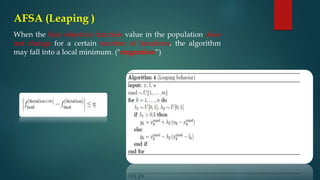
The document presents an overview of the Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm (AFSA), first proposed in 2002, emphasizing its population-based approach and visual scope dynamics. AFSA involves random movement, swarming towards central points, and chasing the best neighboring point based on function values, while also discussing its advantages like global search capability alongside drawbacks including time complexity and low convergence speed. Key aspects such as parameter settings and algorithm behaviors (random, moving, leaping) are outlined, complemented by references for further reading.