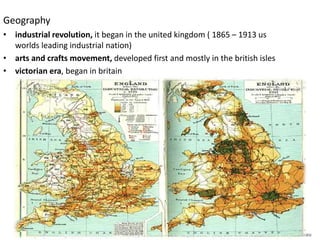
The document provides an overview of the Arts and Crafts Movement and Art Nouveau movements. It discusses key figures like William Morris who reacted against the Industrial Revolution by advocating for traditional craftsmanship. The Arts and Crafts Movement originated in Britain in the 1860s and emphasized honesty in materials, craftsmanship, and design unity. The movement spread to the United States where it influenced architects like Greene and Greene. The document also provides examples of characteristic Arts and Crafts architecture and designs by William Morris, Ashbee, Webb, and others. It notes Art Nouveau differed through its embrace of new materials and protest of traditional styles.














![History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
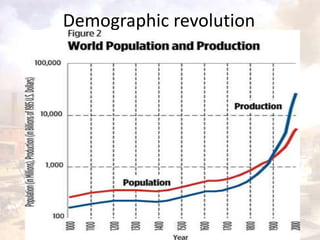
INDUSTRIALIZATION
Effects
– Money
– Alienation
Image Source: http://ia.media-imdb.
com/images/M/MV5BMjMwMDA5NzEwOF5BMl5BanBnXkFtZTcwMzgwNDg3OA@@._V1_SY317_CR5,0,214,317_.jpg
[ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-20-320.jpg)
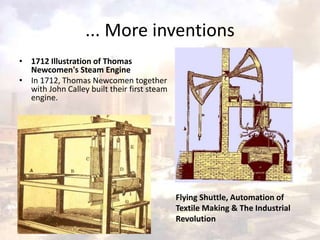
![RESPONSE TO INDUSTRIALIZATION
William Morris (1834 –1896)
C R Ashbee (1863 –1942)
W R Lethaby (1857 - 1931)
Trained as Architects and worked towards unity in the arts.
“to re-establish a harmony between architect, designer and craftsman and
to bring handcraftsmanship to the production of well-designer, affordable,
everyday objects.”
Image Source: http://media.screened.com/uploads/0/235/636117-modern_times_gears.png [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-21-320.jpg)

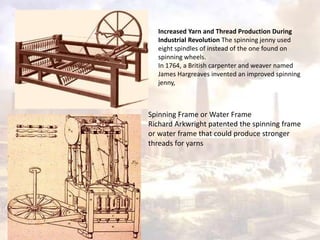
![RESPONSE TO INDUSTRIALIZATION
Individual expression
Vernacular
Use of local materials
“improvement of commercial design always remained as serious a
goal as the restoration of craftsmanship. Groups of leading designers
not only set up craft societies but independent commercial
companies”
Image Source: http://media.screened.com/uploads/0/235/636117-modern_times_gears.png [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-23-320.jpg)


![WILLIAM MORRIS (1834 –1896)
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Influenced by
– Pre-Raphaelite
Brotherhood
– Writings of John
Ruskin
Image Source: hhttp://www.literaryplaces.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2011/10/Portrait-of-William-Morris.jpg [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-26-320.jpg)



![WILLIAM MORRIS TRELLIS
Wallpaper designer by Morris
Image Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:William_Morris_design_for_Trellis_wallpaper_1862.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-30-320.jpg)
![WILLIAM MORRIS RED HOUSE
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Architect - Philip Webb
Image Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/03/The_Red_House%2C_Bexleyheath.JPG [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-31-320.jpg)
![WILLIAM MORRIS RED HOUSE
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Architect - Philip Webb
Image Source: http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_w4ifTToAw5Q/TD8vQOlxSMI/AAAAAAAACh0/LVo4bxKHSfU/s1600/red+house.jpg
[ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-32-320.jpg)
![WILLIAM MORRIS RED HOUSE
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Architect - Philip Webb
Image Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/00/Red_House_window_detail.JPG [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-33-320.jpg)
![History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
C R ASHBEE (1863 –1942)
Influenced by
– Socialism of William
Morris (Established
Guild and School of
Handicraft in 1888, in
the slums
of Whitechapel)
– Works of John Ruskin
Image Source: http://www.utopia-britannica.org.uk/Assets/Ashbee.jpg [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-34-320.jpg)

