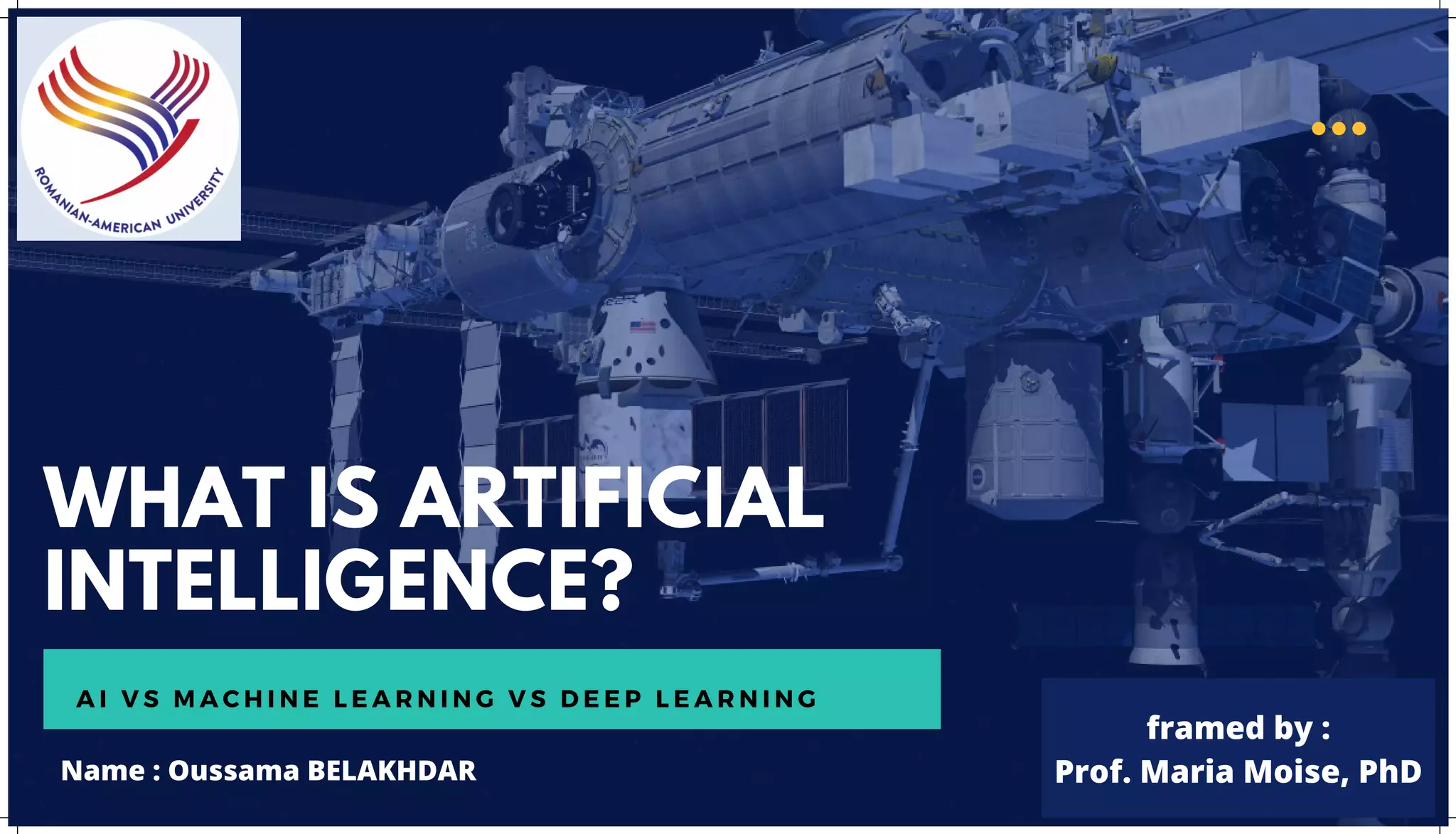
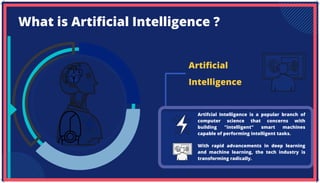
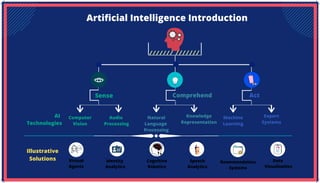
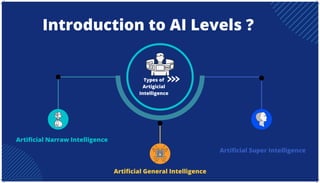
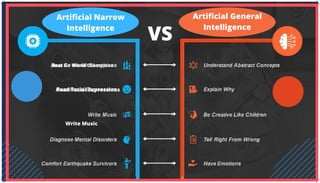
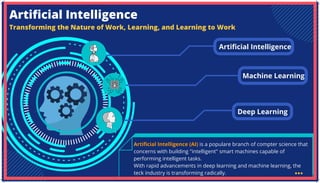
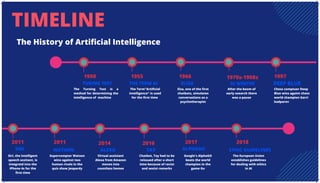
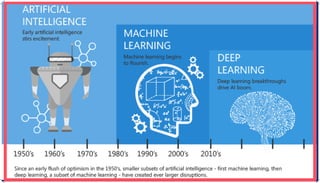
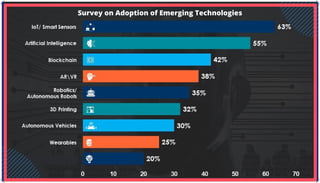
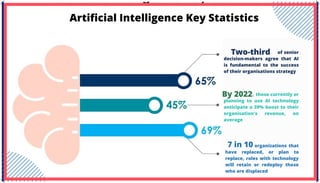
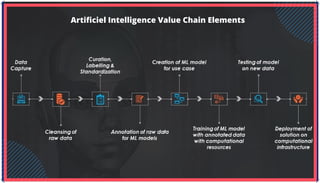
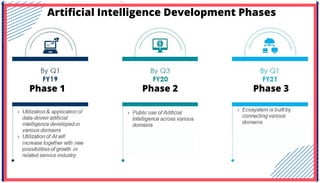
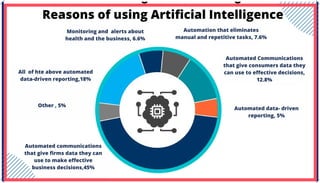
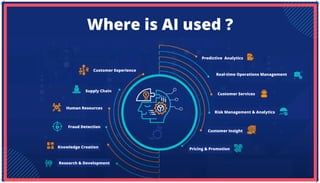
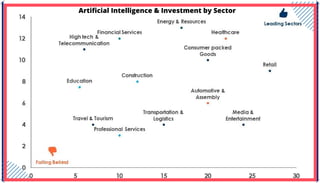
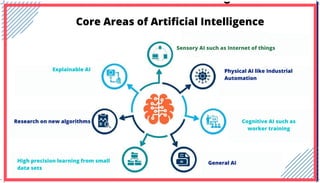
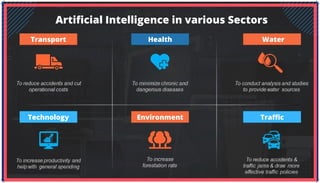
