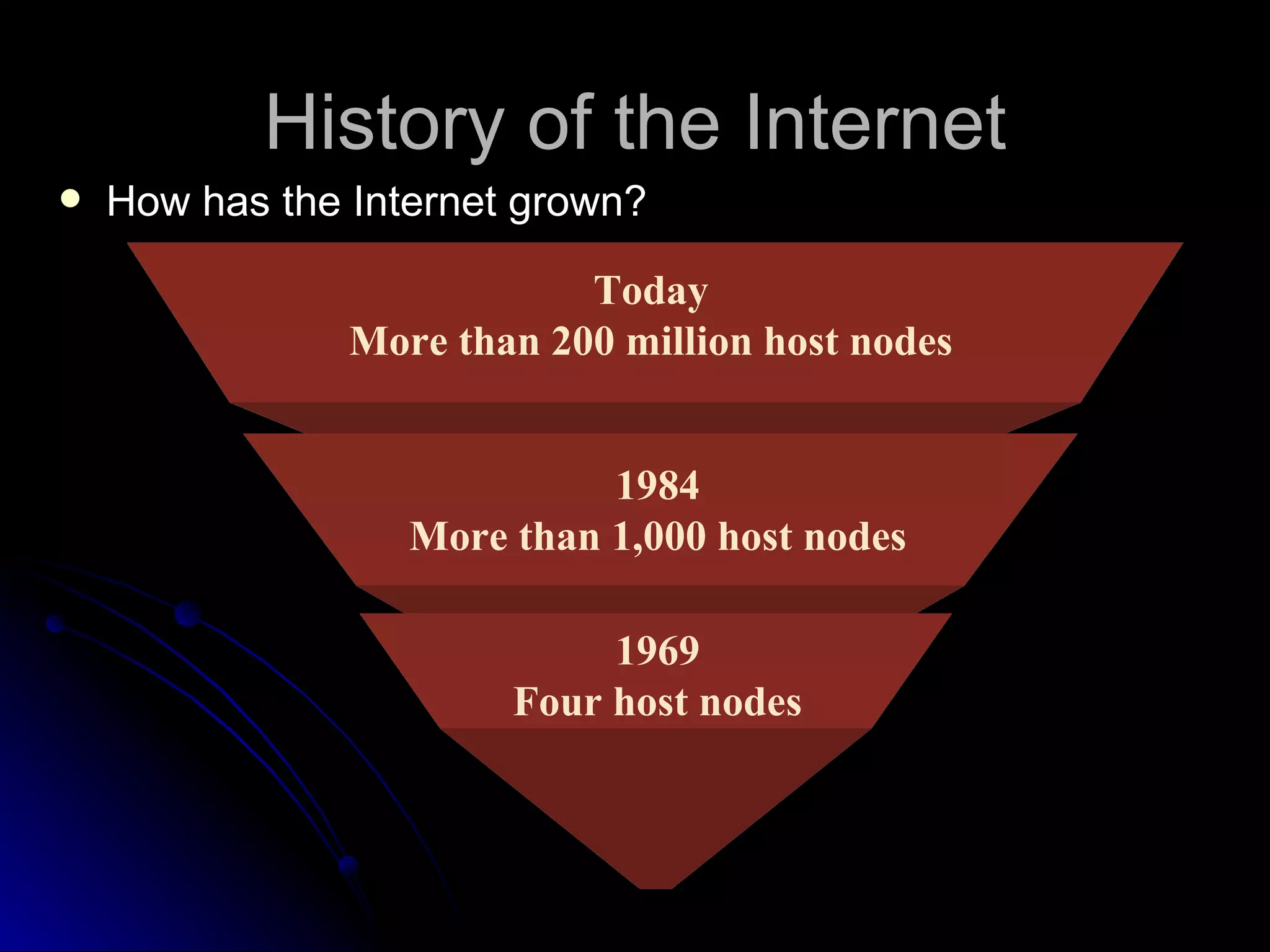
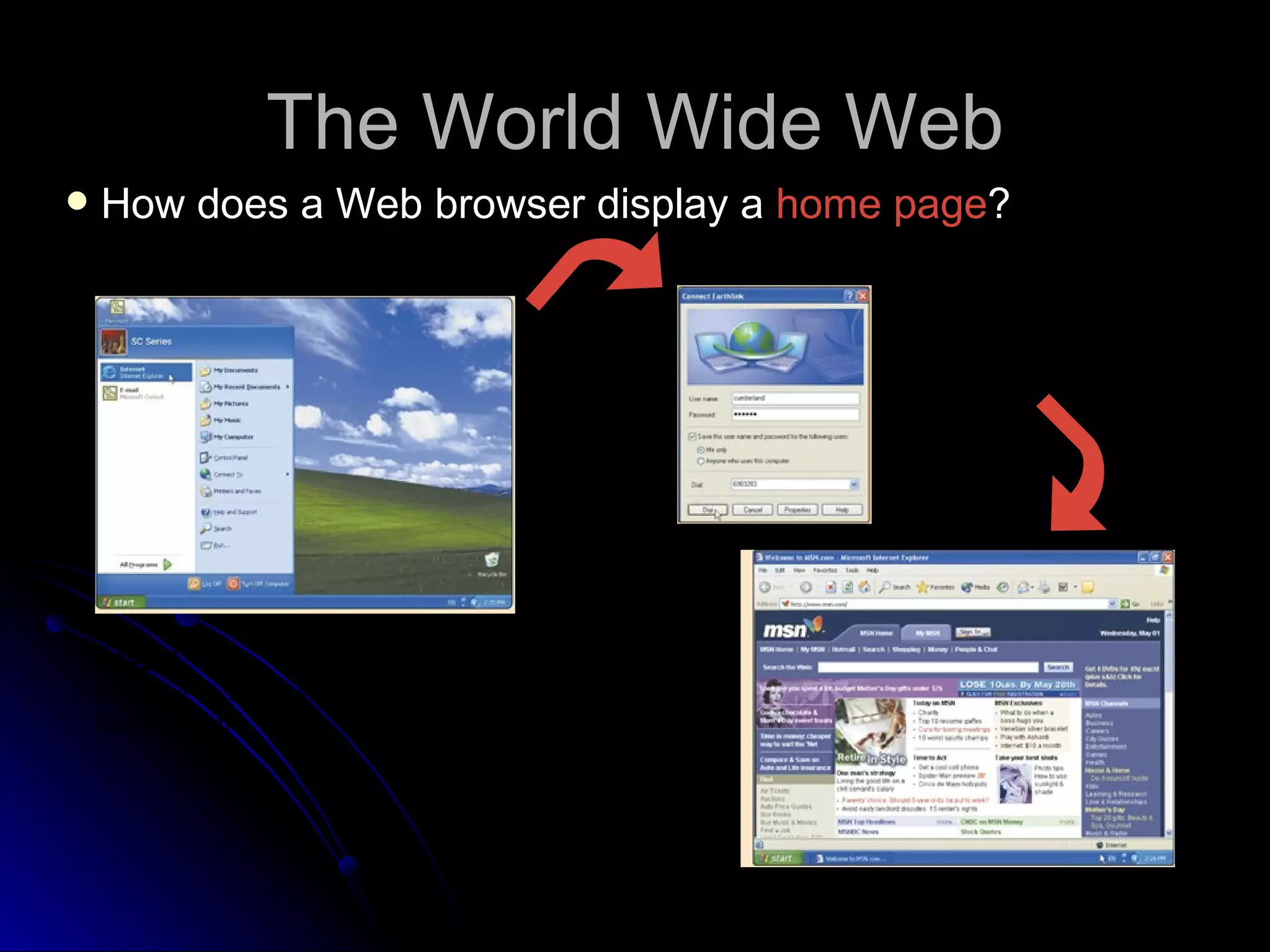
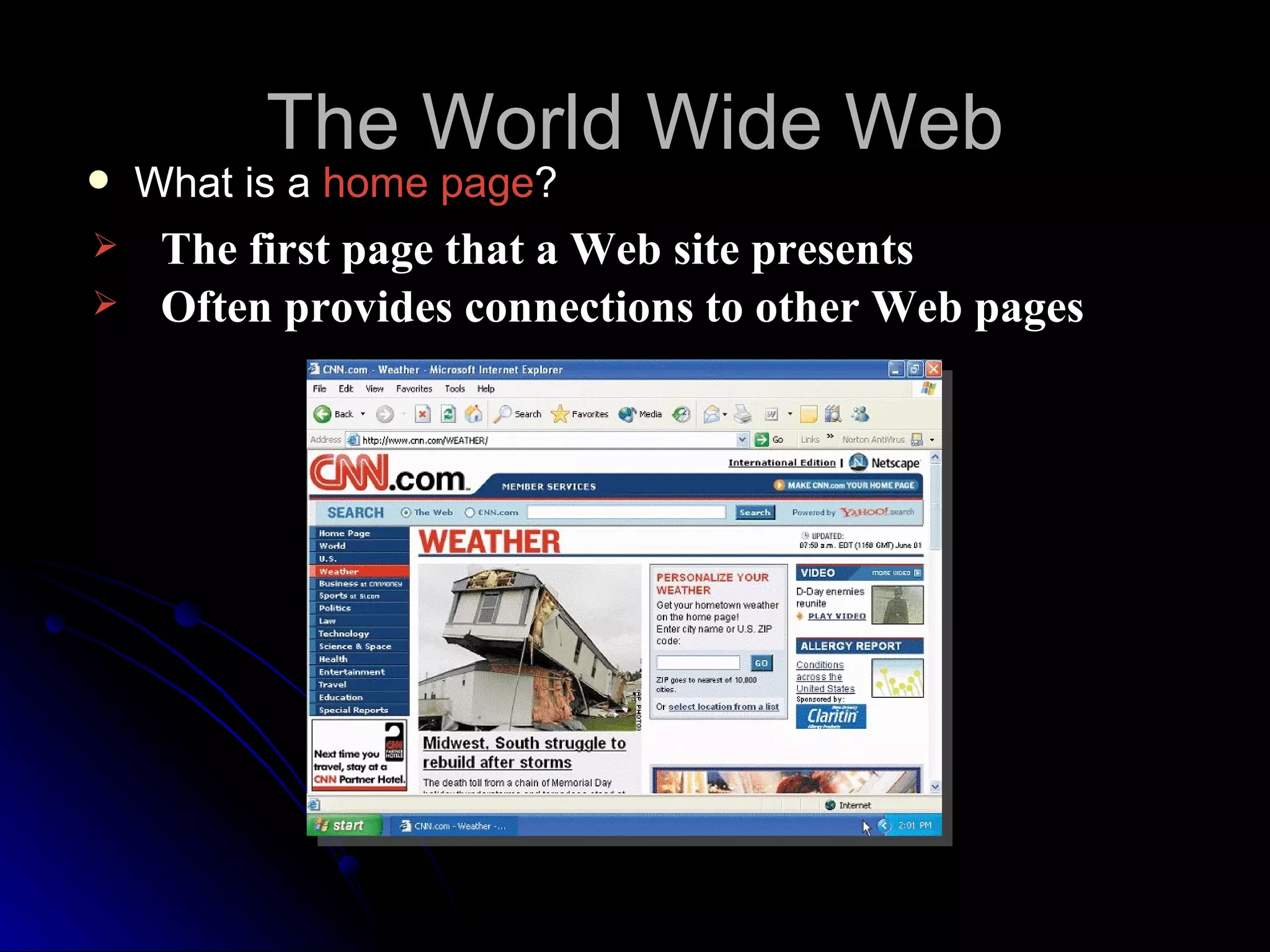
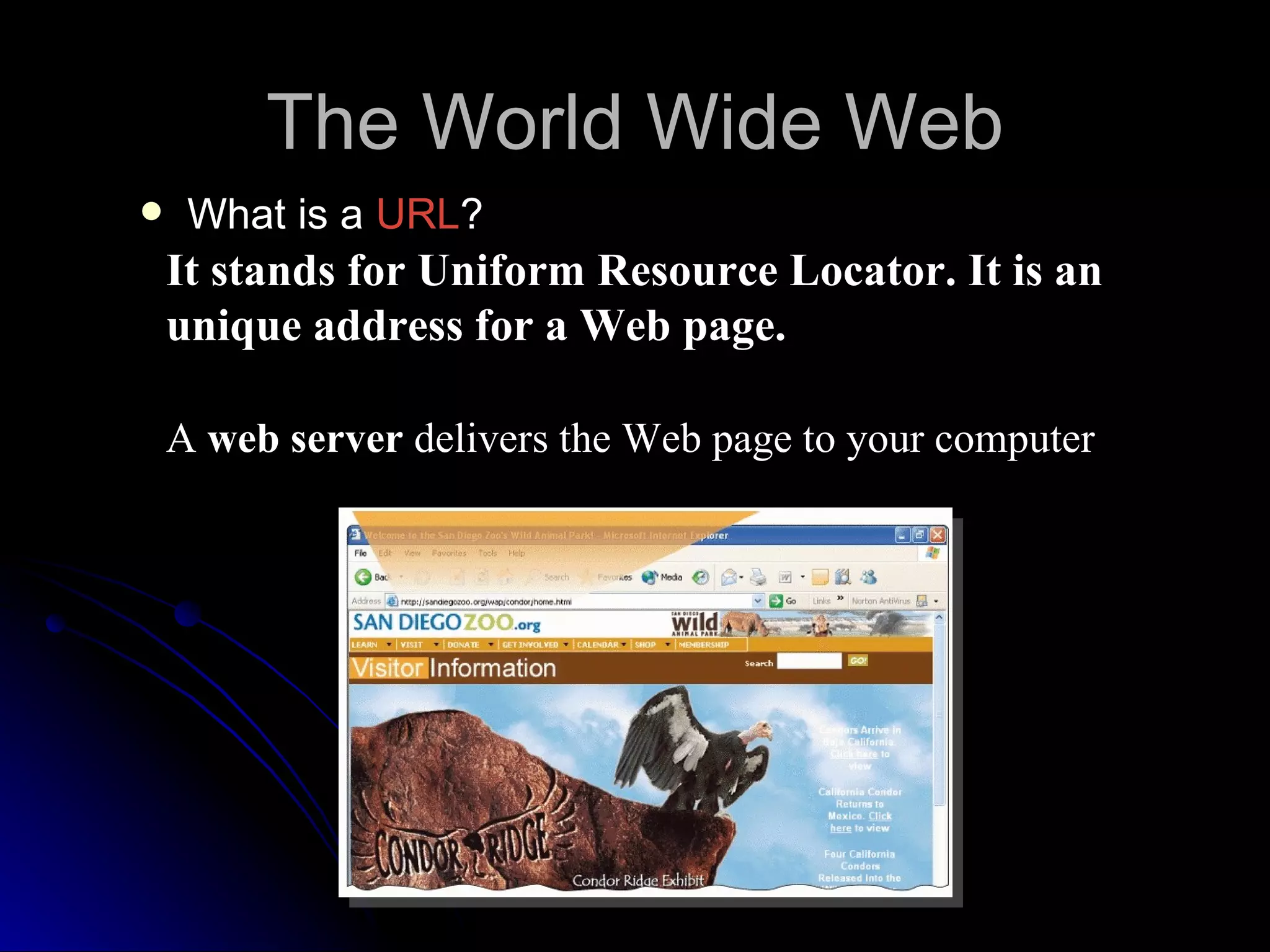