![C R ASHBEE MAHOGANY VENEERED ETAGÈRE
Image Source: http://www.victorianweb.org/art/design/ashbee/3.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-36-320.jpg)
![C R ASHBEE SILVER MOUNTED DECANTER
Image Source: http://farm4.static.flickr.com/3113/3168776759_c1702917e5.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-37-320.jpg)
![W R LETHABY (1857 - 1931)
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Influenced by
– His Father, craftsman
and lay preacher
– Society for the
Protection of Ancient
Buildings
Image Source: http://stoneletters.files.wordpress.com/2012/08/william-lethaby.jpg [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-38-320.jpg)
![W R LETHABY BUILDING AT COLMORE ROW
Image Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/e7/122-124_Colmore_Row.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-39-320.jpg)
![PHILIP WEBB (1857 - 1931)
Architect of the first Arts and
Crafts Building – The Red
House
Image Source: http://www.achome.co.uk/biographies/biographies/webb.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-40-320.jpg)
![History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
PHILIP WEBB - STANDEN
House at West Sussex, England.
Image Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b1/Standen_Exterior.jpg [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-41-320.jpg)
![History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
PHILIP WEBB - STANDEN
House at West Sussex, England.
Image Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/48/Standen_Interior.jpg [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-42-320.jpg)

![INFLUENCE ON USA- DAVID B GAMBLE HOUSE
Image Source: http://www.huntington.org/uploadedImages/Files/images/greenegamble.jpg [ONLINE]
House at West Sussex, England, Designed by Charles Sumner Greene and Henry Mather
Greene (1908)
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-44-320.jpg)
![INFLUENCE ON USA- DAVID B GAMBLE HOUSE
Image Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/2/2d/Gamble_Porch.jpg [ONLINE]
House at West Sussex, England, Designed by Charles Sumner Greene and Henry Mather
Greene
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-45-320.jpg)
![INFLUENCE ON USA- MILLARD HOUSE HOUSE
Image Source: http://millardhouse.com/mhouse237/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/a_splash-2.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
F L Wright (1932)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-46-320.jpg)
![INFLUENCE ON USA- MILLARD HOUSE HOUSE
Image Source: http://millardhouse.com/mhouse237/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/a_splash-1.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
F L Wright (1923)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-47-320.jpg)
![INFLUENCE ON USA- WAINWRIGHT BUILDING
Image Source: http://classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com/1883/flashcards/634705/jpg/wainwright-building.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Architect – Louis Sullivan (1890-91)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-48-320.jpg)
![INFLUENCE ON USA- WAINWRIGHT BUILDING
Image Source: http://larryspeck.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/08/78-710.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Architect – Louis Sullivan (1890-91)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-49-320.jpg)
![INFLUENCE ON USA- WAINWRIGHT BUILDING
Image Source: http://timothypflueger.files.wordpress.com/2010/06/wainwright-building-habs-cropped.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Architect – Louis Sullivan (1890-91)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-50-320.jpg)




![HEYGATE MACKMURDO (1851 – 1941) TITLE PAGE (1883)
“ Mackmurdo’D first graphic expression of Art Nouveau is generally accepted
as his title page for Wren’s City Churches, published by G Allen in 1883”
Image Source: http://www.aiga.org/uploadedImages/AIGA/Content/Inspiration/Voice/ART_Patton_BackStart_300x368.jpg
[ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-55-320.jpg)
![HEYGATE MACKMURDO (1851 – 1941) CHAIR (1883)
Image Source: http://hogd.pbworks.com/f/1254968919/Mackmurdo's%20chair.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-56-320.jpg)
![MAISON DE L'ART NOUVEAU
Image Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/81/Siegfried_bing_exposition_20050227.JPG [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Opened on 1895, Paris](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-57-320.jpg)
![CHARLES RENNIE MACKINTOSH (1868 –1928 )
Image Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Wfm_glasgow_school_of_art.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Glasgow School of Art (1897)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-58-320.jpg)
![CHARLES RENNIE MACKINTOSH (1868 –1928 )
Image Source: http://brst440.commons.yale.edu/files/glasgow-school-of-art.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Glasgow School of Art (1897)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-59-320.jpg)
![CHARLES RENNIE MACKINTOSH (1868 –1928 )
Image Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/16/Wfm_mackintosh_lighthouse.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
The Lighthouse, Glasgow (1895)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-60-320.jpg)
![CHARLES RENNIE MACKINTOSH (1868 –1928 )
Image Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Lighthouse_glasgow_spiral_staircase.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
The Lighthouse, Glasgow (1895)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-61-320.jpg)