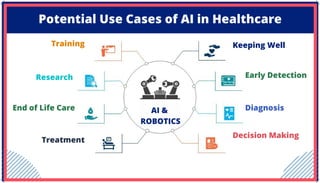
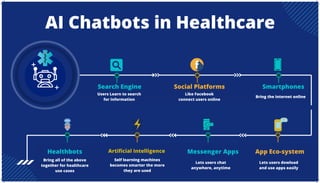
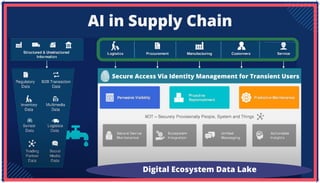
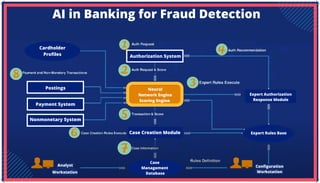
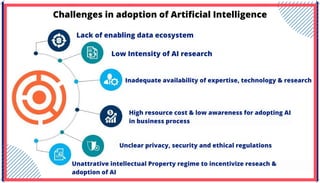
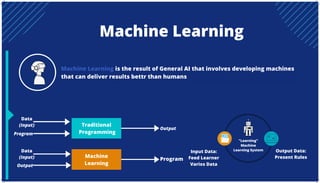
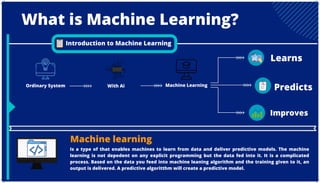
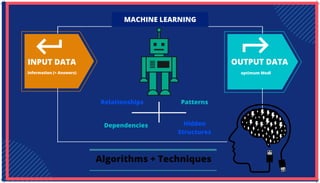
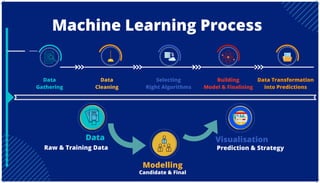
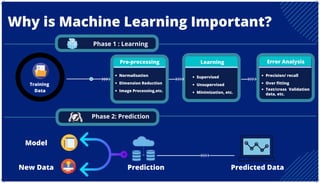
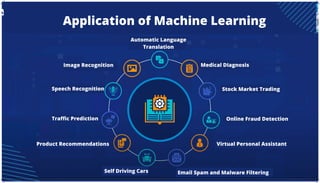
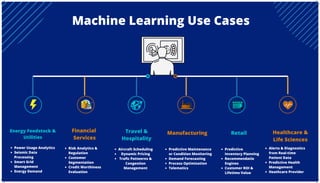
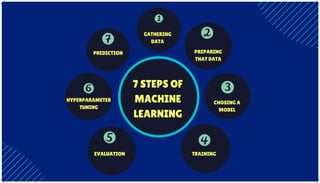
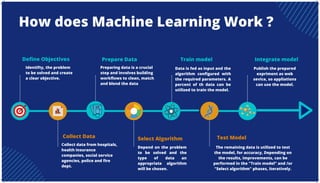
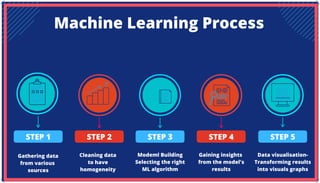
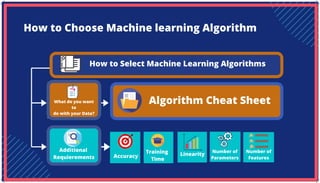
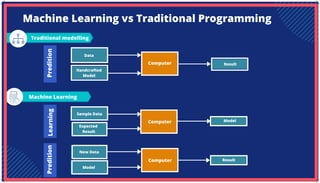
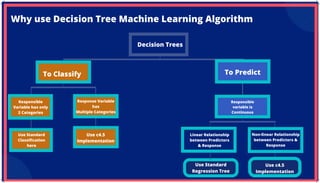
