- The document discusses various problem solving techniques in artificial intelligence including search strategies like BFS, DFS, A*, heuristic search, and beyond classical search methods.
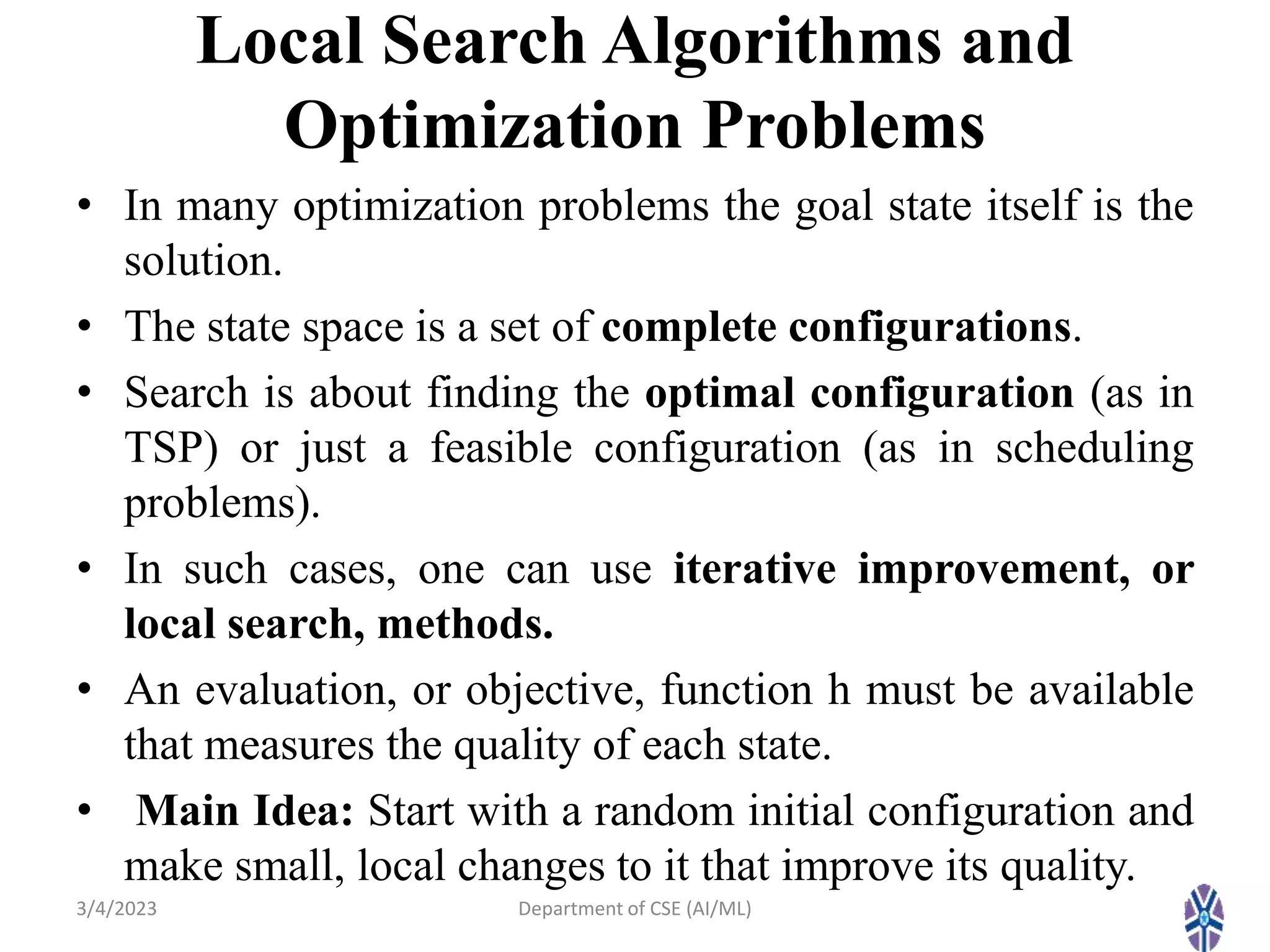
