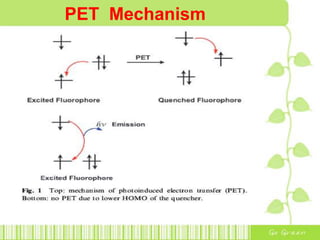
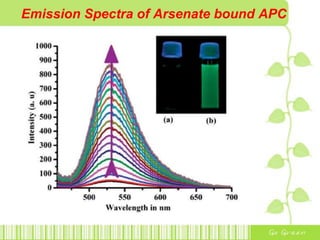
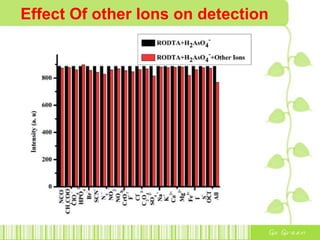
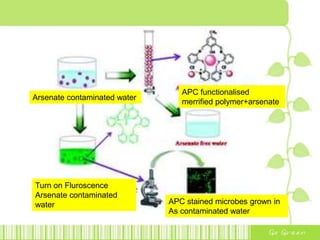
The document discusses the properties and health effects of arsenic, particularly focusing on its contamination in groundwater and the resulting poisoning in populations globally. It details a method using APC-Merrifield polymer for detecting and removing arsenate from drinking water, highlighting the efficiency of this process. The document concludes that this new sensor can simultaneously detect and remove arsenate impurities, establishing a new approach to addressing arsenic contamination.












![Occurence in Water
• However, cationic As(III) species rarely exist in the
environment; rather, toxic arsenic species existing
in the environment are either [HAsO4]2− (AsV ) or
[HAsO3]2− (AsIII ).
• Although inorganic arsenic species(AsIII and AsV )
are present to a greater extent in natural water,
lesser amounts of Monomethylarsonic acid(MMA)
and Dimethylarsonic acid (DMA) also exist
• . Arsenic acid tends to exist as the ions [HAsO4]2−
and [H2AsO4]− in neutral water, whereas arsenous
acid is not ionized.These occur due to erosion of
arsenic rocks.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arsenicsensors-141115054701-conversion-gate02/85/Arsenic-sensors-13-320.jpg)