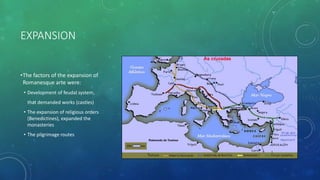
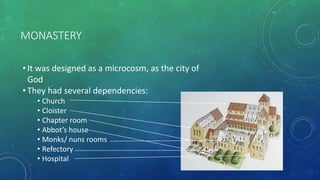
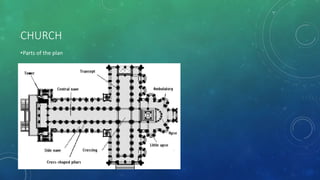
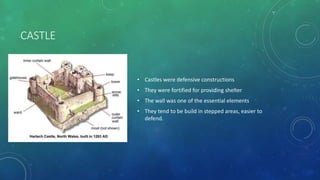
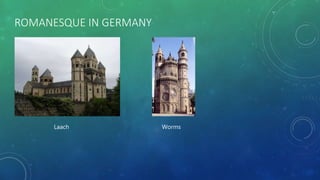
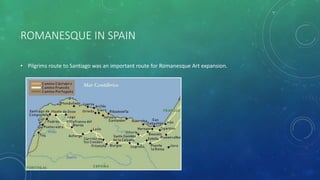
La arquitectura románica, que se desarrolló entre 1000 y 1200 d.C., se caracteriza por sus arcos de medio punto, muros gruesos y bóvedas de cañón, influida por arquitectura romana y estilos regionales. Su expansión fue impulsada por el desarrollo del sistema feudal y rutas de peregrinación, siendo prominente en países como Francia, Italia y España. La arquitectura románica tuvo un impacto duradero en el diseño arquitectónico moderno y simboliza la simetría y la solidez en la construcción de iglesias, monasterios y castillos.