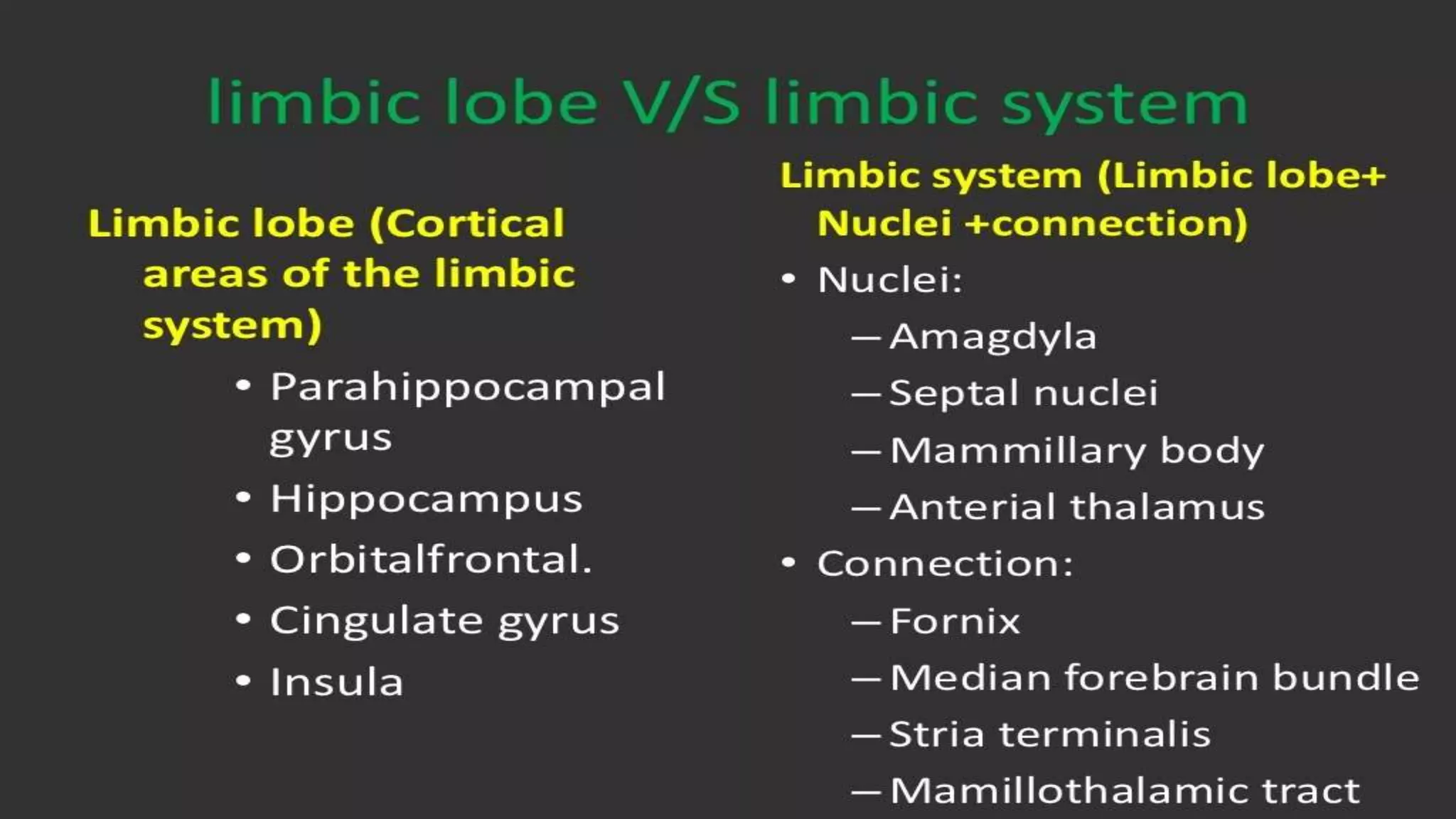
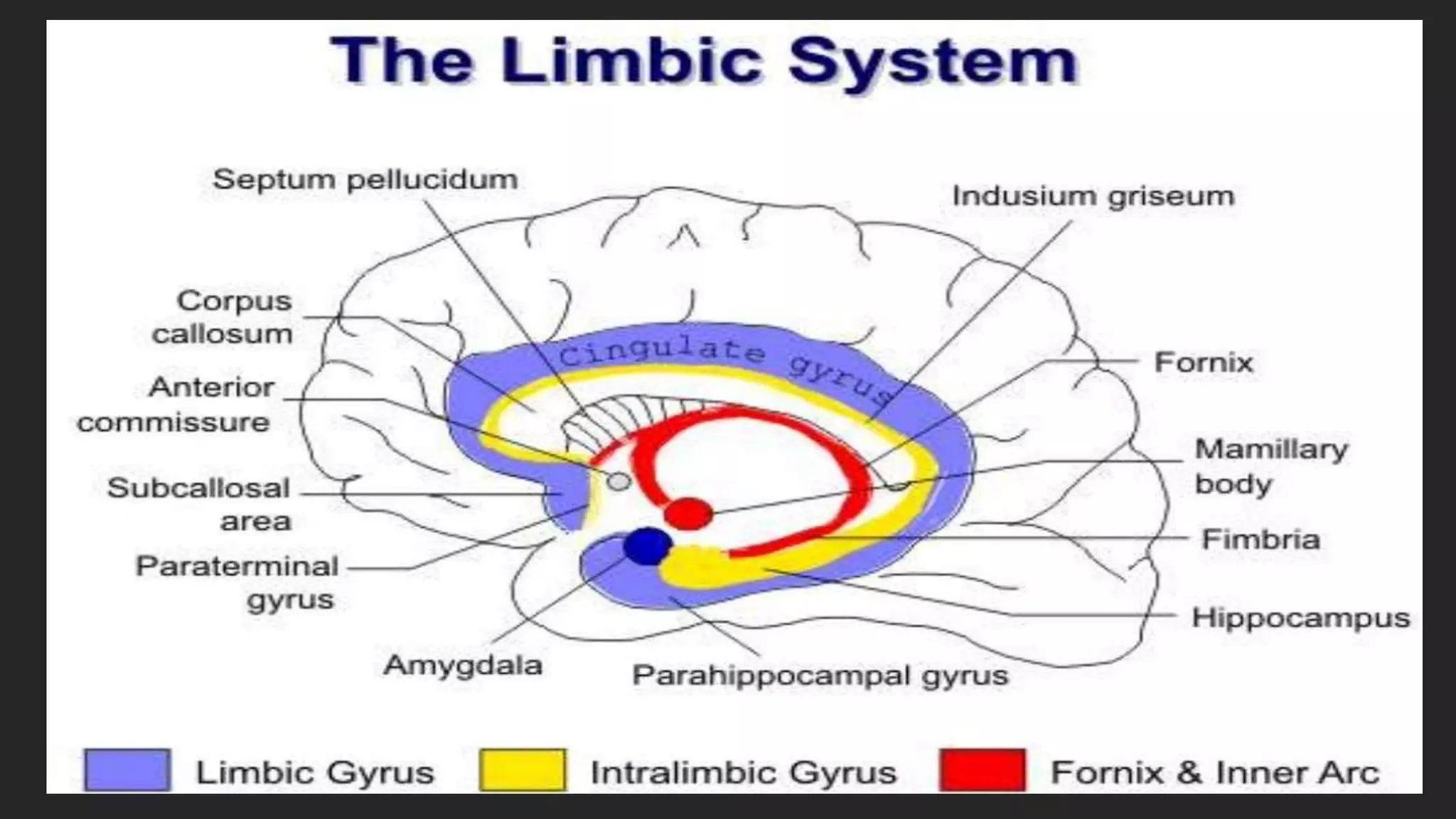
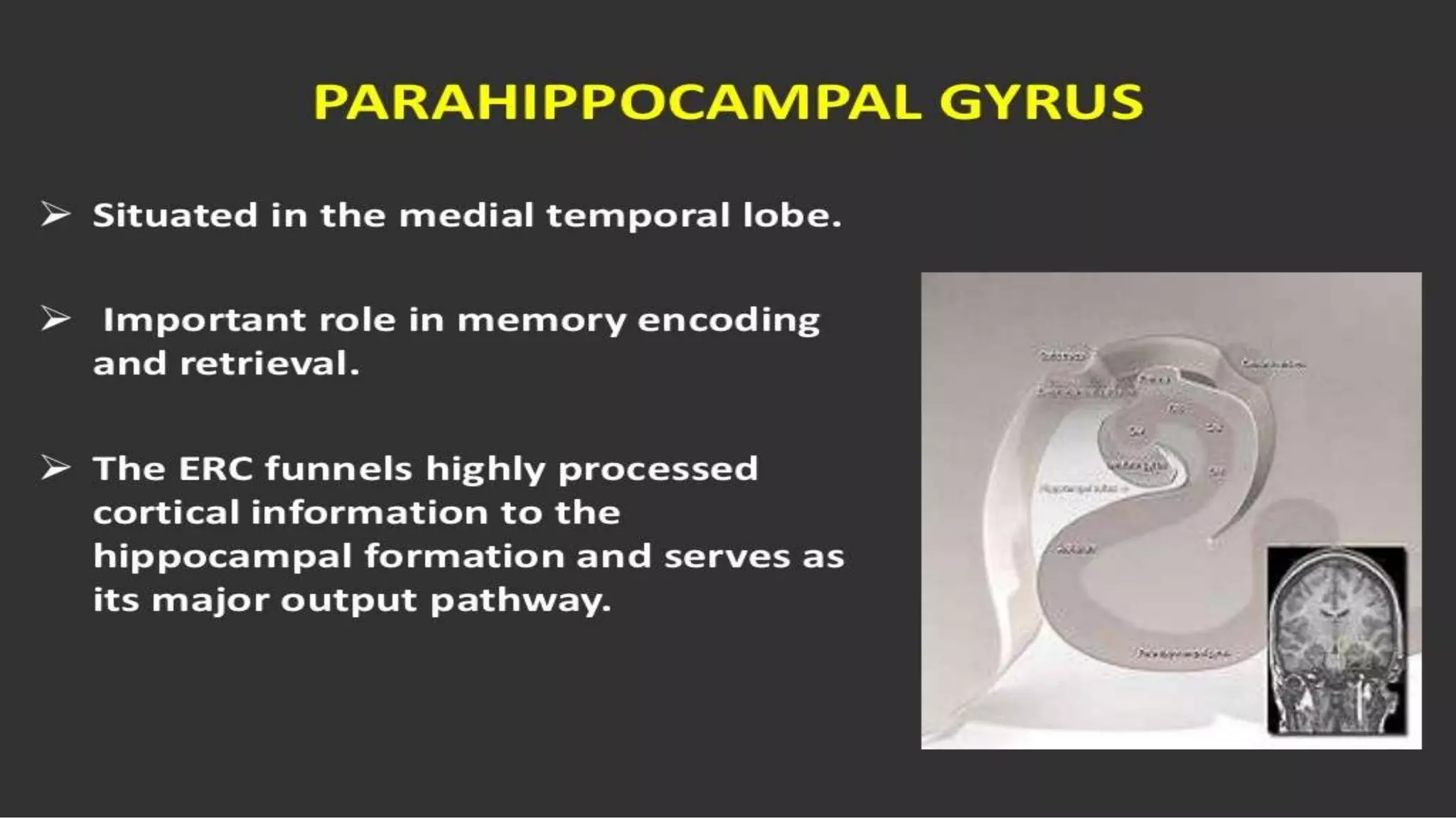
