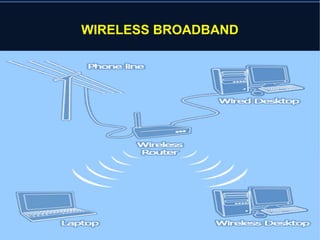
Wireless broadband provides high-speed Internet access over a wide area using wireless technology. It can offer speeds comparable to wired networks like DSL or cable. Fixed wireless networks use stationary connections that can support higher speeds than mobile networks. Wireless Internet service providers (WISPs) offer broadband wireless access, though maximum speeds are typically under 100 Mbps due to limitations of wireless technologies. Demand for wireless broadband in the US has increased the need for additional radio spectrum to be allocated for these services.