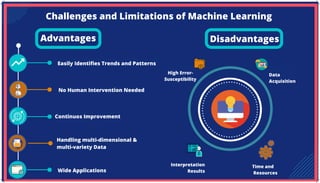
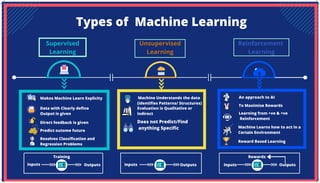
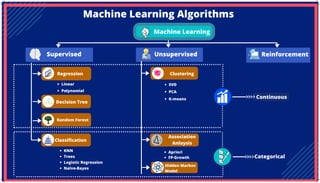
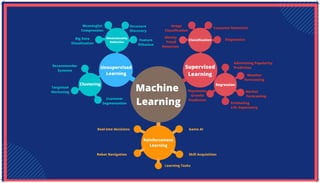
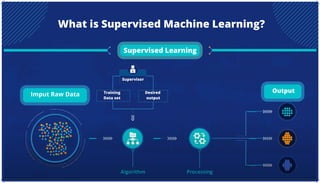
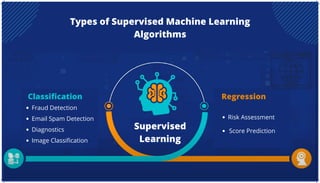
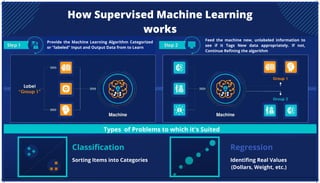
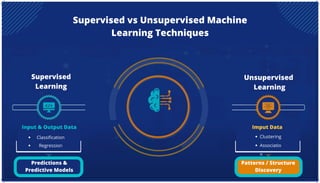
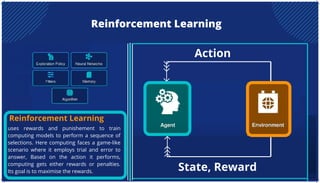
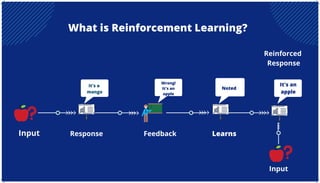
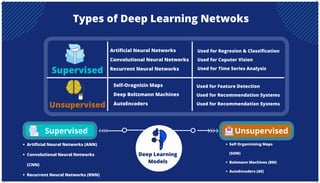
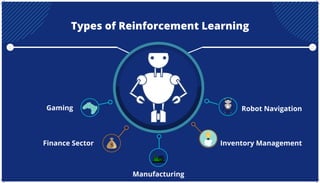
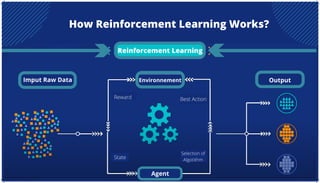
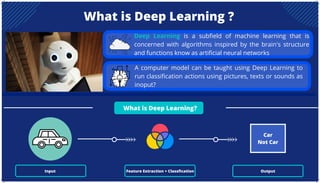
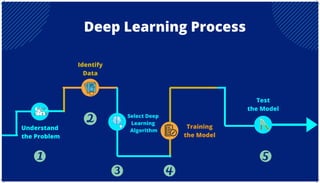
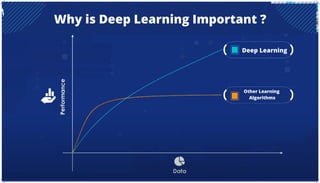
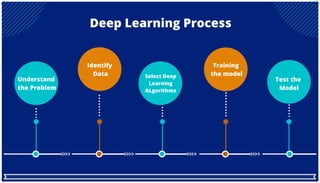