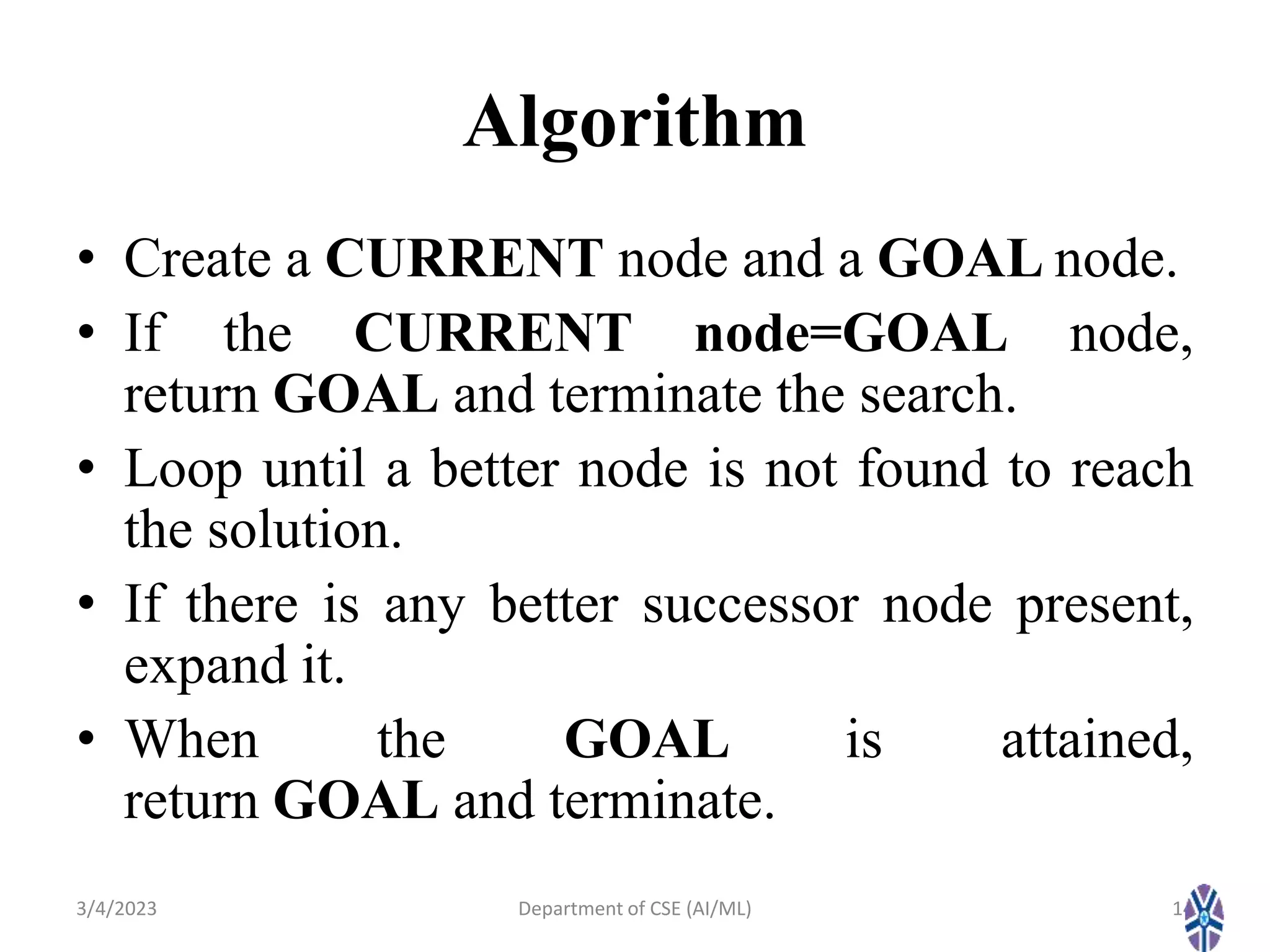
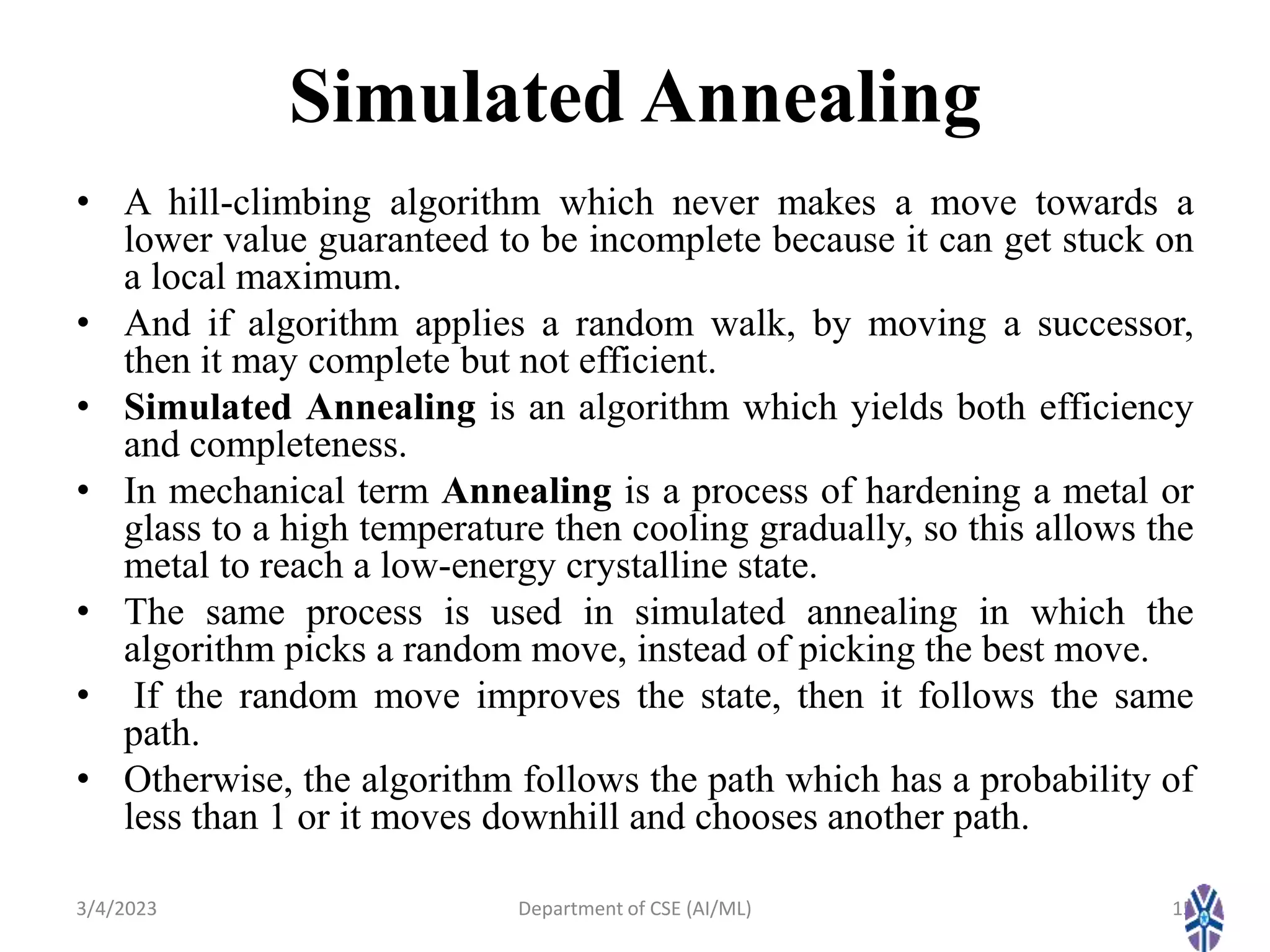
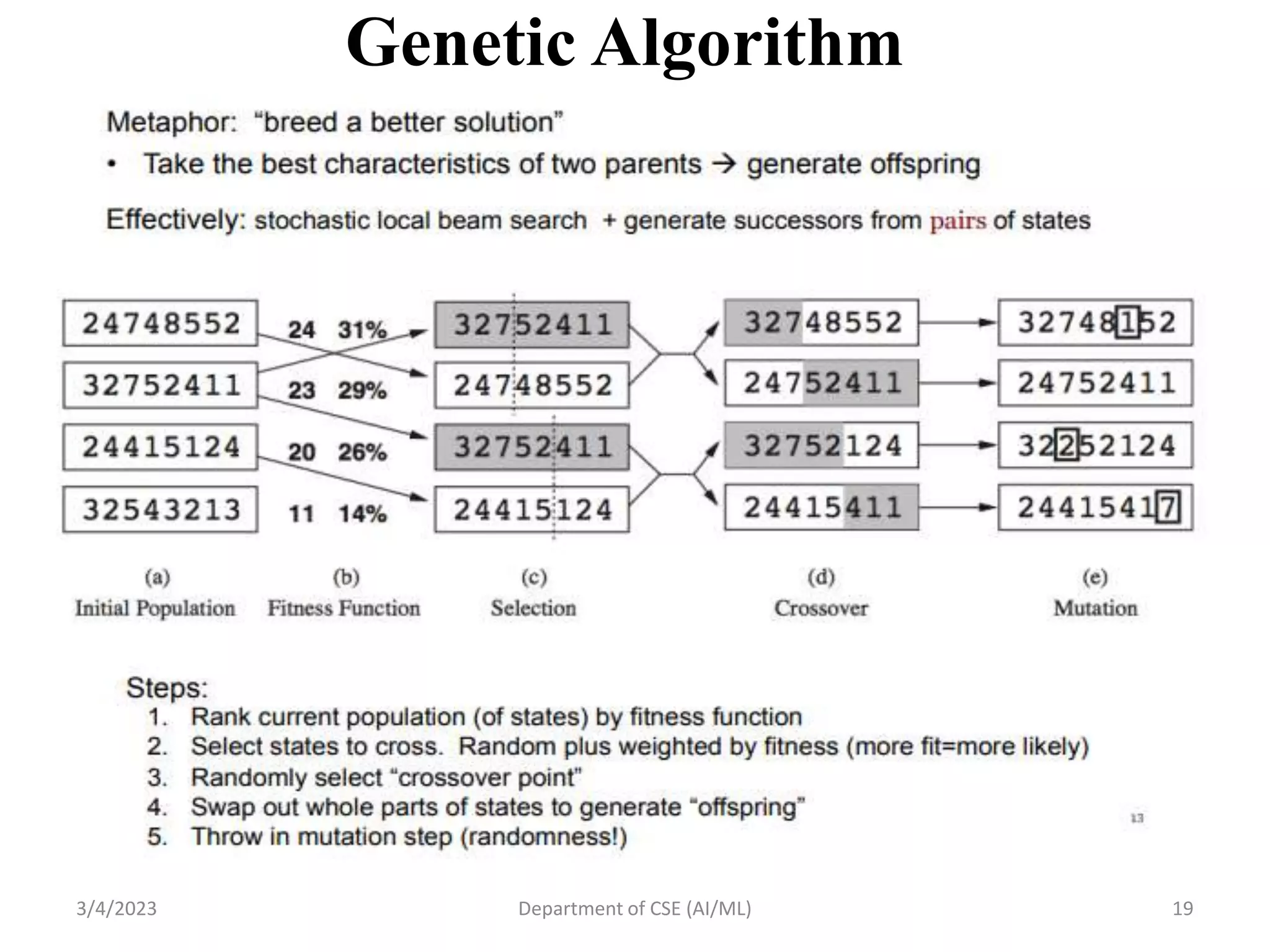