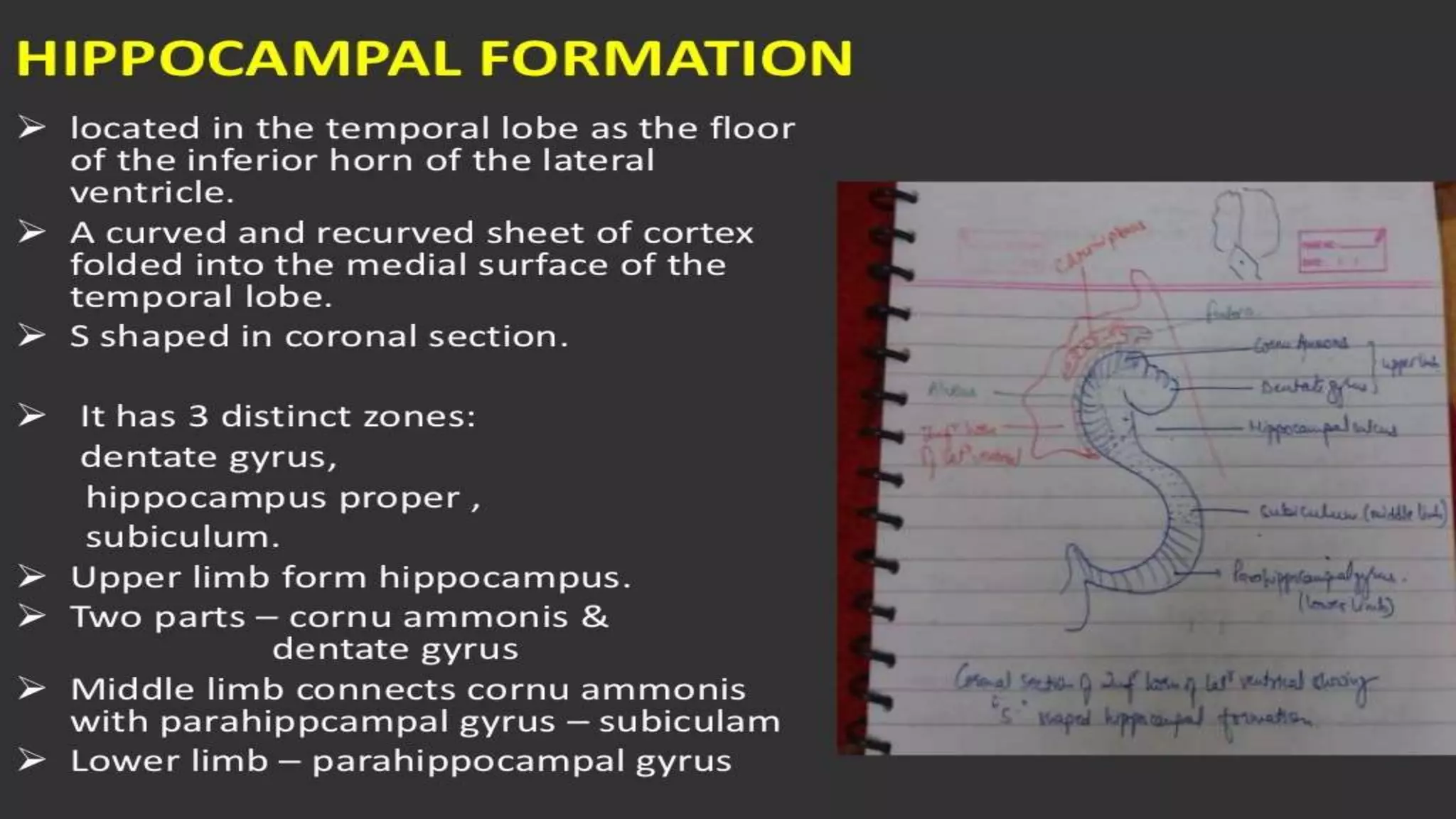
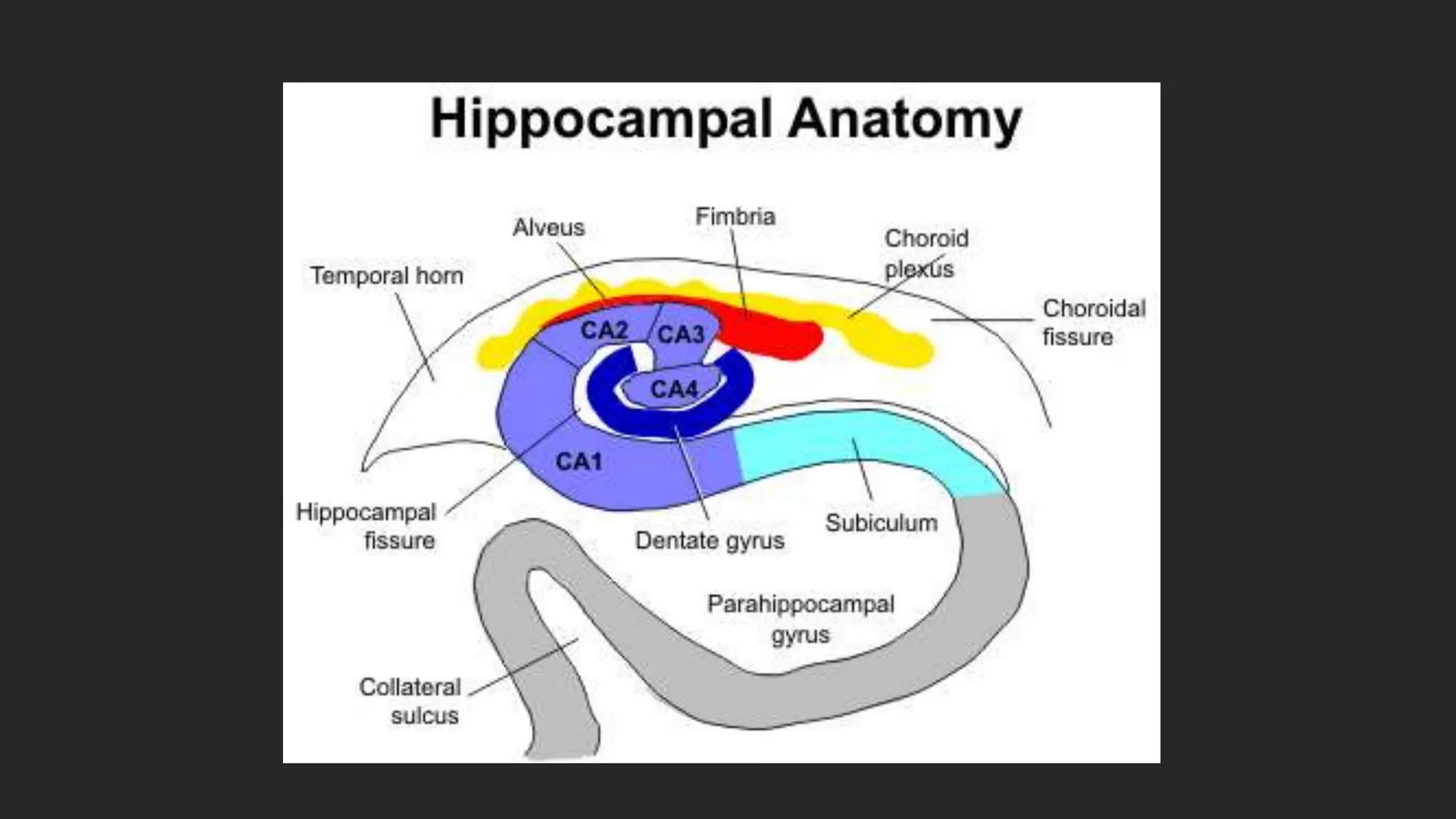
