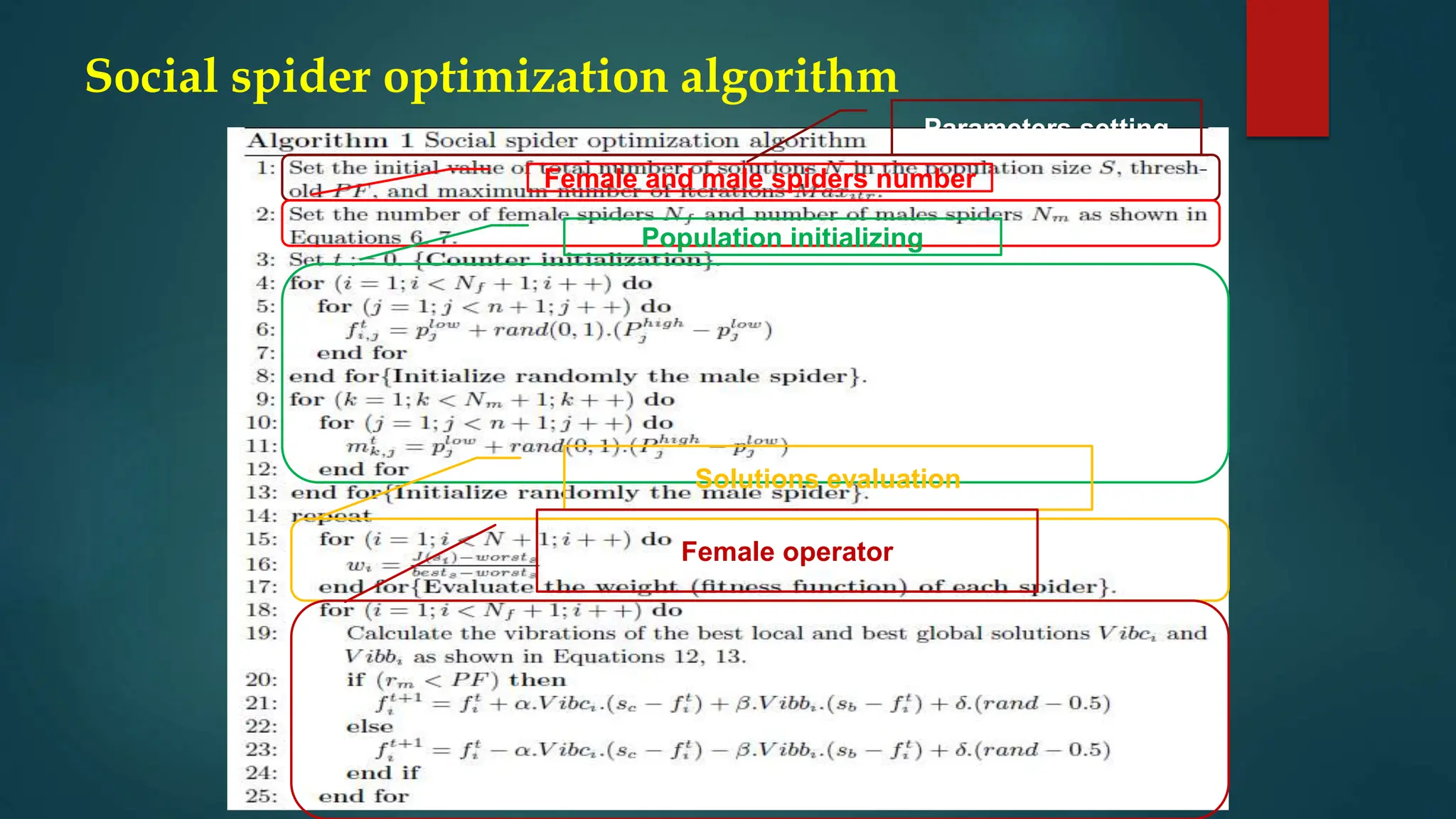
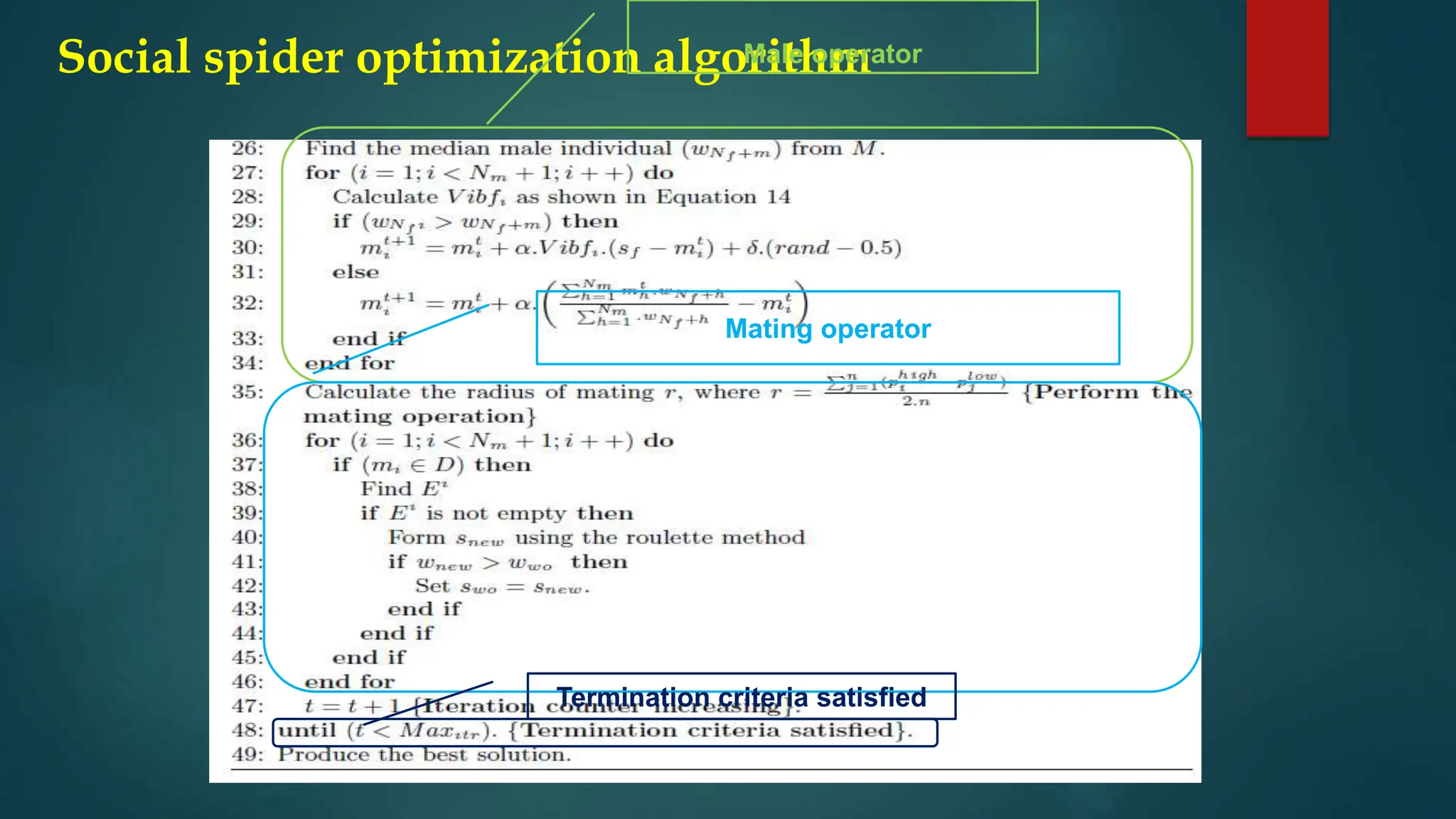
The document discusses the Social Spider Optimization (SSO) algorithm, which is a population-based optimization method inspired by the behavior of social spiders. It outlines key components such as the population structure, fitness evaluation, and the roles of male and female spiders in mating and information exchange. Additional details cover algorithm initialization, modeling of communication through vibrations, and various operators that guide the optimization process.











![Female cooperative operator
•The female spiders present an attraction or
dislike over other irrespective of gender.
•The movement of attraction or repulsion
depends on several random phenomena.
•A uniform random number rm is generated
within the range [0,1].
•If rm is smaller than a threshold PF, an
attraction movement is generated; otherwise, a
repulsion movement is produced as follows.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/socialspideroptimizationsso-240702053928-de09d8c0/75/Social-Spider-optimization-SSO-pptx-13-2048.jpg)