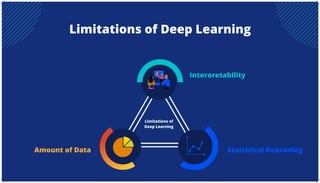
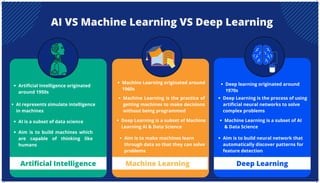
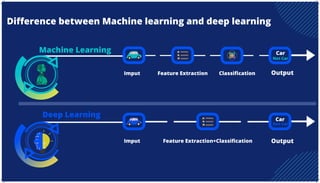
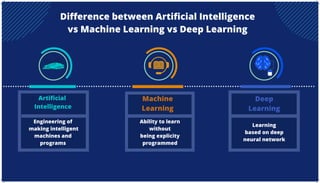
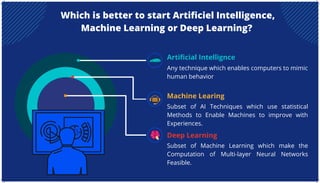
The document is an extensive overview of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning, covering their definitions, history, types, and applications across various sectors. It discusses key concepts like supervised and unsupervised learning, the importance of data, challenges in AI adoption, and provides insights into trends and use cases for these technologies. Moreover, it highlights the implications these advancements have on business and society, alongside the challenges faced in implementation.