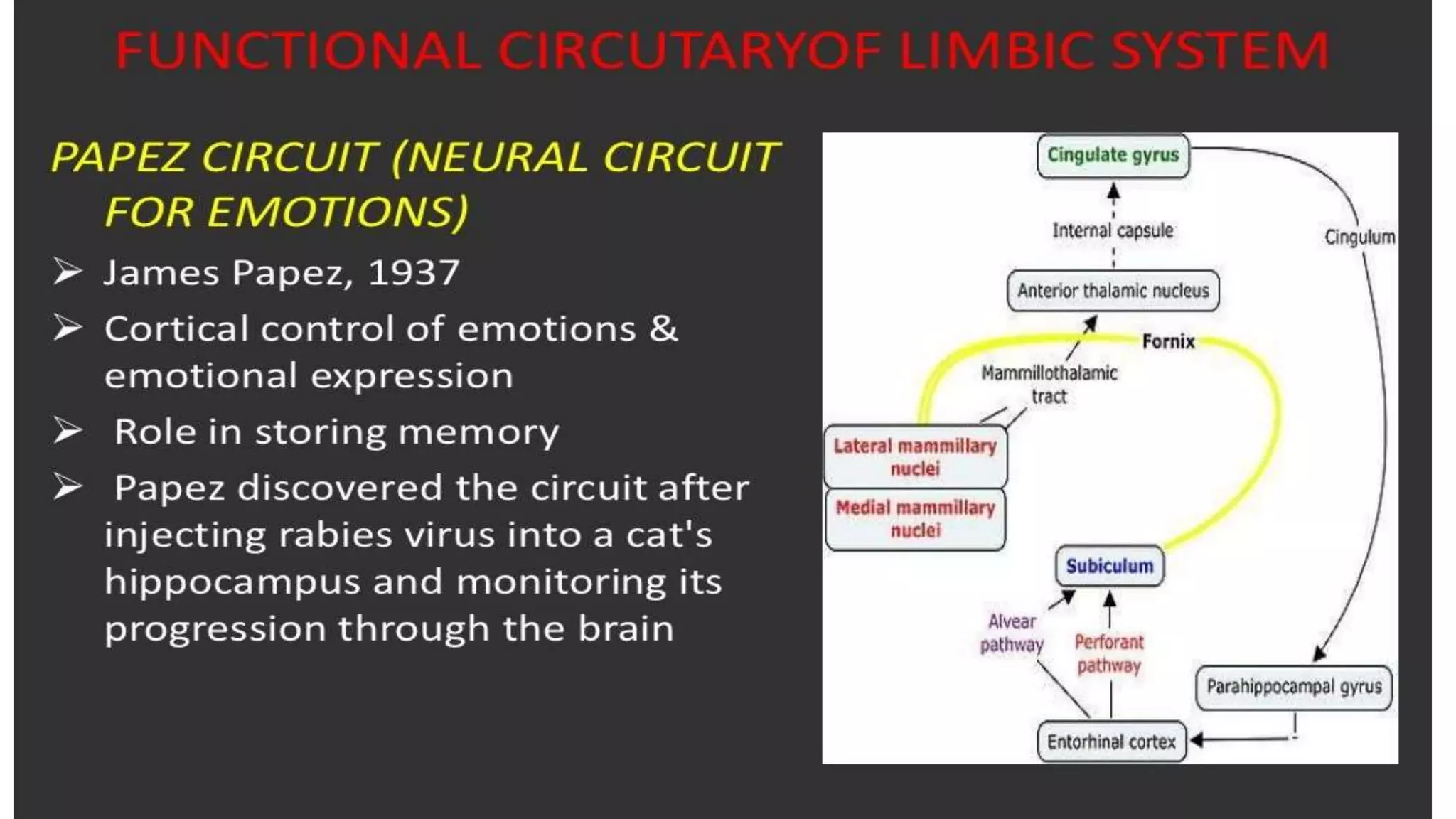
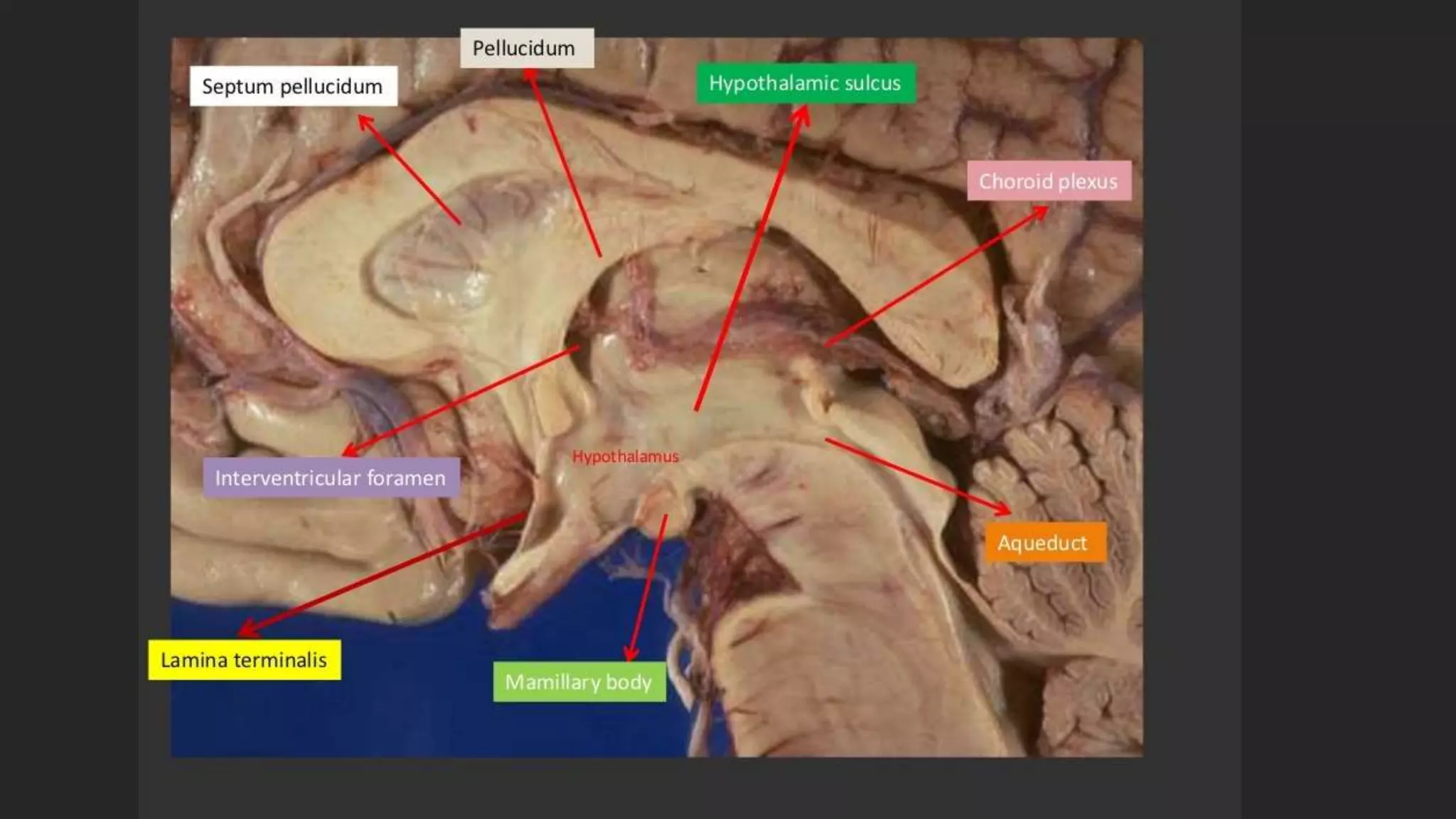
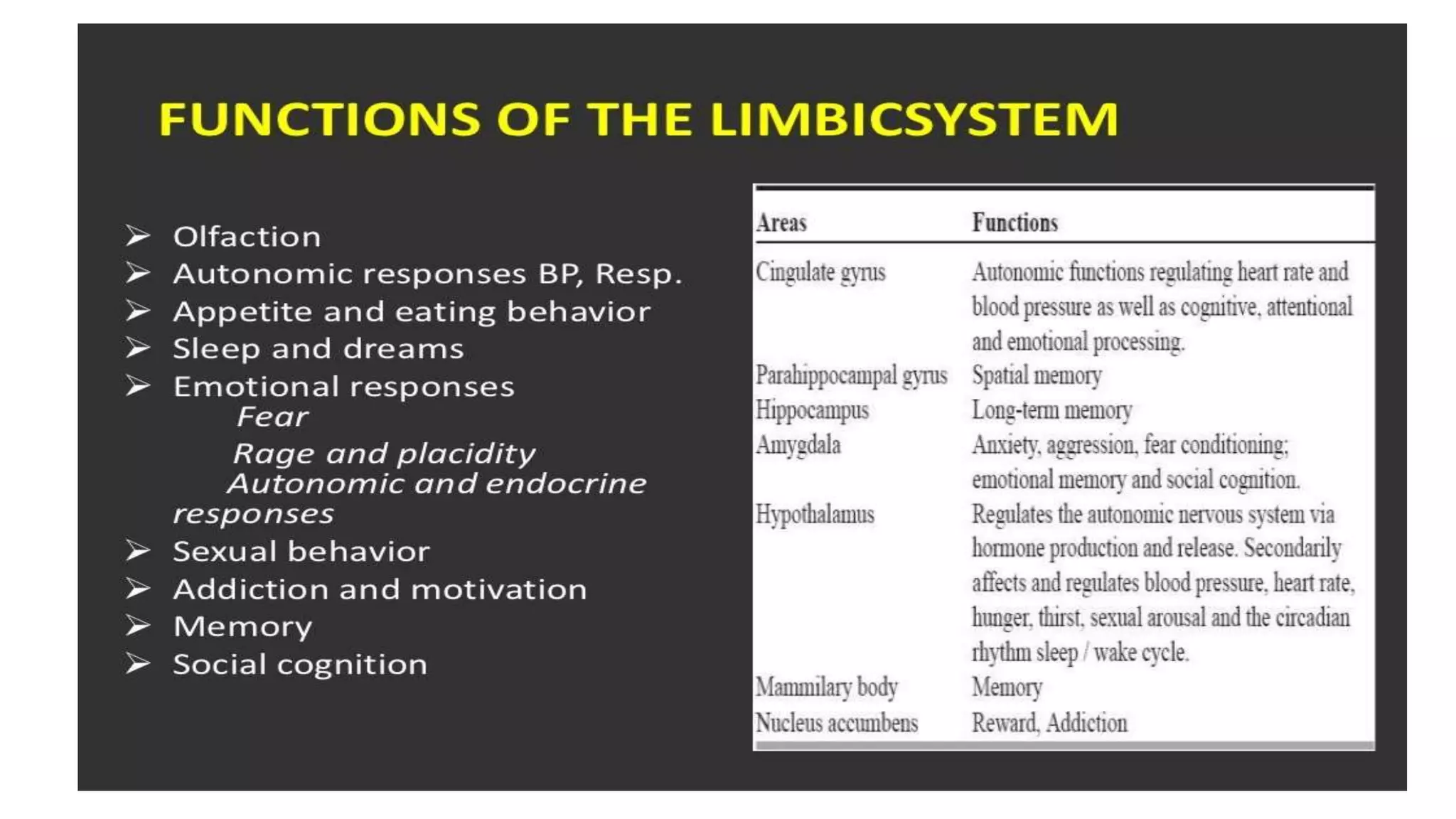