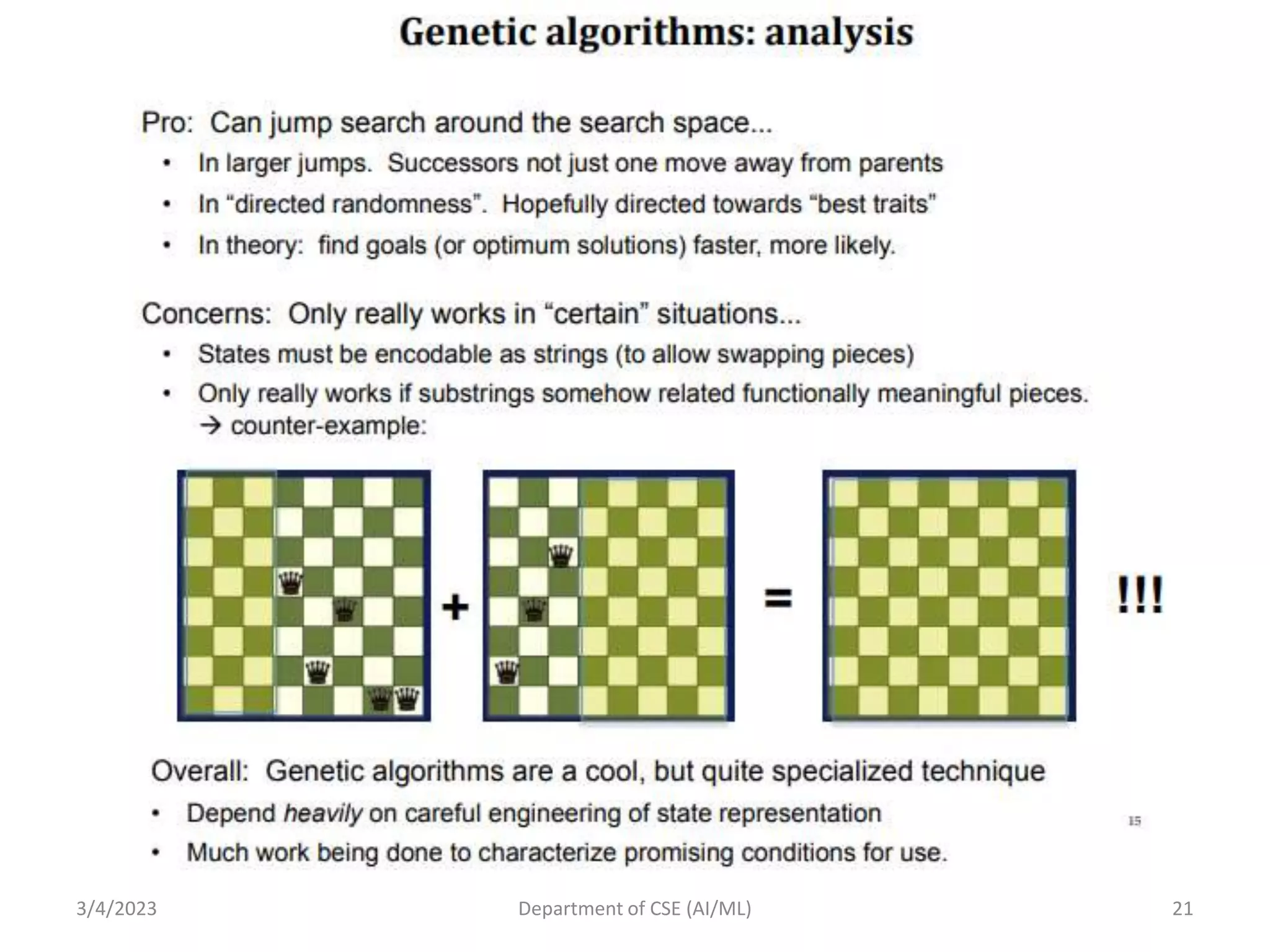
- It describes local search algorithms like hill climbing, simulated annealing, and genetic