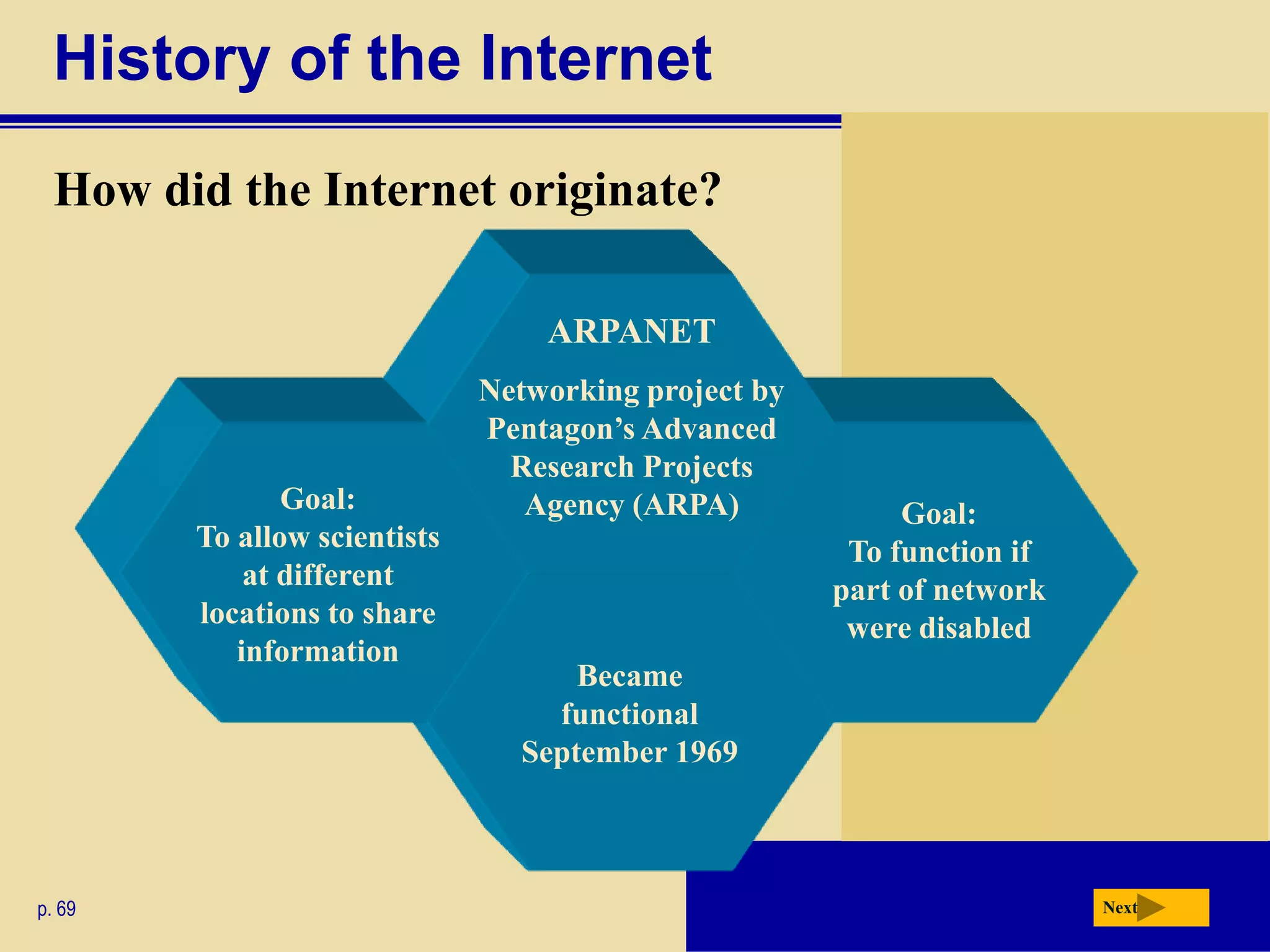
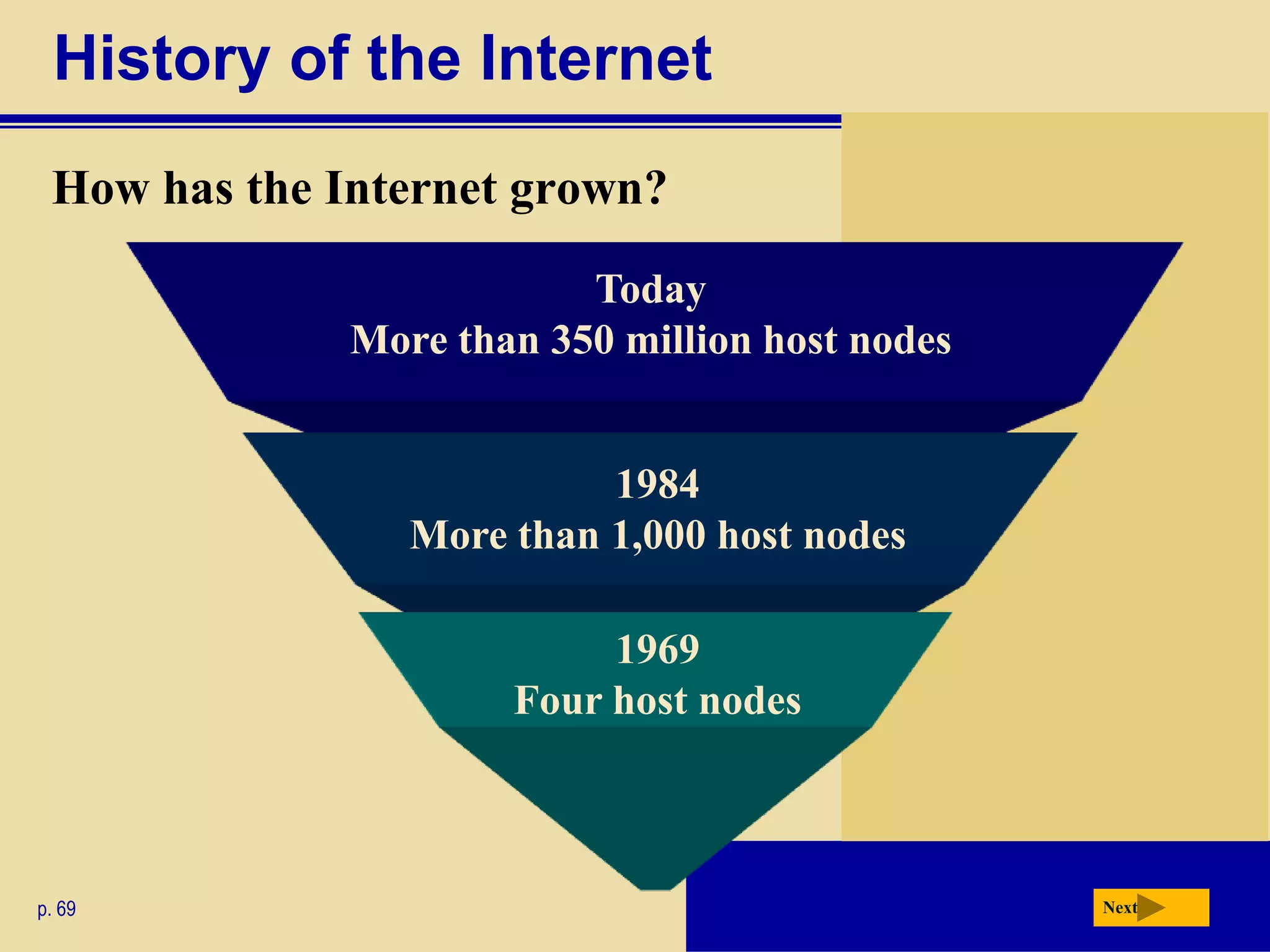
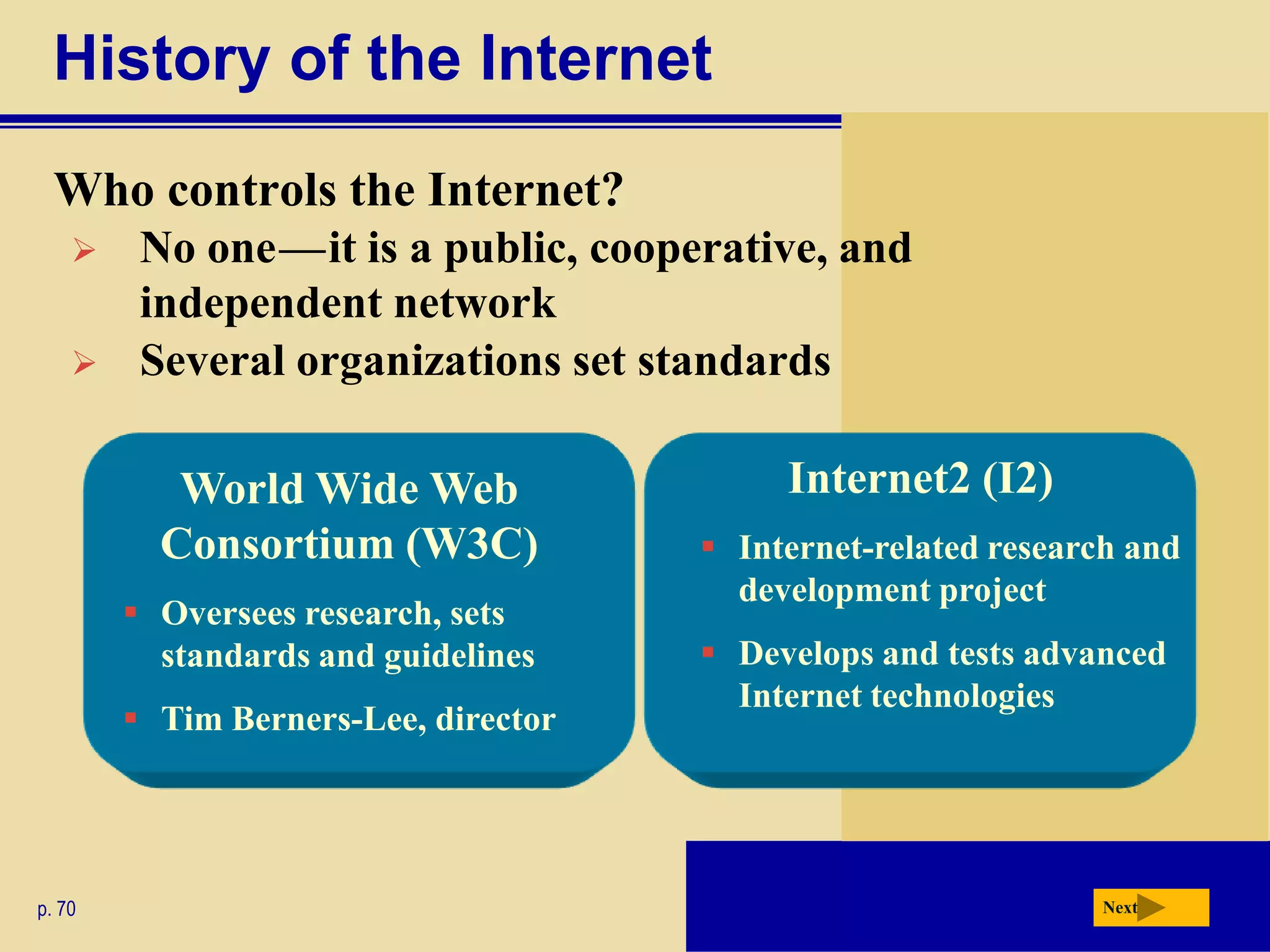
