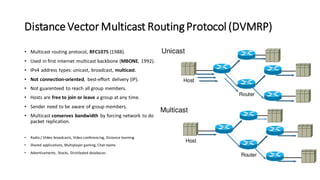
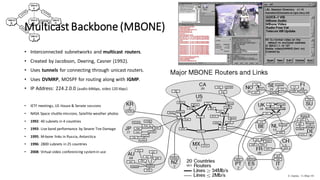
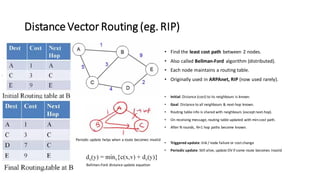
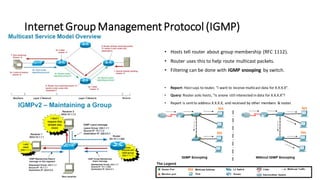
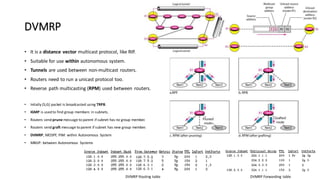
Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP) is a multicast routing protocol that operates over the Internet Multicast Backbone (MBONE) and supports applications like video conferencing and distance learning. It facilitates packet replication for efficient multicast communication and relies on IGMP for group membership management. Key features include the use of class D IP addresses for multicast, periodic updates for routing tables, and mechanisms for pruning and grafting multicast trees based on active group members.