algorithms that are used for large search spaces and optimization problems.
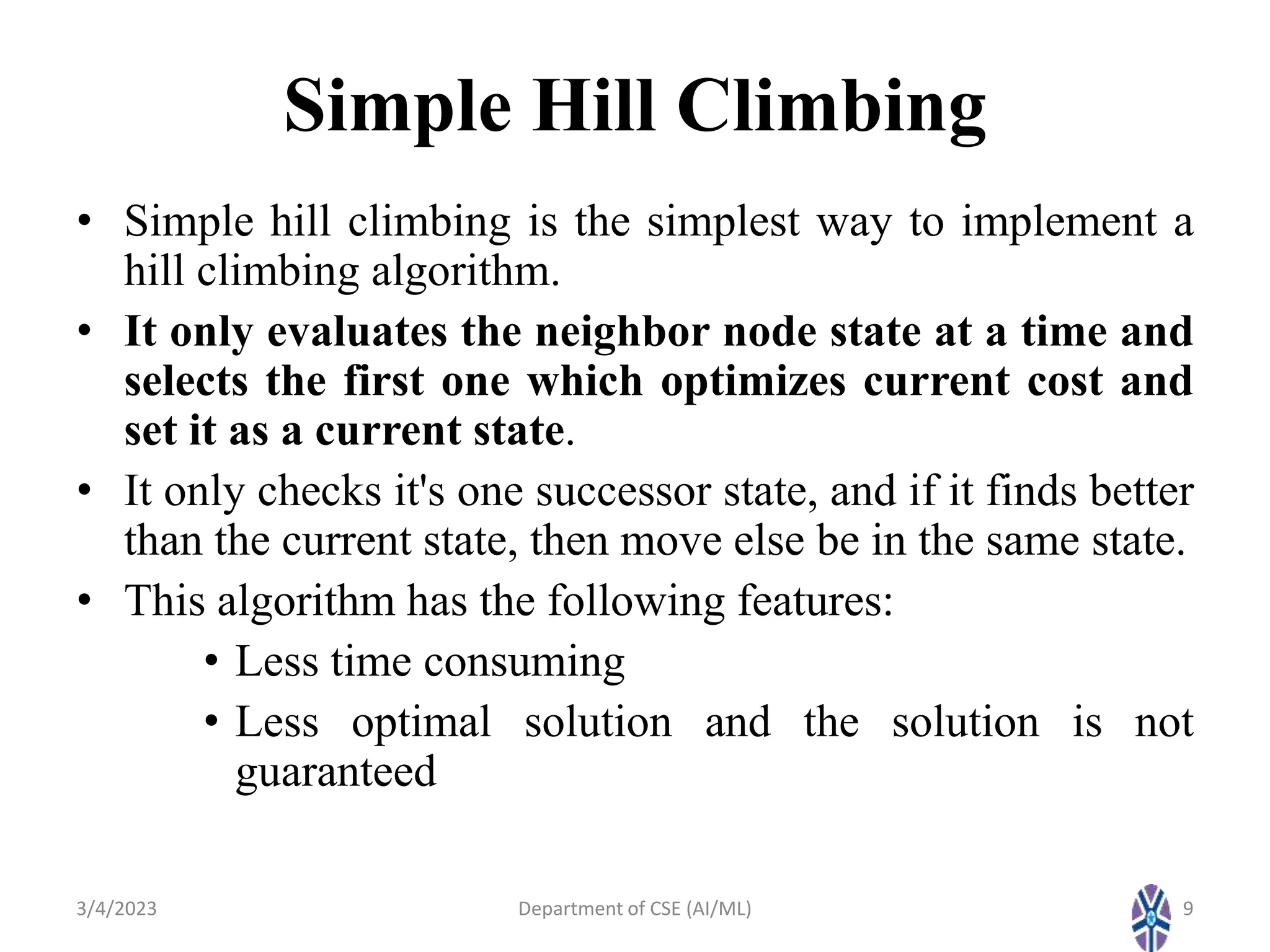
