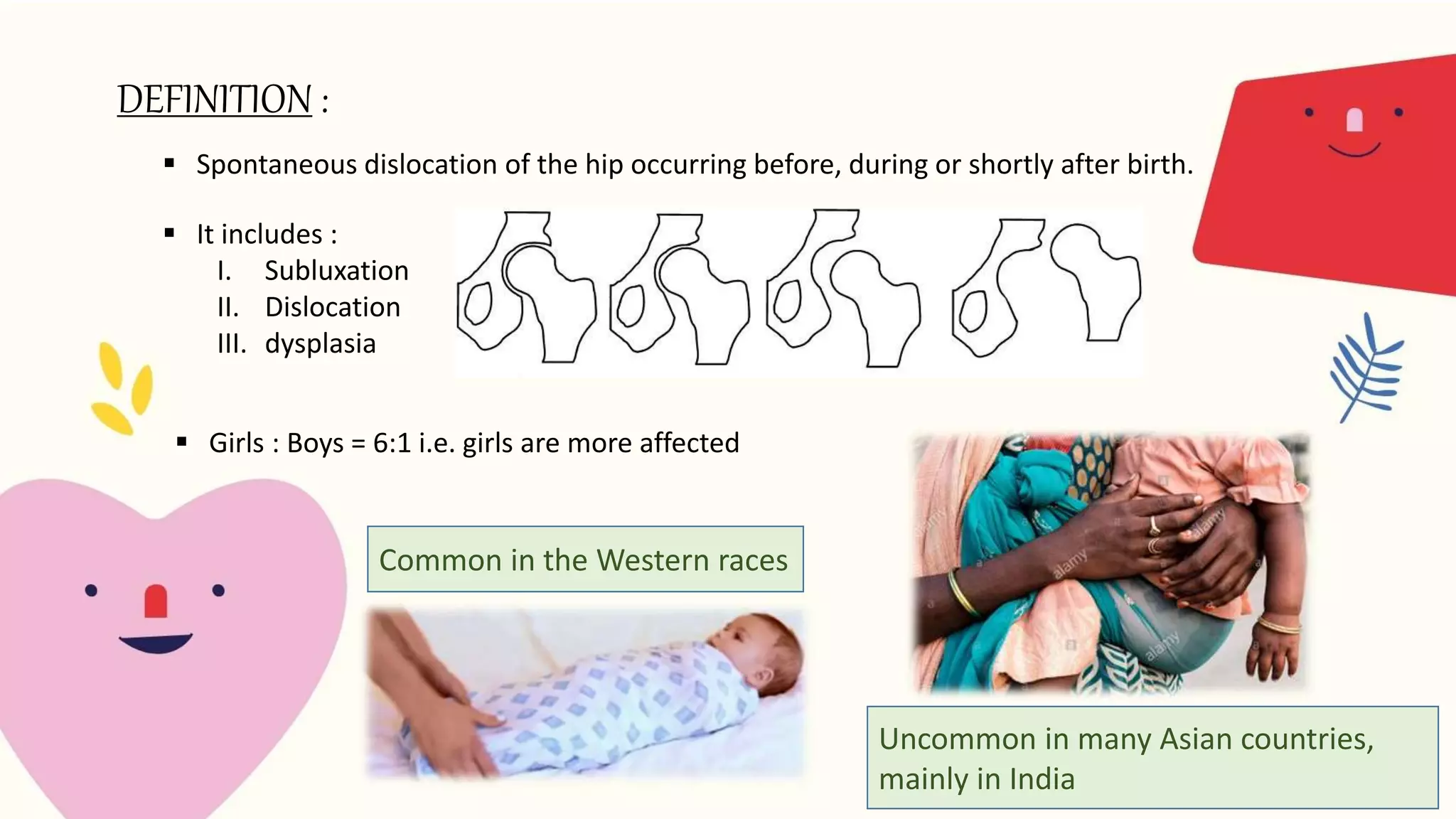
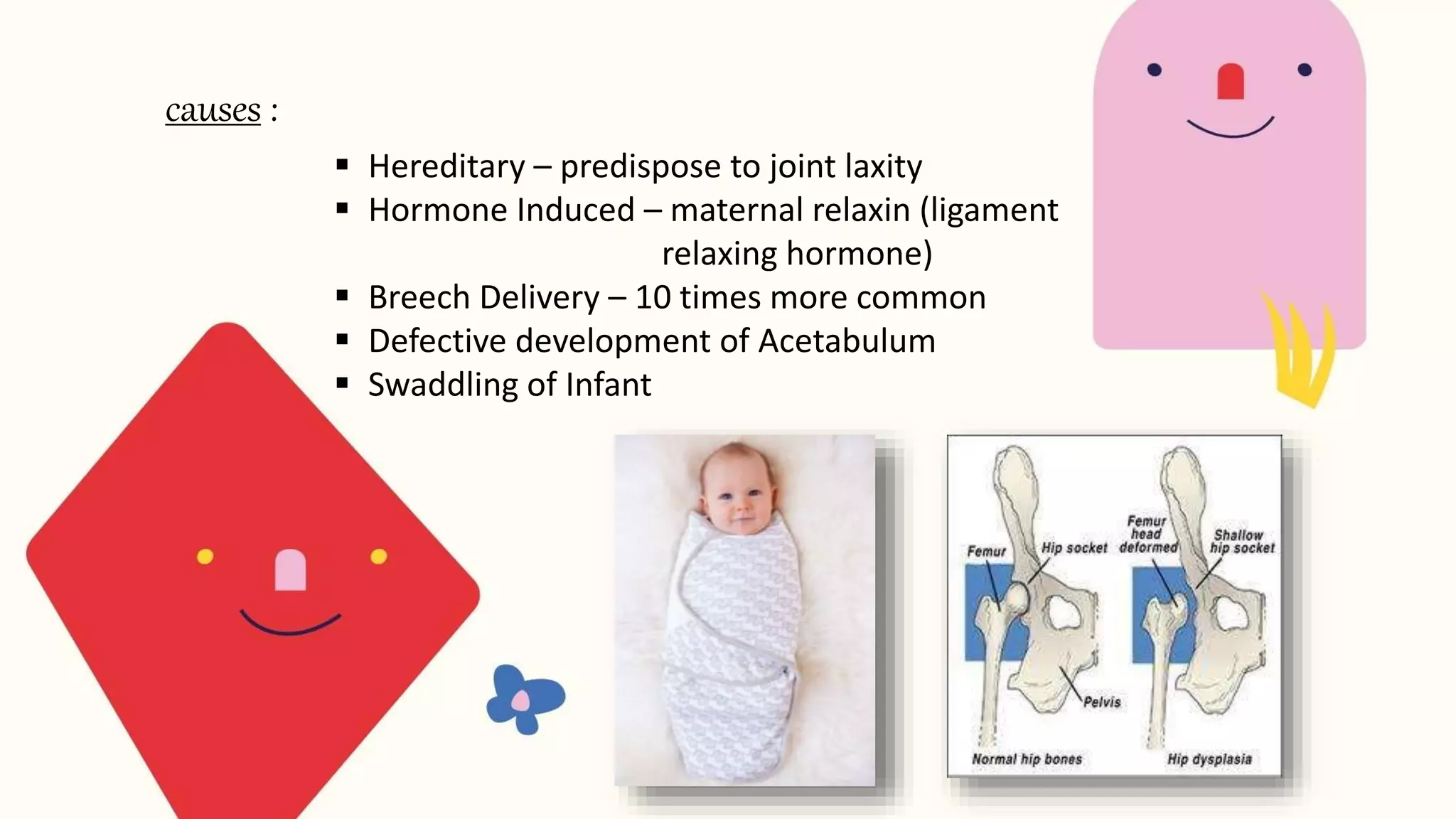
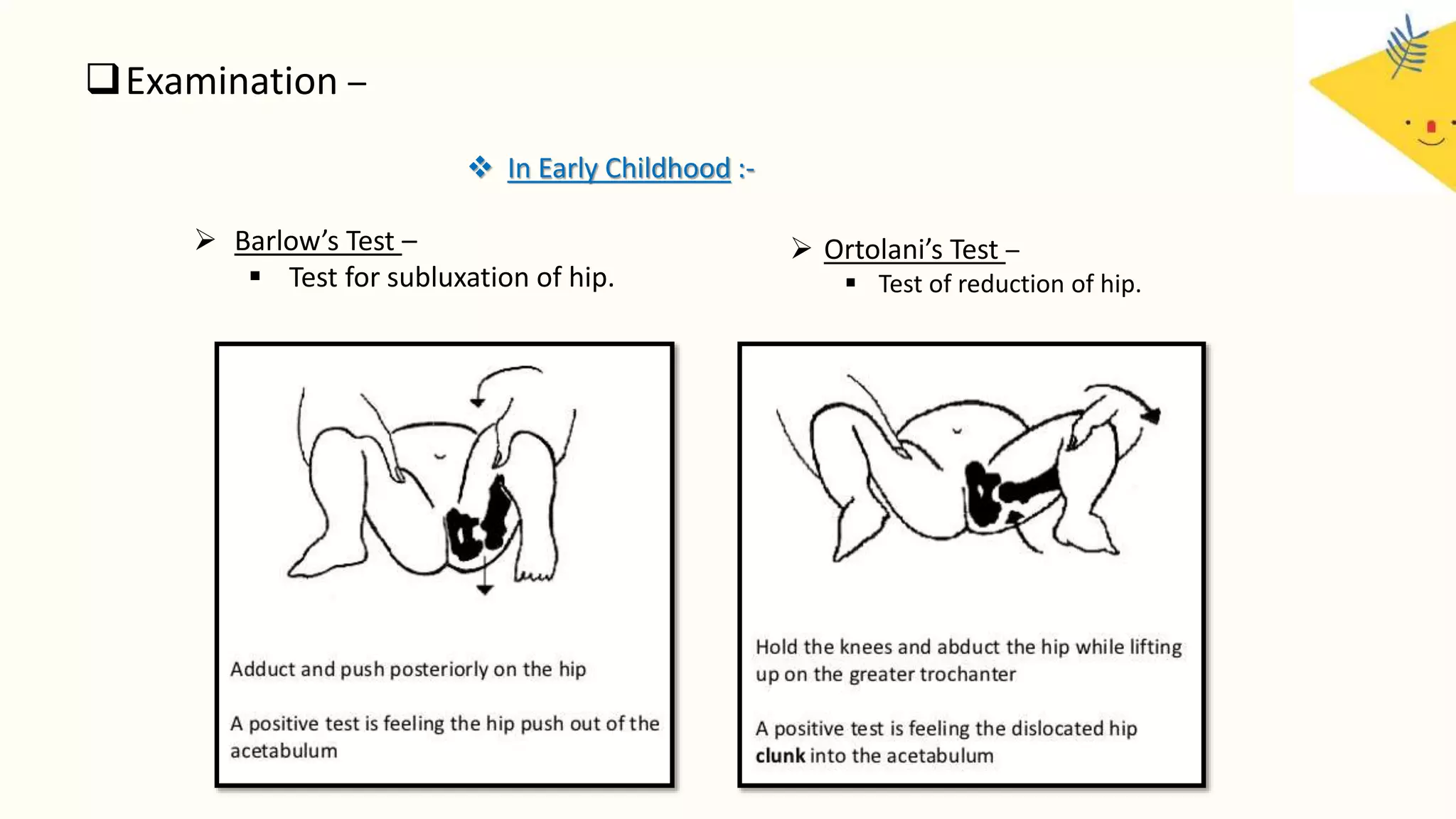
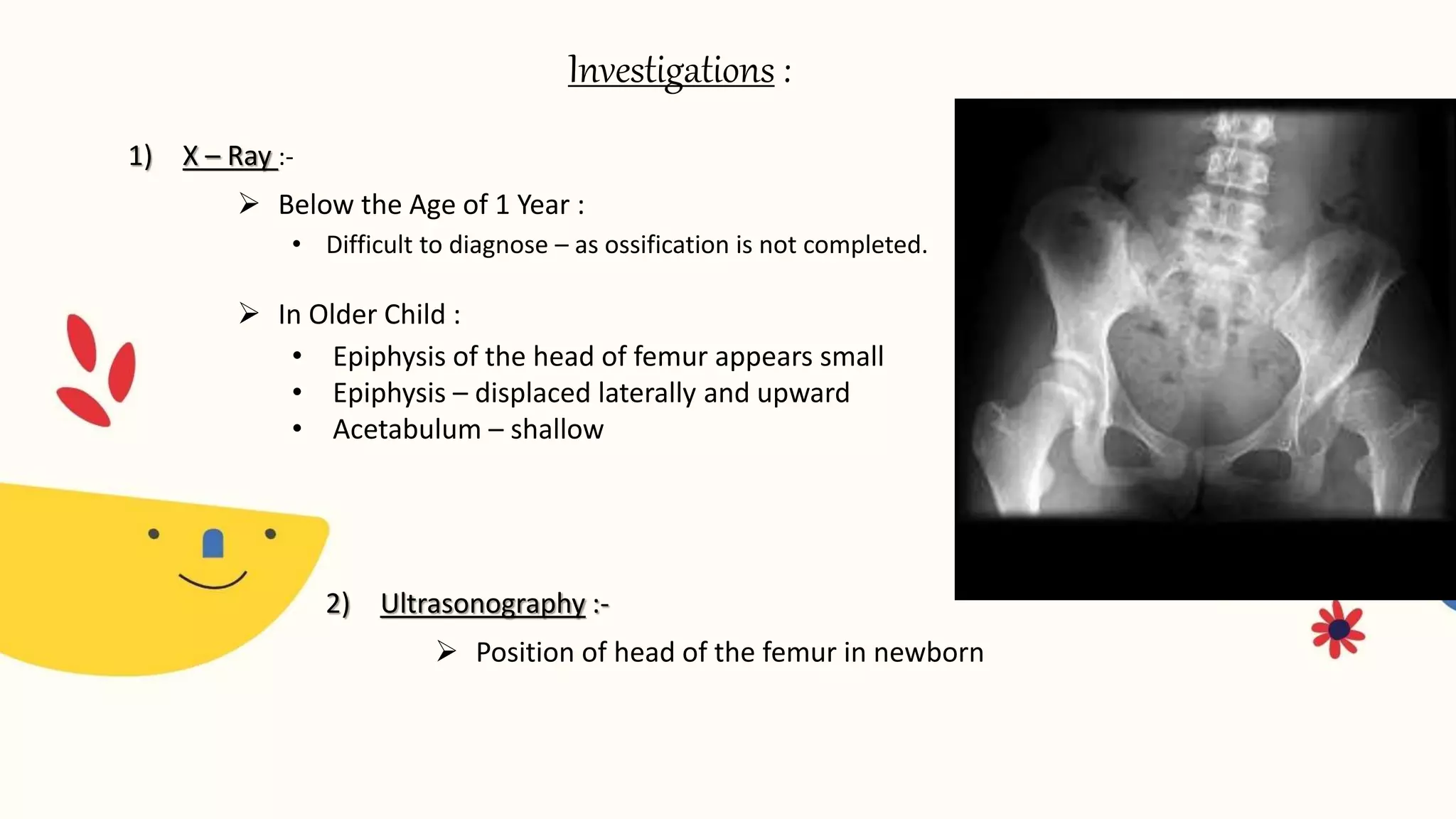