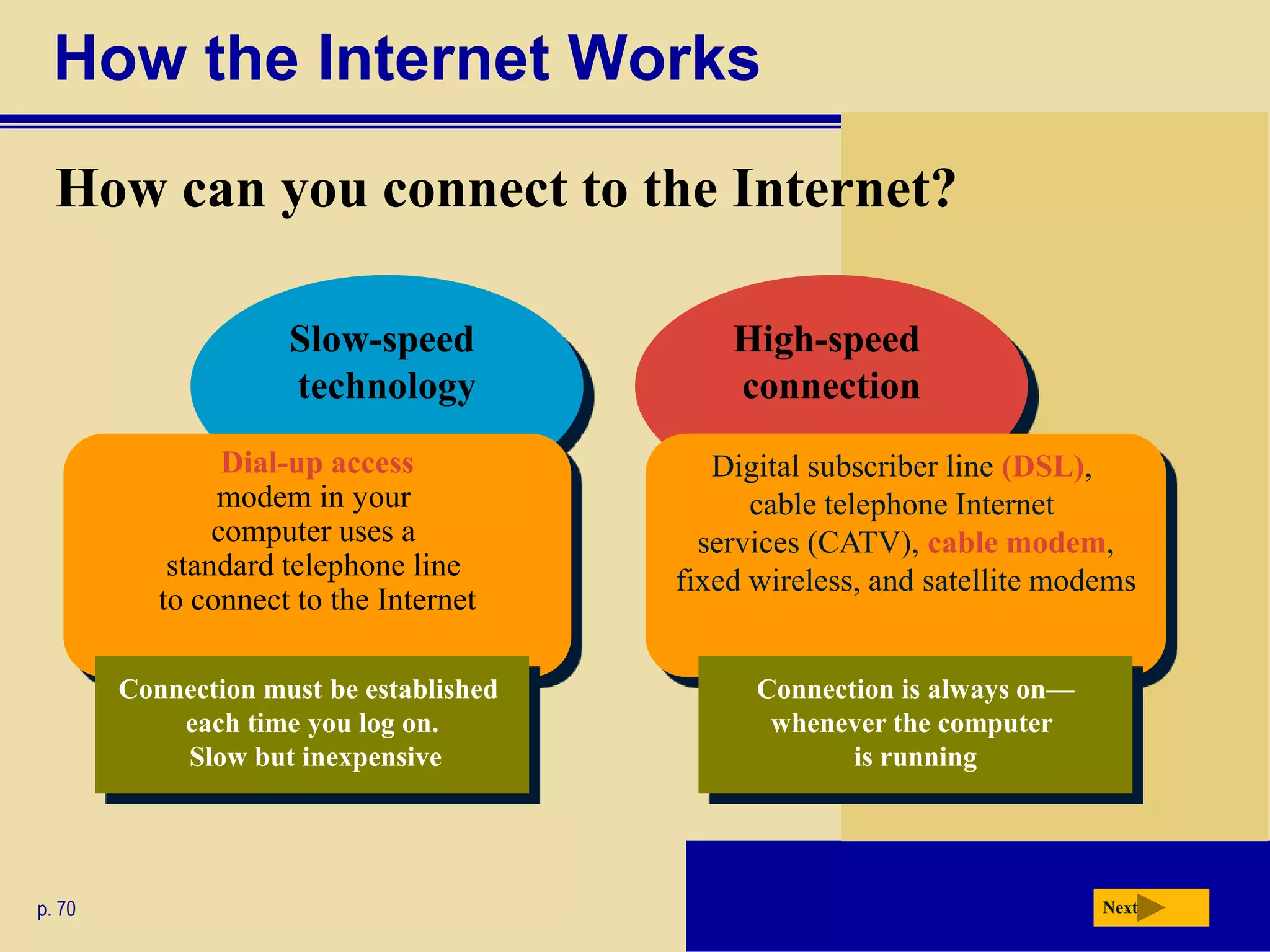
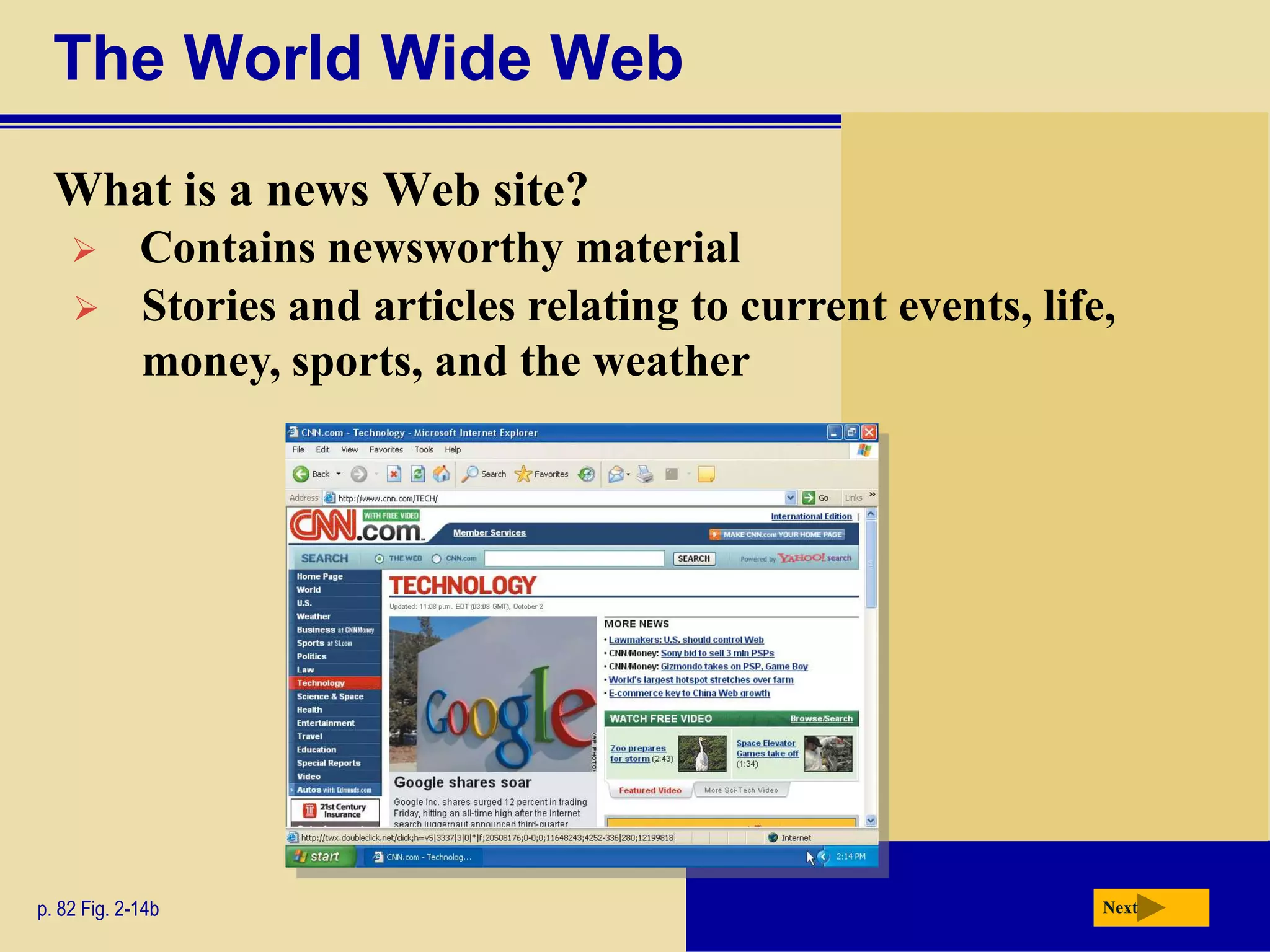
