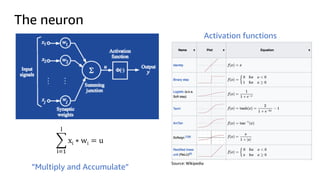
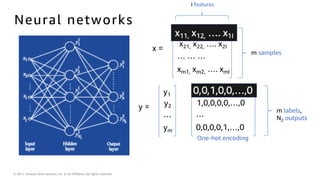
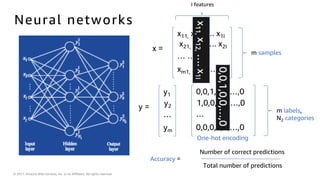
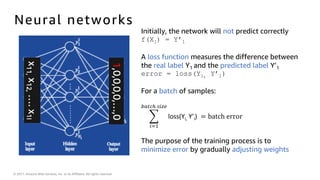
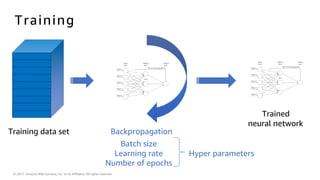
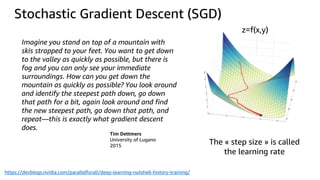
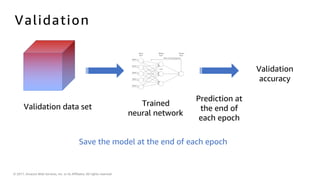
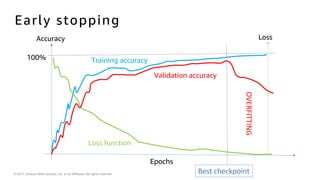
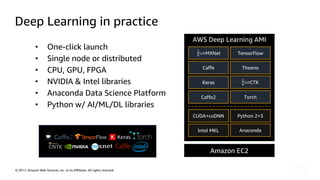
The document introduces deep learning, explaining its concepts and the distinction between artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning. It discusses common myths about AI, provides insights into deep learning in action, and outlines the basics of neural networks and the training process. Additionally, it highlights resources and tools available for implementing deep learning on platforms like AWS and NVIDIA.