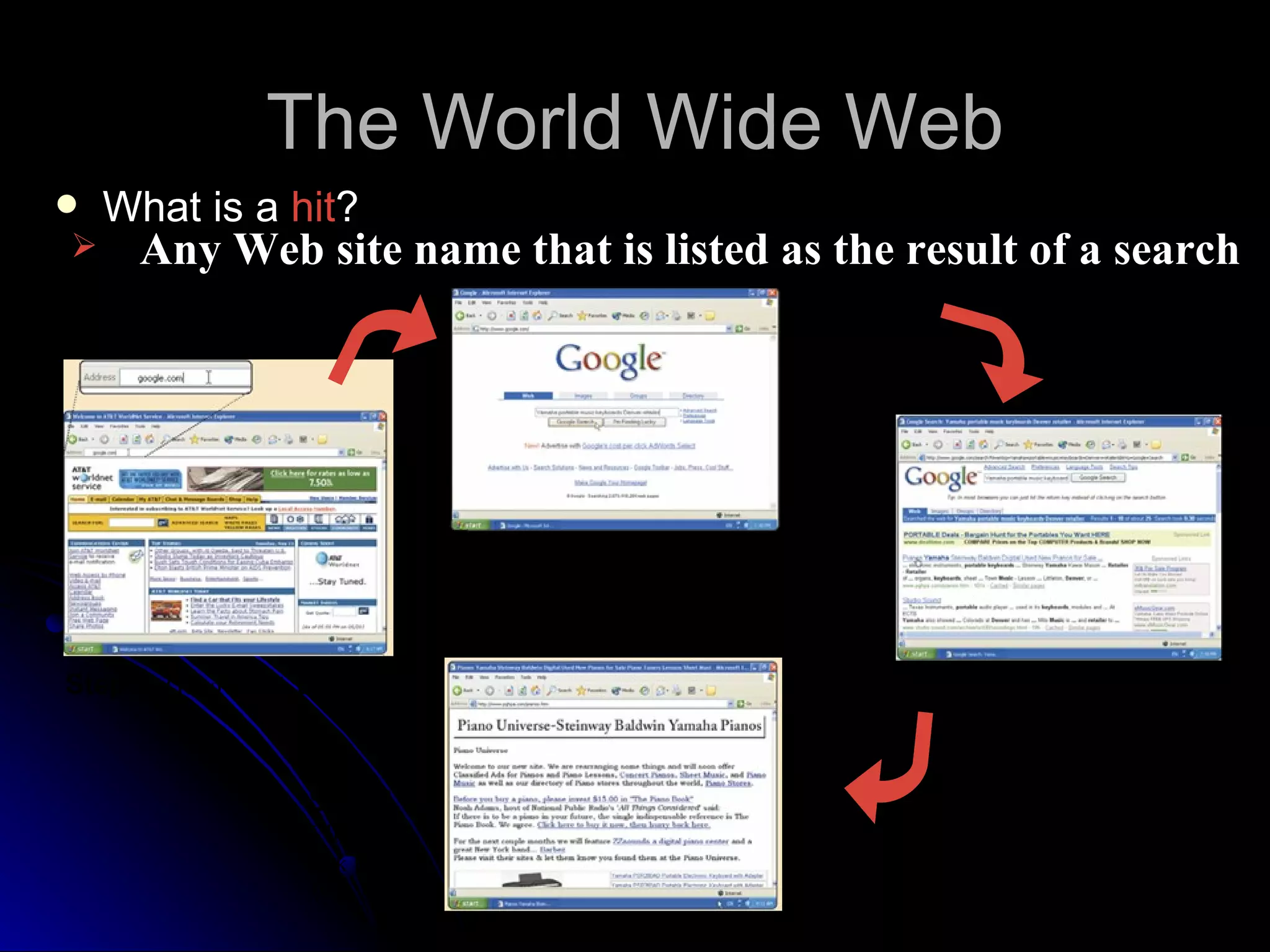
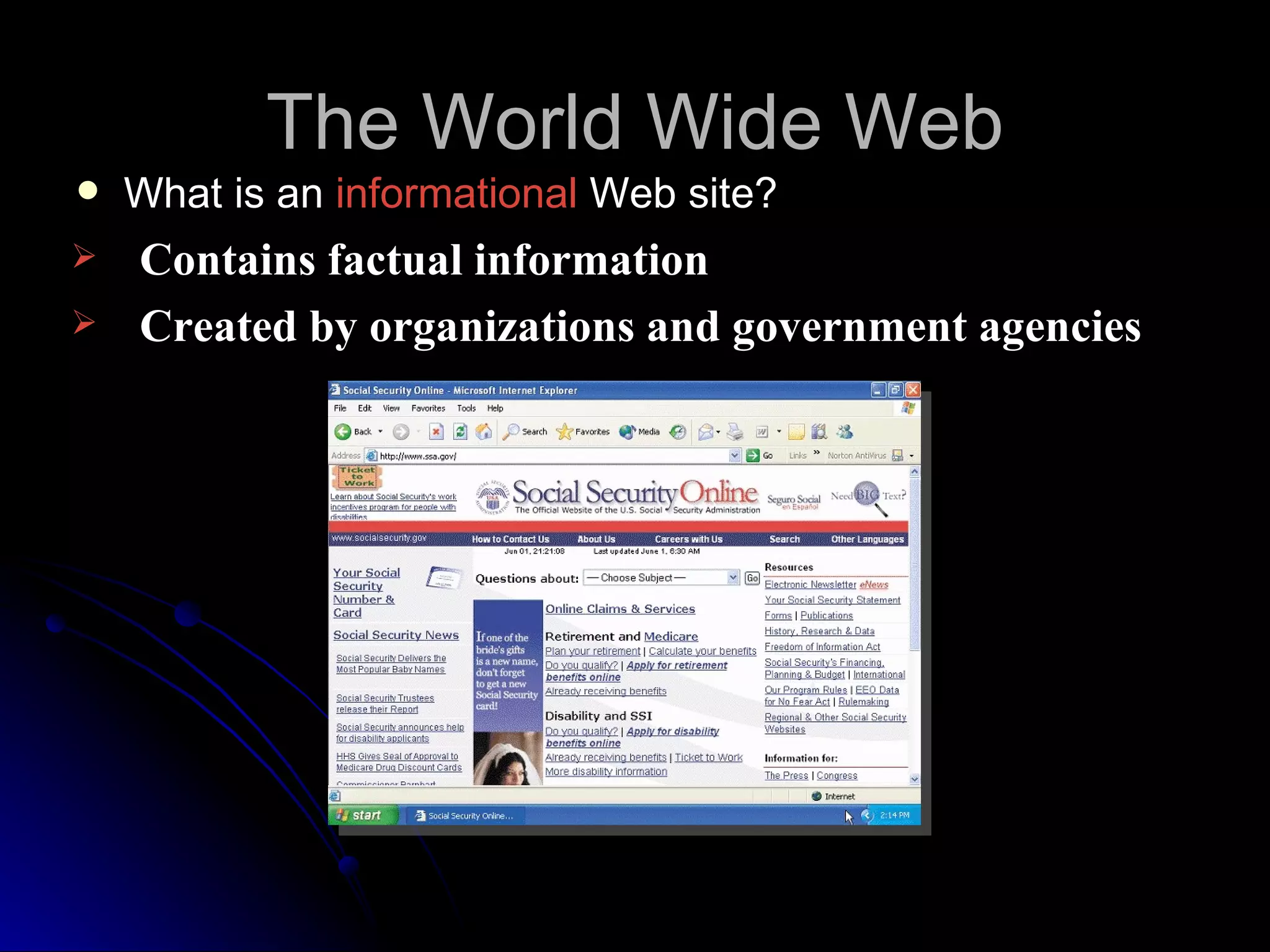
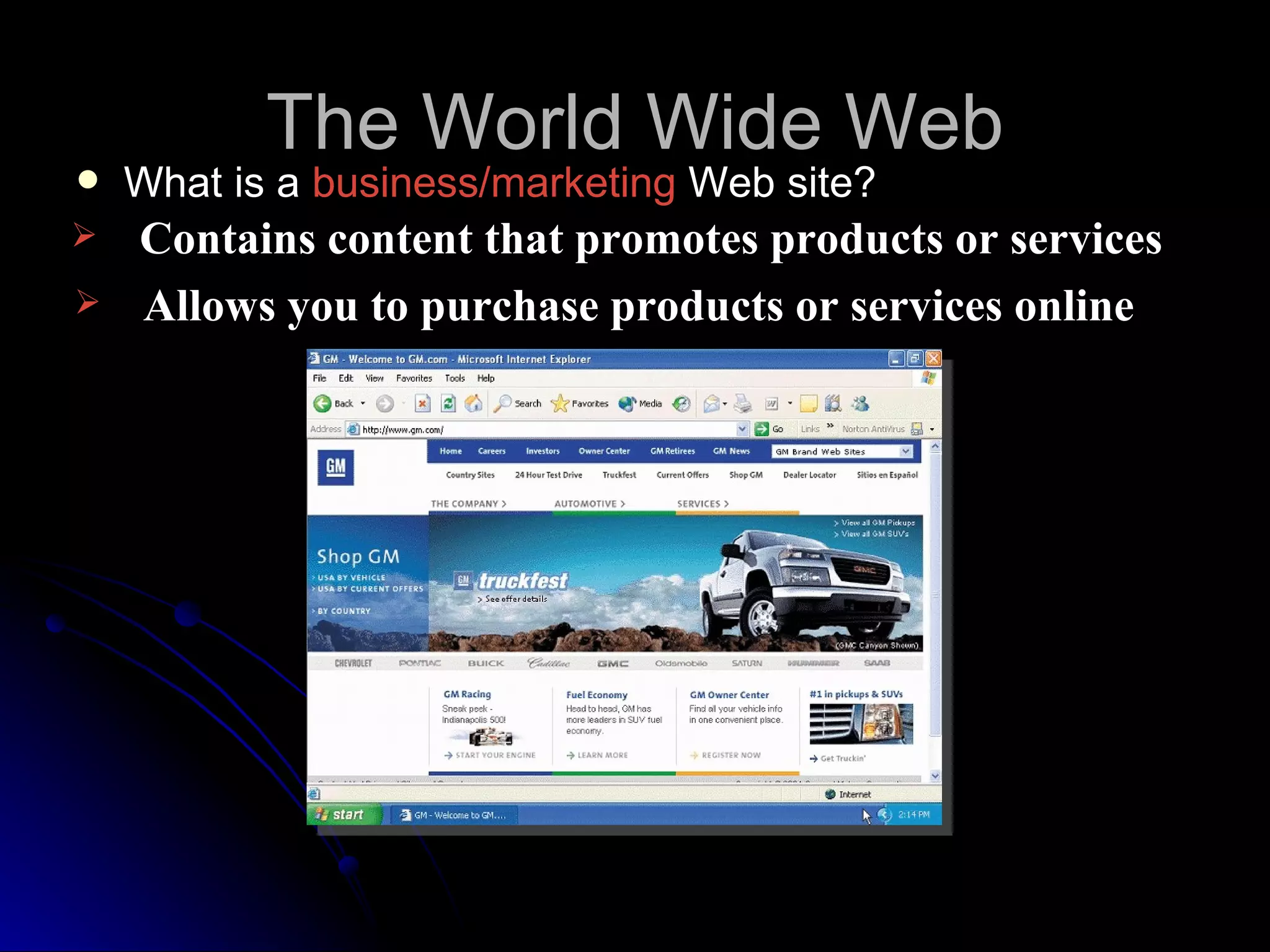
