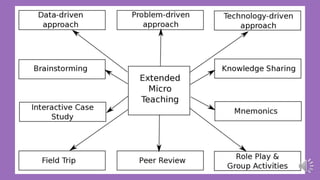
The document discusses the implementation of extended microteaching (XMT) as an innovative teaching pedagogy aligned with India's updated National Education Policy. XMT encompasses ten pedagogical methods, such as brainstorming, knowledge sharing, and technology-driven approaches, aimed at enhancing teacher effectiveness and student engagement in higher education. The findings indicate positive attitudes and intentions from undergraduate teachers towards adopting XMT, emphasizing the need for institutional support and resources for successful implementation.