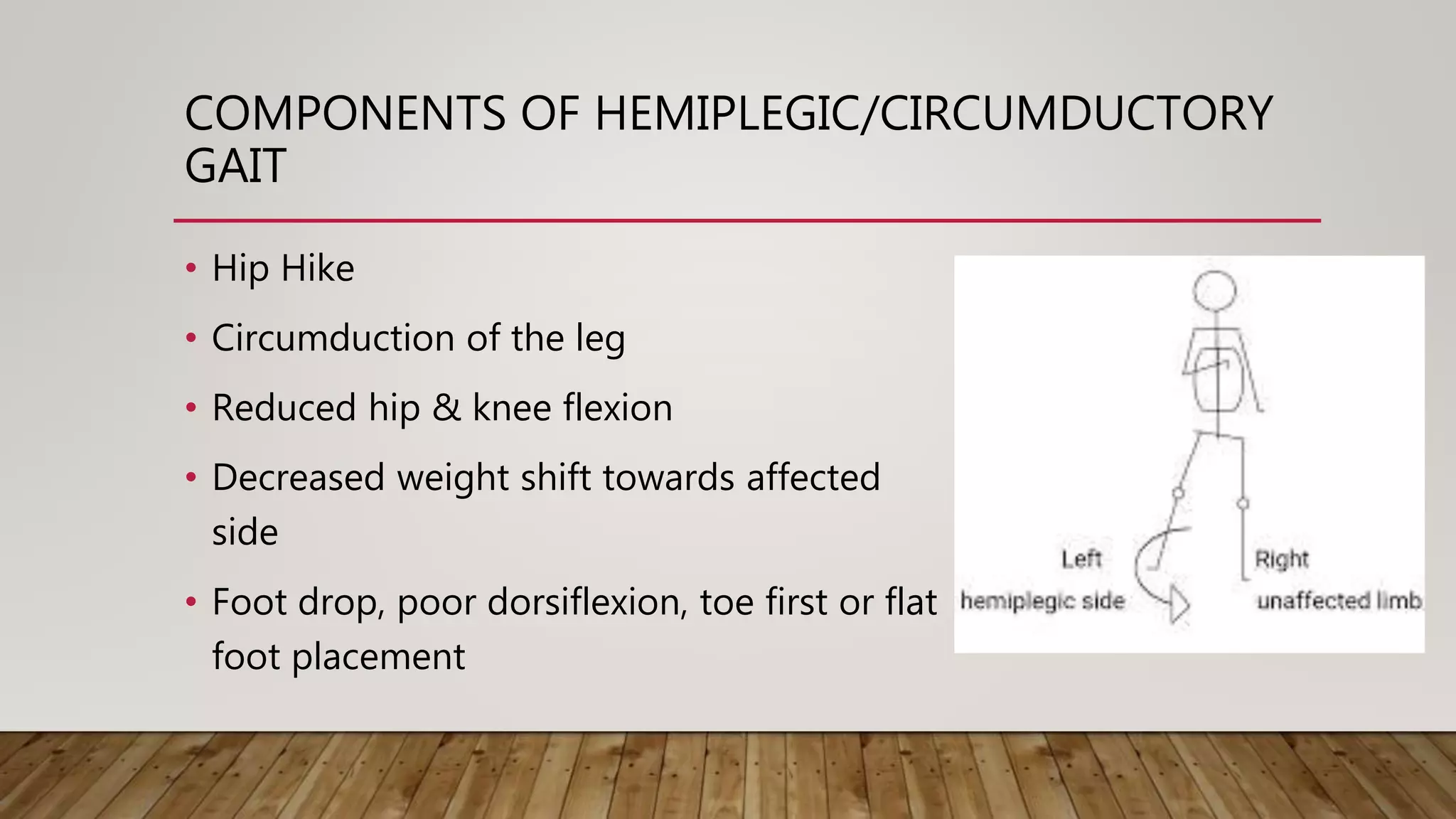
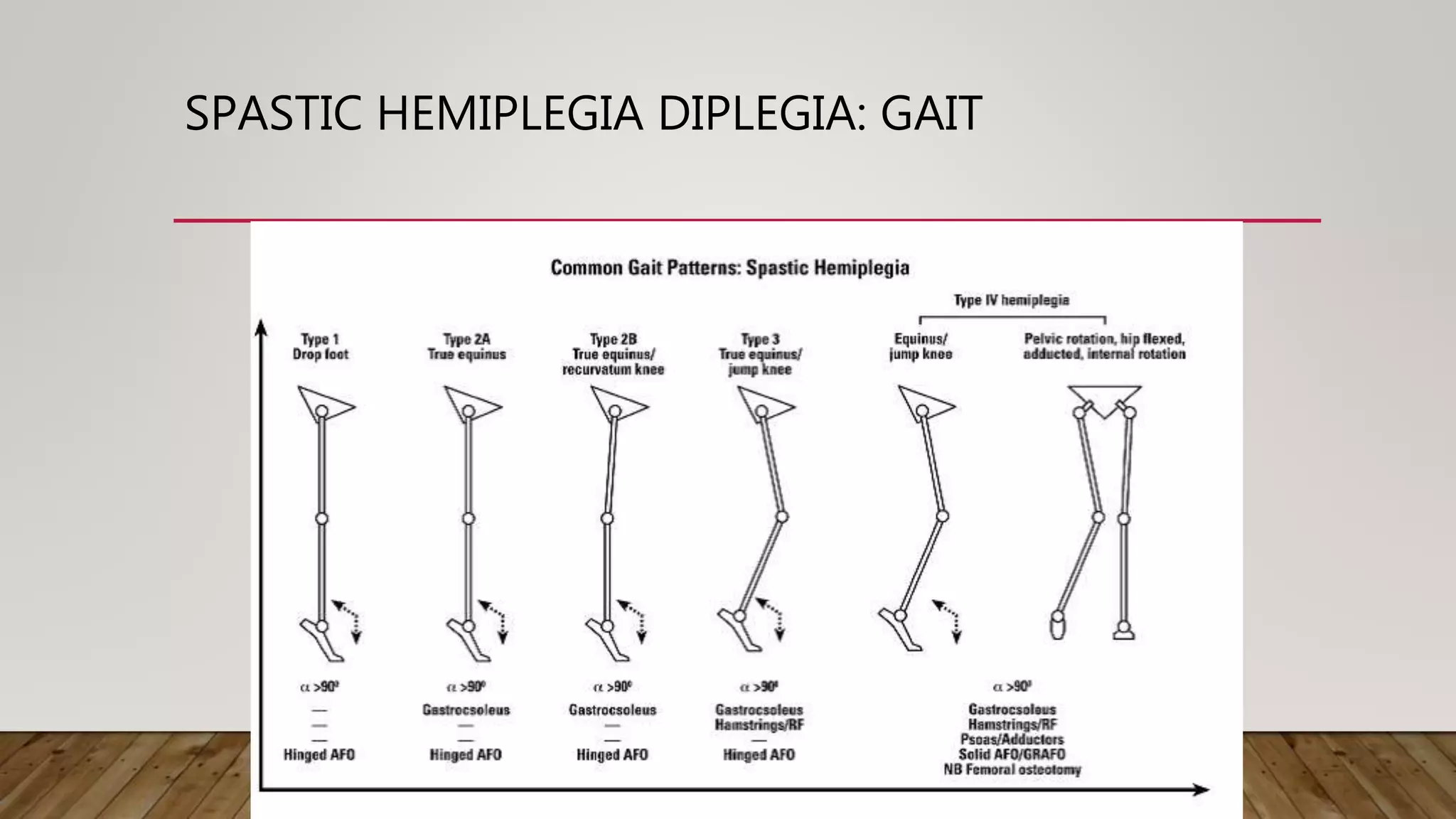
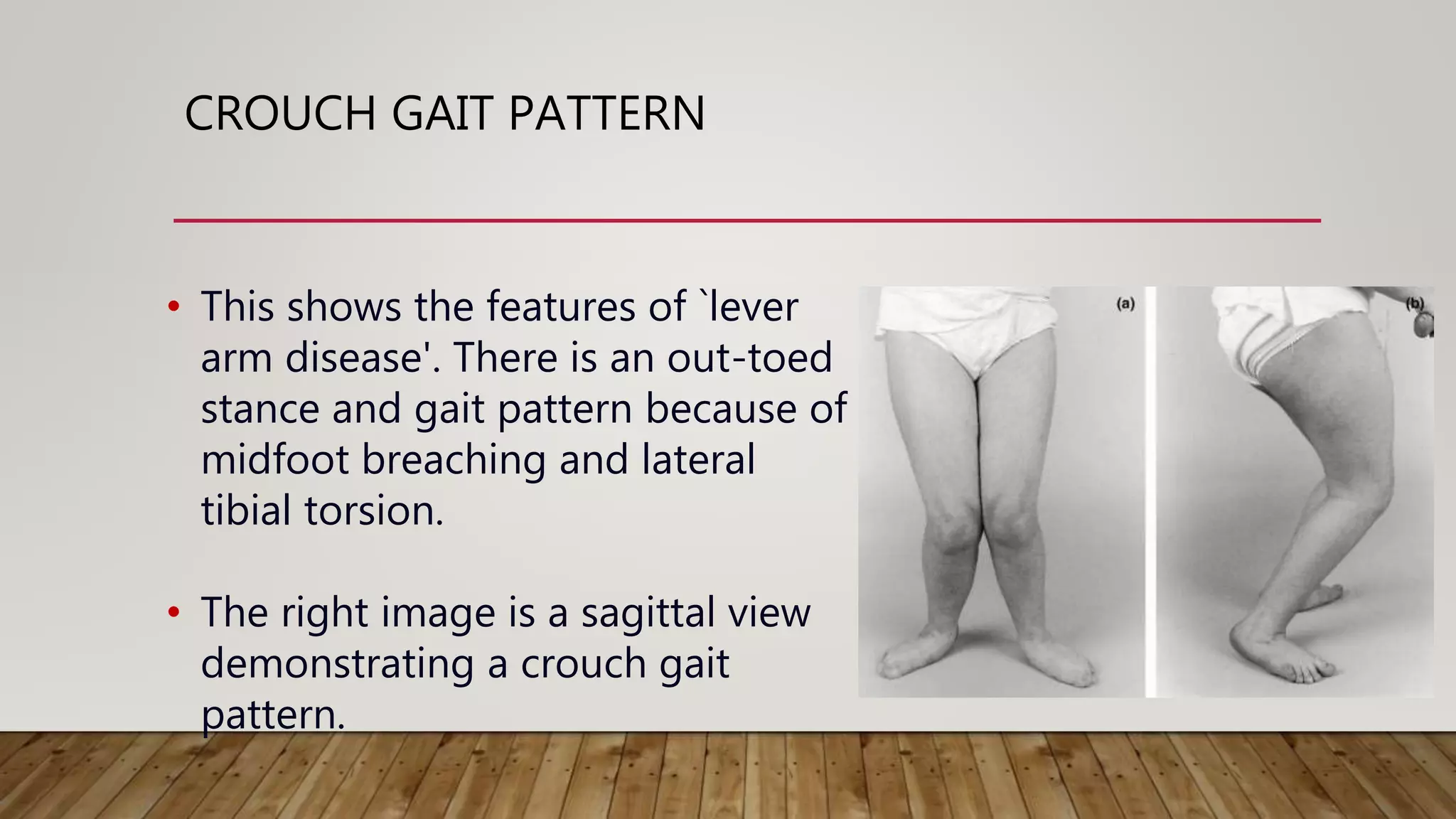
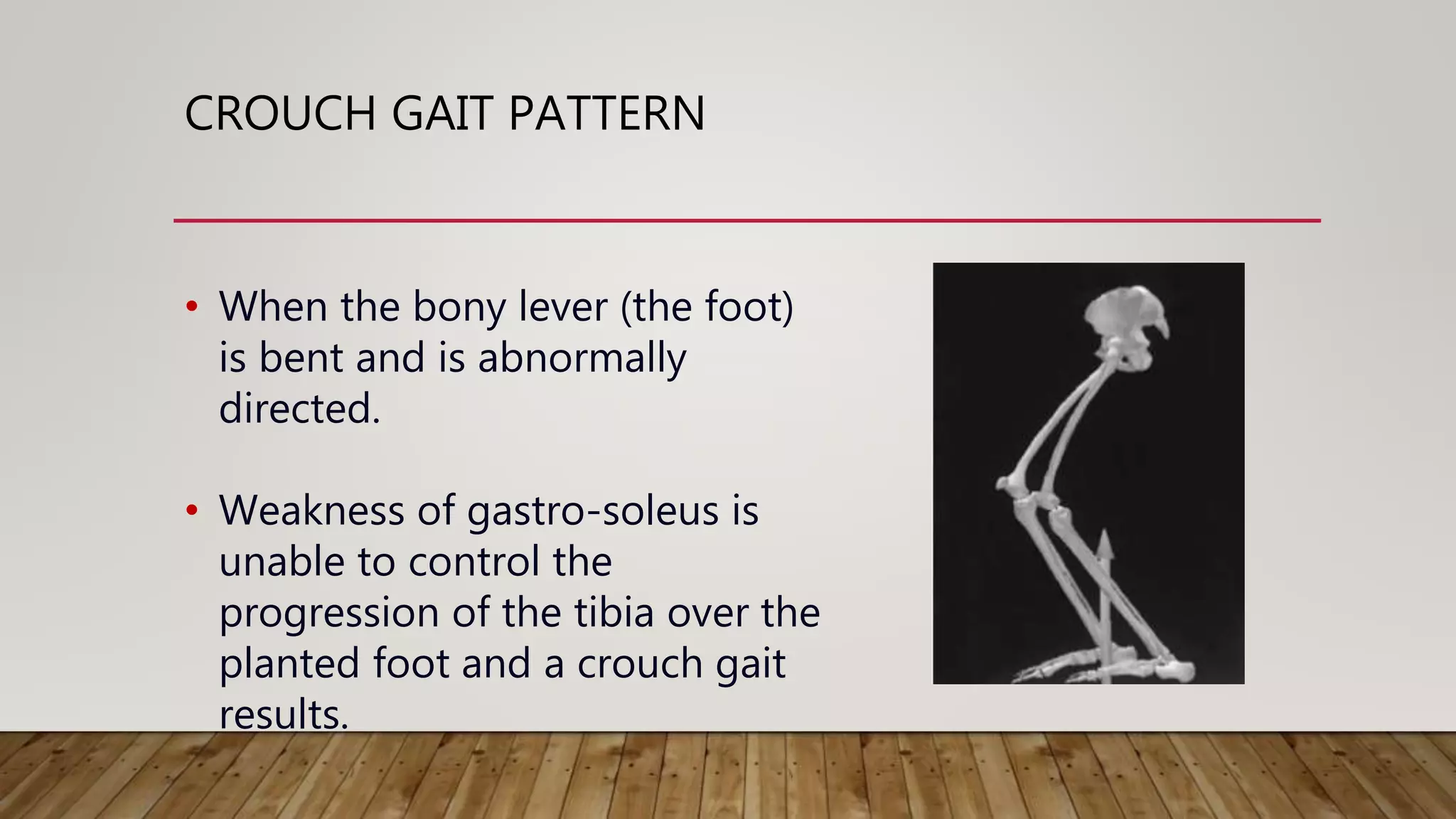