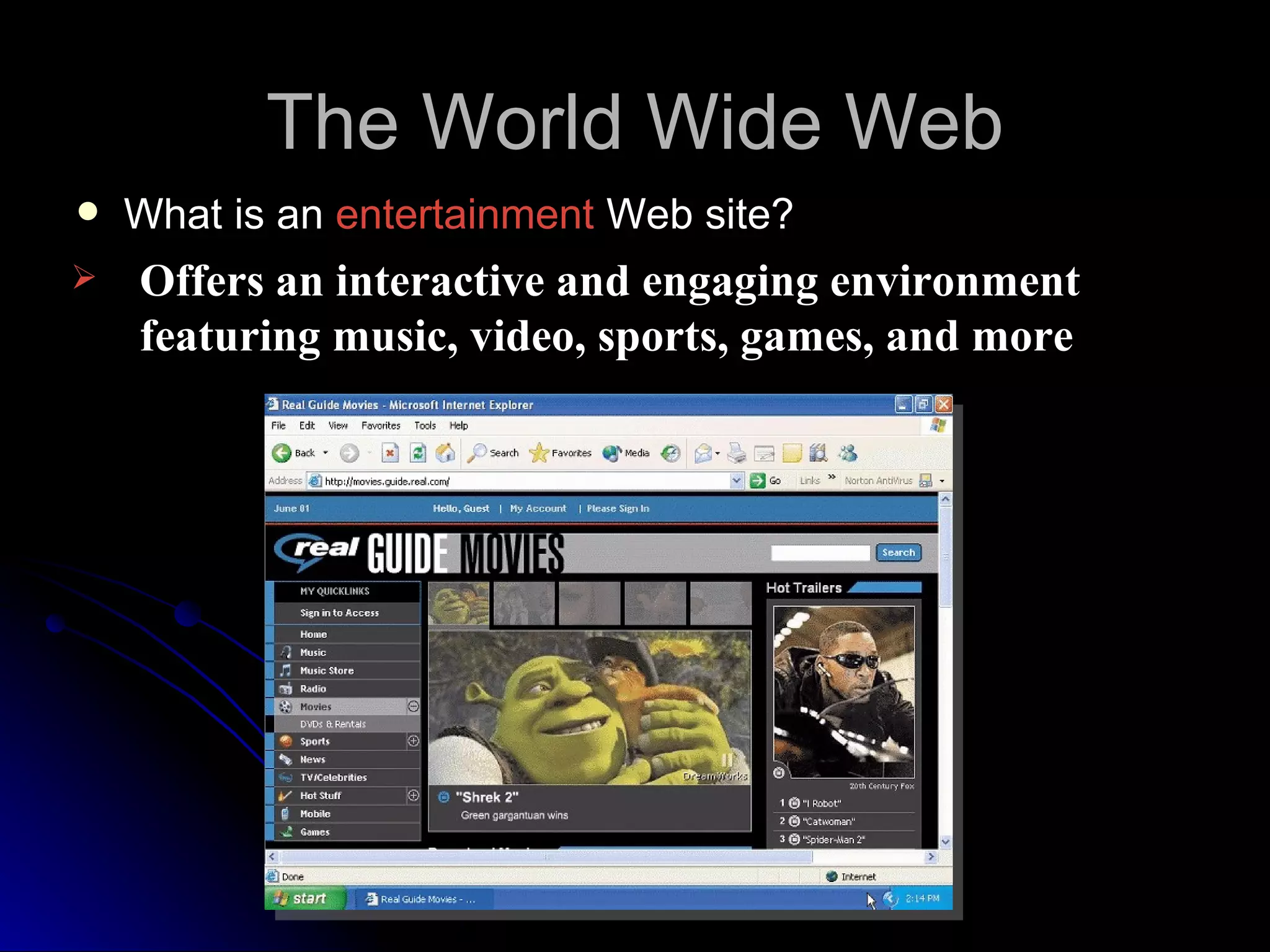
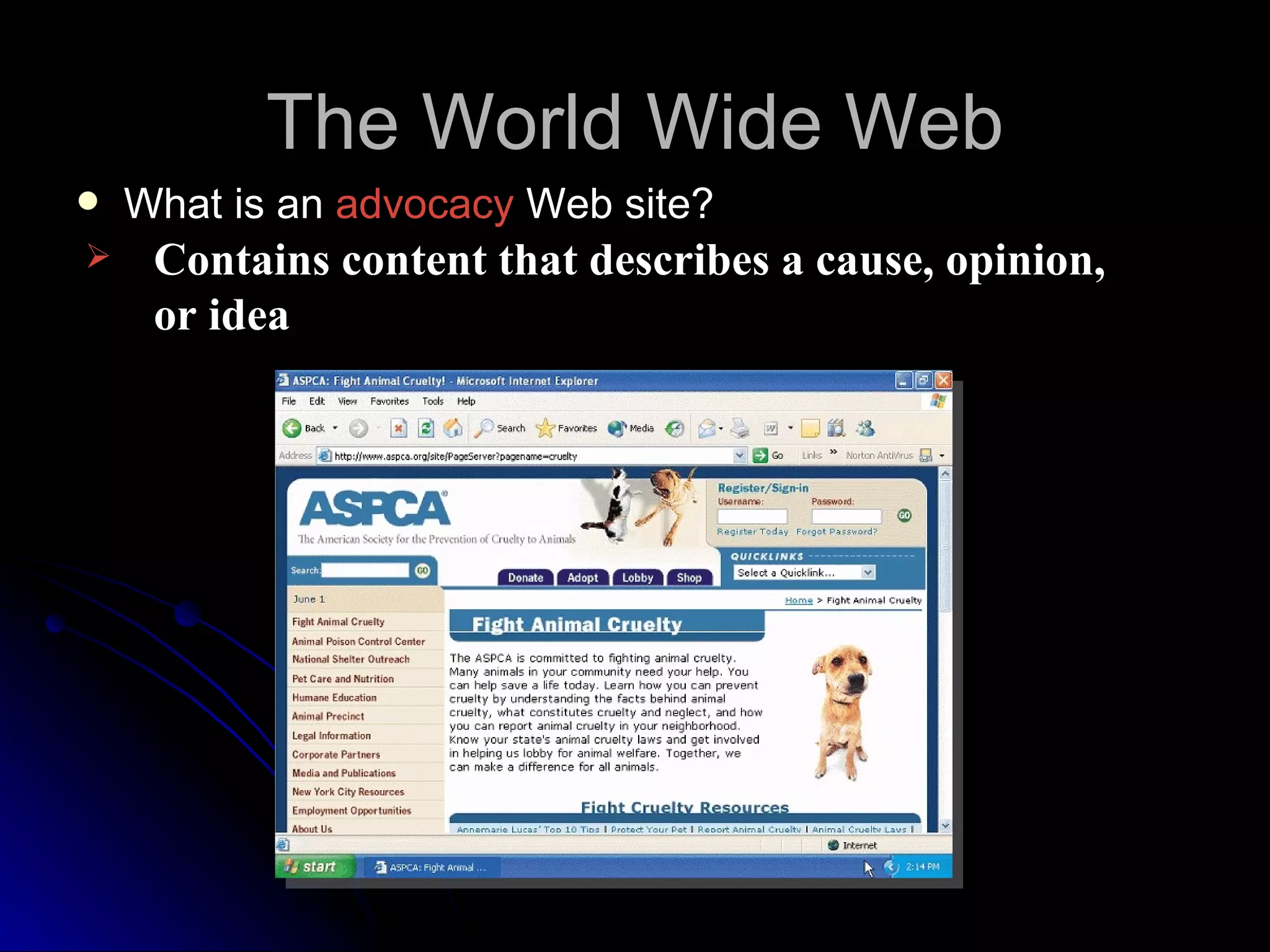
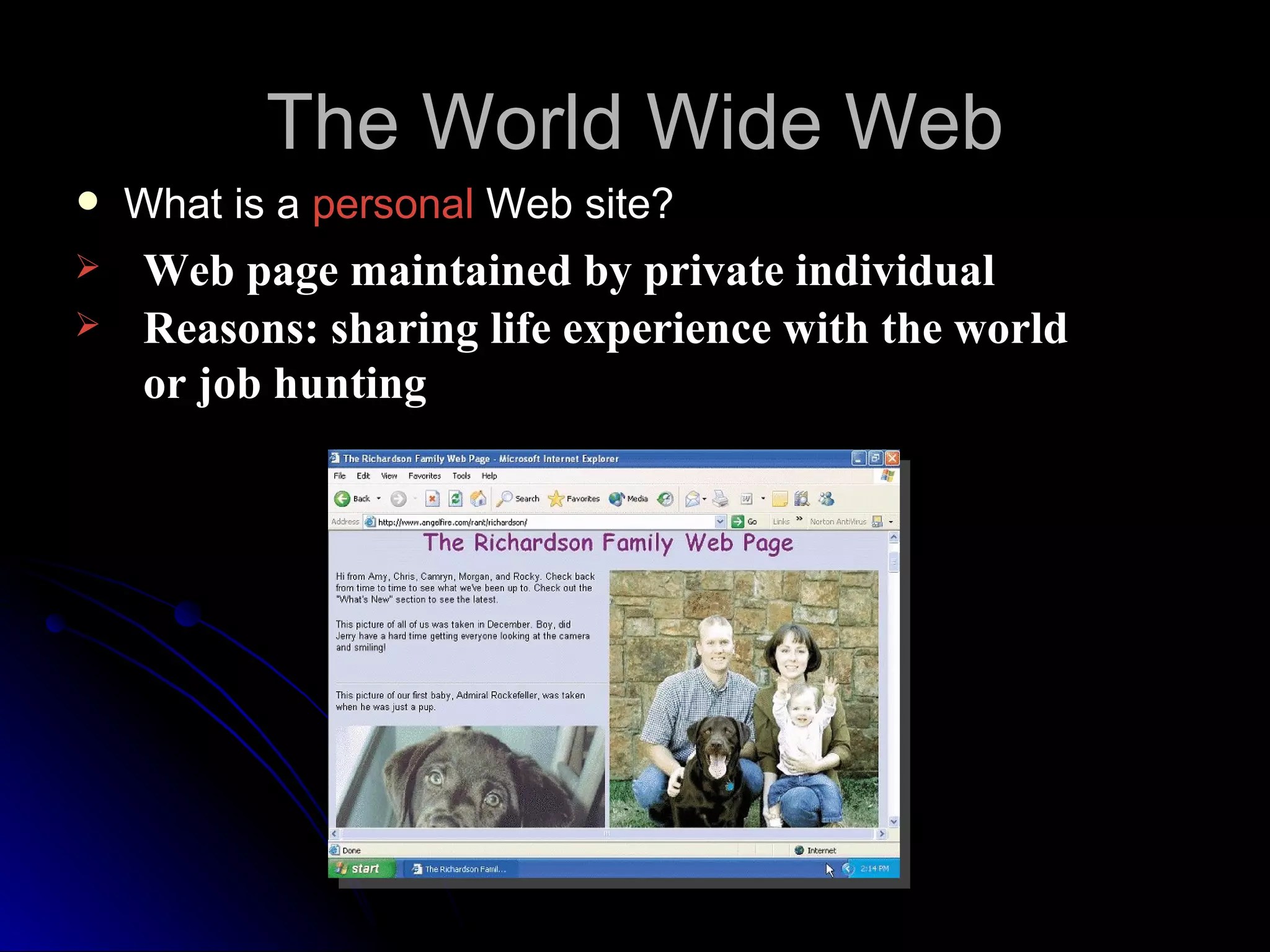
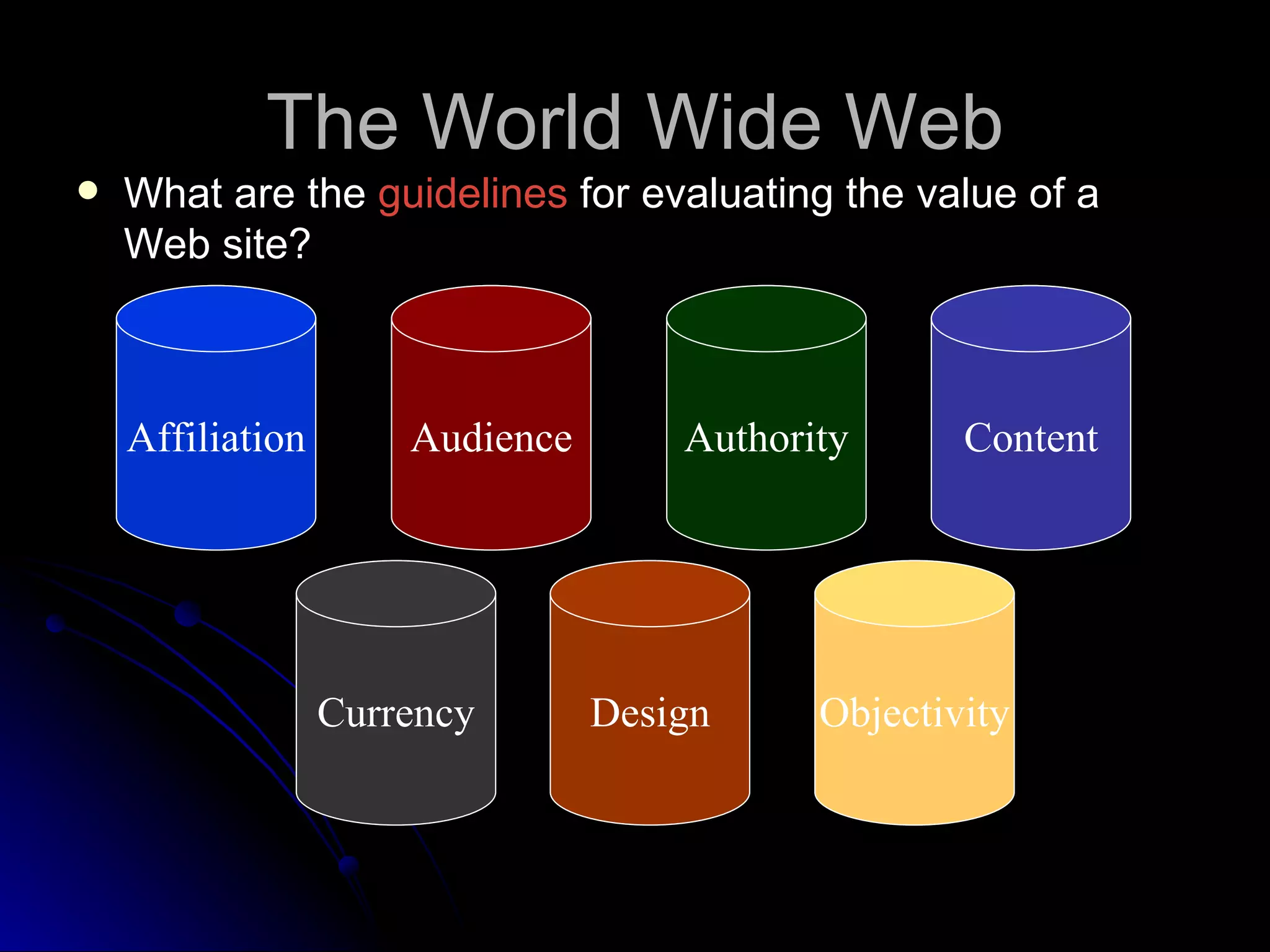