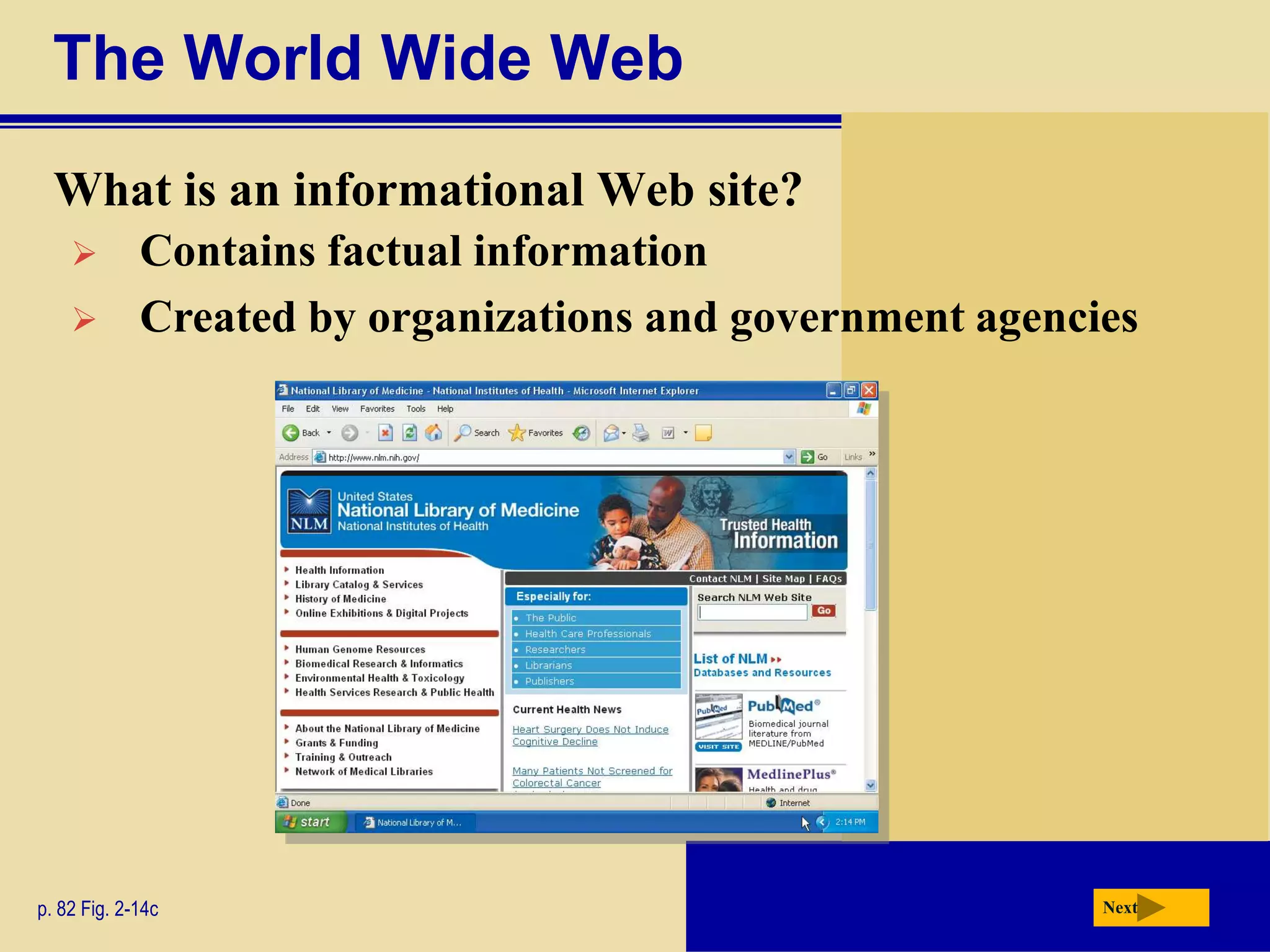
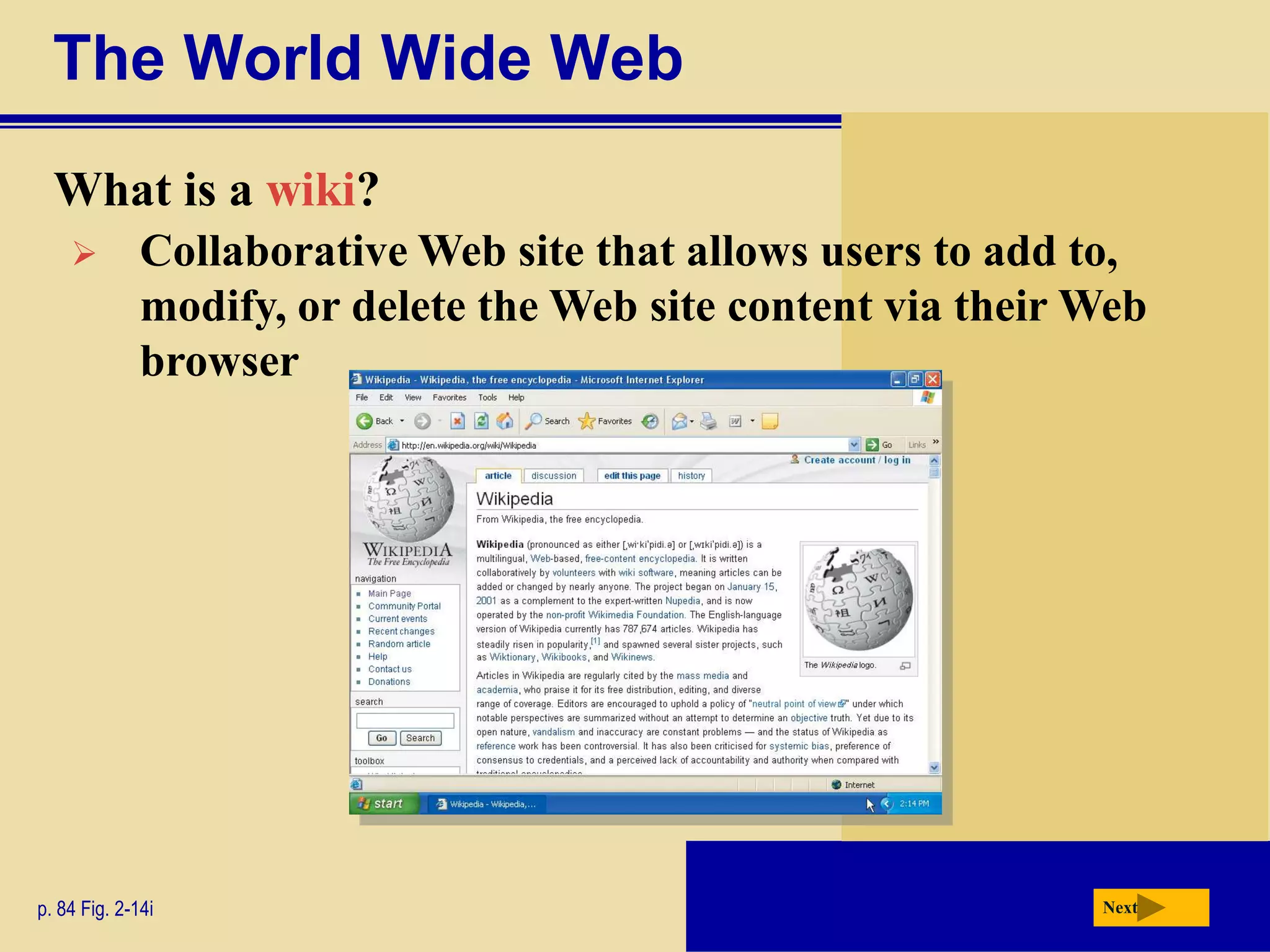
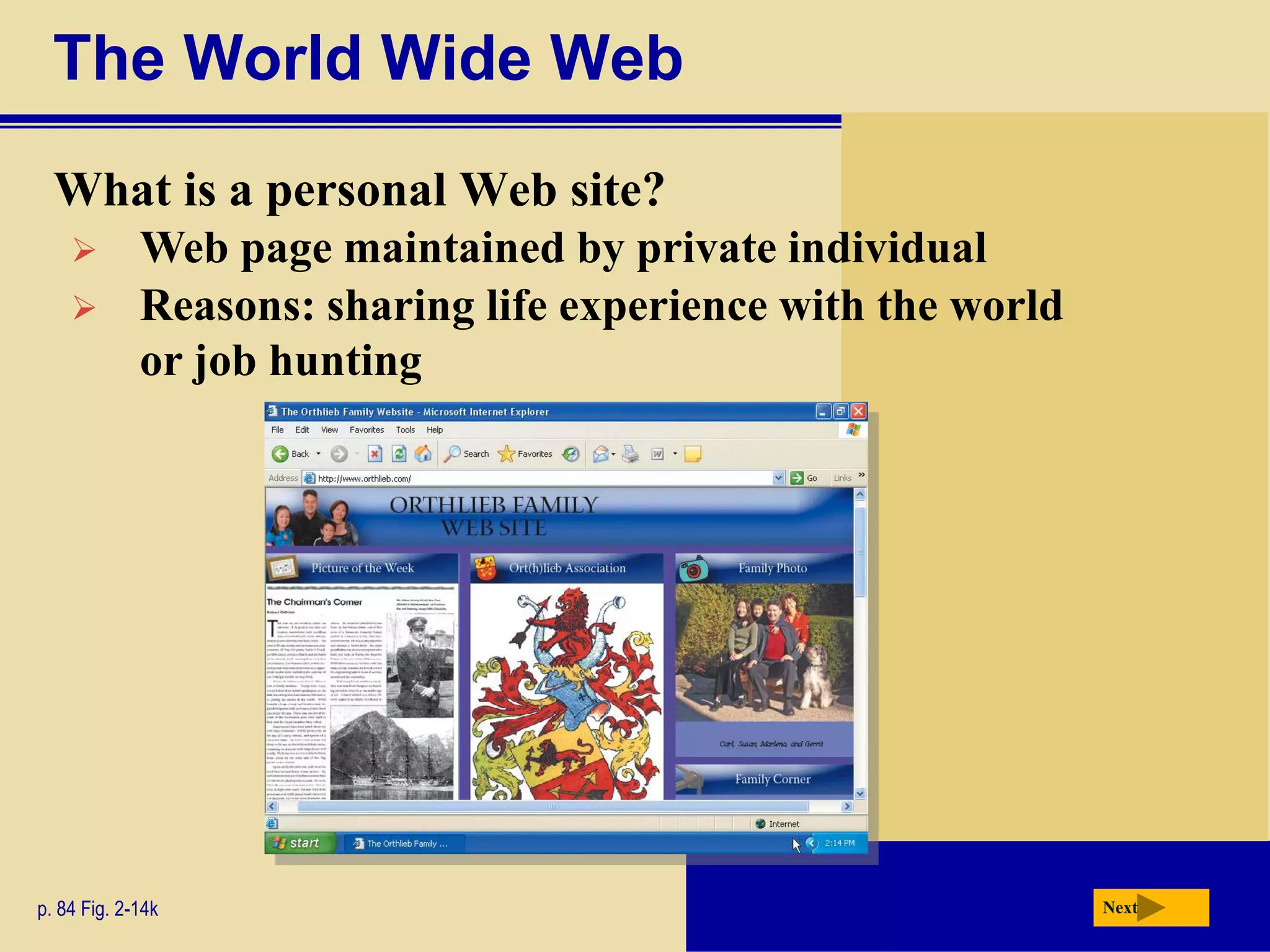
