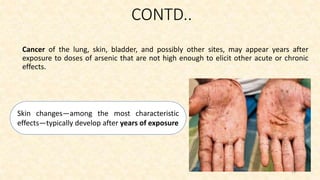
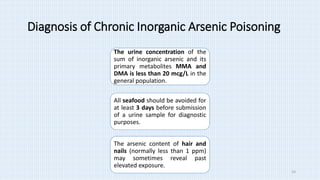
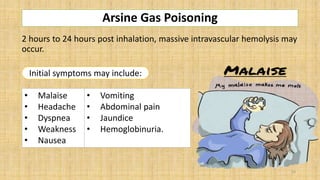
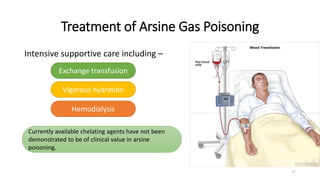
The document discusses arsenic poisoning, detailing its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment, as well as the serious health consequences of exposure. It highlights the acute and chronic forms of arsenic poisoning, with diagnosis methods including urine and blood tests, and the importance of decontamination and supportive care. Additionally, it addresses arsenic contamination in drinking water, particularly in Bangladesh, where governmental initiatives have been implemented to mitigate the issue.