![CHARLES RENNIE MACKINTOSH (1868 –1928 )
Image Source: http://www.urbansuite.co.uk/images/D/charles-rennie-mackintosh-hill-house-chair-1274-1.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Ladderback Chair](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-64-320.jpg)



![ANTONI GAUDÍ (1852 –1926 )
Image Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/e/ee/Sagrada_Familia_01.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Sagrada Família (1883)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-68-320.jpg)
![ANTONI GAUDÍ (1852 –1926 )
Image Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Sagrada_Familia_nave_roof_detail.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Sagrada Família (1883)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-69-320.jpg)
![LOUIS SULLIVAN (1856 –1924 )
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Wainwright building(1890)
Image Source: http://classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com/1883/flashcards/634705/jpg/wainwright-building.jpg [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-70-320.jpg)
![LOUIS SULLIVAN (1856 –1924 )
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Wainwright building(1890)
Image Source: http://media.archinform.net/m/00002620.jpg [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-71-320.jpg)
![VICTOR HORTA (1861 –1947 )
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Tassel House (1893)
Image Source: http://hanser.ceat.okstate.edu/6083/Horta/Tassel/Brussels-Hotel%20Tassel,%20ext.%20facade.jpg [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-72-320.jpg)
![VICTOR HORTA (1861 –1947 )
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Tassel House (1893)
Image Source:
http://hanser.ceat.okstate.edu/6083/Horta/Tassel/Victor%20Horta;%20Brussels,%20Tassel%20House,%201893-
5,%20floor%20plans%20of%20restoration2.JPG [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-73-320.jpg)
![VICTOR HORTA (1861 –1947 )
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Tassel House (1893)
Image Source: http://www.buamai.com/wp-content/uploads/2009/02/91418726_f96132ab6b_o.jpg [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-74-320.jpg)
![History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
ANTONI GAUDÍ (1852 –1926 )
Image Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/14/Casa_Mil%C3%A0_%28Barcelona%29_-
_5.jpg/800px-Casa_Mil%C3%A0_%28Barcelona%29_-_5.jpg [ONLINE]
Casa Milà (1907)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-75-320.jpg)
![ANTONI GAUDÍ (1852 –1926 )
Image Source: http://3.bp.blogspot.com/-
cR6a1iXhLIM/URP0goQXVtI/AAAAAAAAACI/iIA35t7Ysb8/s640/Casa_Mila_Rooftop.jpg [ONLINE]
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Casa Milà (1907)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-76-320.jpg)
![LOUIS SULLIVAN (1856 –1924 )
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Merchants' National Bank (1914)
Image Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:LSGrinnell7.jpg [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-77-320.jpg)
![LOUIS SULLIVAN (1856 –1924 )
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Merchants' National Bank (1914)
Image Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:LSGrinnell3.jpg [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-78-320.jpg)
![PETER BEHRENS (1868 –1940 )
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
AEG Turbine Factory (1908)
Image Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/4a/AEG_by_Peter_Behrens.jpg [ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-79-320.jpg)
![JOSEF HOFFMANN (1870 –1956 )
History of Architecture - II (AP-313) – Arts and Crafts Movement + Art Nouveau
Kubus armchair(1910)
Image Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/19/Josef_Hoffmann_-_Kubus_Fauteuil_%281910%29.jpg
[ONLINE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artscrafts-141014084835-conversion-gate01/85/Arts-crafts-80-320.jpg)



