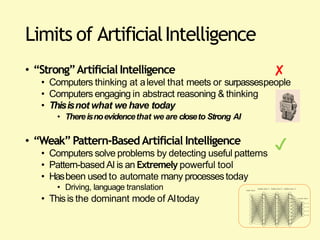
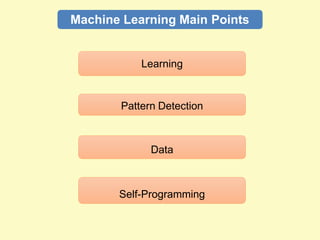
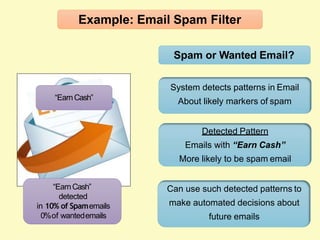
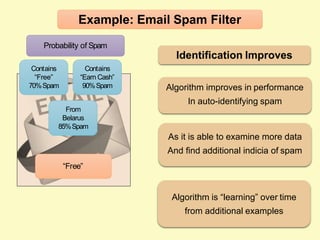
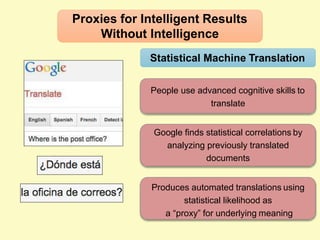
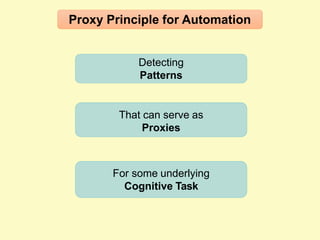
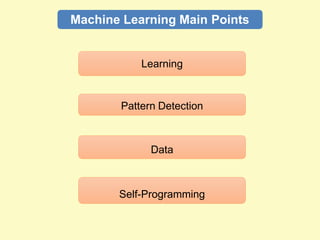
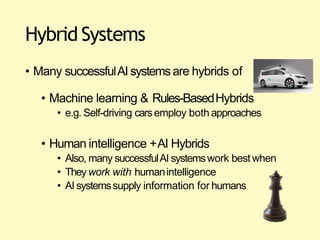
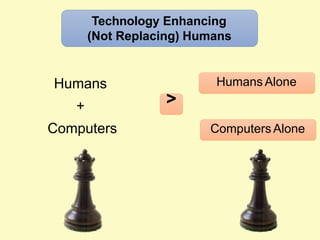
Artificial intelligence (AI) uses computers to solve problems or make automated decisions typically requiring human intelligence. The two major AI techniques are rules-based and machine learning approaches. Rules-based AI uses logical rules to automate processes, while machine learning algorithms find patterns in data to improve performance over time without being explicitly programmed. Today, AI is mostly "weak" and pattern-based, not capable of human-level reasoning, but it has automated many tasks through proxies like statistical patterns. Hybrid systems combining approaches work best.