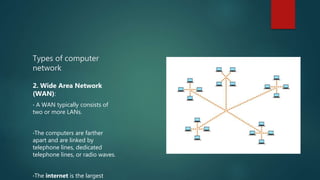
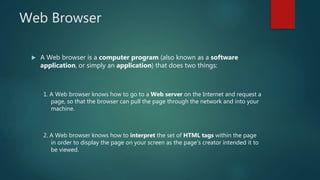
The document provides an introduction to the internet, discussing its definition, history, and basic concepts. It explains that the internet is a global network connecting millions of computers, and describes local and wide area networks. It also defines key terms like servers, clients, the World Wide Web, HTML, web browsers, URLs, and discusses basic internet services like email, file transfer, and telnet. The internet has evolved from a way to search for information to accessing, interacting with and connecting people through new technologies.