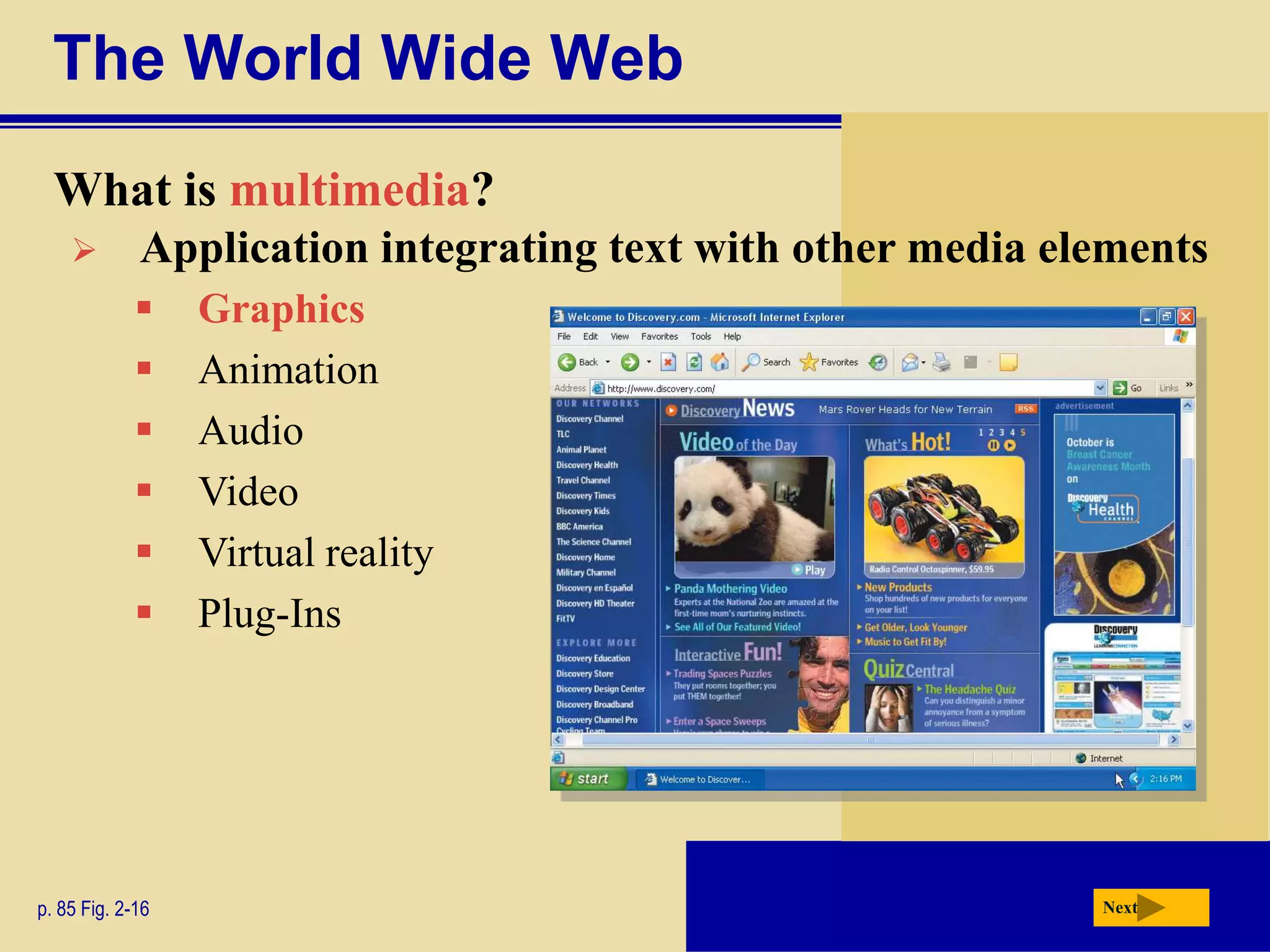
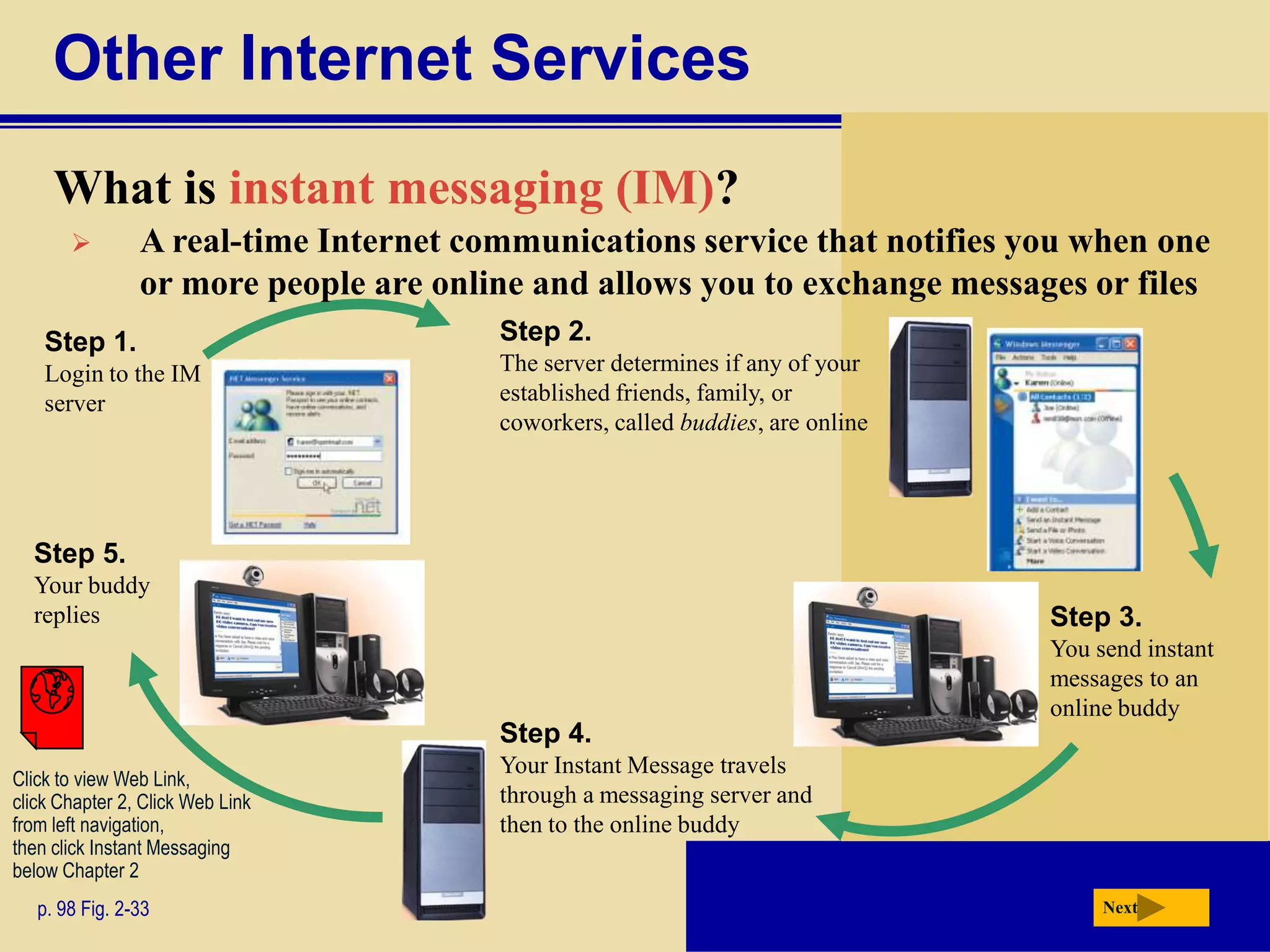
The document discusses the history and development of the Internet and World Wide Web. It describes how the Internet originated from ARPANET and has grown from just four nodes in 1969 to over 350 million nodes today. No single entity controls the Internet. The document also explains how to connect to the Internet, defines common terms like domains, URLs, links, and search engines. It identifies the main types of websites such as portals, news sites, informational sites, and more.