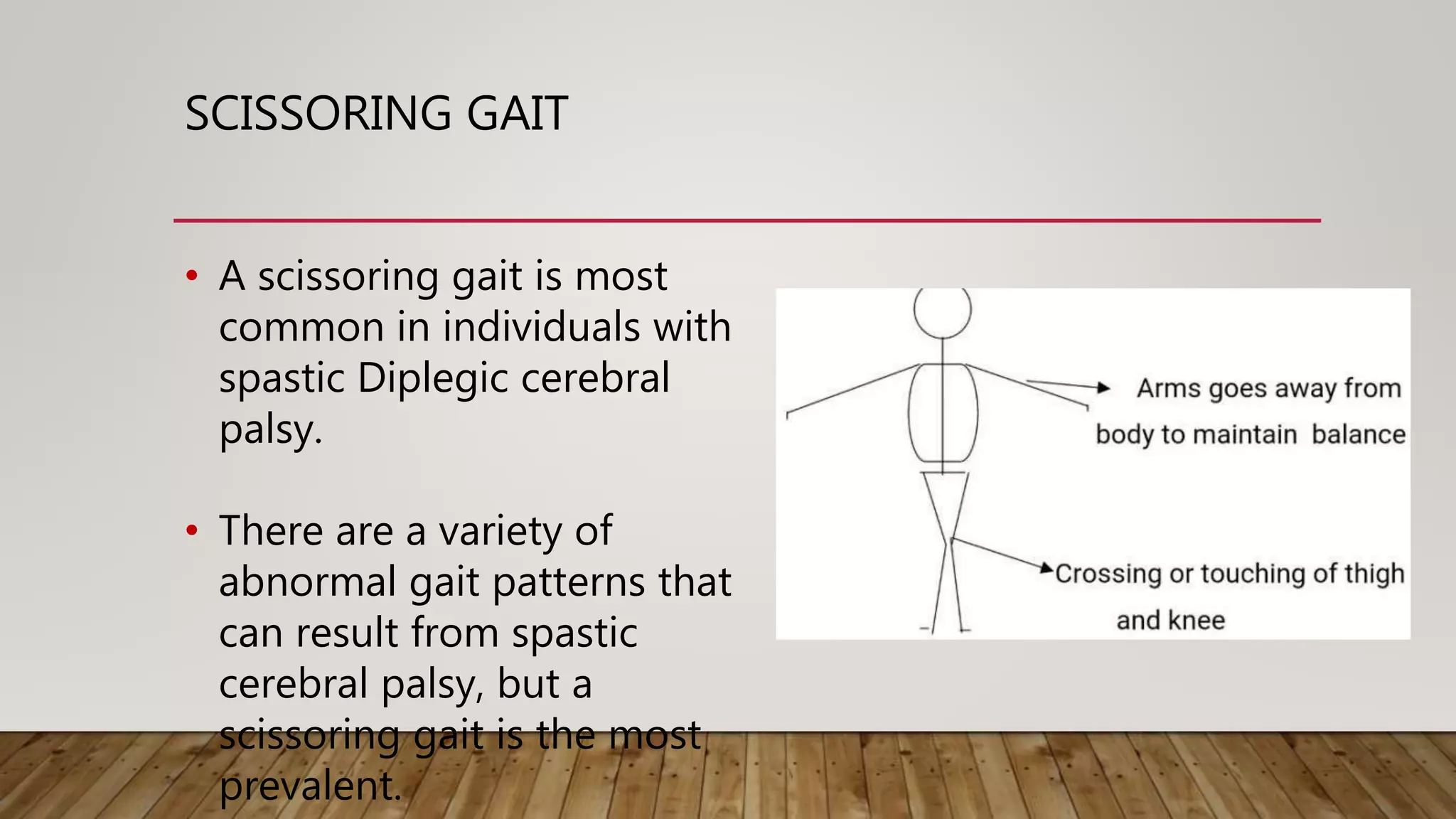
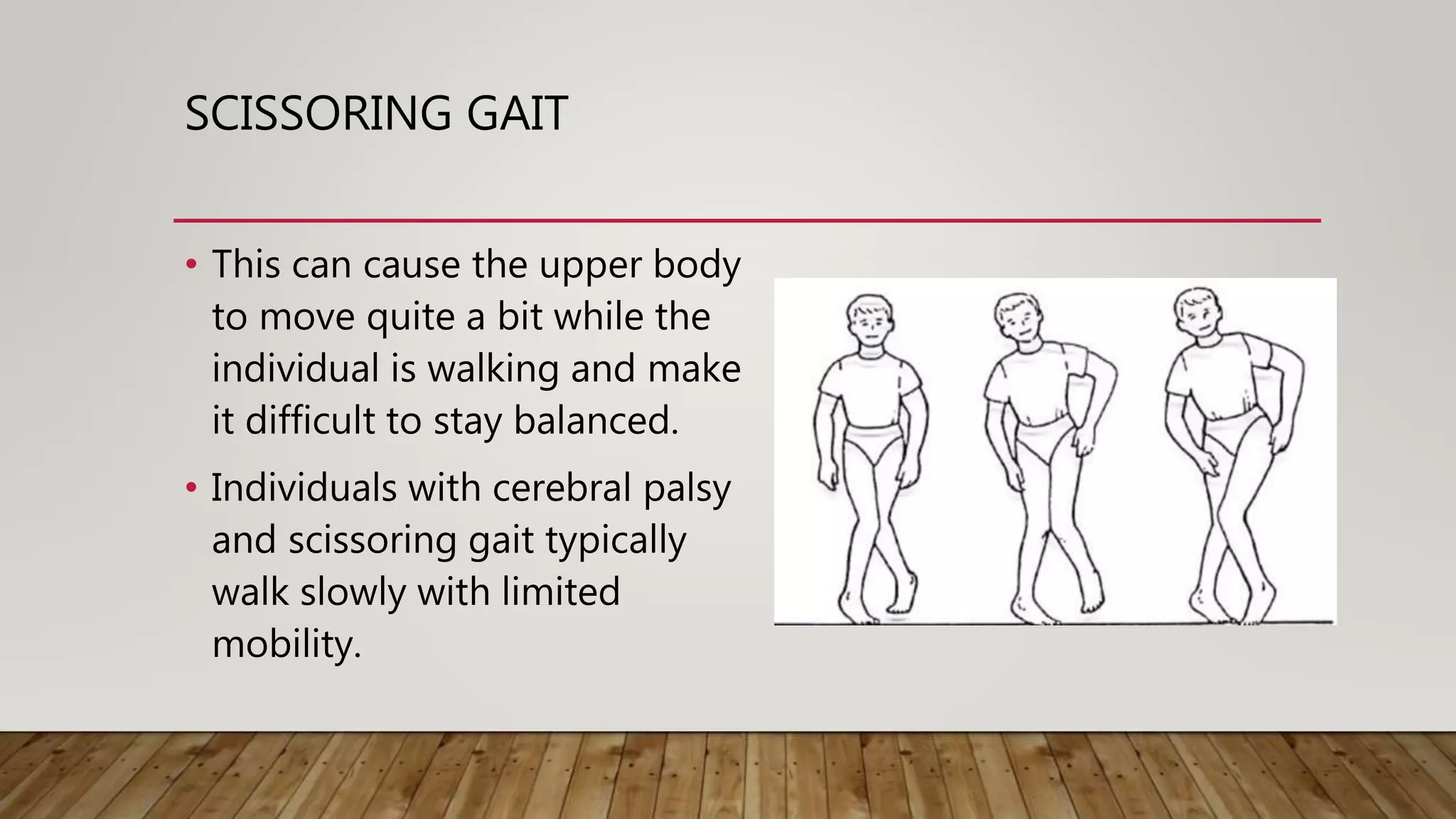
This document discusses neurological gait and gait rehabilitation. It begins by defining normal gait and describing common pathological gaits that can result from neurological conditions, including hemiplegic, spastic diplegic, Parkinsonian, myopathic, and ataxic gaits. Specific characteristics and management approaches are described for each type. Rehabilitation approaches covered include traditional gait training exercises, use of assistive devices, high-tech options like body-weight supported treadmill training and electrical stimulation, as well as strength and balance training. Surgical management is also briefly discussed for some conditions.