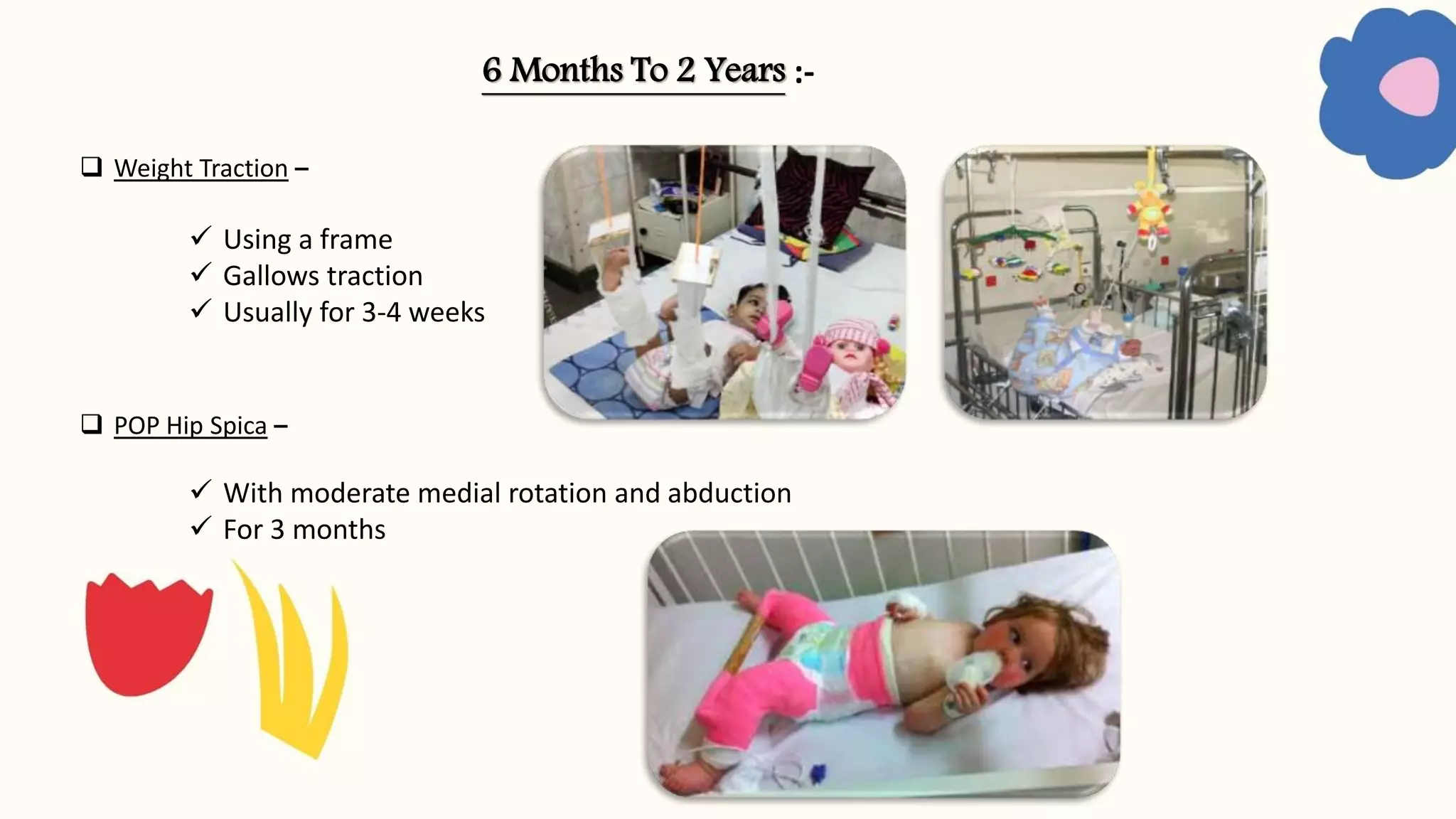
Congenital dislocation of the hip (CDH), also known as developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), is a condition where the femoral head is displaced from the acetabulum. It can occur before, during or after birth. Girls are more commonly affected than boys. Causes may include hereditary joint laxity, breech birth position, or defective acetabulum development. Treatment involves splinting or bracing in infants to encourage reduction, and may require surgery in older children if reduction does not occur. Physiotherapy focuses on maintaining reduction, improving range of motion and strengthening muscles.