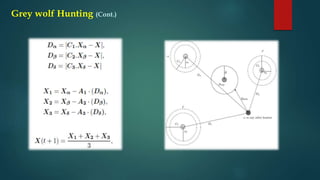
The Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) is a meta-heuristic algorithm that mimics the leadership hierarchy and hunting behavior of grey wolves, proposed by Mirjalili et al. in 2014. It operates through a social structure comprising four levels: alpha, beta, delta, and omega, where solutions are ranked analogously to the wolf hierarchy. The algorithm emphasizes exploration and exploitation in search for optimal solutions using mathematical models for encircling, hunting, and attacking prey.











![Grey wolf encircling prey (Cont.)
Where t is the current iteration, A and C are
coefficient vectors, Xp is the position vector of
the prey, and X indicates the position vector of
a grey wolf.
•The vectors A and C are calculated as follows:
Where components of a are linearly decreased
from 2 to 0 over the course of iterations and r1,
r2 are random vectors in [0, 1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/greywolfoptimizergwo-240627084118-67933d7b/85/Grey-Wolf-Optimizer-GWO-Swarm-Intelligence-12-320.jpg)

![Attacking prey (exploitation)
•The grey wolf finish the hunt by attacking the
prey when it stop moving.
•The vector A is a random value in interval
[-2a, 2a], where a is decreased from 2 to 0 over
the course of iterations.
When |A| < 1, the wolves attack towards the
prey, which represents an exploitation process.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/greywolfoptimizergwo-240627084118-67933d7b/85/Grey-Wolf-Optimizer-GWO-Swarm-Intelligence-15-320.jpg)


