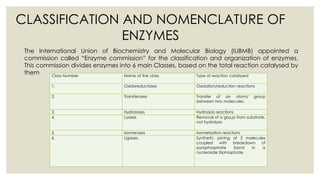
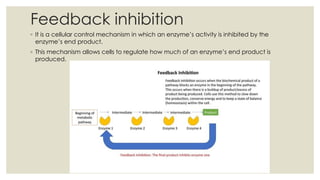
Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions in living cells without undergoing a change themselves. They are usually proteins but can also be RNA. Many enzymes require non-protein cofactors like metal ions or organic molecules to be active. There are over 75,000 known enzymes that are classified and named based on the reactions they catalyze. Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy of reactions, allowing more molecules to reach the transition state. Their activity is affected by factors like temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and can be inhibited by other molecules. Feedback inhibition regulates enzyme activity by inhibiting enzymes using their own end products.