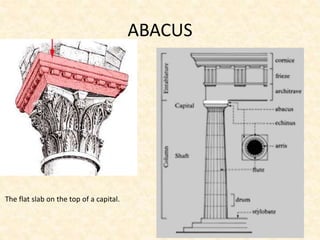
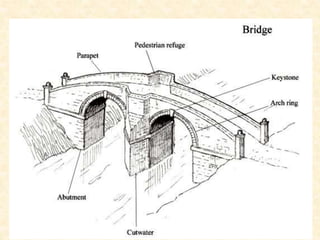
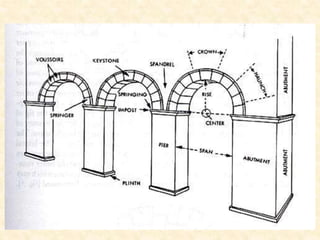
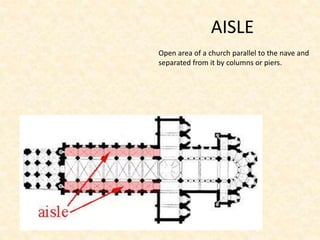
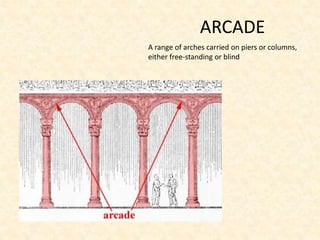
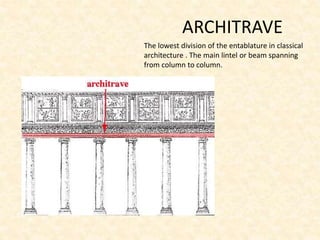
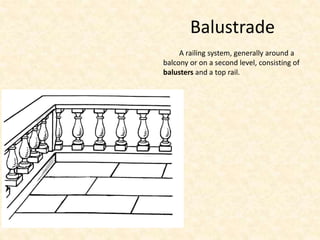
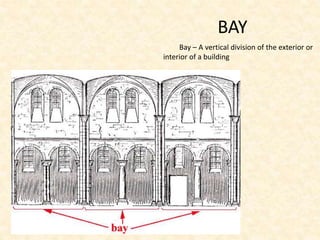
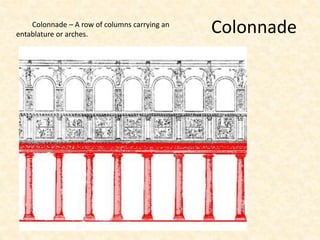
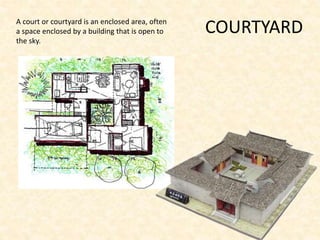
The document defines and provides brief descriptions of various architectural terms. It includes definitions for common structures like acropolis, agora, adobe, aisle, arcade, and attic. It also defines architectural elements like arch, architrave, awning, balcony, balustrade, baptistery, basement, bay, bay-window, buttress, cantilever, chattris, clearstorey/clerestory, coffer, colonnade, cornice, and courtyard. The document serves as a reference for basic architectural terminology.