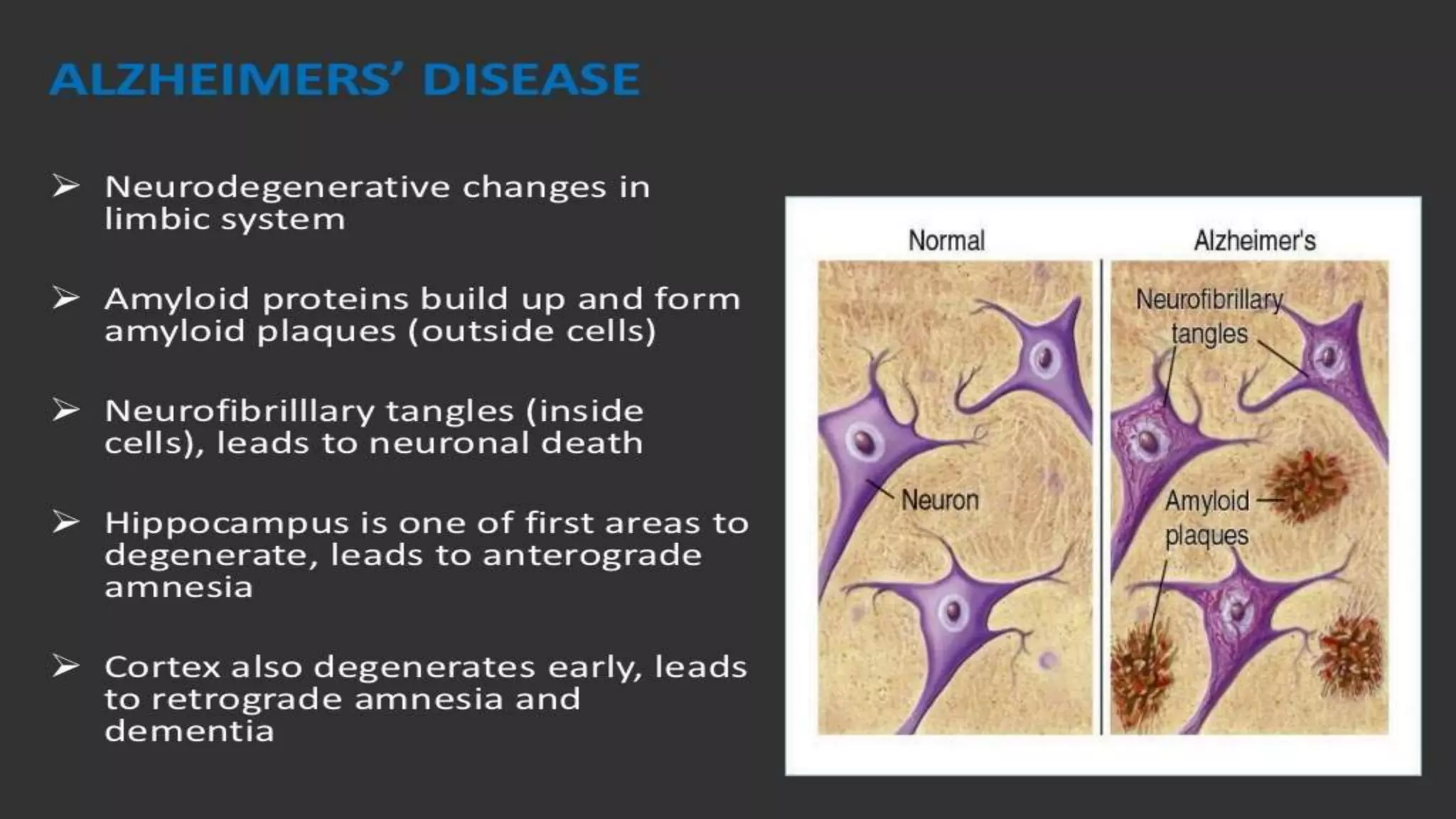
The document details the limbic system, a complex ring of cortical and subcortical structures essential for emotional processing and memory, highlighting its connection to the olfactory lobe. It also discusses the role of the piriform cortex and its relationship with other brain areas, including how compensatory changes enable odor perception during sensory deprivation. Additionally, various clinical syndromes associated with hypo and hyperactivity of the limbic system, such as depression and mania, are outlined.