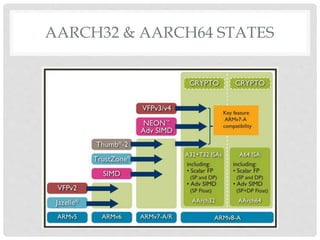
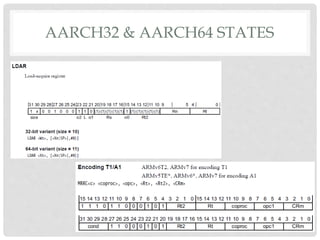
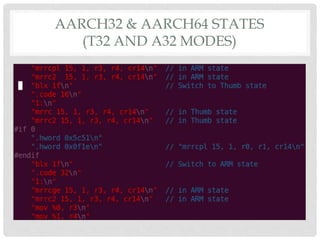
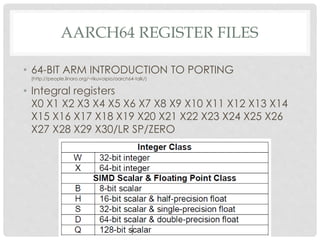
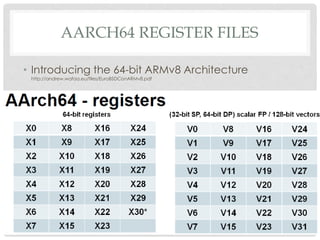
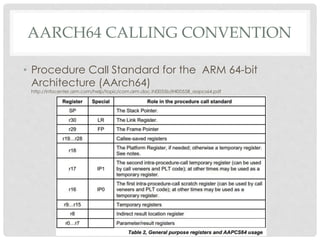
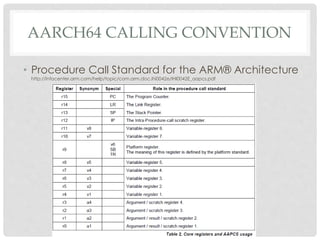
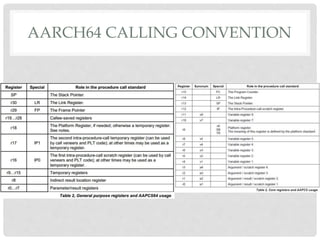
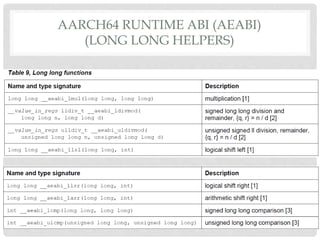
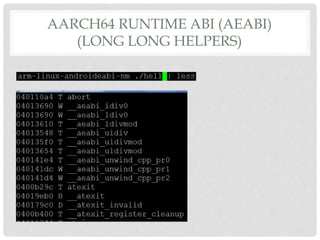
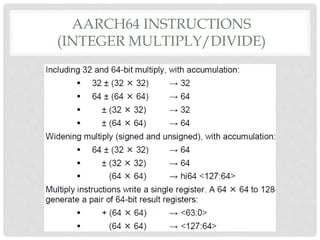
The document provides an overview of ARM64 and 64-bit Android. It discusses the benefits and drawbacks of 64-bit, the 64-bit Android ecosystem including CPUs, compilers, file formats, and runtime. It also outlines the ARM64 instruction set including registers, calling convention, and memory operations. Finally, it reviews the current state of 64-bit Android with 64-bit kernels, compilers, and emulators ready but 64-bit apps and infrastructure software still in development.