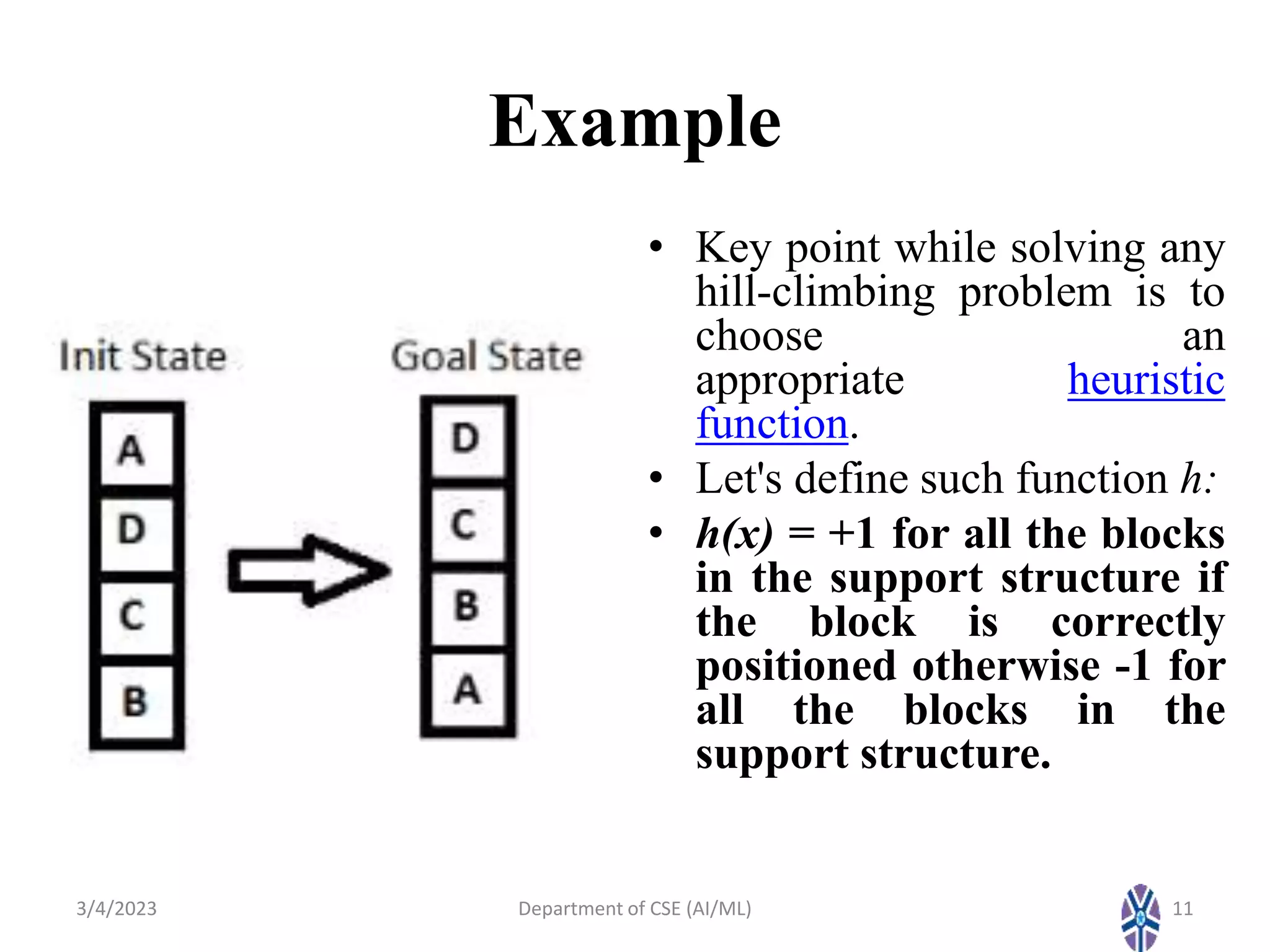
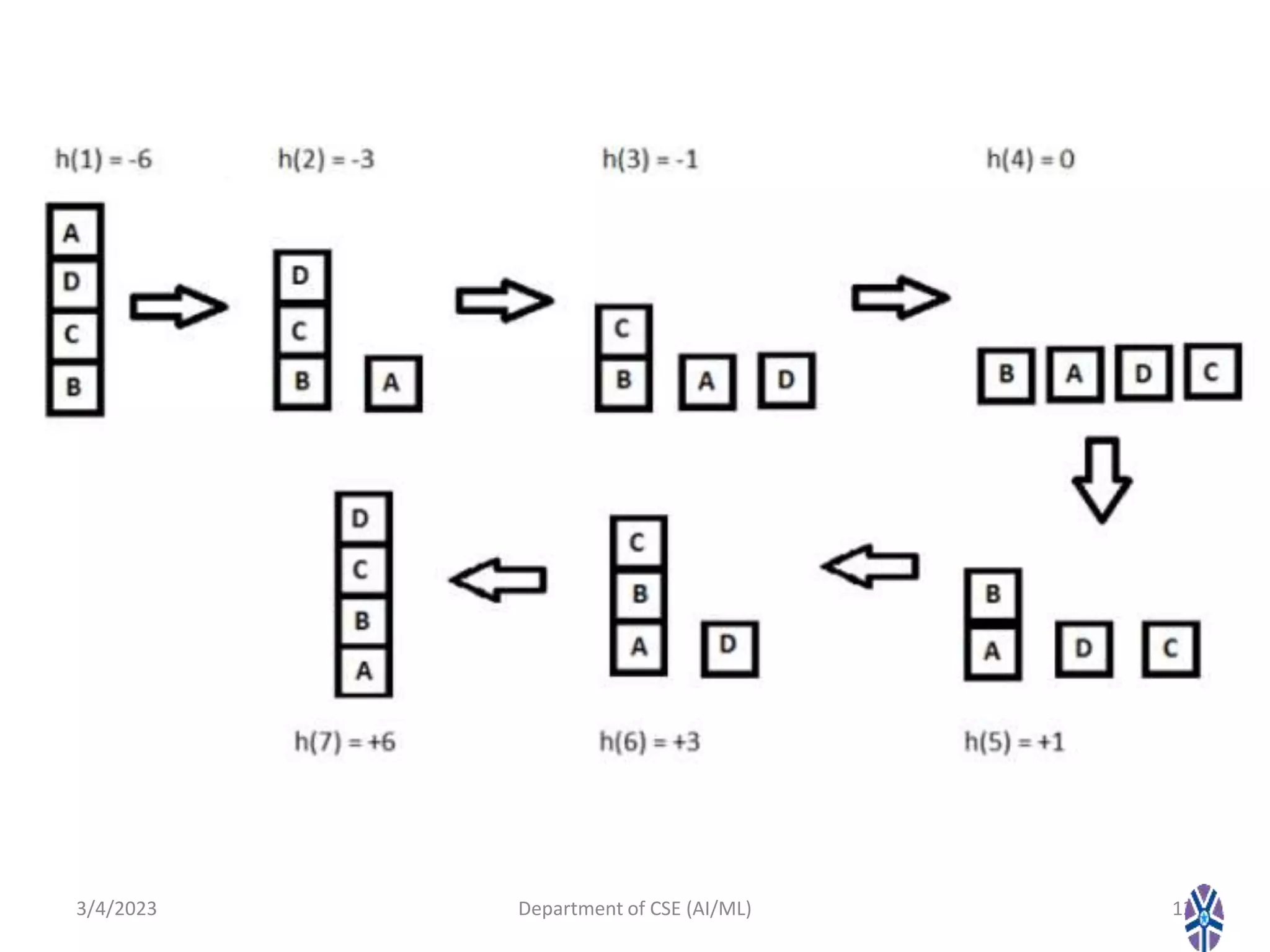
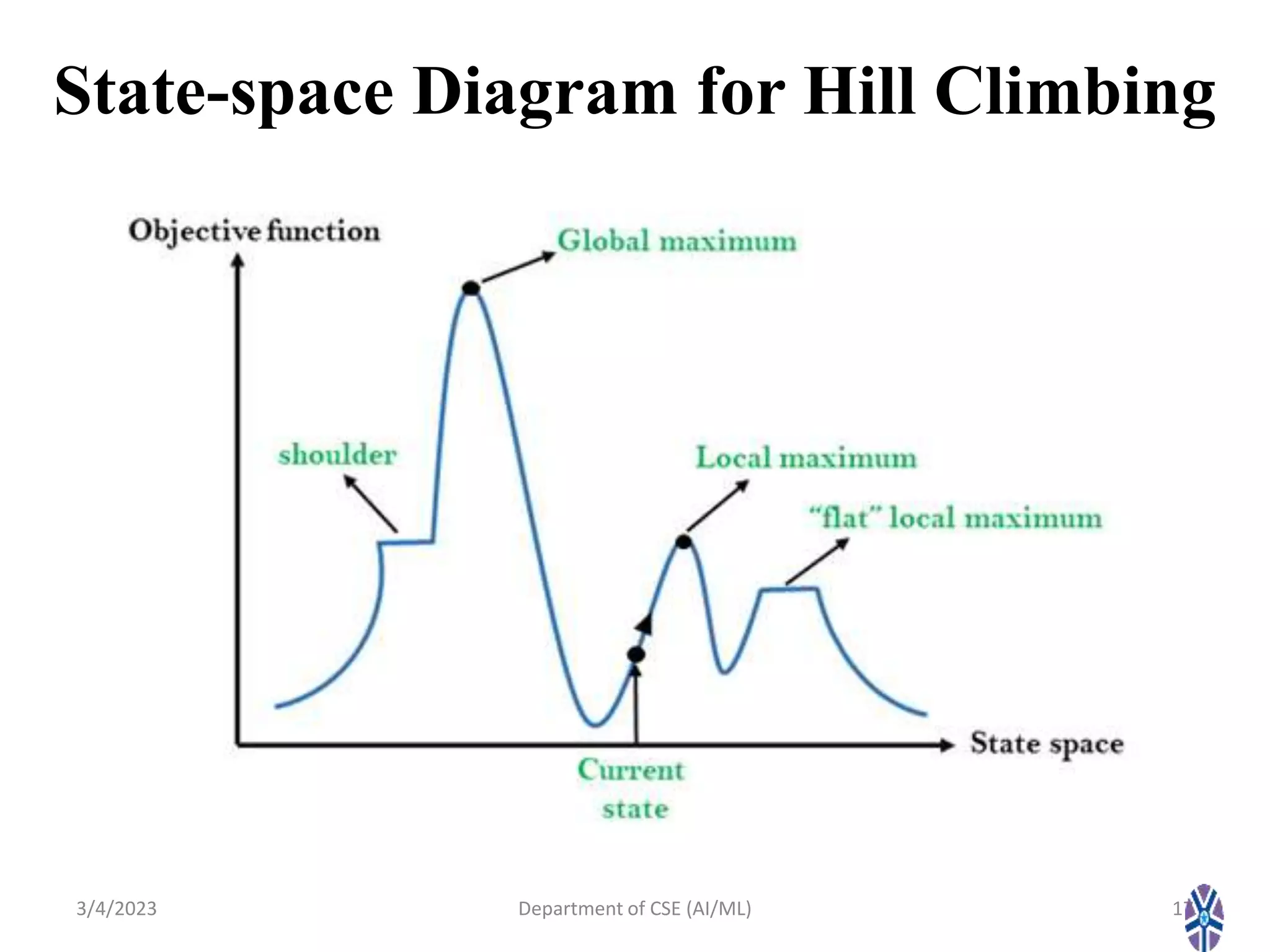
- Various hill climbing techniques - simple, steepest ascent, stochastic, and random restart hill climbing - are explained along with state space diagrams and concepts like local maxima.
- The next session will cover local search in continuous spaces.