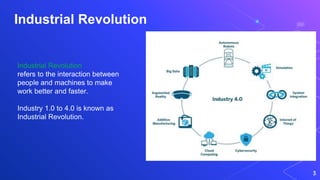
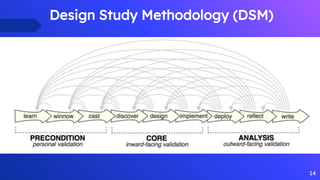
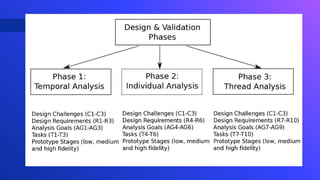
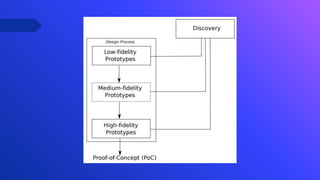
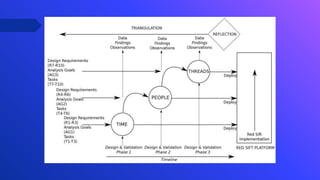
The document describes a design study methodology for developing interactive visualizations to support personalization of health data for patients and users. It involves 3 phases - a pre-condition phase to understand the domain through literature review and expert input, a condition phase to design and implement visualization prototypes through an iterative user-centered process, and a post-condition phase to deploy and validate the solutions. The methodology supports achieving the objectives of understanding healthcare needs, designing interactive visualizations, and validating the solutions with experts.