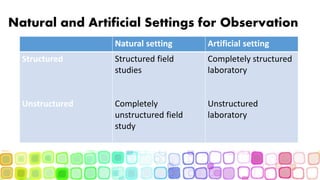
Structured observation involves systematically recording behaviors and can yield both quantitative and qualitative data. It is highly systematic and enables the researcher to generate numerical data for comparisons. There are various types of observations including structured, semi-structured, unstructured, critical incidents, naturalistic/participant, and different natural and artificial settings. Researchers must consider ethics and be cautious of biases like selective attention, reactivity, and expectancy effects to ensure valid and reliable observations.