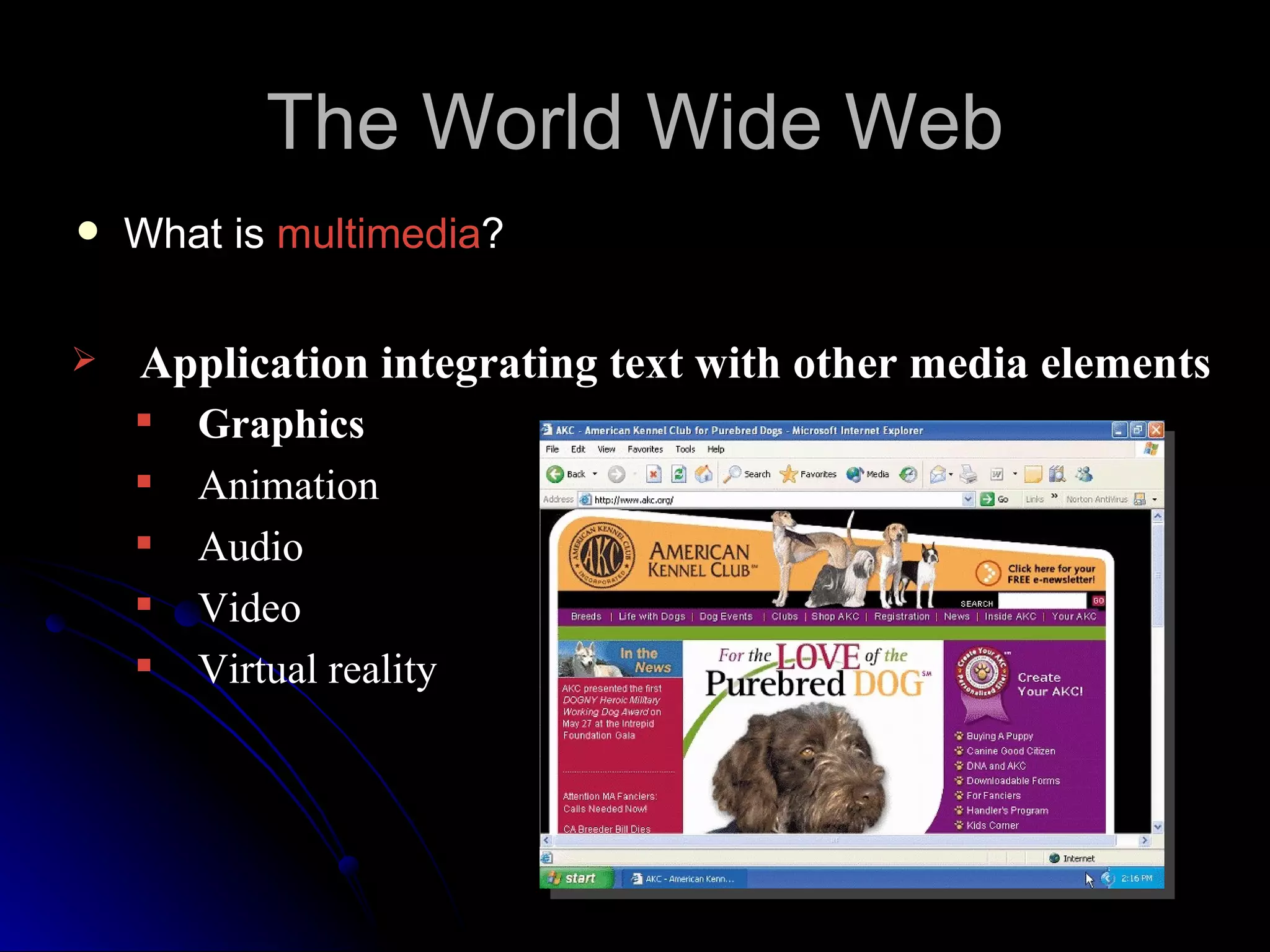
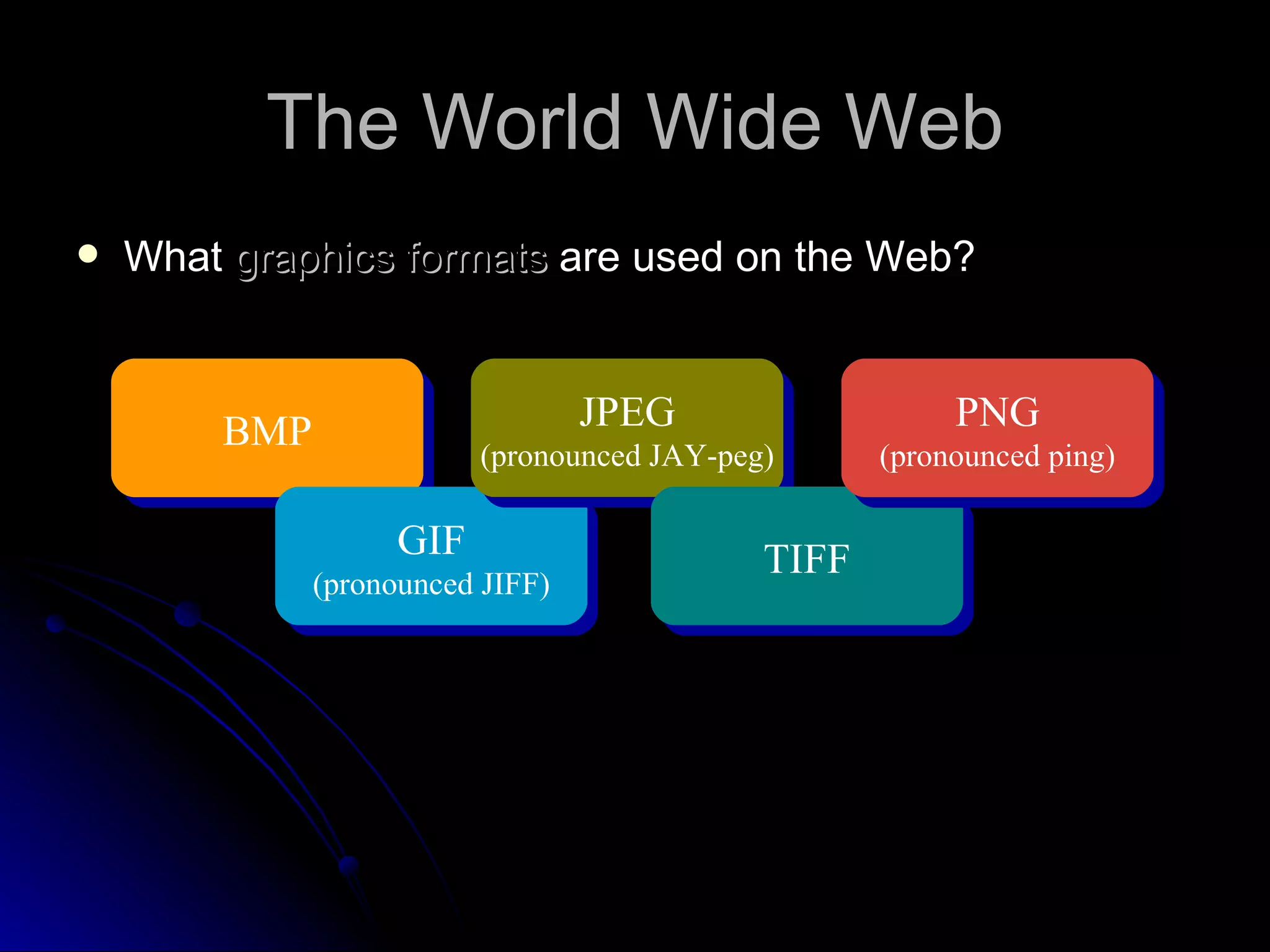
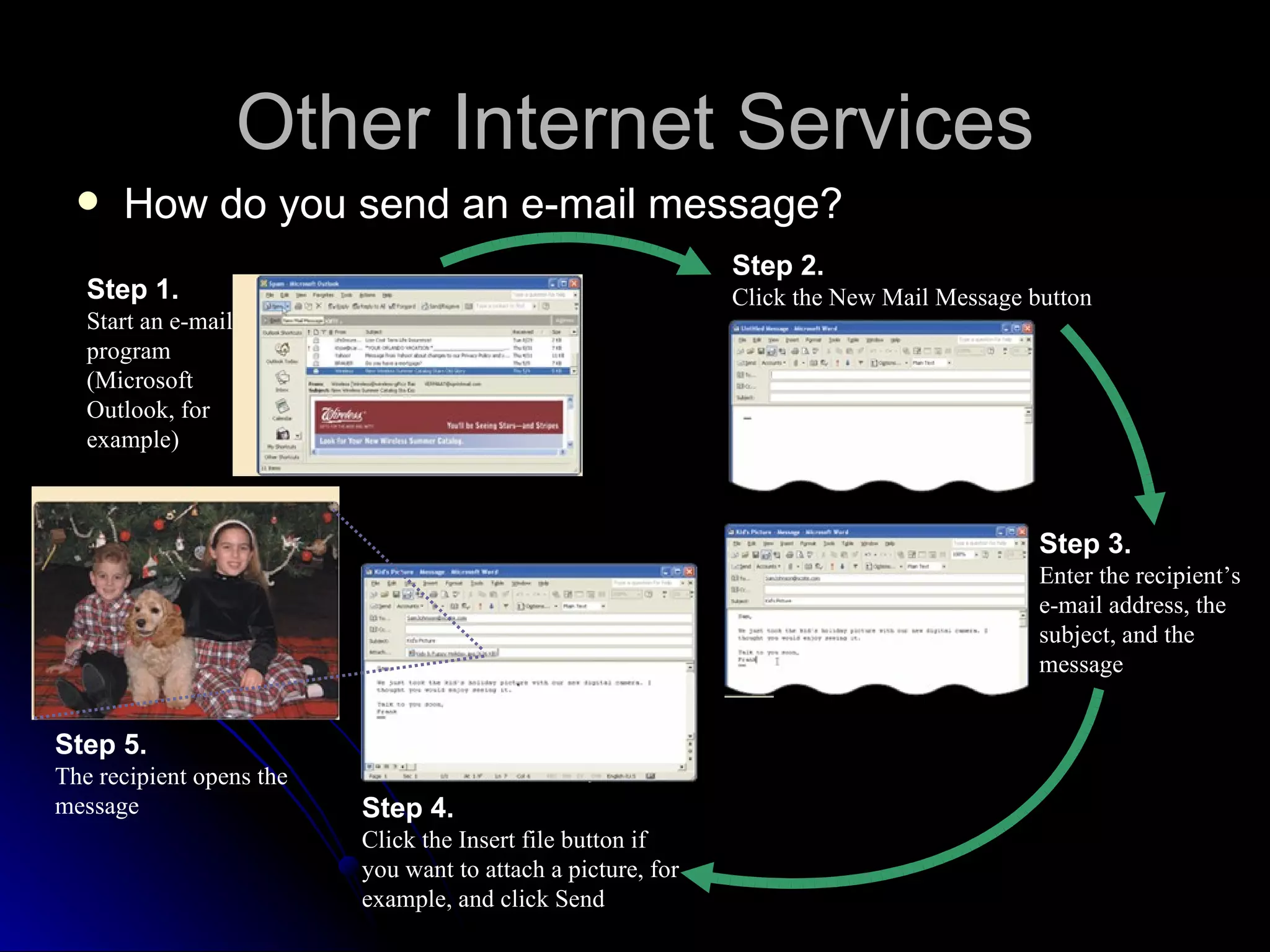
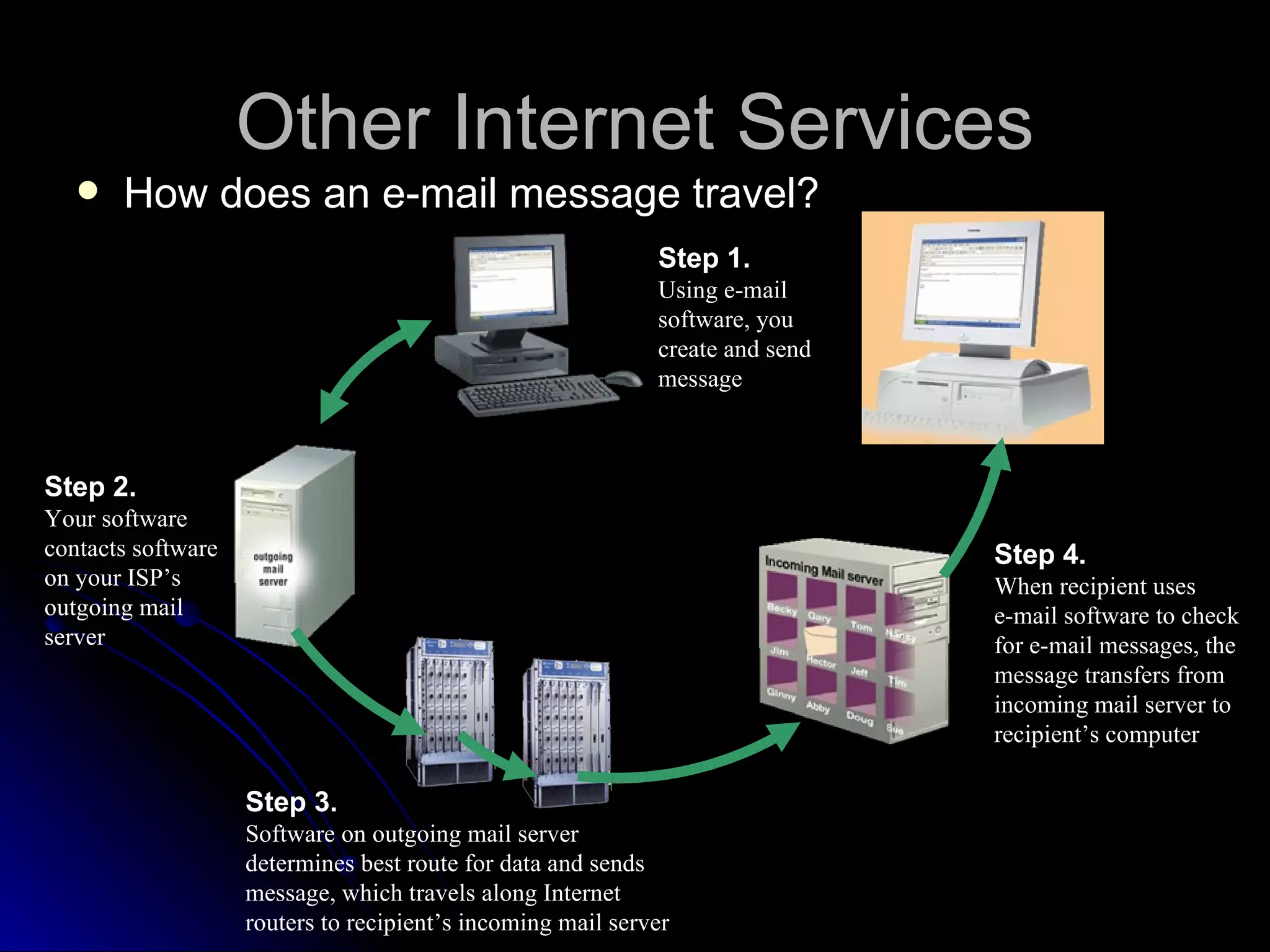
