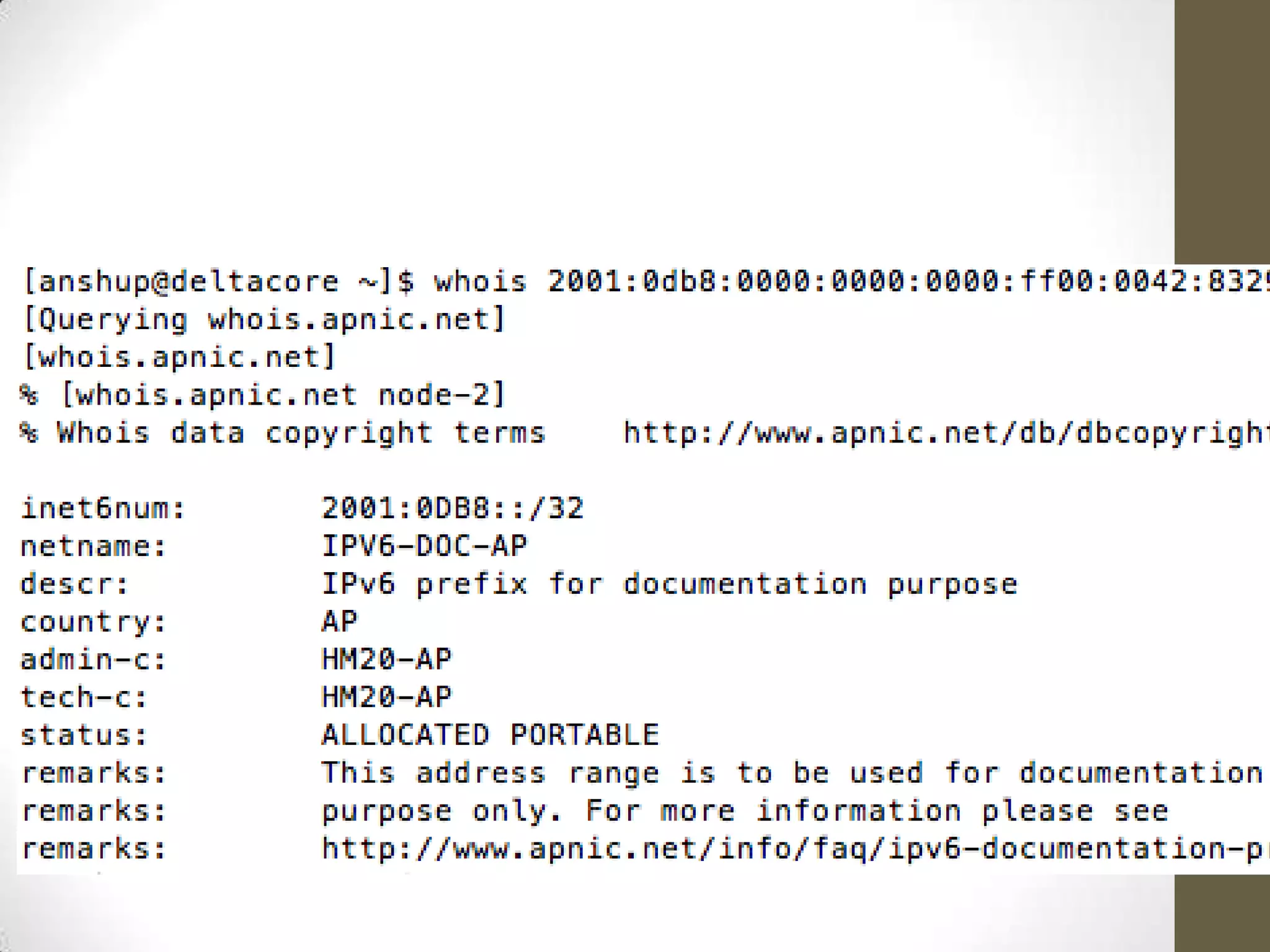
http://6to4.nro.net/
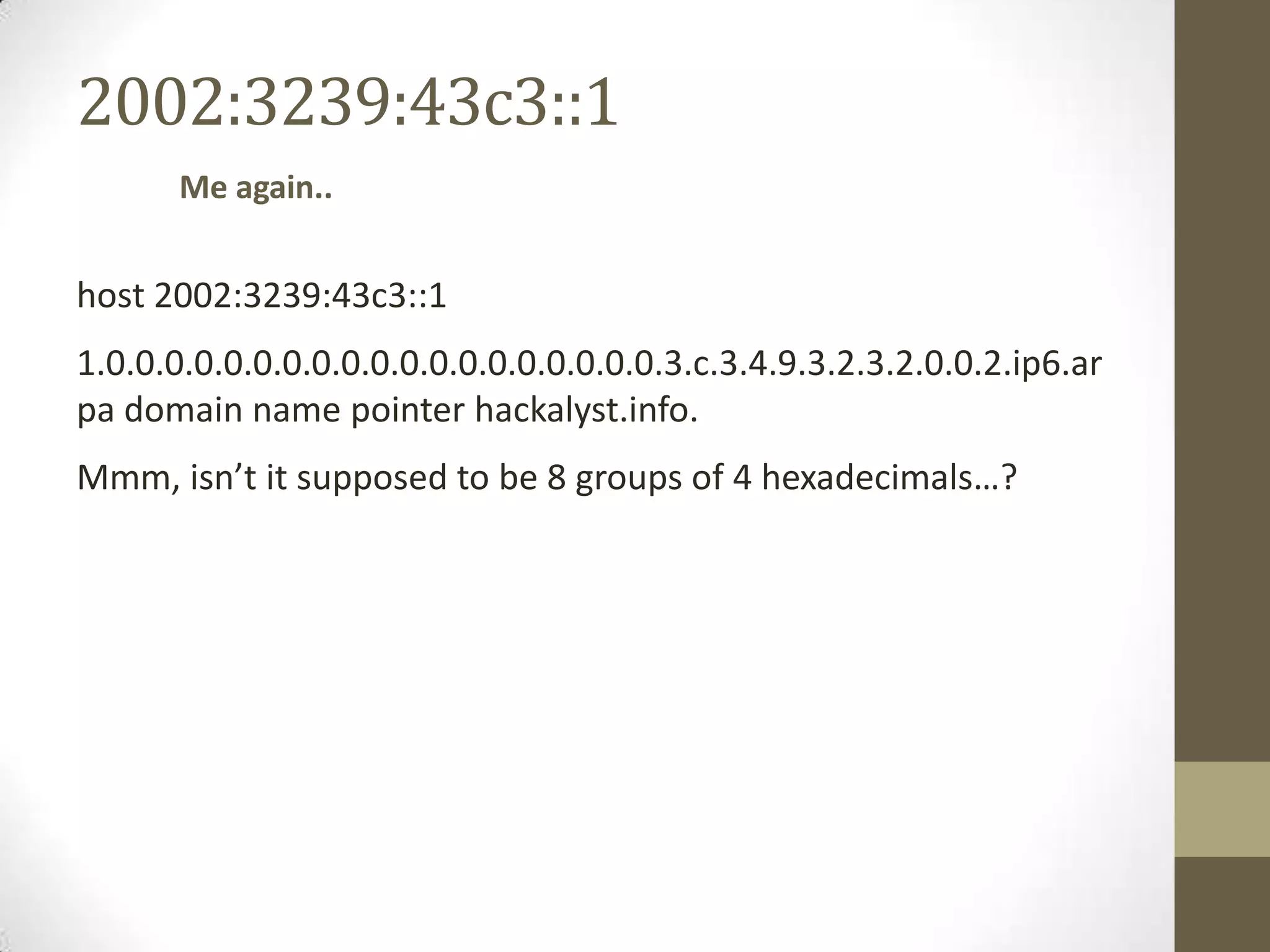
http://[2002:3239:43c3::1]
http://hackalyst.info/2012/06/24/how-to-create-ipv6-reverse-
dns-entry/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/barcamp2012ipv6-120824155536-phpapp02/75/what-why-how-of-IPv6-2002-3239-43c3-1-43-2048.jpg)