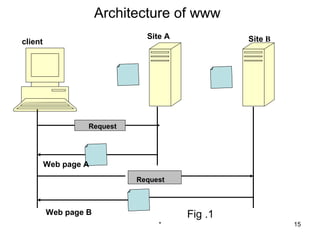
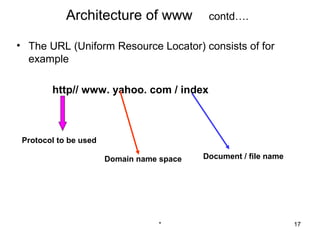
ARPANet was the first wide-area network created by the US Defense Department in 1969. It served as a testbed for new networking technologies and evolved into the modern Internet. The World Wide Web (WWW) is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet using browsers. It allows users to view web pages that contain text, images, videos and other multimedia. Each web page is made up of HTML code and can contain links to other pages located on different servers around the world.