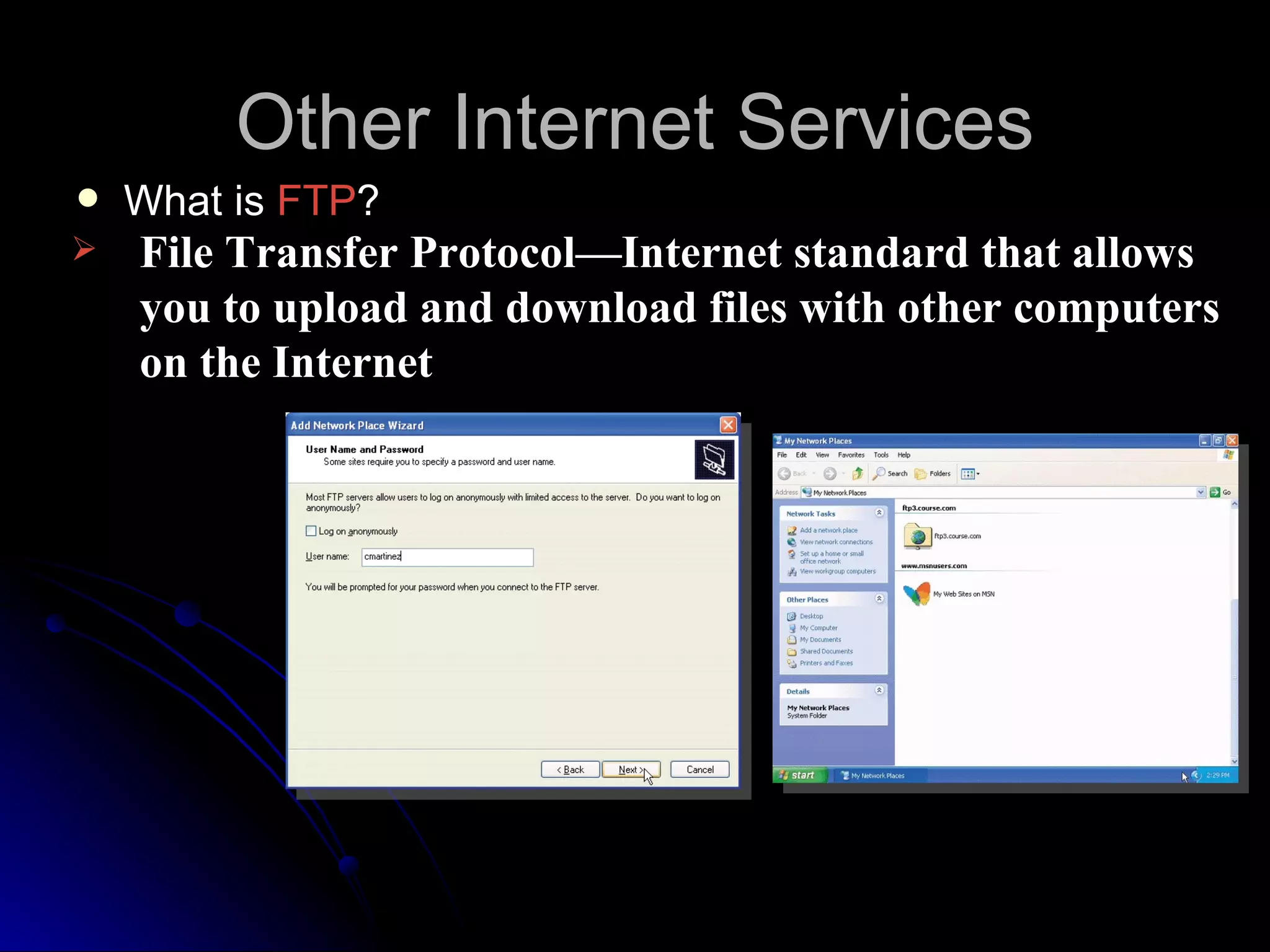
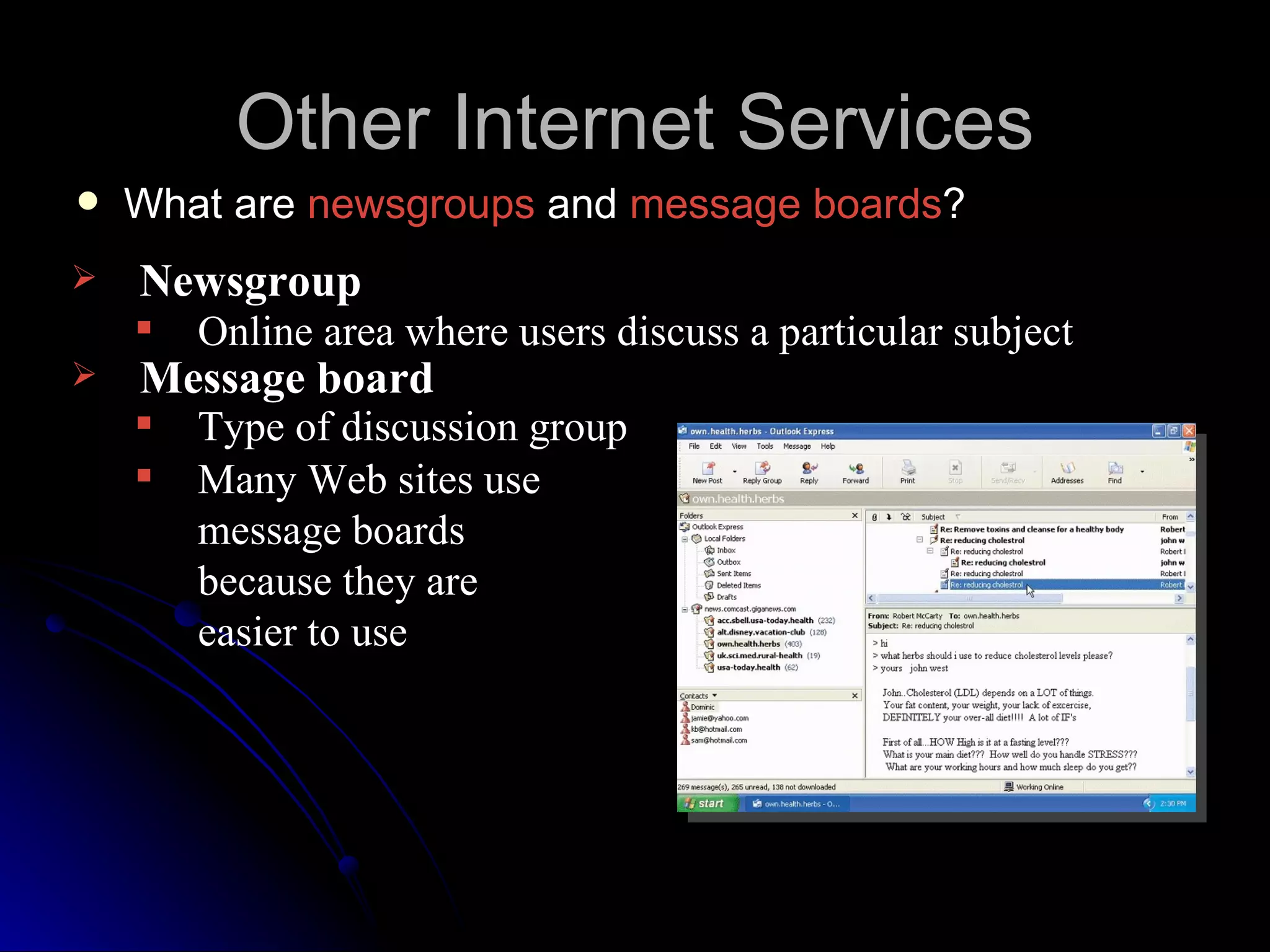
The document discusses the history and services of the Internet and World Wide Web. It begins with the origins of the ARPANET network project in 1969 and how it evolved into the Internet we know today. It then explains the development of the World Wide Web and how users can access and navigate it using web browsers, search engines, links and other features. The document also outlines various internet services like email, forums, chat rooms and e-commerce as well as best practices for online etiquette.